(L1) Alcohol metabolism and oxidative stress
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:25 PM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
Alcohol metabolism
1. Where in the body is alcohol metabolism carried out?
2. Give the enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism
3. Recommended alcohol limits for both mean and women
4. Give the rate of alcohol metabolism
1. Where in the body is alcohol metabolism carried out?
2. Give the enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism
3. Recommended alcohol limits for both mean and women
4. Give the rate of alcohol metabolism
Alcohol metabolism
1. Where in the body is alcohol metabolism carried out?
90% of alcohol metabolism takes place in the liver whilst the rest is excreted passively in urine and on the breath.
2. Give the enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism
Alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase
3. Recommended alcohol limits for both mean and women
For both men and women its recommended that a maximum of 14 units should be consumed per week and spread out over at least 3 days.
4. Give the rate of alcohol metabolism
One unit of alcohol (8g) is eliminated at a rate of 7g per hour
1. Where in the body is alcohol metabolism carried out?
90% of alcohol metabolism takes place in the liver whilst the rest is excreted passively in urine and on the breath.
2. Give the enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism
Alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase
3. Recommended alcohol limits for both mean and women
For both men and women its recommended that a maximum of 14 units should be consumed per week and spread out over at least 3 days.
4. Give the rate of alcohol metabolism
One unit of alcohol (8g) is eliminated at a rate of 7g per hour
2
New cards
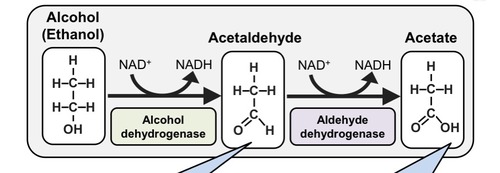
Give the process of alcohol metabolism
Alcohol (ethanol) is converted to Acetaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase.
Acetaldehyde is converted to acetate by aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Acetate is then converted to acetyl CoA and used in the TCA cycle or in fatty acid synthesis.
Smaller amounts of alcohol can also be oxidized by the cytochrome CYP2E1 or by catalase in brain.
Acetaldehyde is converted to acetate by aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Acetate is then converted to acetyl CoA and used in the TCA cycle or in fatty acid synthesis.
Smaller amounts of alcohol can also be oxidized by the cytochrome CYP2E1 or by catalase in brain.
3
New cards
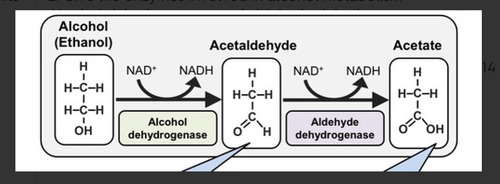
How can alcohol abuse result in liver damage?
Aldehyde dehydrogenase has a role in keeping acetaldehyde toxicity at low levels.
However prolonged and excessive consumption of alcohol can cause sufficient Acetaldehyde accumulation, this can then cause liver damage.
An abundance of excess NADH and Acetyl-CoA leads to changes in liver metabolism causing fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis.
However prolonged and excessive consumption of alcohol can cause sufficient Acetaldehyde accumulation, this can then cause liver damage.
An abundance of excess NADH and Acetyl-CoA leads to changes in liver metabolism causing fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis.
4
New cards
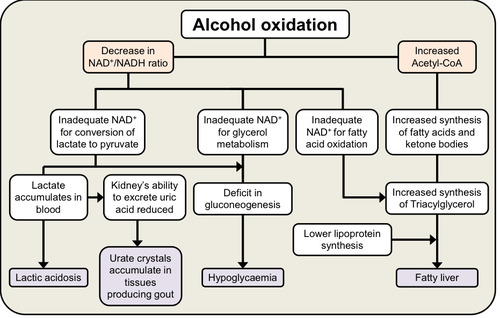
How does alcohol oxidation result in:
1. Fatty liver
2. Hypoglycaemia
3. Gout
4. Lactic acidosis
1. Fatty liver
2. Hypoglycaemia
3. Gout
4. Lactic acidosis
5
New cards
What is Disulfaram and how does it work?
Disulfaram is a drug that can be used to treat alcohol dependence.
It inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase.
This means that Acetaldehyde can't be converted to acetate.
If the patient drinks alcohol, acetaldehyde will accumulate causing the symptoms of a 'hangover'.
This acts as a conditioning technique that causes the association of alcohol with feeling sick.
It inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase.
This means that Acetaldehyde can't be converted to acetate.
If the patient drinks alcohol, acetaldehyde will accumulate causing the symptoms of a 'hangover'.
This acts as a conditioning technique that causes the association of alcohol with feeling sick.
6
New cards
What are free radicals?
A free radical is an atom or molecule that contains one or more
unpaired electrons and is capable of independent ("free")
existence.
Theyre usually very reactive and work to take electrons from other atoms, molecules or ions, this is done to get a pair for the unpaired electron.
Its the reaction of a radical with a molecule that typically generates a
second radical thereby encouraging damage.
unpaired electrons and is capable of independent ("free")
existence.
Theyre usually very reactive and work to take electrons from other atoms, molecules or ions, this is done to get a pair for the unpaired electron.
Its the reaction of a radical with a molecule that typically generates a
second radical thereby encouraging damage.
7
New cards
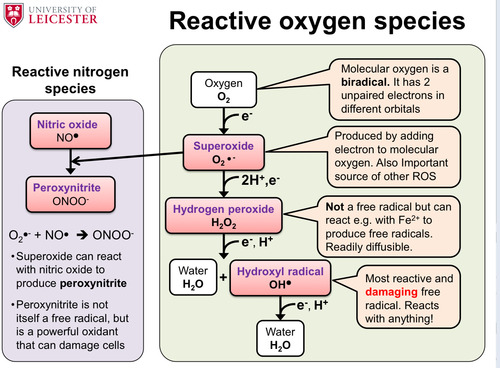
Give the 4 components of the reactive oxygen species and the 2 components of the reactive nitrogen species and describe how they can be made
8
New cards
Explain the two ways in which ROS can cause damage to DNA and what the possible effects of these actions could be
1. The ROS reacts with a base and removes an electron.
This modified base can then lead to mispairing and mutation .
2. The ROS reacts with sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and can cause strand break and mutation on repair
The reaction of the ROS with DNA reaults in DNA damage.
Failure to repair to this damage can lead in mutation that can be permanently embedded in DNA.
This can then lead to cancer.
This modified base can then lead to mispairing and mutation .
2. The ROS reacts with sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and can cause strand break and mutation on repair
The reaction of the ROS with DNA reaults in DNA damage.
Failure to repair to this damage can lead in mutation that can be permanently embedded in DNA.
This can then lead to cancer.
9
New cards
What is the clinical function of 8-oxo-dG?
8-oxo-dG is a mutated form of the deoxyguanosine molecule.
When there are high levels of oxidative stress, it's found in abundance in the body
It can be used as measurement of oxidative damage.
When there are high levels of oxidative stress, it's found in abundance in the body
It can be used as measurement of oxidative damage.
10
New cards
Describe what can happen if DNA damage occurs to proteins
If the ROS reacts with the backbone of the protein it can cause fragmentation.
This fragmentation can then lead to protein degradation.
However if the ROS reacts with the sidechain of the protein it can cause the formation of a modified side chain (e.g the formation of disulphide bonds).
This can cause a change in structure (it affects the tertiary structure) leading to 3 different end points:
Loss of function, gain of function or protein degradation.
This fragmentation can then lead to protein degradation.
However if the ROS reacts with the sidechain of the protein it can cause the formation of a modified side chain (e.g the formation of disulphide bonds).
This can cause a change in structure (it affects the tertiary structure) leading to 3 different end points:
Loss of function, gain of function or protein degradation.
11
New cards
Disulphide bonds
1. Role
2. Where they form
3. How can ROS cause inappropriate disulphide bond formation?
4. Effects of inappropriate disulphide bond formation
1. Role
2. Where they form
3. How can ROS cause inappropriate disulphide bond formation?
4. Effects of inappropriate disulphide bond formation
1. Role
Disulphide bonds are involved in the folding and stability of some proteins.
2. Where they form
The bonds form between thiol groups of cysteine residues (-SH).
3. How can ROS cause inappropriate disulphide bond formation?
Inappropriate disulphide bond formation can occur if ROS takes electrons from cysteines.
4. Effects of inappropriate disulphide bond formation
This can result in misfolding, crosslinking and disruption of function.
Disulphide bonds are involved in the folding and stability of some proteins.
2. Where they form
The bonds form between thiol groups of cysteine residues (-SH).
3. How can ROS cause inappropriate disulphide bond formation?
Inappropriate disulphide bond formation can occur if ROS takes electrons from cysteines.
4. Effects of inappropriate disulphide bond formation
This can result in misfolding, crosslinking and disruption of function.
12
New cards
Describe the damage inflicted onto lipids by ROS
1. A Free radical extracts a hydrogen atom from a polyunsaturated fatty acid in the membrane lipid
2. A lipid radical is formed which can react with oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical
3. This initiates a chain reaction as more lipid radicals are being formed.
4. This causes damage to the membrane lipid bilayer and the integrity of the membrane fails.
2. A lipid radical is formed which can react with oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical
3. This initiates a chain reaction as more lipid radicals are being formed.
4. This causes damage to the membrane lipid bilayer and the integrity of the membrane fails.
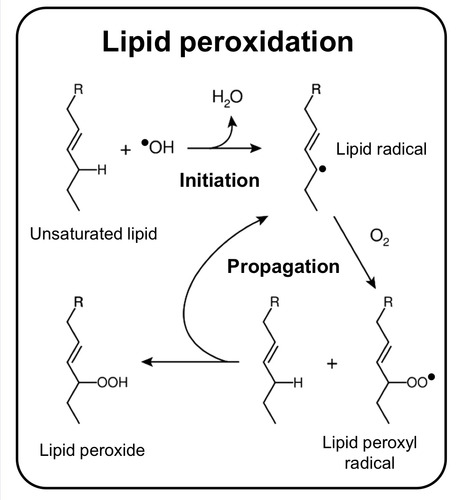
13
New cards
Give 3 endogenous and 4 exogenous sources of biological oxidants
Endogenous:
• Electron transport chain
• Nitric oxide synthases
• NADPH oxidases
Exogenous:
• Radiation (Cosmic rays, UV light,
X-rays)
• Pollutants
• Drugs (e.g Primaquine (anti-malarial) )
• Toxins (e.g Paraquat (herbicide))
• Electron transport chain
• Nitric oxide synthases
• NADPH oxidases
Exogenous:
• Radiation (Cosmic rays, UV light,
X-rays)
• Pollutants
• Drugs (e.g Primaquine (anti-malarial) )
• Toxins (e.g Paraquat (herbicide))
14
New cards
How can the electron transport chain act as a source of ROS
• NADH and FADH2 supply electrons (e−) from metabolic substrates
• Electrons pass through the ETC and reduce oxygen to form H2O at Complex IV
• However sometimes electrons can accidently escape chain and react with dissolved O2 to form superoxide
• Electrons pass through the ETC and reduce oxygen to form H2O at Complex IV
• However sometimes electrons can accidently escape chain and react with dissolved O2 to form superoxide
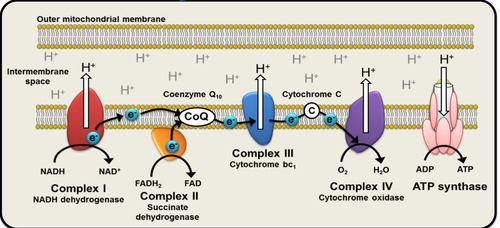
15
New cards
What is the function of nitric oxide synthases and list the different types.
Give the function of nitric oxide and list its effects at toxic levels.
Give the function of nitric oxide and list its effects at toxic levels.
These enzymes are used to convert the enzyme arginine to citrulline and nitric oxide.
It results in the oxidation of NADPH to NADP+.
It results in the oxidation of NADPH to NADP+.
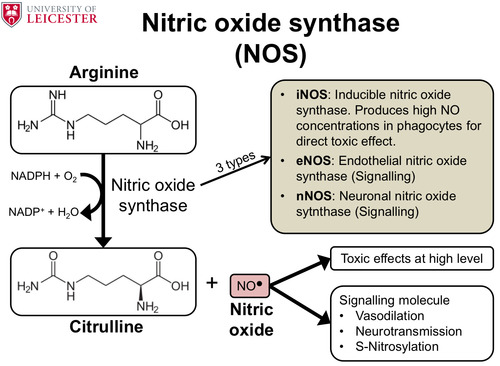
16
New cards
Respiratory burst
1. What is it?
2. What is its function?
3. Enzymes involved in the process
4. Effect of chronic granulomatous disease
1. What is it?
2. What is its function?
3. Enzymes involved in the process
4. Effect of chronic granulomatous disease
1. What is it?
It's the rapid release of superoxide which breaks down into H2O2 and peroxynitrite from phagocytic cells (e.g. neutrophils and monocytes).
The H2O2 is convereted to Hypochlorite (bleach)
2. What is its function?
The ROS, hypochlorite and peroxynitrite destroy invading bacteria.
3. Enzymes involved in the process
NADPH oxidase- This enzyme is used to convert NADPH to NADP to produce superoxide from oxygen.
iNOS- Used to produce NO*
Myeloperoxidase- Its ised to produce hypochlorite from H2O2
4. Effect of chronic granulomatous disease
This is a genetic defect in the NADPH oxidase complex which causes enhanced susceptibility to bacterial infections resulting in:
Atypical infections, Pneumonia, Abscesses, Impetigo, Cellulitis
It's the rapid release of superoxide which breaks down into H2O2 and peroxynitrite from phagocytic cells (e.g. neutrophils and monocytes).
The H2O2 is convereted to Hypochlorite (bleach)
2. What is its function?
The ROS, hypochlorite and peroxynitrite destroy invading bacteria.
3. Enzymes involved in the process
NADPH oxidase- This enzyme is used to convert NADPH to NADP to produce superoxide from oxygen.
iNOS- Used to produce NO*
Myeloperoxidase- Its ised to produce hypochlorite from H2O2
4. Effect of chronic granulomatous disease
This is a genetic defect in the NADPH oxidase complex which causes enhanced susceptibility to bacterial infections resulting in:
Atypical infections, Pneumonia, Abscesses, Impetigo, Cellulitis
17
New cards
List the 3 types of cellular defences
1. Superoxide dismutase and catalase
2. Glutathione
3. Free radical scavengers
2. Glutathione
3. Free radical scavengers
18
New cards
How can superoxide dismutase and catalase be used to defend the cell from oxidative stress?
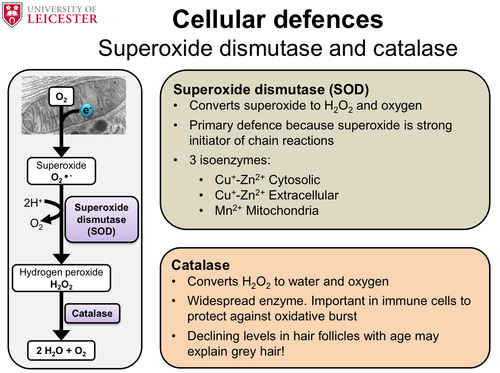
19
New cards
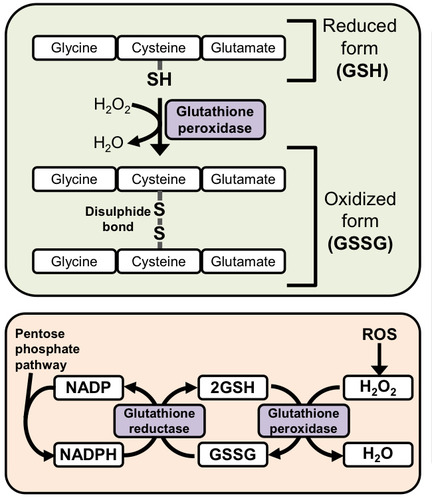
How can glutathione be used to defend the cell from oxidative stress?
Glutathione is a a tripeptide thats synthesised by the body to
protect against oxidative damage.
The thiol hroup (SH) of cysteine resudeus donate electrons to the ROS. GSH will then react with another GSH to form disulphide (GSSG).
This action is catalysed by glutathione peroxidase which requires selenium to work.
The GSSG is then reduced back to GSH by
glutathione reductase which catalyses the transfer of electrons
from NADPH to the disulphide bond.
protect against oxidative damage.
The thiol hroup (SH) of cysteine resudeus donate electrons to the ROS. GSH will then react with another GSH to form disulphide (GSSG).
This action is catalysed by glutathione peroxidase which requires selenium to work.
The GSSG is then reduced back to GSH by
glutathione reductase which catalyses the transfer of electrons
from NADPH to the disulphide bond.
20
New cards
Give 3 functions of NADPH
1. Reducing power for biosynthesis
2. Maintenance of GSH levels
3. Detoxification reactions
2. Maintenance of GSH levels
3. Detoxification reactions
21
New cards
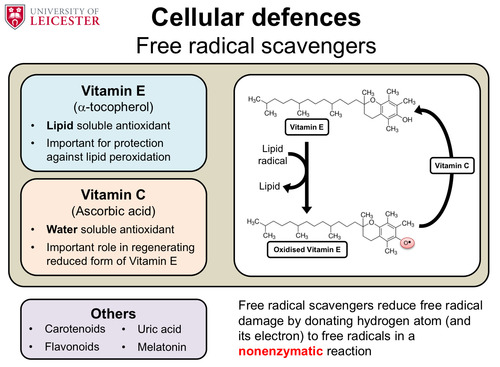
How can free radical scavengers be used to defend the cell from oxidative stress?
Vitamin E and Vitamin C are the main free radical scavengers.
22
New cards
Galactosaemia and the effects of this
A deficiency in any of the 3 galactose enzymes results in galactose being converted to galactitol by aldose reductase causing Galactosaemia.
This process uses up NADPH reserves which compromises defences against ROS damage.
It can result in symptoms such as cataracts as the crystallin protein in the lens of the eye is denatured.
This process uses up NADPH reserves which compromises defences against ROS damage.
It can result in symptoms such as cataracts as the crystallin protein in the lens of the eye is denatured.
23
New cards
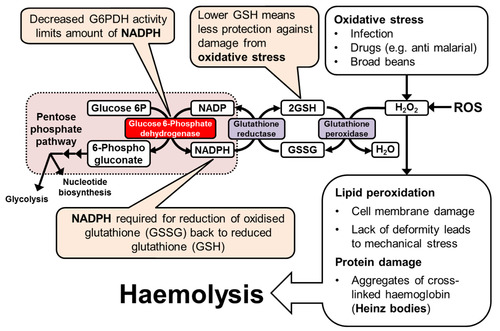
G6PDH Deficiency
1. Role of G6DPH
2. What can cause oxidative stress
3. Effect on RBC
4. Effect of G6PDH deficiency
1. Role of G6DPH
2. What can cause oxidative stress
3. Effect on RBC
4. Effect of G6PDH deficiency
1. Role of G6DPH
G6PDH is found in the phosphate pentose pathway.
Its an enzyme thats used to produce NADPH from NADP and 5c pentose phosphates.
2. What can cause oxidative stress
Infection, drugs and broad beans
3. Effect on RBC
RBC can be very heavily affected by G6PDH deficency as its only source of NADPH is the pentose ohosphate pathway so of their G6PDH enzyme is ineffective theres no way to return glutathione to its reduced state.
As well as this RBC are used to carry oxygen so theyre more easily affected by ROS.
4. Effect of G6PDH deficiency
This deficiency can cause lipid peroxidation (cell membrane damage) and protein damage.
The protein damage results in aggregates of cross linked haemoglobin known as heinz bodies.
This results in haemolysis
G6PDH is found in the phosphate pentose pathway.
Its an enzyme thats used to produce NADPH from NADP and 5c pentose phosphates.
2. What can cause oxidative stress
Infection, drugs and broad beans
3. Effect on RBC
RBC can be very heavily affected by G6PDH deficency as its only source of NADPH is the pentose ohosphate pathway so of their G6PDH enzyme is ineffective theres no way to return glutathione to its reduced state.
As well as this RBC are used to carry oxygen so theyre more easily affected by ROS.
4. Effect of G6PDH deficiency
This deficiency can cause lipid peroxidation (cell membrane damage) and protein damage.
The protein damage results in aggregates of cross linked haemoglobin known as heinz bodies.
This results in haemolysis
24
New cards
What are Heinz bodies?
These are oxidized, precipitated hemoglobin embedded in the membrane on RBCs.
This will alter the rigidity of the cell membrane.
This will alter the rigidity of the cell membrane.
25
New cards
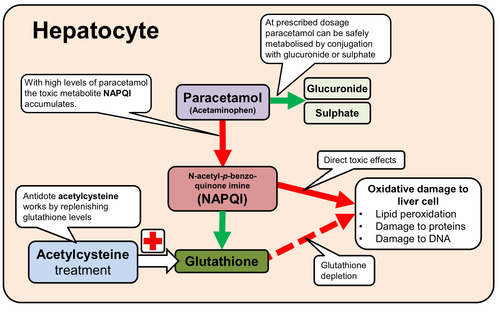
Metabolism of paracetamol
1. Where does this take place?
2. Use of paracetamol at normal dosage
3. Effects of excessive use of paracetamol
4. Treatment to excessive ingestion of paracetamol
1. Where does this take place?
2. Use of paracetamol at normal dosage
3. Effects of excessive use of paracetamol
4. Treatment to excessive ingestion of paracetamol
26
New cards
Symptoms of haemolysis
1. Anaemia
This is a condition that results in a deficiency of RBCs/ haemoglobin in the blood.
The HB concentration is below normal for the age and gender of the patient.
Theres an increase in the concnetration of breakdown products in the blood e.g bilirubin.
Theres an increase in RBC production and retuculocytes in the blood to try and keep the Hb levels up
2. Dark urine
This is due to the presence of haemoglobin (haemoglobinuria) in the urine.
3. Jaundice
Bilirubin is a yellow by-product of the breakdown of RBCs made from the metabolism of the haem group pf haemoglobin.
It's normally excreted in the bile and urine.
Jaundice is caused by high bilirubin levels.
This is a condition that results in a deficiency of RBCs/ haemoglobin in the blood.
The HB concentration is below normal for the age and gender of the patient.
Theres an increase in the concnetration of breakdown products in the blood e.g bilirubin.
Theres an increase in RBC production and retuculocytes in the blood to try and keep the Hb levels up
2. Dark urine
This is due to the presence of haemoglobin (haemoglobinuria) in the urine.
3. Jaundice
Bilirubin is a yellow by-product of the breakdown of RBCs made from the metabolism of the haem group pf haemoglobin.
It's normally excreted in the bile and urine.
Jaundice is caused by high bilirubin levels.