Solutions
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Combines Part 1 & Part 2 from the lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
solution
liquid dosage form
solution (USP def.)
a preparation that contains one or more dissolved chemical substances in a suitable solvent or mixture of mutually miscible solvents
True
T/F: The defining characteristic of a solution is all solutes are uniformly dispersed as individual molecules
drug molecules, excipient molecules
What in a solution are present as individual molecules
False
T/F: There are particles in a solution
homogenous
A solution is what?
Homogeneous
Any sample of any size taken from any part of the container has the same concentration of all solutes as any other sample of any size taken from any other part of the container
True
T/F: Solutes do not separate from the solvent nor each other during storage.
less
The concentration of each solute in a solution is ____ than its solubility in the mixture
True
T/F: There are solution dosage forms designed for almost every route of administration
interchangeable
A solution is NOT …
highest dissolved concentration
The solubility of a drug is the _____ that can be prepared in a particular mixture
Polarity of the solvent system
The major factor on solubility is what?
Higher
Most things are soluble at what temperature?
Fridge temp & room temp
With storage temperature, need to consider the range of what 2 values?
Cosolvent
mixture of miscible liquids used as solid (ex.water & alcohol)
Complex agents
interaction w/ 2 differs compounds resulting in higher solubility
Soluble agents
self-form surfactants
Cosolvent, Complexing Agents, Solubilizing Agents
Some excipients may increase the apparent solubility of another solute in the mixture through …
Weak electrolytes solubility
What does solution pH determine?
2 – 8
The range of acceptable pH values for oral solutions is …
1 – 8
The range of pH values in the body is …
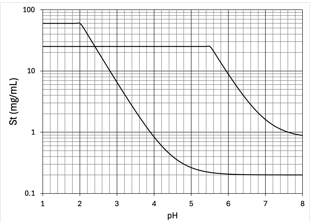
weak acids
Solubility of _____ increases as pH of the mixture is increased
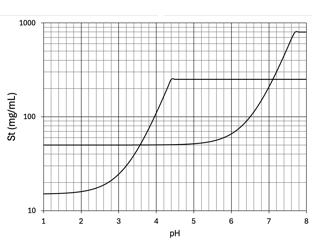
weak bases
Solubility of _____ decreases as pH of the mixture is increased
Precipitation
A change in product pH due to adding anything to the solution may change the solubility of one or more solutes
This can cause what?
Highly polar
Water is …
Moderately polar
alcohol
polarity intermediate
Water & alcohol mixture have what?
Increase solubility of the drug/other solutes
What can excipients do to solutions?
True
T/F: There is a weighted average between water & alcohol when mixed.
Cyclodextrins
What is a common complexing agent
higher
The complex of itraconazole and ß-cyclodextrin has much ____ solubility in water than itraconazole alone
micelles form
Hydrophobic solutes partition into the micelle core, meaning that …
Excipients increasing drug solubility/other solutes
The following image is an example of what?
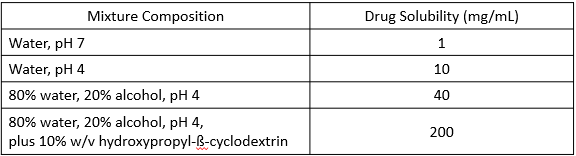
homogenous (no prep required), customizable doses, easily swallowed
What are the advantages for solutions?
packaging & ship are expensive
One of the disadvantages for solutions is that water is heavy, meaning that
chemical degradation reactions occur frequently in solutions
Why is the shelf life shorter in a solution than solid dosage form?
low
The solubility of some drugs is too ___ to make a solution with a reasonable volume
calibrated device, patient/caregiver training
For accurate dose measurement, what is required?
Solvent
always contain water, with the purpose to dissolve all solutes
single solvent/ cosolvent system
Solution can contain …
cosolvent system
2+ mixture of miscible liquids used as solvent
Purified water USP
What is used in oral or topical solutions
Municipal drinking water or tap water
What is NOT used in oral/topical solutions
Contains ions that cause precipitation/catalyze drug degradation
Why is municipal tap water not accepted for pharmaceutical solutions?
Divalent Cations
What catalyze drug degradation reactions
False
T/F: Purified Water USP contains more than 0.01 mg/mL dissolved solutes
distillation, reverse osmosis, or ion exchange, or a combo of these method
Purified Water USP may be prepared by what?
Ion exchangers
remove ionic solutes (Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42–, Fe2+, Cu2+, SO42–)
Reverse osmosis
removes ions and organic solutes
Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42–, Fe2+, Cu2+, SO42–
The following ion can:
precipitate drugs/other solutions in a drug product
catalyze drug degradation reactions
contain dissolve organic compounds (drugs)
Alcohol (ethanol)
Miscible with water
May be used in oral or topical products
Intoxication caution
True
T/F: Products must be labeled w/alcohol content while non-drug products are exempt from this requirement
< 10% v/v
FDA limit alcohol content: For adults & children >12 it is …
<5% v/v
FDA limit alcohol content: For children 6-12 it is …
<0.5% v/v
FDA limit alcohol content: For children <6 it is …
Glycerin
Miscible with water
Oral or topical products
Similar polarity to alcohol
Used as alcohol substitute
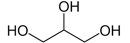
Propylene glycol
Miscible with water
Oral or topical products
Similar polarity to glycerin and alcohol
Used as an alcohol or glycerin substitute
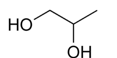
Polyethylene glycol 300/400
Miscible with water
Oral or topical products
Similar polarity to alcohol, glycerin, propylene glycol
Polyether with hydroxyl group at each end
Number indicates approximate molecular weight
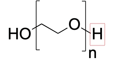
molecular weight
What is the difference between the Polyglcol 300 vs 400
Isopropyl alcohol
Miscible with water
Topical products only
Similar polarity to ethanol
Acetone
Miscible with water
Topical products
Oils
Lower polarity than alcohol
Not miscible with water
Maybe miscible w/ some alcohols
Used in topical solutions
more polarity
When using oil, why is medium chain triglyceride better to use than vegetable oil?
Isopropyl myristate, Isopropyl palmitate
Similar to MCT (solvent prop); used in topical products, cosmetics,
pH adjusters
meets the target pH range through adding HCl or NaOH
HCl
added to reduce the pH to the target range if the pH is too high after mixing all other components
NaOH
added to increase pH to the target range if the pH is too low after mixing all other components
NaOH
In this example what should be added to meet the pH target range for this solution

Drug/excipient solubility, CHEM stability, & patient safety
The target pH range includes:
True
T/F: The product is dependent on the chemical stability
buffer
Minimize pH changes due to small additions of H+ or OH
buffer
a weak electrolyte in solution with pH within 1 unit of it’s pKa value
H+ or OH–
_______ may come from containers or reactions within the product
3.5-5.5
Sodium acetate pKa 4.5, what is the buffer pH range?
6.2-8.2
Sodium phosphate (NaH2PO4– /Na2HPO42–) pKa 7.2, the buffer range from pH is
2.1 - 7.4
Sodium citrate has 3 carboxyl groups – pKa 3.1, 4.8, 6.4; the buffer range is
easier dose measurement & administration(less spilling) + placebo effect to induce patient confidence
Why would higher viscosity than water be desired?
polymer
compound w/ repeating unit structure
Polyvinylpyrrolidone
water soluble polymer that is synthetic that increases viscosity a lot
Methylcellulose 2%
make solution more resistant
HPC, HPMC
soluble water polymer that do the same thing as methylcellulose
Xanthan gum
help w/ developing bacteria & collecting it (derived from nature)
Flavors
mask objectionable tastes and improve patient adherence
Colors
enhance patient perception and recognition of flavor
Sweeteners
add sweet sensation to flavor to mask objectionable tastes
Sucrose
promotes tooth decay & increases blood glucose
False
T/F: Zero calories’ sweeteners like Sucralose, Saccharin & Aspartame are less sweet than Sucrose.
Sorbitol
The only Zero calorie sweetener that is less sweet than sucrose is …
Preservatives
inhibit microbiological growth from microorganisms that are introduced during or after manufacturing
Preservatives used in oral products
Benzoic acid, Sorbic acid, benzyl alcohol are example of what?
Methylparaben
prevent mold growth
Antioxidants
prevent drug degradation through protect the drug and other excipients from oxidation
True
T/F: One way to remove oxygen is to have compounds consume free oxygen (O2) in solution quickly to reduce the oxidation of other solutes
Chelating agents
bind to metal ions in solution to inhibit ion-catalyzed oxidation of other solutes
Ascorbic acid
Vitamin C, great antioxicant for the body
compounds that consume O2 quickly
Ascorbic acid, sodium bisulfite, sodium metabisulfite, & propyl gallate are examples of …
chelating agents
Ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA)
Edetate disodium
Sodium citrate
are examples of …
flavoring
In this example, Citric acid monohydrate is being used for

growth prevention
In this example, methylparaben sodium is being used for …
