Respiration in Yeast Practical
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Aerobic respiration
Cell respiration which happens in the presence of oxygen in the mitochondria of the cell, in animals and plants
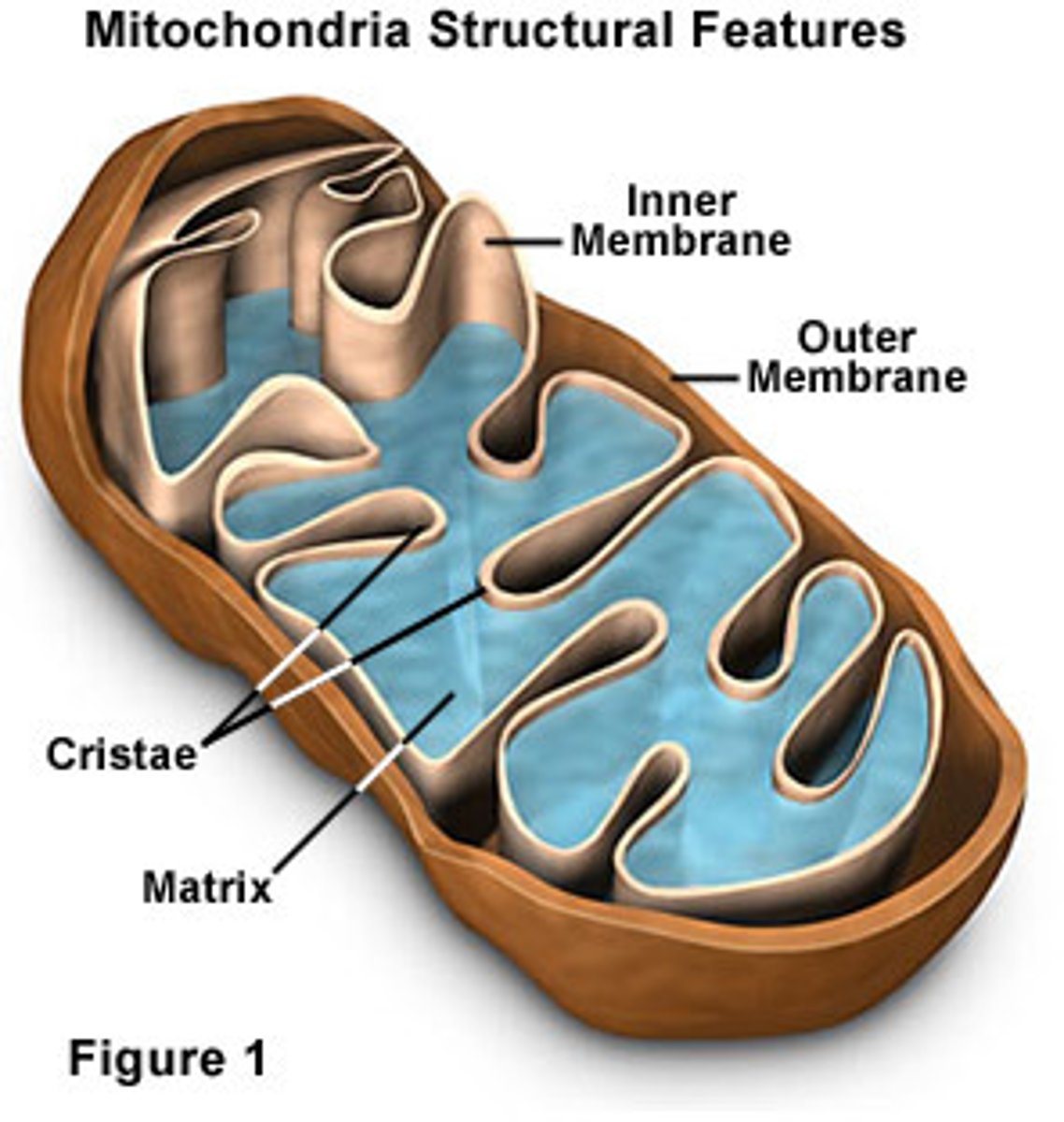
Anaerobic respiration
Cell respiration which happens in the absence of oxygen

Fermentation
Anaerobic respiration in plant and yeast cells which produces ethanol and carbon dioxide

Word equation for fermentation
Glucose -> carbon dioxide + ethanol (+energy)
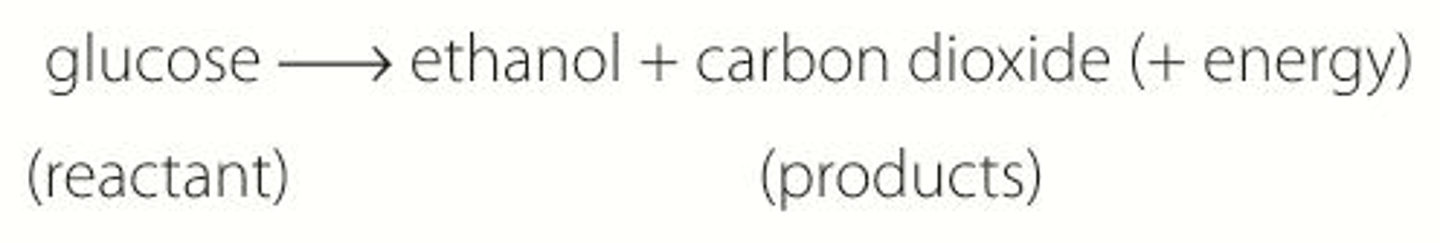
Uses of fermentation
The manufacture of bread and alcoholic drinks

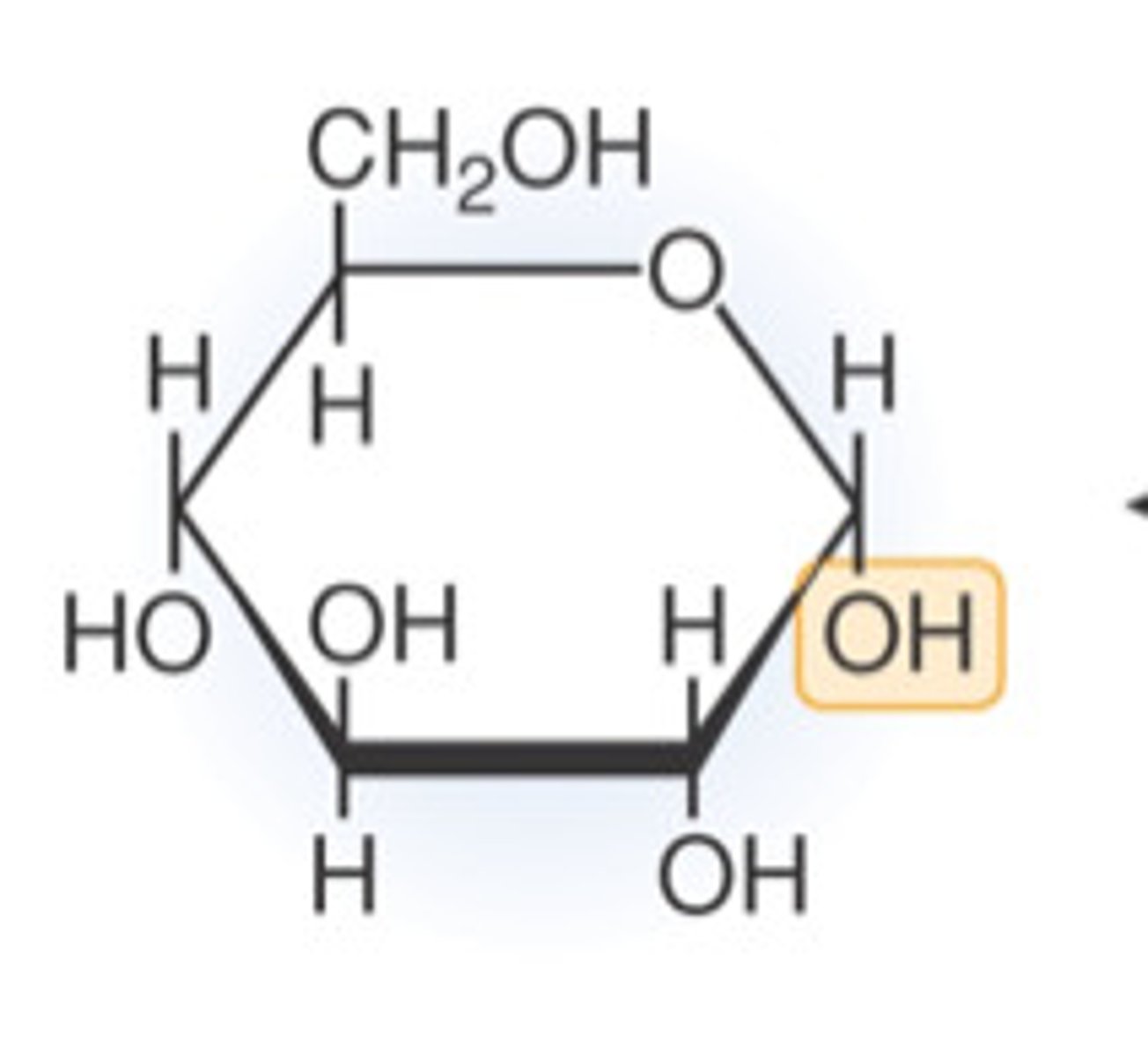
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important energy source in living organisms, the only reactant for the fermentation reaction
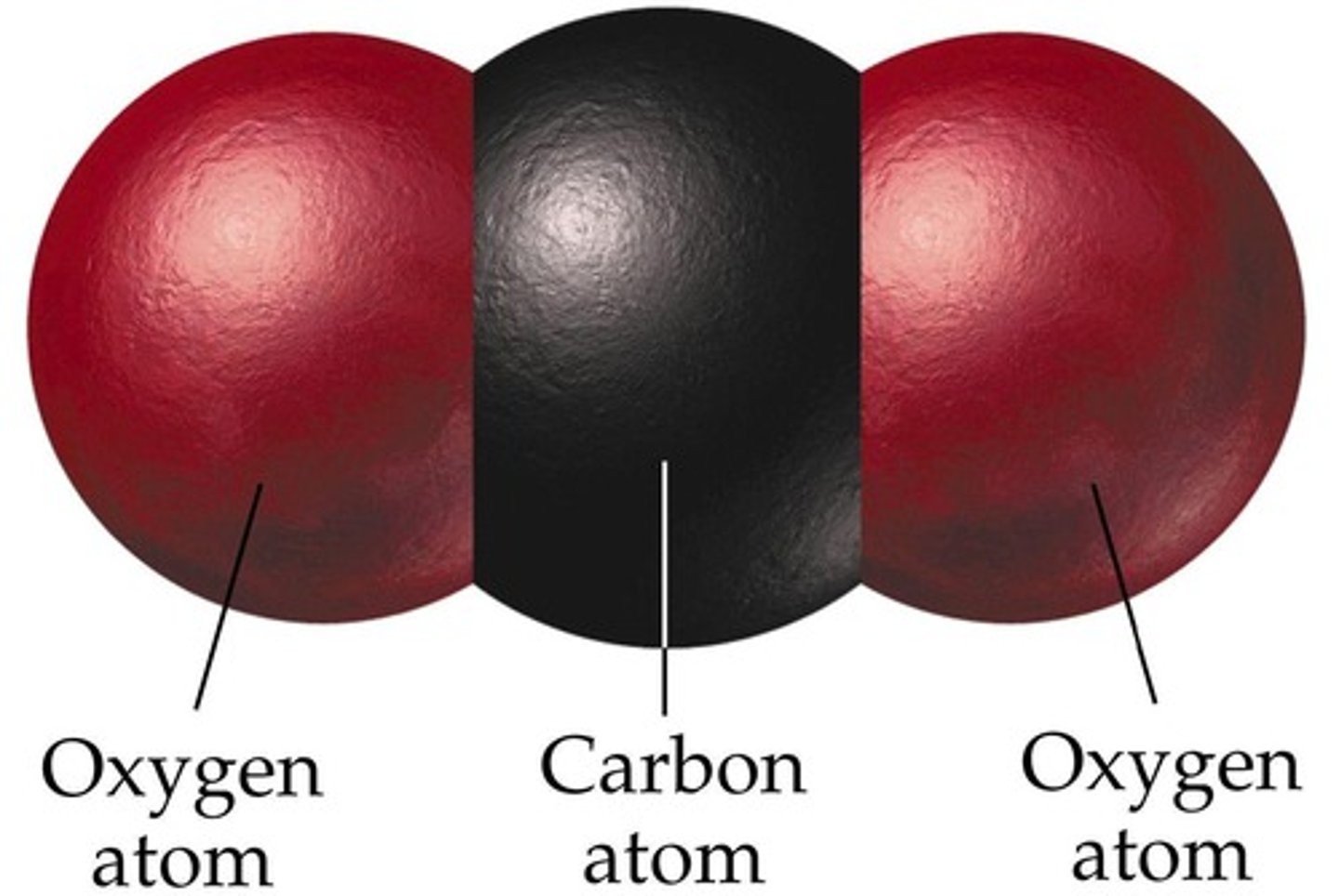
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
A byproduct of fermentation, can be used to make bread and contributes to alcohol production
Anaerobic respiration in yeast practical
Anaerobic respiration can be demonstrated by removing oxygen from the surroundings of yeast, the products of fermentation can then be observed
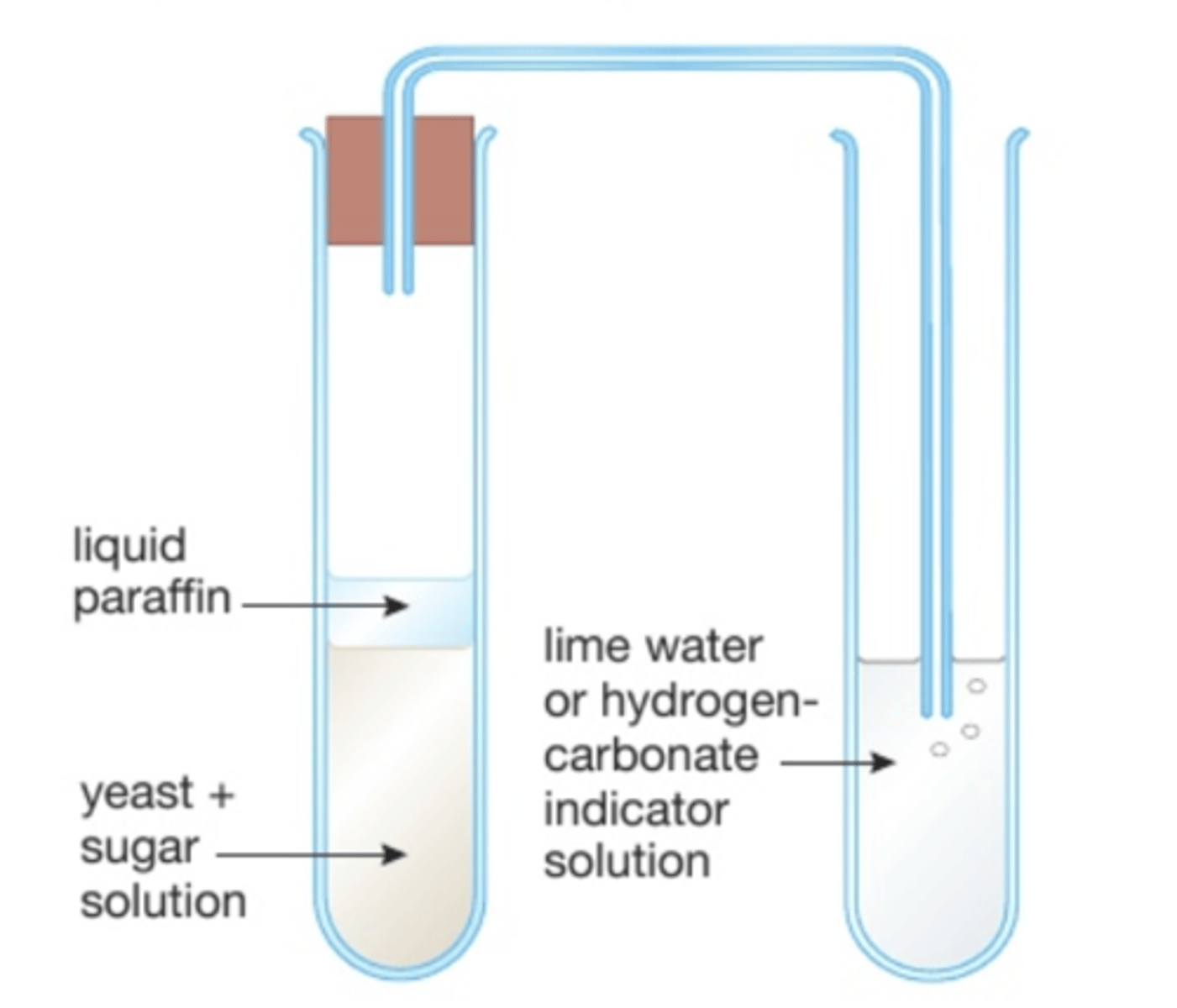
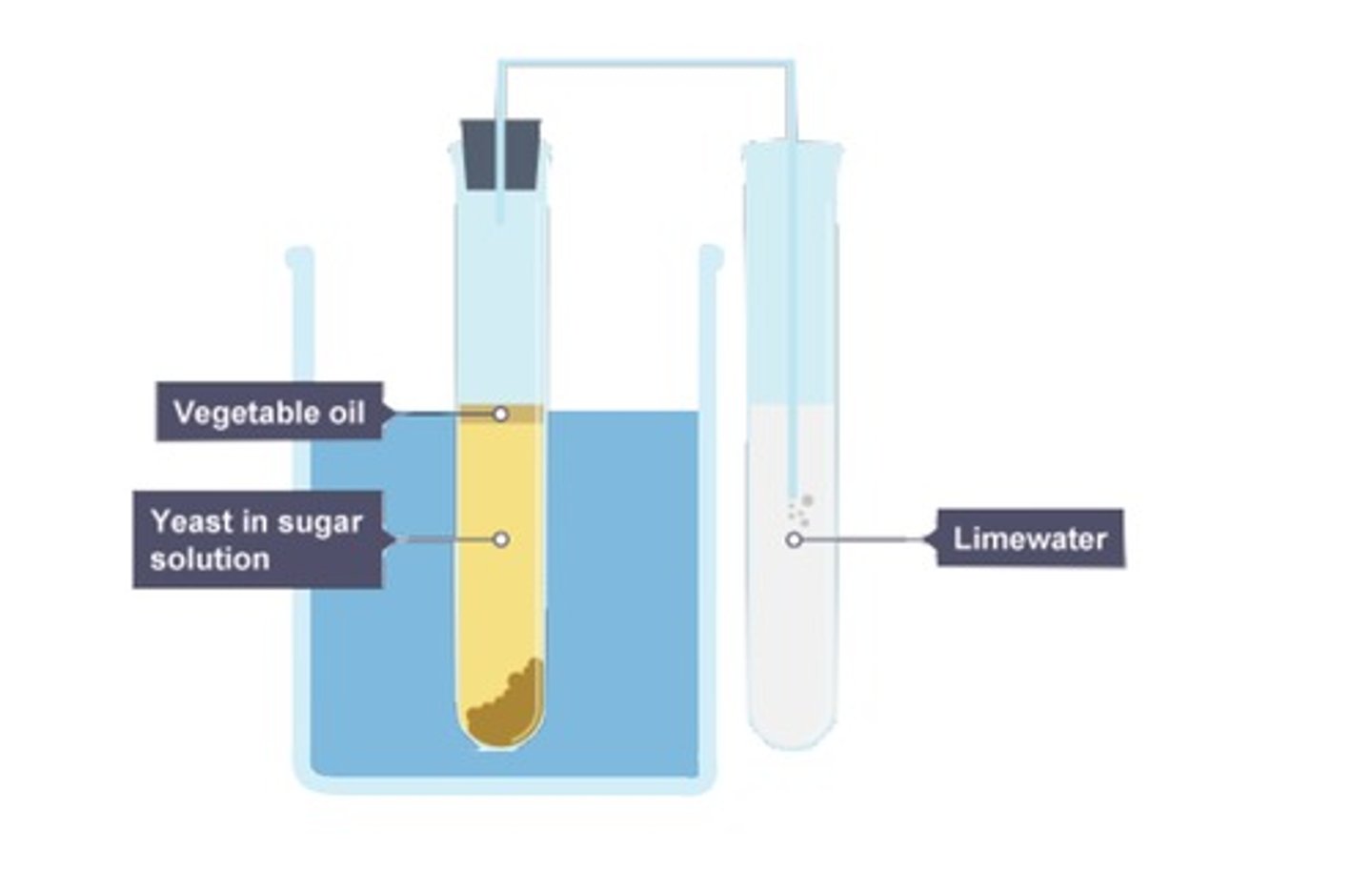
Removing oxygen
Adding an oil layer will prevent a solution of yeast obtaining oxygen from the air
Sterilisation
It is important that the equipment and glucose solution is sterile, as this could lead to contamination which would affect the results of the experiment
Temperature
Should be controlled and kept warm for yeast fermentation, a set temperature condition can be achieved using a water bath

Yeast solution
The solution that is required for this practical consists of yeast, water and sterile glucose, with a suspended layer of oil above the solution
Acclimatisation
It is important that the yeast solution is given time to settle, particularly when there may still be oxygen present in the solution which would lead to aerobic respiration and affect the results
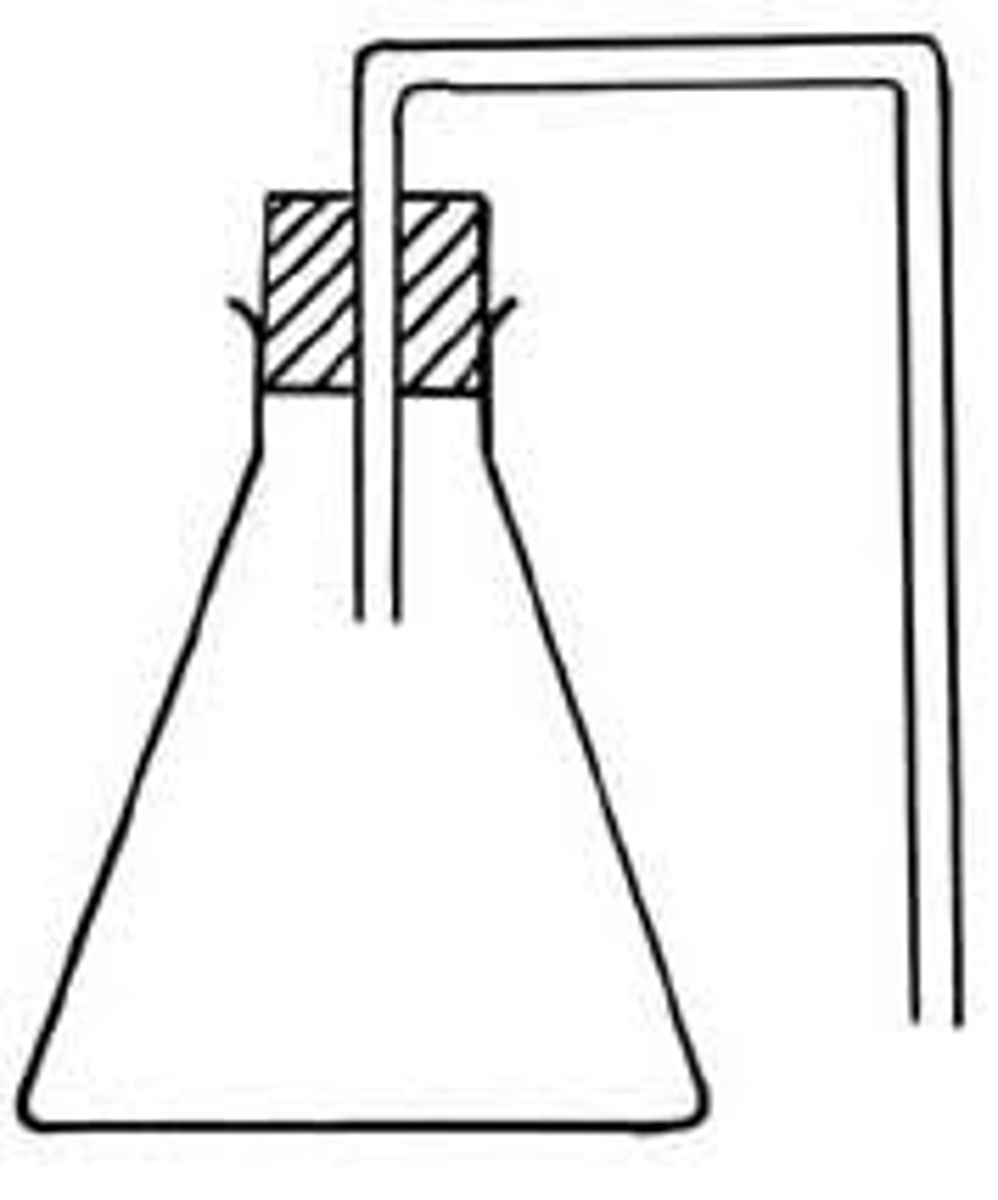
Bung and delivery tube
The yeast solution should be in a boiling tube with a bung attached to a delivery tube, this allows the gas products of fermentation to be collected
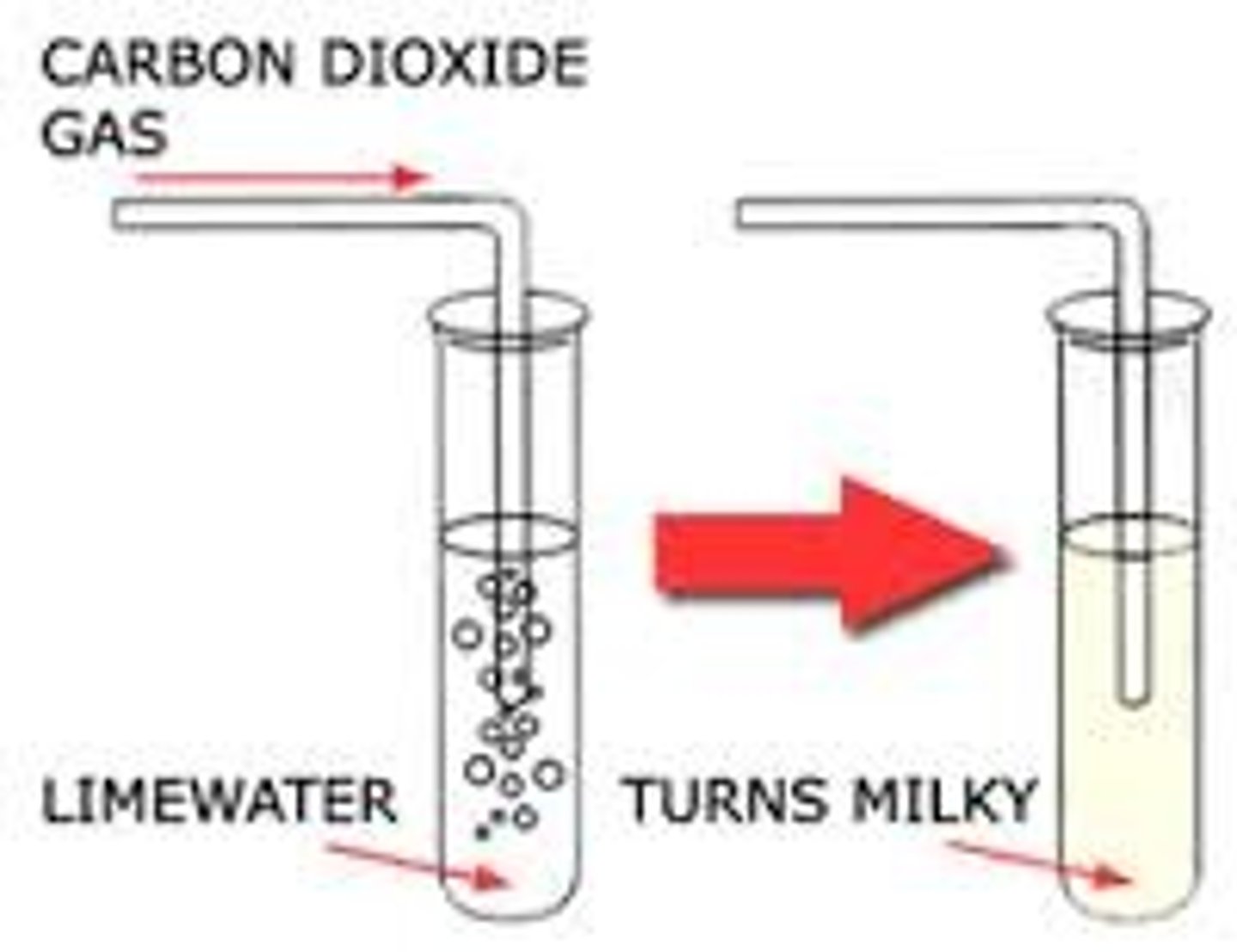
Limewater test
A solution that can confirm the presence of carbon dioxide, if CO2 is bubbled in limewater it will cause the solution to change from colourless to a milky or cloudy precipitate
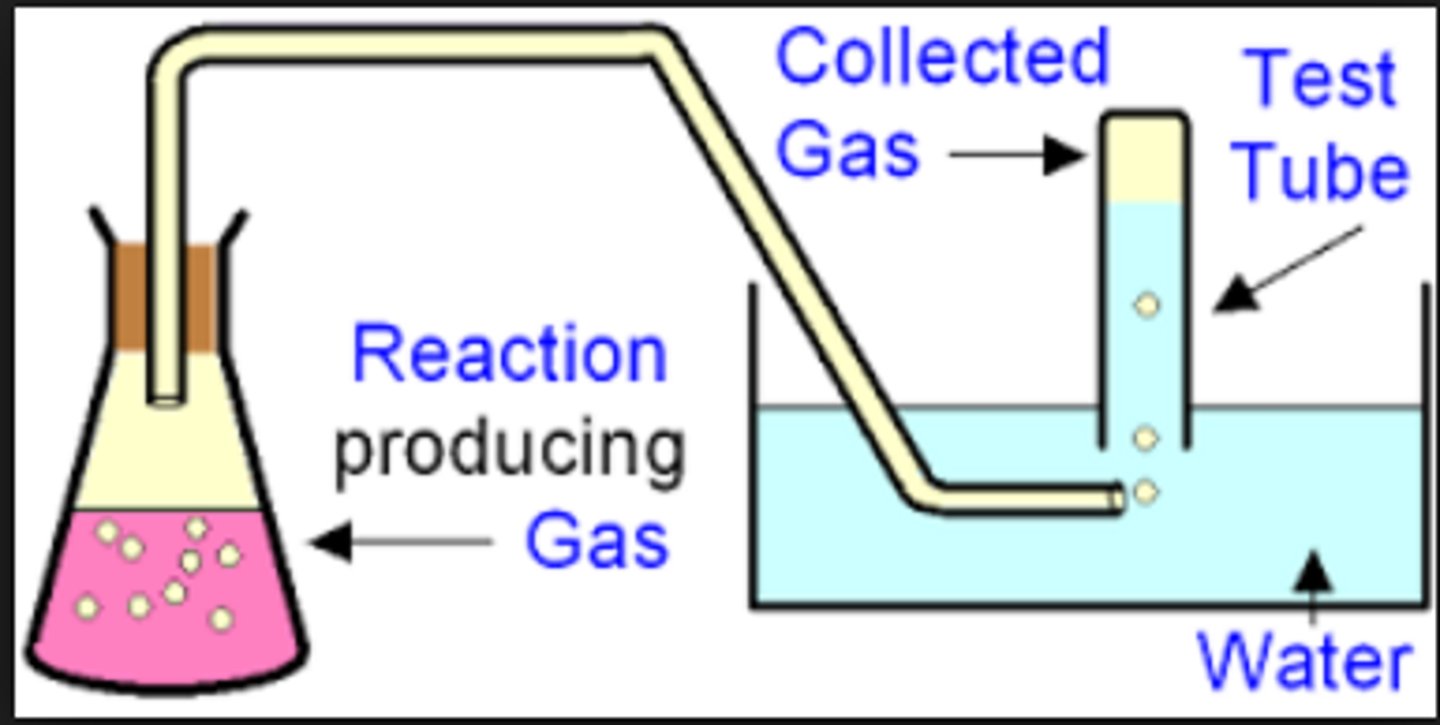
Water displacement
A method that can be used to measure the rate of fermentation by how much carbon dioxide is produced, carbon dioxide will displace water from an inverted measuring cylinder that can be recorded
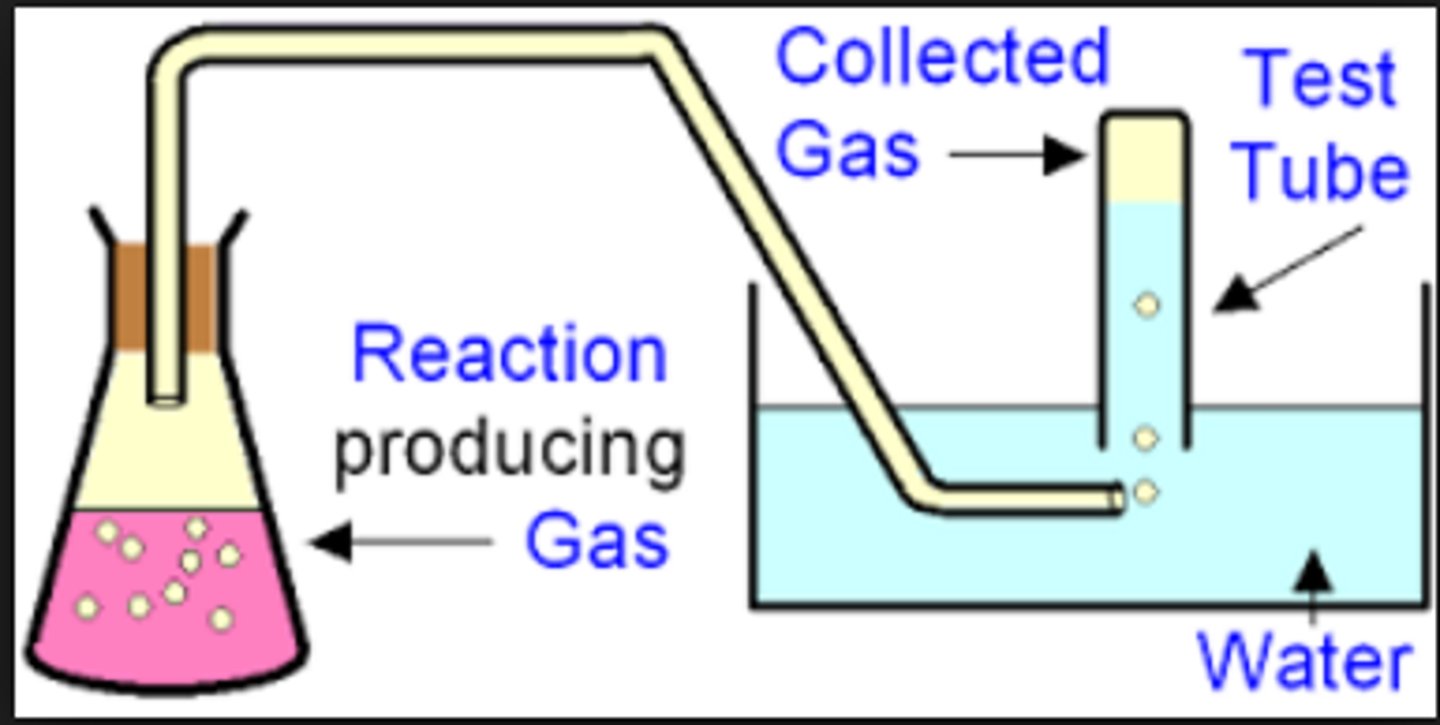
Carbon dioxide bubbles
Yeast will produce bubbles of carbon dioxide when undergoing fermentation, CO2 gas will travel down the delivery tube and will form bubbles in an inverted measuring cylinder that is full of water
Measuring rate of fermentation
By measuring how much water has been displaced from the measuring cylinder over a set period of time, the volume of carbon dioxide and the rate of carbon dioxide production (or fermentation) can be determined
Dependent variable
The variable that is measured, in this case it is the rate of fermentation or volume of carbon dioxide produced by yeast for a set duration
Independent variable
The variable that is changed, in this case it could be the temperature that the yeast is fermented at or the type of sugar that is used as a food source for yeast

Control variables
The variables that should be kept the same, in this case it could be the time each test is recorded for, the volume of solutions, the concentration of glucose
Expected results for changed temperature
The rate of fermentation, which is the amount of carbon dioxide produced over a set time, will be greatest when yeast is kept at an optimum temperature