Membrane Structure and Function
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary related to the structure and function of cellular membranes, including terms related to transport mechanisms and the properties of the plasma membrane.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Plasma membrane
A structure conserved across domains that regulates cell interactions and environmental exchanges.
Fluid mosaic model
Describes the plasma membrane as a mosaic of proteins floating in or on the fluid lipid bilayer.
Amphipathic
Referring to molecules like phospholipids that have both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-fearing) regions.
Selective permeability
Property that allows some substances to pass through the membrane more easily than others.
Passive transport
Movement of molecules across a membrane without the use of energy, typically along a concentration gradient.
Active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves solutes against their concentration gradient.
Bulk transport
Transport of large molecules across the plasma membrane through vesicles.
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell expels materials in vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane.
Endocytosis
Process in which cells absorb molecules by engulfing them in a vesicle.
Phagocytosis
Type of endocytosis where a cell engulfs large particles or cells (cell eating). Absorption of food into a vacuole. Really large molecules.
Pinocytosis
Type of endocytosis often referred to as 'cellular drinking,' where the cell engulfs liquid. Smaller molecules than in phagocytosis but too large for passive transport.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Process where cells take in specific substances by the inward budding of the plasma membrane.
Transport proteins
Proteins that assist in the movement of substances across the cell membrane.
Channel proteins
Transport proteins that provide corridors for specific molecules or ions to pass through the membrane.
Carrier proteins
Proteins that undergo conformational changes to shuttle materials across the membrane.
Aquaporins
Specialized channel proteins that facilitate the rapid transport of water across the plasma membrane.
Sodium-potassium pump
Active transport mechanism that moves sodium ions out of and potassium ions into the cell.
Cotransport
Mechanism in which the diffusion of one substance is coupled with the transport of another against its gradient.
Membrane potential
The voltage difference across a membrane that affects the movement of ions.
Electrogenic pump
A transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane, such as the sodium-potassium pump.
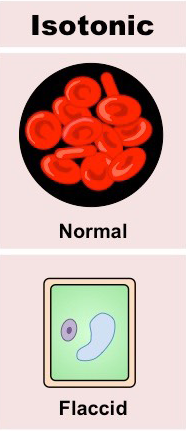
Isotonic
The concentration of water is equal on both sides of a membrane, resulting in no net movement of water.
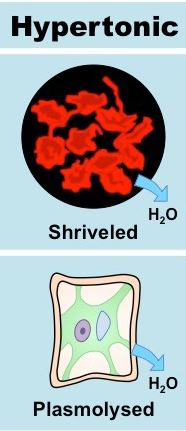
Hypertonic
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes compared to the inside of a cell, causing water to exit the cell.
Hypotonic
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes compared to the inside of a cell, causing water to enter the cell.

Concentration Gradient
The gradual change in concentration of solutes in a solution between two regions, influencing the direction of movement of substances across a membrane. High to low.
Facilitated Diffusion
The process by which molecules pass through a cell membrane via special protein channels, allowing substances to move across the membrane without energy, following their concentration gradient. A type of passive transport.
Plasmolyzed
A condition in plant cells where the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall due to water loss in a hypertonic environment, causing the plant to wilt. Net movement of water out of the cell.
Flaccid
A state of plant cells where they are not turgid due to insufficient water, resulting in a soft and limp texture. This condition can arise when the surrounding solution is isotonic. Condition of being soft and limp.
Turgid
A condition in plant cells where they are fully swollen and firm due to water uptake, typically in a hypotonic environment, promoting structural support and optimal function. Prefered/stable condition for plants.
Lysed
A condition in cells where the cell membrane has ruptured due to excessive water uptake, typically occurring in a hypotonic environment, leading to cell death. Result of excessive swelling and cell bursting.