4.4 Newton’s Laws of Motion
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Newton's First Law states:
What is required to change motion of an object?
What is the resultant force if the forces are balanced and the body must be…?
Newton's First Law states: A body will remain at rest or move with constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force
Resultant force required to change the motion of an object: To speed up, slow down, change direction
Forces on a body are balanced the resultant force is 0 the body must be: At rest, Moving at a constant velocity
Force is a vector:
Forces are balanced:
Resultant force:
Force is a vector: split the forces into horizontal and vertical components
Forces are balanced: forces acting to the left = the forces acting to the right, forces acting upward = forces acting downward
Resultant force: vector sum of all the forces acting on the body
Newton's Second Law states that:
Equation:
Where does acceleration always act?
Unbalanced forces act on an object, object experiences a _______ force
Resultant force acts ____ _____ of the object's _____, the object will:
What would happen if the resultant force acts on object at an angle to its direction of motion?
Newton's Second Law states that: The resultant force acting on an object with a constant mass is directly proportional to its acceleration
F = ma
Acceleration always acts in same direction as resultant force
Unbalanced forces act on an object, object experiences a resultant force
Resultant force acts along direction of the object's motion, the object will: Speed up (accelerate), Slow down (decelerate)
If resultant force acts on object at an angle to its direction of motion, it will: Change direction
Force ______ quantity: ______ and _______
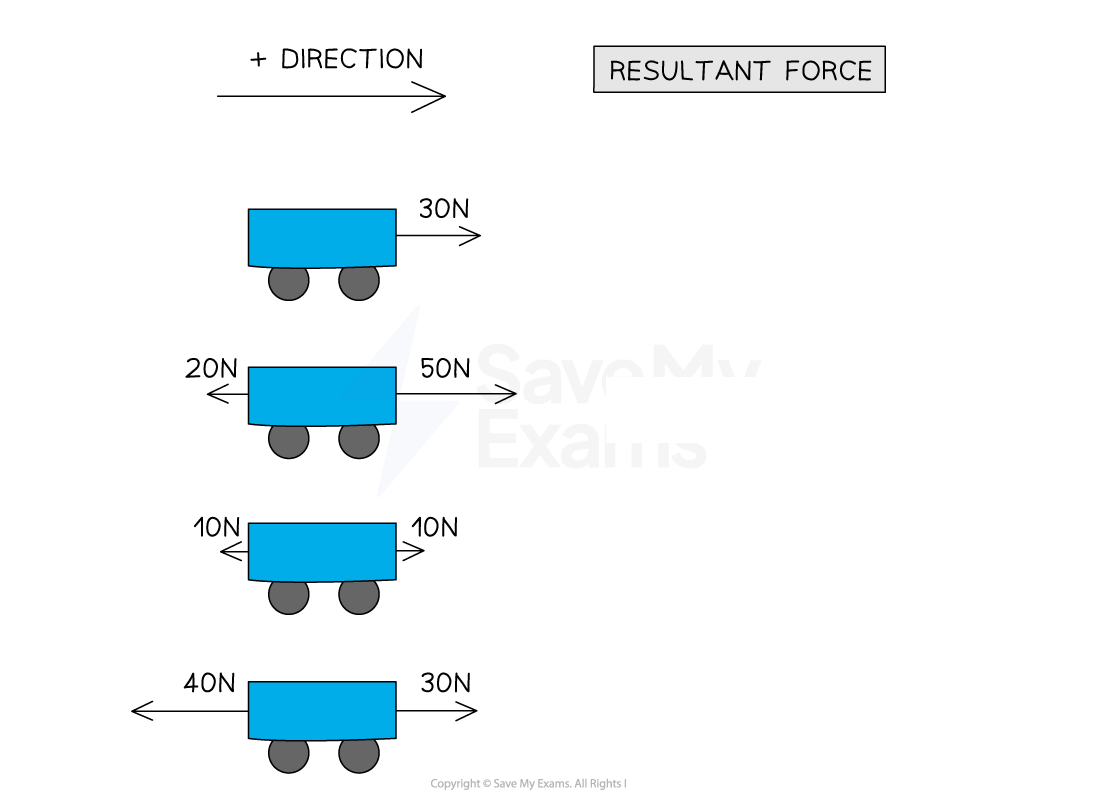
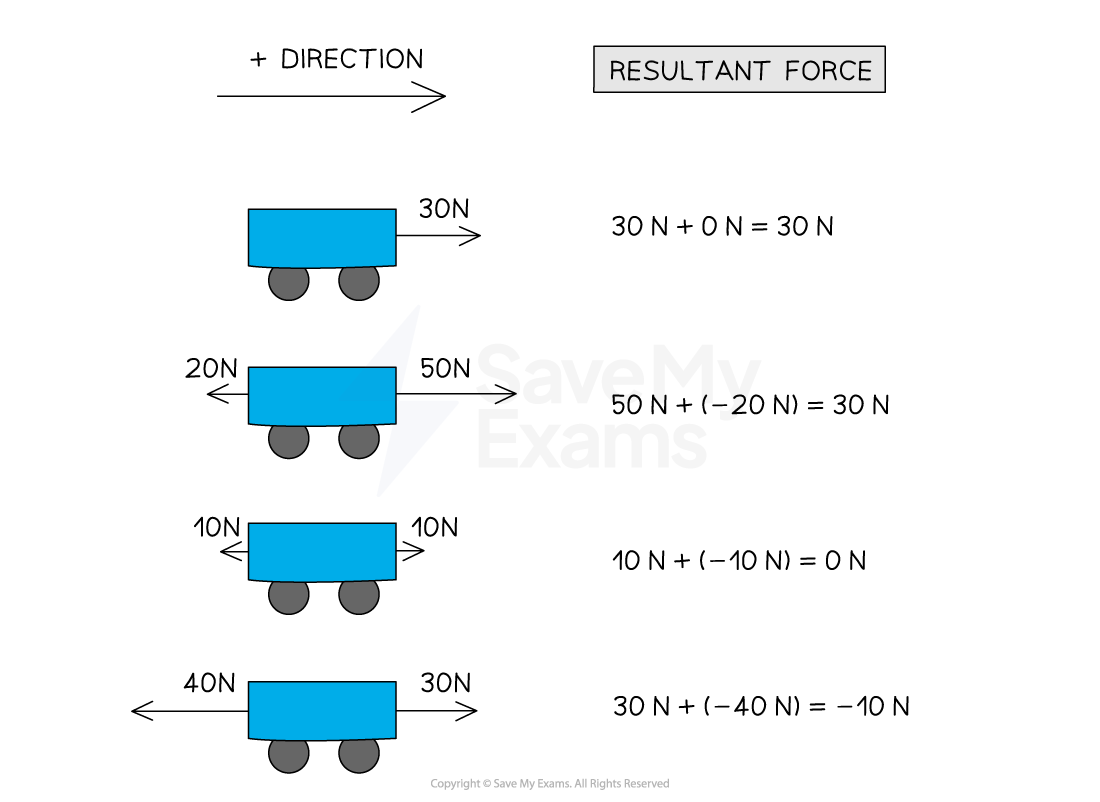
What is a resultant force a sum of
What is the positive direction?
Resultant forces on a body can be ______ or ______ depending on their __________
Resultant force acts at an angle to the direction of motion, the magnitude and direction found by:
Force vector quantity: magnitude and direction
Resultant force is vector sum of all the forces acting on the body
Objects in motion, positive direction is in the direction of motion
Resultant forces on a body can be positive or negative depending on their direction
Resultant force acts at an angle to the direction of motion, the magnitude and direction found by: Combining vectors, Scale drawings
Acceleration ______ quantity: _____ and _____
Resultant force acts in direction of an object's ______, acceleration is ______
Resultant force ________ direction of object's motion, acceleration is _______
Acceleration acts in the same direction as the resultant force
Acceleration vector quantity: magnitude and direction
Resultant force acts in direction of an object's motion, acceleration is positive
Resultant force opposes direction of object's motion, acceleration is negative (deaccelerates)
Acceleration acts in the same direction as the resultant force
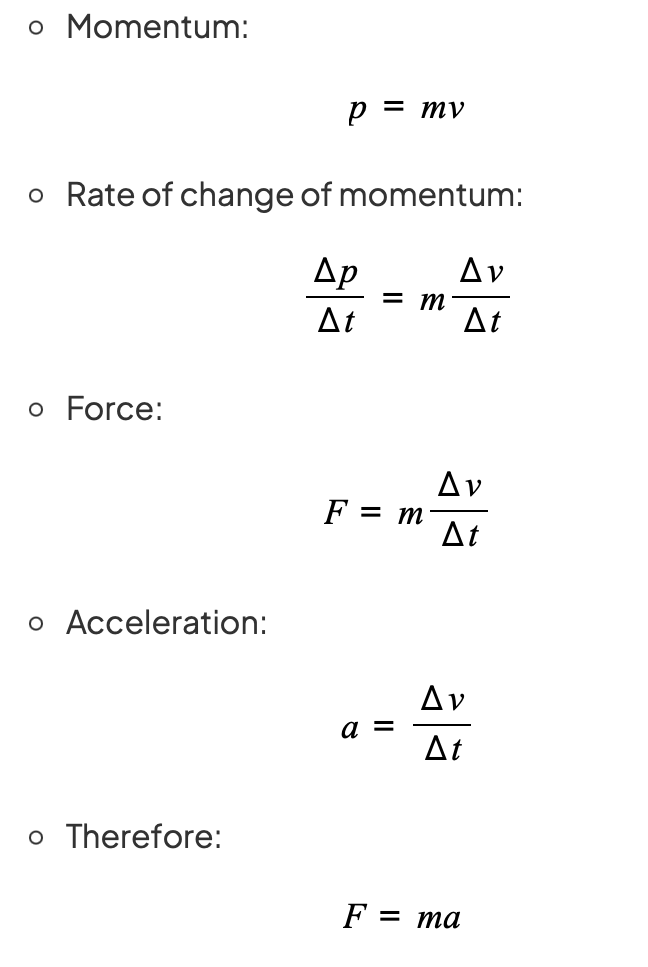
Newton's second law (momentum)
Change in momentum is in the _______ direction as the ______ force
Newton's second law : The resultant force on an object is equal to its rate of change of momentum
Change in momentum is in the same direction as the resultant force
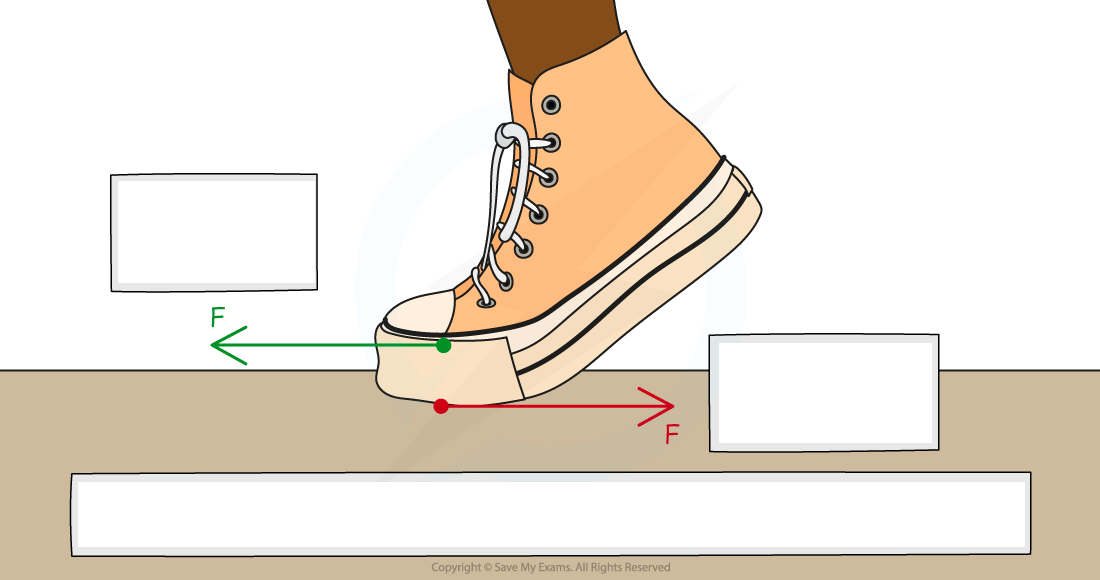
Newton's Third Law states:
Two objects interact, forces involved are in _____: ______-law pairs
A Newton's third law force pair must be:
Explain diagram
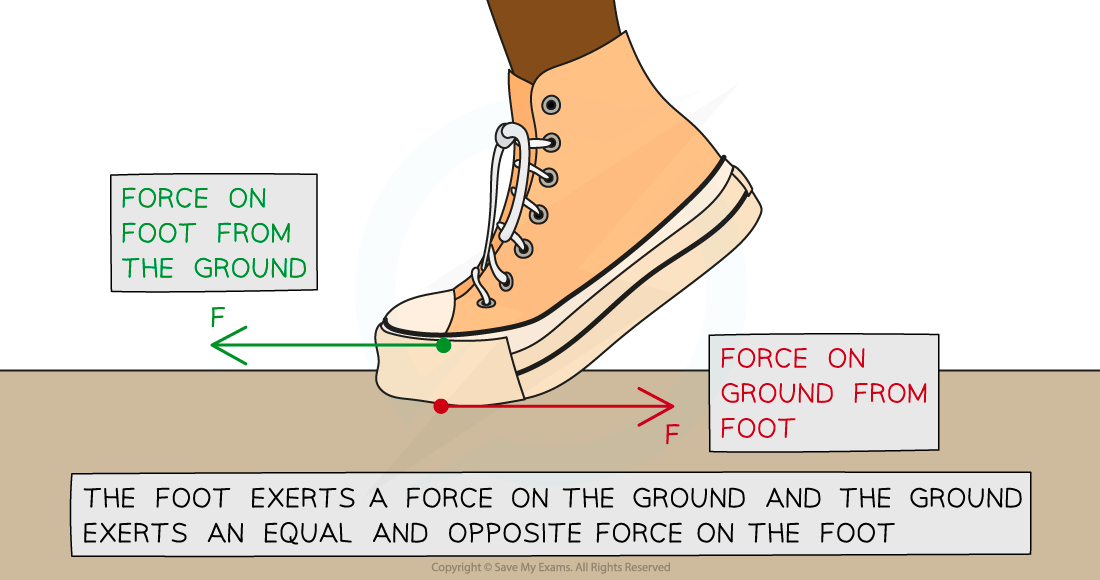
Newton's Third Law states: If Object A exerts a force on Object B, then Object B will exert a force on Object A which is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction
Two objects interact, forces involved are in pairs: third-law pairs
A Newton's third law force pair must be:
Same type of force, same magnitude, Opposite in direction, Acting on different objects
Foot pushes on the ground and the ground pushes back on the foot.
Both forces are normal contact force, equal magnitude, opposite in direction, acting on different objects (the foot and the ground)