antibodies 5)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
What is an antibody?
Y shaped proteins made by plasma cells that form antigen-antibody complex during immune response
2
New cards
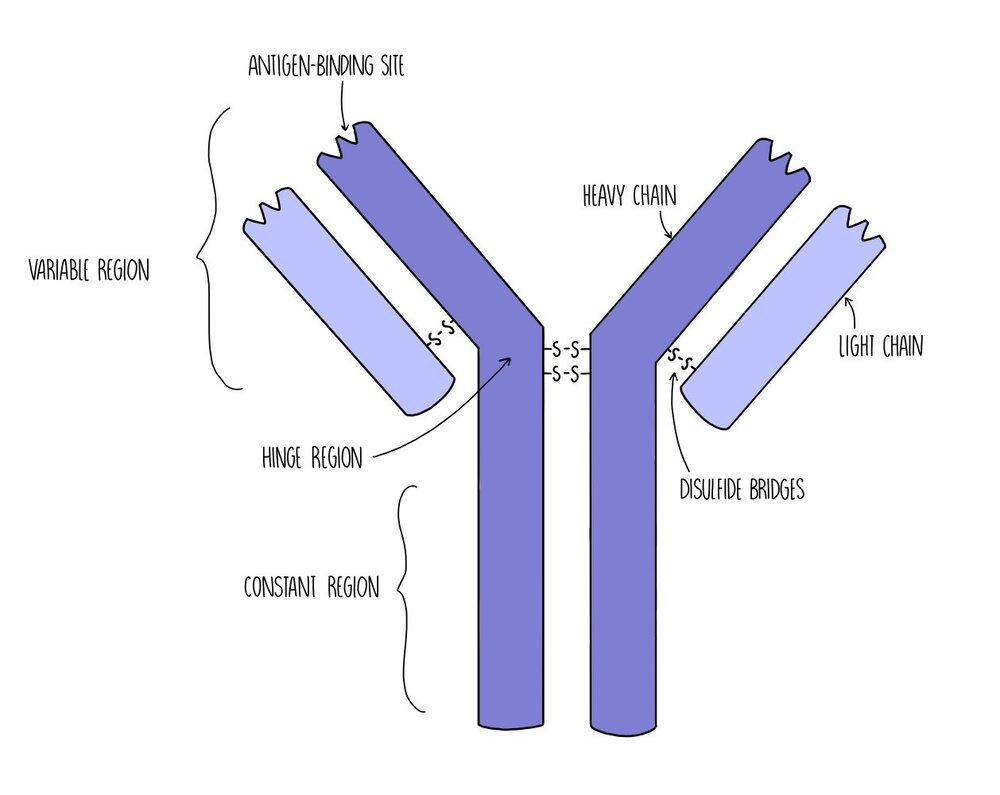
Explain the structure of an antibody (5)
-quaternary structure protein.
-Y shaped molecule with 4 polypeptide chains → 2 heavy chains, 2 light chains.
-Variable region → contains a specific binding site, that fits very precisely onto a specific antigen to form antigen-antibody complex
BS :different for each antibody.
-Generic constant region → allows attachment to phagocytic cells.
-Hinge regions → allows for flexibility; hence can bind to multiple antigens
-Y shaped molecule with 4 polypeptide chains → 2 heavy chains, 2 light chains.
-Variable region → contains a specific binding site, that fits very precisely onto a specific antigen to form antigen-antibody complex
BS :different for each antibody.
-Generic constant region → allows attachment to phagocytic cells.
-Hinge regions → allows for flexibility; hence can bind to multiple antigens
3
New cards
How do antibodies lead to the destruction of an antigen? (2)
1)Agglutination; cells clump together, making it easier for phagocytes to locate them .
(agglutination is possible because each antibody has 2 antigen binding sites.)
2)serve as markers; stimulate phagocytes to engulf cells.
ANTIBODIES do not destroy antigens directly, but prepare antigen for destruction.
(agglutination is possible because each antibody has 2 antigen binding sites.)
2)serve as markers; stimulate phagocytes to engulf cells.
ANTIBODIES do not destroy antigens directly, but prepare antigen for destruction.
4
New cards
State how antibodies deal with infection via neutralisation
Antibodies bind to toxins on a virus
Prevents the binding of these toxins
Prevents the binding of these toxins
5
New cards
State 3 applications of monoclonal antibodies
medical treatment
medical diagnosos
pregnacy tests
medical diagnosos
pregnacy tests
6
New cards
State the two ways monoclonal antibodies are used to treat cancer
Direct monoclonal antibody therapy
Indirect monoclonal antibody therapy
Indirect monoclonal antibody therapy
7
New cards
Explain direct monoclonal antibody therapy for cancer
Monoclonal antibodies produced which have a binding site → specific /complementary to cancer cell antigens.
Antibodies given to patient + attach themselves to receptors on cancer cells.
Blocks chemical signals that stimulate uncontrolled growth
Therefore, the monoclonal antibodies prevent the cancer cells growing and as they are designed to only attach to cancer cells they do not cause harm to other normal cells
Antibodies given to patient + attach themselves to receptors on cancer cells.
Blocks chemical signals that stimulate uncontrolled growth
Therefore, the monoclonal antibodies prevent the cancer cells growing and as they are designed to only attach to cancer cells they do not cause harm to other normal cells
8
New cards
Explain indirect monoclonal antibody therapy
Cancer can also be treated with monoclonal antibodies complementary to the antigens outside of cancer cells, which have drugs attached .
Cytotoxic / radioactive drug attached to monoclonal antibodies.
Cancer cells die when antibody attaches.
Cytotoxic / radioactive drug attached to monoclonal antibodies.
Cancer cells die when antibody attaches.
9
New cards
What are the advantages of antibody therapies with monoclonal antibodies?
Specific
Reduces side effects
Smaller doses of drug required (indirect only)
Reduces side effects
Smaller doses of drug required (indirect only)
10
New cards
What does ELISA stand for?
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
detect and quantify the precense of specific antigens or antibodies e.g proteins, hormones, toxins, pathogens
detect and quantify the precense of specific antigens or antibodies e.g proteins, hormones, toxins, pathogens
11
New cards
Describe the steps in the indirect ELISA test
1. Apply sample to surface (antigens attach)
2. Wash to remove unattached antigens
3. Add specific antibody + leave to bind
4. Wash to remove excess antibody
5. Add second antibody with enzyme attached to bind with first antibody.
6. Add colourless enzyme substrate to change colour.
7. Quantity = intensity
2. Wash to remove unattached antigens
3. Add specific antibody + leave to bind
4. Wash to remove excess antibody
5. Add second antibody with enzyme attached to bind with first antibody.
6. Add colourless enzyme substrate to change colour.
7. Quantity = intensity
12
New cards
What's the difference between direct / indirect ELISA tests?
Indirect = two different antibodies
Direct = one specific antibody
Direct = one specific antibody
13
New cards
Recall the 2 reasons why we need a ELISA control well
shows that only the enzyme is causing a colour change
washing is effective / all unbound antibody is washed away
washing is effective / all unbound antibody is washed away
14
New cards
How are monoclonal antibodies used in pregancy testing?
a mother's urine has human chorionic gonadotrophin hcg found in placenta
monoclonal antibodies on the pregnancy strip bind to these antibodies, which are linked to coloured particles
hcg-antibody-colour complex moves along the strip until it's trapped by a different type of antibody, creating a coloured line
monoclonal antibodies on the pregnancy strip bind to these antibodies, which are linked to coloured particles
hcg-antibody-colour complex moves along the strip until it's trapped by a different type of antibody, creating a coloured line
15
New cards
Describe 3 ethical considerations in the use of monoclonal antibodies?
• Animal testing → involves use of mice in antibody production + tumour cells.
• Informed consent → patients must know all risks + benefits of the drugs.
• Drug trials → testing on volunteers can be dangerous; issues over trial conduct.
• Informed consent → patients must know all risks + benefits of the drugs.
• Drug trials → testing on volunteers can be dangerous; issues over trial conduct.
16
New cards
What are monoclonal antibodies ?
is a single type of antibody that can be isolated and cloned
17
New cards
How are monoclonal antibodies produced?
1)a mouse is injected with an antigen
2)this stimulates the b cells found in the spleen cells to produce the antibodies against the antigen.
spleen is then removed
B cell is isolated and
fused with tumour cells to form hybridoma cells.
4)the hybridoma cells continuingly produce monoclonal antibodies.
5)the monoclonal antibodies are harvested. By being collected and purified
2)this stimulates the b cells found in the spleen cells to produce the antibodies against the antigen.
spleen is then removed
B cell is isolated and
fused with tumour cells to form hybridoma cells.
4)the hybridoma cells continuingly produce monoclonal antibodies.
5)the monoclonal antibodies are harvested. By being collected and purified