Y10 Graphics End of Year
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
physical properties of a material
ones that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of a material
absorbency, density, fusibility, electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity
physical properties: absorbency
the ability of a material to soak up a liquid
physical properties: density
the mass per unit volume - a measurement of the mass of a material and how much space it takes up. a more dense material will feel heavier for its size
physical properties: fusibility
the ability of a material to melt into a liquid or molten state when heated. normally associated with metals & polymers
physical properties: electrical conductivity
the ability to conduct electricity. metals are good conductors, while polymers are good insulators
physical properties: thermal conductivity
the ability to conduct heat. metals are good conductors, while polymers are good insulators
working/mechanical properties of a material
the material’s ability to resist certain external forces being applied to it
strength, hardness, toughness, malleability, ductility, elasticity
working/mechanical properties: strength
the ability to withstand force e.g. by resisting compression (squashing) or tension (stretching)
working/mechanical properties: hardness
the ability to resist abrasive wear
working/mechanical properties: toughness
the ability to withstand sudden stress or shocks
working/mechanical properties: malleability
the ability to permanently deform when worked without breaking. also known as plasticity
working/mechanical properties: ductility
the ability to be drawn out or stretched without breaking
working/mechanical properties: elasticity
the ability to bend and return to shape without breaking when subjected to a force
selection of materials or components: functionality
what the material is intended to do and how it performs for the user
selection of materials or components: aesthetics
how attractive/pleasing the material needs to be in a product in terms of form, colour, and texture
selection of materials or components: environmental factors
the energy consumption, pollution, and sustainability from the material’s initial sourcing and extraction, manufacture, use, and disposal
selection of materials or components: availability
materials need to be readily available in their raw form / as components
materials that are specialist, scarce, or difficult to source will have a higher cost. the use of stock materials will benefit designers and customers
selection of materials or components: cost
the cost of the raw material and processing, through to the manufacture of the product
heavily influenced by the scale of production
selection of materials or components: social factors
companies must consider social factors when selecting materials.
the needs of the people have high priority, for example the specific needs of children, disabled, or elderly
factors in a consumer society e.g. trends & fashions may be a factor
selection of materials or components: cultural factors
different faiths & beliefs may impact the development of products
this doesn’t just impact design - the origin of materials may also be important e.g. materials derived from animals need to be carefully considered
selection of materials or components: ethical factors
materials can be purchased from ethical sources e.g. wood that has been responsibly managed by the FSC or products endorsed by the fairtrade foundation (means workers haven’t been exploited)
why are standard/stock forms of materials helpful in selection of materials or components
makes the material more cost effective as it gives designers ready-made materials that can be incorporated into their designs
force definition
a load that has been applied, measured in newtons (N)
stress definition
produced as a load is applied to a material and may cause it to deform
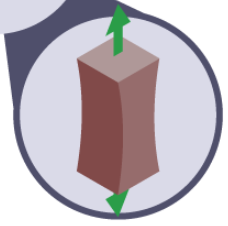
tension
pulling force e.g. a rope
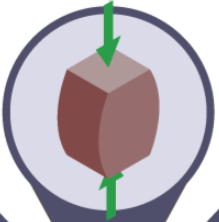
compression
force pressing on a material - being squashed
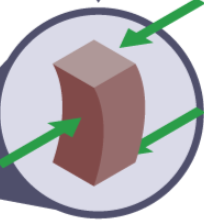
bending
forces at an angle to the material causing both tension & compression at the same time
neutral axis: the point between the tension and compression forces
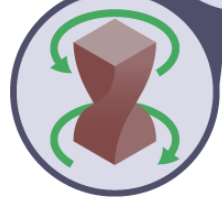
torsion
twisting force, often along the length of a material
shear (force)
when two parallel forces that are out of alignment are acting against each other e.g. blades of scissors acting against each other to shear paper
static load
load that doesn’t move and is constant e.g. books sitting on a shelf
dynamic load
load that is unstable or moving, which tends to increase the force applied to the material e.g. someone walking over a footbridge
ecological issues associated with product design
deforestation = loss of wildlife & soil erosion
mining = changes to the landscape, loss of habitat, noise and vibration
farming = loss of habitat (as farmers expand into new areas to find good soil)
transportation of products = pollution (from fuel usage)
production of carbon (during manufacture)
use of finite raw materials
use of landfill = chemical leaks into the ground, poisoning wildlife & humans
ecolocical issues - sustainability
companies must consider sustainability of the manufacture, use, and disposal of their products
sustainable products reduce demand on non-renewable raw materials and energy sources, produce less waste, and reduce pollution
carbon footprint
the amount of CO2 emissions that is directly or indirectly attributed to an individual / company, including:
extraction, transportation, processing and manufacture of products
power consumption (e.g. electrical power)
recycling & end-of-life disposal of products
travel e.g. commuting, holidays etc
how to reduce carbon footprint
energy: efficient house insulation, low energy lighting, alternative energies, turn down heating
water: reduce water use, turn off taps
travel: low carbon vehicles or car sharing, minimise number of journeys
recycling: recycle used glass, plastics, and paper
offsetting: offset carbon emissions by a tree planting programme
sustainability improvements - transportation
materials, parts, and product need to be transported, resulting in lots of ‘product miles’. these can be minimised by:
reducing the number of journeys by fitting more onto transport vehicles by making products smaller, lighter, and with less packaging
reducing length of journeys by using distribution hubs & moving processing plants closer to the source of materials
changing the energy source of vehicles to renewable sources (from fossil fuels)
sustainability improvements - leaner design
ecological impact needs to be considered at the beginning of the life of a product - at the design stage. the designer could:
use less materials / parts & include renewable materials / standardised parts
use easily separated parts for recycling
use energy efficient / repeatable manufacturing processes
reduce the amount / type of packaging
make products more sustainable - rechargeable, easy maintenance
ecological issues - recycling & reuse
recycling/reuse of products/materials is ecologically responsible, improves sustainability, and benefits the environment
goods can be made cheaper by not using new materials e.g. newly extracted aluminium costs 2x as much as recycled ones & 90% more energy is needed to extract raw aluminium
ways to reduce ecological issues - paper & boards
farm trees effectively to renew supply & reduce deforestation
recycle to reduce demand on raw material
use fewer toxic chemicals in processing
ways to reduce ecological issues - timber
FSC management of timber use & supply
farm trees effectively to sustain supply
ways to reduce ecological issues - systems
create rechargeable, energy efficient products to conserve energy
recycle batteries to reuse chemicals
use efficient processing methods
make printed circuit board parts easier to recycle
ways to reduce ecological issues - metals
recycle to reduce demand on raw materials
reduce environmental impact of mining, deforestation etc
use more efficient processing methods
ways to reduce ecological issues - textiles
recycle to reduce demand on raw materials
use natural (not synthetic) fibres
use reuse schemes e.g. charity donations
use fewer toxic chemicals in processing
ways to reduce ecological issues - polymers
minimalize environmental impact of drilling, fracking & processing oil
development of biodegradable polymers
recycle to reduce demand on raw material
society definition
a large organised group of people living together, such as a town, country, or continent
social issues: safe working conditions
companies have to ensure (so far as is practical) the health, safety, and welfare at work of all employees
health & safety at work act 1974 - strictly monitored & enforced (by the health & safety executive HSE) legislation about health & safety at work, covering welfare facilities, ventilation, cleanliness, space, lighting, temps, working hours, shift patterns, training etc
workers’ pay protected by minimum wage since 1999
safe working conditions - the fairtrade organisation
the fairtrade organisation looks at the interests of farmers & workers in other countries (who don’t have the same protection as in the UK) to ensue they have good working conditions, aren’t discriminated against, and are paid fairly
social issues: impact on others
companies must ensure that their products have a positive impact on people e.g:
source local products to help the local economy & support other jobs
design products so they don’t offend e.g. offensive logos / banding
donate to local / national / world charities or help at local volunteer events
social issues: reducing pollution
pollution has harmful effects on people’s lives e.g. it can cause respiratory diseases & chemical pollution of soil / water contributing to illnesses
atmospheric pollution is due to substances (e.g. CO2 emissions, toxic fumes, particles from factories) being released into the atmosphere, and contributes to global warming
some countries committed to reducing atmospheric pollution in the Paris agreement (2014) which was signed by 175 countries & aims to keep the rise in global temps below 2oC in the century
oceanic pollution is due to harmful substances (e.g. household waste, chemicals, particles of plastics) released into the ocean. 80% is from outside the water e.g. dumping of waste, sewage, chemical spills etc. legislation is being introduced to reduce this e.g. a ban on microbeads in cosmetics
the six Rs
checklist of points that should be considered in the development of a product
reduce the amount of material, consumables, energy usage in product
reuse the product for the same or a different purpose
recycle the product & use recycled materials
rethink whether there’s a better way of doing the product’s job
refuse to by products that are unsustainable
repair the product & ensure it’s easy to do so
the six Rs: 1. reduce
consider if it’s possible to reduce the amount of:
material in the manufacture of the product
consumables needed in the product (e.g. changing a vacuum cleaner to be bagless)
energy usage by using more energy efficient processes
the six Rs: 2. reuse
consider if it’s possible to reuse:
the product again for the same purpose by refilling it (e.g. ink cartridges / carrier bags)
try to get the max use out of the product before it wears out / has to be discarded
the product/parts of it for a different purpose (e.g. drinks bottles, textile insulation, bags for life)
the six Rs: 3. recycle
polymers, metals, textiles, timbers, paper and boards can all be recycled. consider if you can:
reprocess the waste in a product in the same system or to make something else
collect waste for commercial recycling
use recycled materials in a product
substitute unrecycled materials for recyclable ones
design/use products that are easy to dismantle to make recycling parts easier
the six Rs: 4. rethink
rethink product & how we use them - is there a better what of doing the same job that has less of an effect on the environment
the six Rs: 5. refuse
refuse to buy materials/products that are unsustainable
the six Rs: 6. repair
when designing the product, ensure that:
the product can be easily repaired to extend its life & reduce need for replacement to reduce manufacturing
spare parts are available
what is paper made from
wood specifically grown for making paper
other sources include recycled newspaper & recycled cloth
which type of wood is traditionally used to make paper
softwoods as their fibres are longer so they make stronger paper
however demand for paper is high so hardwoods & softwoods are also used
recycled fibres can’t be used endlessly so you need to have new fibres from wood pulp
most timber comes from coniferous trees (also used are deciduous trees, straw, bamboo, flax, ehmp)
pulping
breaking down wood / recycled materials to extract the fibres - the process used in making paper
paper making process
process removes lingin (what gives fibres structure) to allow fibres to be separated & reformed
trees are specifically grown for paper & harvested
logs are de-barked (bark is poor quality) and timber is chipped - cut into small pieces (2.5cm)
chips are made into pulp (mechanically or with chemicals) and the pulp is washed, refined, cleaned, and sometimes mixed with chemicals e.g. bleach, dyes, sizing agents
water is drained away on a wire screen (pulp is 99% water before) leaving a mat of damp fibres
damp fibres are calendared (put through a roller to remove the rest of the water & press it into a uniform thickness). more calendaring = more gloss
finished paper is dried and wound into rolls to be distributed & sent to factories to be cut into size
life cycle assessment
a method of assessing the environmental impact of the manufacture and use of materials and products
allows us to assess the impact of a product’s life ‘cradle to grave’
life cycle assessment of paper
lots of trees & vegetation are cut down to make paper & some companies replace the threes they cut down but it’s difficult to replace old ones with young ones of the same value - new trees take years to grow & old trees have established wildlife habitats, and are more effective at absorbing CO2. trees lost near rivers can cause banks to fall in causing flooding & loss of marine life (streams & rivers become blocked)
paper can be recycled but only a set number of times as it becomes weaker when recycled
when chemicals (fillers, colours etc) are washed into water supplies they can cause environmental concerns e.g. contamination of water
making boards
when it’s a single sheet it’s made the same way as paper, but they can also be made up of more than one layer (e.g. duplex board, foil-lined board)
some have a complex structure to provide impact resistance / increased strength e.g. corrugated card
how to select materials
materials are selected based on their working properties:
how they look
what they’re commonly used for
how they’re manufactured
how they perform in use
what makes them unique
selecting papers & boards
functionality: what the design does, for who, measurable performance factors
scale of production: processing, joining methods, manufacturing capability
environmental factors: sustainability, waste management, energy demands, recycling
aesthetics: how it looks, use of colour, texture, form
availability: availability of standard sizes/forms and components
cost: cost of the raw material, conversion into usable material, budget available, target price
mechanical properties: strength, tension, compression, shear
physical properties: absorbency, density, weight, fusibility
social factors: disabilities, religious groups, age of consumer, obsolescence
ethical factors: sourcing raw materials, manufacture, fair trade organisations
cultural factors: fashion, trends, faiths, background / beliefs of user
finishes: how long it’s intended to last, whether further protection is needed against decay
improving properties for papers & boards
flexibility - by scoring lines so the material can be bent into boxes / packaging
rigidity - by folding (stiffening)
surfaces - by lamination & encapsulation, also reinforcing the material
available formats for papers & boards
commercially available paper & card is available in standard forms. this is more cost effective & designers can incorporate standard forms into designs
sheet: a single piece of paper
roll: used on an industrial scale as they can be fed into machinery for continuous printing e.g. books & magazines
ply: two or more layers of paper combined together using embossing / adhesive to form multi-ply (or two-ply) paper e.g. napkins, receipts that self-copy to a second layer
set standards of paper & boards
measured by:
length & width normally in mm
weight in gsm (grams per square meter)
thickness in microns (1/1000th of a millimetre, μm)
colour - white paper is graded on whiteness
common gsm, micron, whiteness measurements for paper & board
gsm (weight)
60-120gsm = printing paper
over 160gsm = card
over 220gsm = board
microns (thickness)
a greetings card would be ~300microns (0.3mm) thick
whiteness (colour)
the higher the number, the whiter it is
copier paper between 130-170
types of paper & board
mounting board (1000-2000μm) - relatively thick & rigid with colour on one side, used for picture framing
newsprint (45-55gsm) - thin, low quality, low cost, lightweight paper. rough surface, off-white colour
tissue paper (10-35gsm) - lightweight, coloured, used for absorbency properties and crafts
copier paper (80gsm) - low cost, available, smooth surface, good whiteness
standard sizes for paper (A, B, C series)
A series: used at home & work, A0-A10, halve in size with every increase in number (A10 is the smallest, A0 is huge)
B series: larger sizes used for posters & in industry
C series: smaller sizes used for envelopes, the size of a A series piece of paper folded in half (C5 = A5 in half)
fasteners
used to join paper / card temporarily or permanently
treasury tag: connects sheets through punched holes
binder clip / bulldog clip: holds sheets together using a variety of actions
paper fastener: connects smaller numbers of sheets through punched holes
slide bunder: temporarily holds sheets together
staple: applied with stapling tool to hold sheets together
paperclip: simple method to hold a few sheets
sealing
paper & board can be closed securely through sealing in various ways
gummed envelope: water soluble gum along envelope flap is moistened to seal
self-adhesive envelope: covering over glue is peeled off to seal, or a flap can have a strip of latex which seals when pressed together
wax seal: wax is melted over area and is left to harden
string and button: string wrapped around two buttons to close package
binding
binding methods are used to combine multiple sheets of paper
perfect binding: pages gathered in smaller groups with a hard / flexible outer cover and glued at the spine - used in most books
comb binding: combs fit through punched holes allowing pages to lie flat - low cost & popular
coil / spiral binding: spiral of plastic / metal wire is threaded through holes, allowing pages to lie flat
saddle stitching: wire on a roll fed through pages and cut to make staples, limited number of pages, e.g. magazines
scales of production: one-off/prototype
a single unique product that’s individually designed e.g. furniture, wedding dresses
prototype is a type of one-off production that’s a unique concept experimental model, the first example of a design
high quality to exact specifications, made by skilled workers, is unique
expensive (cost of materials is higher), labour intensive, long production times
scales of production: batch
a set number of products made in limited quantities or limited time e.g. textbooks, designer clothes
allow customers a wider choice of designs, quick response to demand, economics of scale (high unit output) so materials can be bought in bulk, can respond to seasonal demand
must be stored, re-tooling machines for different processes could be costly, some processes will be repetitive as larger numbers made
scales of production: mass
efficiently & consistently produces many products at a low cost per unit, with automated systems and parts added in sequence in a production line e.g household appliances, kids toys & clothes - design changes are limited
cheaper materials in high quantities, high level of quality control, low unit cost, cheaper labour
high initial set up cost, if production line breaks manufacture is halted, repetitive, less flexibility to respond to market
scales of production: continuous
manufacturing thousands of identical high-demand product components / materials 24 hours a day e.g. standard single components e.g. buttons, nuts, bolts, rivets, lego blocks, drinks cans, sheet materials e.g. glass & steel
removes cost of stopping & starting production process, cheaper materials in high quantities
automation = staff redundancy, little flexibility to change production without large costs
need for production aids
manufacturing can be very labour intensive so manufacturers use aids to speed up processes
production aids: reference points / datums
it’s important to have a constant point to make measurements from that’s identified before marking out
reference point will usually be a square edge or corner, and it can be a datum edge for metal / plastics or a face side & face edge for wood
reference point can be machined first so it’s accurate & all measurements are taken from it
production aids: patterns
patterns: replicas of the product that’s to be made
accuracy of pattern is related to quality of the product to be made
patterns can be made from cheaper material e.g. paper / wood which is easier to work and can be used many times or re-made as the design changes
can be made by hand but using CAD (computer aided design) is quicker
wallpaper is an example of use of patterns
production aids: templates
templates are used to ensure shapes, positions, or markings are accurate & consistent throughout the design & production process. they guarantee that information is placed correctly and shapes are drawn & cut precisely
they’re often made to the exact size of the shape to be cut / location of holes to be drilled. they can be fitted onto a material to easily transfer markings, and can be used once then discarded, with more copies made when needed
templates can be used for quality control by checking the final product’s shape after it’s been made
production aids: jigs
jig: a device for holding work in place to help when carrying out repetitive manufacturing methods
jigs hold work in the same position and the cutting tool is guided to the correct place e.g. for drilling accurate holes in wood
advantages of patterns, jigs & templates
greater productivity
quicker production
simplifies more complex processes
reduced costs
increased accuracy, quality, and tolerance
tolerance
an allowable margin of error to ensure that a part will still function as long as it’s in the tolerance range
tolerances are set with an upper & lower limit and can relate to size, weight, colour, strength, quantity etc
parts manufactured within tolerance always fit, and it can be dangerous if they don’t do this e.g. a nut & bolt being loose in an aircraft engine
quality control
a quality control system is set up throughout the manufacturing process to check that parts & assembled product are to the correct standard & within tolerance
QC equipment is expensive to set up so most companies use random sampling - more cost effective than checking every product individually
quality control tests
paper & boards - registration marks / colour charts: used for multiple printing processes to show that each process has been accurately lined up
timber - go/no go fixture tool / gauges: used to check the upper & lower limits of tolerance - it’s in tolerance if it fits within the larger opening (go) and doesn’t fit within the smaller opening (no go). can be used quickly as there’s no measurement involved
textiles - inspection of printed material: printed fabric often has a mismatch in pattern & this is particularly important when fabric is joined. fabric is visually inspected in manufacture & when sewn together
electrical & mechanical systems - timbers for exposure ‘soak’ times: timing how long a PCB should be exposed to the UV light, developer or etchant, as overexposure can lead to breaks in tracks
metals - depth stops and guides: depth stops fitted to machinery to ensure work is cut to the right length / depth
polymers - CNC laser settings: make sure laser cutters have the correct info about kerf allowance, material and thickness so they cut accurately
offeset lithography
used for long printing runs (books, magazines, packaging, posters) by transferring the image to be printed from the plate to a roller / blanket cylinder and then to the paper - plate doesn’t come into contact with the paper
the litho-printing plate cylinder has a relief image on it(image stands out from the surface), and plates are made from flexible polymers / aluminium
litho-printing plate is dampened with water (to repel ink from non-image areas)
ink is applied to litho-printing plate as it rotates
ink is transferred to offset blanket cylinder as they rotate against each other
ink is transferred to the paper / card as it’s pulled through the rollers from the pressure of the blanket cylinder & impression cylinder
only one colour can be printed at a time
colour models: CMYK
uses layers of coloured ink to partially or entirely reduce the light reflected from the lighter background e.g. white paper. colours used are cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black)
colour models (RGB)
adds layers of the three primary colours to produce a broad array of colours
die cutting
once printing is completed, the finished sheet needs to be accurately cut to shape using a die cutting machine
dies: the cutters used to create the shapes. made of hardened steel blades (rules) that are expensive to produce but reusable. they are fitted to stamping machines to carry out the process
the material is cut with the dies and rubber ejectors push it out. waste is recycled
the paper/board can be creased using rounded rules to allow for folding
rollers can sometimes be fitted with cutters to cut continuous runs
measuring equipment
ruler to measure distance and draw a straight line
protractor to measure angles
set square to draw lines at specific angles
french curves to draw curves of different sizes
cutting equipment
guillotine to cut a large number of paper sheets at once with a straight edge
craft knife to cut & score paper & cardboard, particularly useful when cutting internal shapes
compass cutter to cut a circle / arc from paper / thin card
rotary cutter to cut a circle / arc from thicker cardboard
die cutter to cut, crease, and perforate paper & card at high speed & accuracy
laser cutter to perform perfect intricate cuts to paper & card
coatings & surface alterations
paper & board can be protected by laminating, giving a shiny water resistant surface while being thick and durable, making the material last longer. the paper / board is put in a plastic sleeve which is heated & pulled through rollers, bonding the two surfaces of the film together and sealing the product in
paper can be modified with chemicals e.g. bleach to make it whiter
sizing is when chemicals are added to give the paper a protective glaze that prevents it from being absorbent and makes it suitable for use with wet marker pens - the ink won’t bleed
clay can be added to card to make a paper plate
clear UV sensitive liquid can be applied to card to give it a high gloss finish - this is better for the environment than lamination as laminated polymer is harder to recycle
printing: offset lithography
relief printing plate on rollers onto paper
advantages: inexpensive, prints on a variety of papers, high speed, good quality images
disadvantages: high set up costs, needs to be flat, damp can stretch paper / affect colour
uses: books, magazines, packaging, posters
surface treatments & finishes
used to enhance functional & aesthetic properties of papers & boards
printing, embossing, UV varnishing
printing: flexography
flexible relief printing plate on rollers, papers fed from a roll
advantages: inexpensive as high volume, inks dry quickly, high speed
disadvantages: high set up costs, lower quality, print runs in excess of 500k
uses: newspapers, sweet papers, low cost magazines
printing: screen printing
ink printed through finely woven fabric, non-print area masked
advantages: prints of a variety of surfaces, good for short runs
disadvantages: long drying times, lack detail
uses: posters, mugs, t-shirts, point of sale displays
printing: gravure
rotary printing using engraved cylinder
advantages: high speed, consistent colour & quality on a variety of papers
disadvantages: high set up costs
uses: high quality magazines & books, stamps
printing: photocopying
drum charged when exposed to original copy, toner fixes to charged areas, transferred to paper and fused by heat
advantages: high speed, good for small batches, can be double sided, low cost, convenient
disadvantages: can fade over time, variable quality as ink is used, expensive for long runs
uses: home or business, flyers, documents