AQA Psychology - Approaches to Psychology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
1
New cards
Who was the first person to call themself a psychologist?
Wundt
2
New cards
What is **Introspection**?
* A technique pioneered by Wundt to gain insight into how mental processes work
* People are trained to report their inner experiences **in detail** when presented with a stimulus
* Wundt used this to establish psychology as a science
* People are trained to report their inner experiences **in detail** when presented with a stimulus
* Wundt used this to establish psychology as a science
3
New cards
Give one example of **research** that used introspection
## ^^Griffiths (1994)^^
⤷ conducted a study on gamblers using **introspection** as a research method.
* The study interviewed 30 regular fruit machine players and asked them to describe their thoughts and feelings while playing
* The study found that gamblers experienced a range of emotions while playing, including excitement, frustration, and a sense of control.
* Gamblers often used **cognitive strategies** to justify their behaviour, such as believing that they had a system for winning.
* The study provided insight into the psychology of gambling and the subjective experiences of gamblers
⤷ conducted a study on gamblers using **introspection** as a research method.
* The study interviewed 30 regular fruit machine players and asked them to describe their thoughts and feelings while playing
* The study found that gamblers experienced a range of emotions while playing, including excitement, frustration, and a sense of control.
* Gamblers often used **cognitive strategies** to justify their behaviour, such as believing that they had a system for winning.
* The study provided insight into the psychology of gambling and the subjective experiences of gamblers
4
New cards
Give **criticisms** of **Introspection** as a method of investigation
* Introspection only allows insight into the persons conscious thoughts meaning unconscious ideas or prejudices that may affect their way of thinking are supressed
* Introspection has no way of verifiying the truth it accuracy of the information provided
* Introspection has no way of verifiying the truth it accuracy of the information provided
5
New cards
Define **Empiricism**
Learning about behaviour through direct observation or experience
6
New cards
Give **one** criticism of Wundt’s contribution to society
Not all processes could be observed in the same scientific manner. For example, **learning** and **emotions** were not able to be definitively studied at the time
7
New cards
Give **4** features of the scientific method in psychology
* Objective - no researcher input, solely based on research support
* Systematic - observations are carried out in an orderly way
* Replicable - If it can be repeated by others an produce the same result
* Reliable - will produce the same/similar result every time it is done
* Systematic - observations are carried out in an orderly way
* Replicable - If it can be repeated by others an produce the same result
* Reliable - will produce the same/similar result every time it is done
8
New cards
Evaluate the **scientific approach**
* %%Strength:%% They are able to establish causes of behaviour based on empirical and objective research
* ==Limitation:== Not all psychologist share the view that human behaviour can be explored using scientific methods as human behaviour is not subject to laws and regularity
* ==Limitation:== Not all psychologist share the view that human behaviour can be explored using scientific methods as human behaviour is not subject to laws and regularity
9
New cards
Describe the **emergence of psychology as a a science**
In the early 20th century, behaviourists questioned whether or not psychology could be classed as a science, as it previously was seen as a **philosophical subject**. Wilhelm Wundt pioneered the **scientific evolution of psychology**
10
New cards
What is the **psychodynamic approach**?
The idea **behaviour** is **influenced** by the **unconscious**
11
New cards
Who came up with the psychodynamic approach?
Freud
12
New cards
What are the two main drives according to the psychodynamic approach?
* Eros - life drive associated with positive emotions such as love
* Thanatos - death drive which is associated with negative emotions such as fear, hatred and anger
* Thanatos - death drive which is associated with negative emotions such as fear, hatred and anger
13
New cards
How might a persons unconscious affect their behaviour?
Distressing events in childhood May lead to abnormal behaviours in adulthood
14
New cards
What three components make up personality?
* Id
* Ego
* Superego
* Ego
* Superego
15
New cards
What is the Id?
Present at birth - it involves instincts and basic drives such as sex and aggression
16
New cards
What is the Ego?
Balances the Id & Superego - when balance can’t be achieved, abnormal behaviour results e.g anxiety disorders from an overdeveloped superego
17
New cards
What is the superego?
Developers after socialisation - conscience and moral standards
18
New cards
According to the psychodynamic approach, how do we deal with traumatic events?
The ego deploys defence mechanisms to cope with the conflicting views of the superego and Id
⤷ Repression
⤷ Denial
⤷ Displacement
⤷ Repression
⤷ Denial
⤷ Displacement
19
New cards
What is **repression**? (and give an example)
Repression is used when the Ego can’t handle the **pain** or **guilt** caused by a memory, so it is forced into the unconscious i.e *a child who was abused by a parent has no recollection of the events*
20
New cards
What is **displacement**? (and give an example)
The unconscious redirection of an emotion to an easier target i.e *angry at your boss but want to keep your job so you shout at the intern*
21
New cards
What is **denial**? (and give an example)
The Ego will deny an event so if can’t cause anxiety i.e *a drug addict may say they are in control and deny their addiction*
22
New cards
What are the psychosexual stages?
Stages in which conflict just be resolved by an expenditure of sexual energy otherwise, a fixation may occur
23
New cards
What is a fixation?
Being stuck at a particular point in psychosexual development which could lead to specific psychological disorders
24
New cards
Name the **five** psychosexual stages in order
1. Oral Stage
2. Anal Stage
3. Phallic Stage
4. Latency Stage
5. Genital Stage
25
New cards
What is the **oral** stage?
Primary source of pleasure comes from the @@**mouth** and **sucking**@@
⤷ fixation may look like… **smoking** and **overeating**
⤷ fixation may look like… **smoking** and **overeating**
26
New cards
What is the **anal** stage?
Primary source of pleasure comes from the anus
⤷ fixation may look like… **orderliness** and **messiness**
⤷ fixation may look like… **orderliness** and **messiness**
27
New cards
What is the **phallic** stage?
Main source of pleasure comes from genitals + where elektra/ Oedipus complex arises
⤷ fixation may look like… **masturbation**
⤷ fixation may look like… **masturbation**
28
New cards
What is the **latency** stage?
Development of other activities such as school, friends and hobbies means less concentration on the sexual area - *previous conflicts repressed, resulting in little being recalled from childhood*
29
New cards
What is the **Oedipus** complex?
The son wants to posses his mother sexually and so subconsciously tries to get rid of his father
⤷ often results in arguing and fighting with father
⤷ often results in arguing and fighting with father
30
New cards
What is the Elektra complex?
The daughter wants to possess her father sexually so subconsciously tries to get rid of her mother
⤷ results in arguing/ fighting with mother
⤷ results in arguing/ fighting with mother
31
New cards
Give a weakness of Freud’s psychodynamic approach
**Androcentric** - mainly focuses on men, meaning his views on female sexuality were much less developed. This might mean that treatment based on this approach is ineffective on women
**Culture Bias** - Sue & Sue argue that psychodynamic approach has little relevance to those from non western cultures. Many cultures (for example, **Chinese**) oppose dealing with traumas openly
**Culture Bias** - Sue & Sue argue that psychodynamic approach has little relevance to those from non western cultures. Many cultures (for example, **Chinese**) oppose dealing with traumas openly
32
New cards
Give an example of **research into** **Freud’s theory**
## Fisher & Greenberg
* Fisher and Greenberg conducted a meta-analysis of studies on Freud's psychoanalytic theory.
* Some support was found for Freud's theory, particularly in regards to early childhood experiences and the role of unconscious processes
* Fisher and Greenberg concluded that while Freud's theory had some merit, it was not a comprehensive or fully accurate explanation of human behavior.
* Fisher and Greenberg conducted a meta-analysis of studies on Freud's psychoanalytic theory.
* Some support was found for Freud's theory, particularly in regards to early childhood experiences and the role of unconscious processes
* Fisher and Greenberg concluded that while Freud's theory had some merit, it was not a comprehensive or fully accurate explanation of human behavior.
33
New cards
Give one **issue** with the **psychodynamic approach**
* Gender Bias
* Environmentally deterministic
* Environmentally deterministic
34
New cards
What is the humanistic approach?
Behaviour is influenced by free will
35
New cards
Where does humanistic psychology fit as an approach?
1950s - previously there were two approaches only, psychoanalytic and behaviourist
36
New cards
What prompted psychologists to develop the humanistic approach?
Psychoanalysis was too deterministic and Behaviourism didn’t account for individual choice
37
New cards
What are the 4 principles of Humanistic psychology?
* Humanistic psychology emphasises personal experience and personal responsibility for our own behaviour
* It focuses on individuals potential to become their best self
* People are innately good
* Mental, emotional and social difficulties have resulted from situations that have been experienced
* It focuses on individuals potential to become their best self
* People are innately good
* Mental, emotional and social difficulties have resulted from situations that have been experienced
38
New cards
What are conditions of worth?
Conditions we believe we must meet to gain acceptance
39
New cards
What is congruence?
A match between psychological attributes and behaviour
40
New cards
What is free will?
The belief we are self determined
41
New cards
What is self concept?
The way in which we perceive ourself
42
New cards
What is self actualisation?
Désire tu be the best one can be
43
New cards
What is unconditional positive regard?
A psychologist’s acceptance and support regardless of the clients actions
44
New cards
What is empathy?
Ability to sense another’s emotions
45
New cards
Who is the key figure in humanistic psychology?
Abraham Maslow
46
New cards
Draw Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
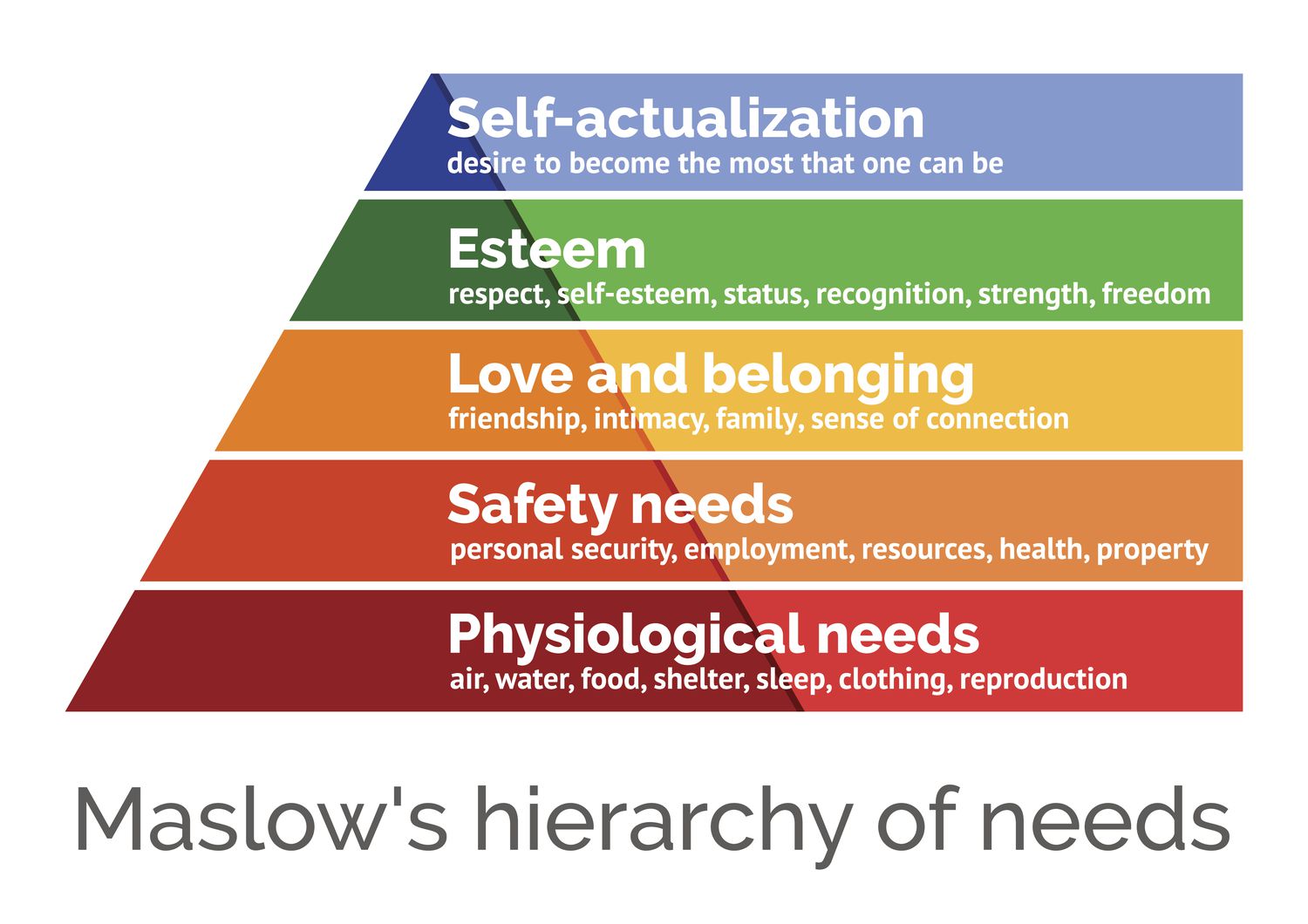
47
New cards
Explain Roger’s definition of self concept
Self concept is made of:
* Self Worth - how we think and feel about ourselves
* Self image - how we see ourselves
* Ideal self - who we’d like to be
* Self Worth - how we think and feel about ourselves
* Self image - how we see ourselves
* Ideal self - who we’d like to be
48
New cards
Explain how conditions of worth can stop us from being fully functioning
* Client has conditions of worth and low self worth
* This is due to incongruence between their actual self and ideal self
* They are unable to be their happiest self
* This is due to incongruence between their actual self and ideal self
* They are unable to be their happiest self
49
New cards
Describe humanistic psychology and counselling
Humanistic therapists show unconditional positive regards to dissolve the client’s conditions of worth
50
New cards
Give a strength of Humanism
### Has real world application to economic development
⤷ Hagerty (1999) found that countries in the early stages of economic development were in the lower levels of Maslow’s hierarchy
⤷ Countries in the later stages of economic development were in the higher stages of Maslow’s hierarchy
⤷ Hagerty (1999) found that countries in the early stages of economic development were in the lower levels of Maslow’s hierarchy
⤷ Countries in the later stages of economic development were in the higher stages of Maslow’s hierarchy
51
New cards
Give an issue regarding the humanistic approach to psychology
### Determinism v Free Will
⤷ Humanism focuses on the belief that we have free will to act as we please and all our situations are able to be changed by us. This may be seen as unrealistic due to biological and environmental causes of poor mental health and psychological functioning which develop independently.
⤷ Humanism focuses on the belief that we have free will to act as we please and all our situations are able to be changed by us. This may be seen as unrealistic due to biological and environmental causes of poor mental health and psychological functioning which develop independently.
52
New cards
What is the biological approach?
Behaviour is influenced by genes and neurochemistry
53
New cards
What are the fundamental beliefs of the biological approach?
* All thoughts and behaviour just have a biological cause
* Genetic traits may be passed down through causing psychological abnormalities
* Chemical and hormonal changes may also cause behaviours
* Genetic traits may be passed down through causing psychological abnormalities
* Chemical and hormonal changes may also cause behaviours
54
New cards
Define **Heredity**
The passing of genetic traits from parents to offspring
55
New cards
Define Genotype
A particular set of genes a person has
56
New cards
Define Phenotype
Characteristics of an individual determined by genes and the environment
57
New cards
Give an example of where genotype may differ from observable traits
In adopted twins, they may have the same genotype but because of a difference in environment, they will have different phenotype
58
New cards
Give a limitation of the biological approach
### Biological Reductionism
⤷ It reduces behaviour to pure biology which ignores environmental factors that may cause behaviour. The fact that MZ twins do not have a 100% concordance rate means that there must be some level of environmental influence
⤷ It reduces behaviour to pure biology which ignores environmental factors that may cause behaviour. The fact that MZ twins do not have a 100% concordance rate means that there must be some level of environmental influence
59
New cards
Give a strength of the biological approach to psychology
### Real World Application
⤷ Research form biological psychologists has been instrumental in the development of drugs to combat psychological disorders i.e antidepressants or SSRI’s
⤷ Research form biological psychologists has been instrumental in the development of drugs to combat psychological disorders i.e antidepressants or SSRI’s
60
New cards
Outline the relationship between evolution and the biological approach
Charles Darwin’s publication – **On the Origin of Species (1859)** – described the process of natural selection ; characteristics that are not suited to a species’ environment will **die out** as it struggles to survive, and with time will evolve over generations so that only adaptive characteristics remain in **future offspring**
61
New cards
Describe the role of neurochemistry in psychology
* Dopamine has been linked to depression and OCD
* Serotonin has been linked to aggression
* Serotonin has been linked to aggression
62
New cards
What is the cognitive approach?
Behaviour is influenced by internal mental processes
63
New cards
What are internal mental processes?
Processes that occur within one’s own mind that affect or influence behaviour - examples are persception, memory and problem solving
64
New cards
T/F: Internal mental processes can be directly observed
False - these cannot be directly observed but they may be observed by resulting behaviour, brain scans and theoretical models
65
New cards
What is a schema?
Defined by **Bartlett**, A schema is a mental structure with a set of expectations that represent a view of the world
66
New cards
Give benefits of a schema
* Take shortcuts when interpreting information
* Allow us to fill in gaps about a person, place or event
* Make the world more predictable
* Allow us to fill in gaps about a person, place or event
* Make the world more predictable
67
New cards
Give some limitations of a schema
* Makes memory less accurate
* Might form the basis of prejudices
* Might form the basis of prejudices
68
New cards
Explain the computer model description of the brain
Information is inputted through the senses, encoded into the memory and then combined with previously stored information to complete a task
69
New cards
Explain the storage of memory using a computer model
* Information stored on a hard disk is LTM
* Information stored on the RAM is working memory
* RAM is cleared and reset when the task being carried out is finished
* Information stored on the RAM is working memory
* RAM is cleared and reset when the task being carried out is finished
70
New cards
What are theoretical models?
The process of using a simplified pictorial representation of a particular mental process i.e working memory model or multi store model
71
New cards
Give a strength of the cognitive approach
\
### Real World Application
⤷ In social psychology, research using the cognitive approach is used to explain depression as the result of faulty thinking processes and serves as the basis for CBT
### Real World Application
⤷ In social psychology, research using the cognitive approach is used to explain depression as the result of faulty thinking processes and serves as the basis for CBT
72
New cards
Give a limitation of the cognitive approach
### Ignores emotion and motivation
⤷ Emotional and social factors also influence our behaviour. An example of this is anxiety and memory, in that when we are anxious, our memory tends to be less reliable
⤷ Emotional and social factors also influence our behaviour. An example of this is anxiety and memory, in that when we are anxious, our memory tends to be less reliable
73
New cards
Give an issue with the cognitive approach of psychology
### ^^Machine Reductionism^^
⤷ It presents people as information processing machines and ignores the influence of emotions on behaviour. A better approach would be a more holistic one, which incorporates emotion and internal mental processes
⤷ It presents people as information processing machines and ignores the influence of emotions on behaviour. A better approach would be a more holistic one, which incorporates emotion and internal mental processes
74
New cards
Describe the emergence of cognitive neuroscience
### Cognitive neuroscience
⤷ The scientific study of the biological structures that underpin cognitive processes - cognitive neuroscientists are concerned with **social cognition** as well as the **brain regions** **associated** with it
⤷ The scientific study of the biological structures that underpin cognitive processes - cognitive neuroscientists are concerned with **social cognition** as well as the **brain regions** **associated** with it
75
New cards
Give an example of a practical application of cognitive neuroscience
Using fMRI, it is possible to work out which parts of the brain are involved in the processing of words
76
New cards
Describe what is meant by **behaviourism**
Behaviour is influenced by the environment. All behaviour is learned observable behaviour
77
New cards
What is Social Learning theory?
SLT - Behaviour is influenced by the interaction between others and the environment. Behaviour is learnt through observation and imitation
78
New cards
What is classical conditioning?
Learning behaviour through association
79
New cards
Give the **main research example** into Classical conditioning
Pavlov + Salivation in his dogs
80
New cards
Summarise each stage of Pavlov’s experiment
summarise each stage of Pavlov's classical conditioning experiment
summarise each stage of Pavlov's classical conditioning experiment
Pavlov's classical conditioning experiment involved the following stages:
1. Before conditioning: The unconditioned stimulus of food(UCS) naturally elicits an unconditioned response of salivation (UCR) from the subject.
2. During conditioning: The UCS is paired with a neutral stimulus (NS) - the bell, repeatedly until the NS becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) that elicits a conditioned response (CR) from the subject.
3. After conditioning: The CS alone elicits the CR from the subject, without the presence of the UCS.
Overall, Pavlov's experiment demonstrated how a neutral stimulus can become associated with a natural response through repeated pairing, resulting in a conditioned response to the previously neutral stimulus
1. Before conditioning: The unconditioned stimulus of food(UCS) naturally elicits an unconditioned response of salivation (UCR) from the subject.
2. During conditioning: The UCS is paired with a neutral stimulus (NS) - the bell, repeatedly until the NS becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) that elicits a conditioned response (CR) from the subject.
3. After conditioning: The CS alone elicits the CR from the subject, without the presence of the UCS.
Overall, Pavlov's experiment demonstrated how a neutral stimulus can become associated with a natural response through repeated pairing, resulting in a conditioned response to the previously neutral stimulus
81
New cards
Explain the importance of timing in classical conditioning
If the time between the presentation of the UCS and NS is great, conditioning does not occur
82
New cards
What is extinction in classical conditioning?
The conditioned response is not permanent, after a few presentations of the CS without the UCS, it loses its ability to produce the CR
83
New cards
What is spontaneous recovery?
After extinction, if the conditioned stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus are paired again,the link between them us formed much more quickly
84
New cards
What is stimulus generalisation?
Once conditioned, animals will also respond to other stimuli similar to the conditioned response
85
New cards
Give one example of classical conditioning in humans
* The Little Albert study conducted by Watson and Rayner is an example of classical conditioning in humans.
* The study involved conditioning a young boy to fear a white rat by pairing its presence with a loud, startling noise.
* The boy eventually began to fear not only the rat, but other similar objects as well.
* The study demonstrated the principles of classical conditioning and its potential effects on human behavior.
* The study involved conditioning a young boy to fear a white rat by pairing its presence with a loud, startling noise.
* The boy eventually began to fear not only the rat, but other similar objects as well.
* The study demonstrated the principles of classical conditioning and its potential effects on human behavior.
86
New cards
Give one strength of classical conditioning
It has lead to the development of treatments such as systematic desensitisation, which is used to reduce the learned conditioned response associated with the conditioned stimuli
87
New cards
Give one criticism of classical conditioning
### ^^Lacks ecological validity^^
⤷ the research is often conducted in lab with canfefully controlled conditions which may not reflect real life
⤷ the research is often conducted in lab with canfefully controlled conditions which may not reflect real life
88
New cards
What is operant conditioning?
Developed by Thorndike (1898), operant conditioning is learning through reinforcement
89
New cards
Differentiate between positive effects and negative effects
Positive effects (rewards) lead to the stamping in of a behaviour
Negative effects (punishment) leads to the stamping out of a behaviour
Negative effects (punishment) leads to the stamping out of a behaviour
90
New cards
What is positive reinforcement?
When a behaviour produces a consequence that is satisfying or pleasant i.e praise to a child of food to a pigeon
91
New cards
What is negative reinforcement?
When a behaviour leads to the removal of something unpleasant i.e rats suffering electric shock press a lever that turns it off (do it confuse with punishment)
92
New cards
T/F: Both types of reinforcement increase the likelihood of a behaviour
True - They both stamp in a behaviour
93
New cards
What is a Skinner box?
* B.F. Skinner conducted research on operant conditioning using a device called a Skinner box.
* The Skinner box contained a lever or button that an animal could press to receive a reward, such as food or water.
* Skinner observed how animals learned to associate their behavior with the reward, and how they could be trained to perform specific actions through reinforcement.
* Skinner also studied the effects of punishment on behavior.
* Skinner's research contributed to our understanding of how behavior is shaped by consequences.
* Skinner's research has applications in fields such as education and psychology.
* The Skinner box contained a lever or button that an animal could press to receive a reward, such as food or water.
* Skinner observed how animals learned to associate their behavior with the reward, and how they could be trained to perform specific actions through reinforcement.
* Skinner also studied the effects of punishment on behavior.
* Skinner's research contributed to our understanding of how behavior is shaped by consequences.
* Skinner's research has applications in fields such as education and psychology.
94
New cards
What is positive punishment?
Addition of a negative stimulus i.e a teenager grounded for staying out late
95
New cards
What is negative punishment?
Removal of a pleasant stimulus i.e a teenager losing their phone
96
New cards
Give a strength of operant conditioning
### Operant conditioning has lead to development of treatments such as Token Economy
⤷ TE is used to manage the negative symptoms of schizophrenia by using primary and secondary reinforcers
⤷ TE is used to manage the negative symptoms of schizophrenia by using primary and secondary reinforcers
97
New cards
Give a criticism of operant conditioning
### Skinner’s research is based on animals and so may not be able to be generalised to humans
⤷ His reliance on rats and pigeons means he cannot tell us about human behaviour, as humans have some degree of free will which is not solely determined by reinforcers
⤷ His reliance on rats and pigeons means he cannot tell us about human behaviour, as humans have some degree of free will which is not solely determined by reinforcers
98
New cards
Describe and outline the **social learning model**
Bandura et. al found that the normal behaviourist model ignored cognitive processes so created a model which incorporated **mediational processes**
99
New cards
Explain the **4** **mediational** processes
* Attention - whether we notice the behaviour
* Retention - whether we remember the behaviour
* Reproduction - whether we are **able** to perform the behaviour
* Motivation - whether the perceived rewards outweigh the perceived costs
* Retention - whether we remember the behaviour
* Reproduction - whether we are **able** to perform the behaviour
* Motivation - whether the perceived rewards outweigh the perceived costs
100
New cards
Define **Modelling**
An attitude or behaviour needs to be modelled by either live models (parents, sibling etc) or symbolic (TV characters)