Module 6: Plant Responses to stimuli
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/53
Last updated 11:27 AM on 4/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
Tropism
growth movement whose direction is determined by the direction from which the stimulus strikes the plant.
2
New cards
Positive Tropism
form of tropism where the plant, or a part of it, grows in the direction from which the stimulus originates
3
New cards
Negative Tropism
form of tropism where the plant, or a part of it, grows away from the direction which the stimulus originates
4
New cards
Phototropism
the ability of the plant to re-orient the shoot growth towards a direction of light source.
5
New cards
Coleoptile
cylindrical organs that ensheath the first leaf and shoot apex in grass seedlings
6
New cards
Phototropism will fail to occur and it will not bend to the direction of light
What will happen if the coleoptile is covered?
7
New cards
There will be no interference in the phototropism and the plant will bend in the direction of light.
What will happen if the plant is covered but the coleoptile is still exposed?
8
New cards
Phototropins
proteins that receive blue light during phototropism
9
New cards
releases hydrogen ions in the shaded region of the stem which causes a decrease in the pH.
How does auxin affect the growth of the plant during phototropism?
10
New cards
activates expansin that causes the cells to swell and forces the stem to bend towards the light.
Explain what happens when pH level is decreased during phototropism
11
New cards
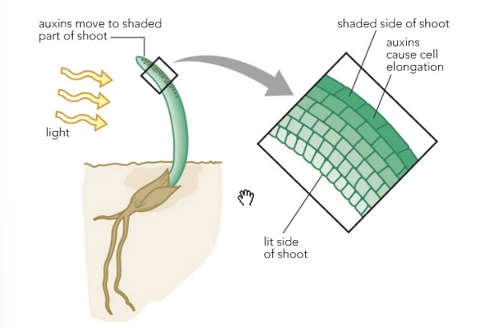
the darker side of the stem
Which side does auxin move when exposed to light?
12
New cards
Etiolation
phenomenon where plants grown in the dark have elongated stems, are white or yellow (due to lack of chlorophyll), and have small leaves.
13
New cards
Etioliation
a mechanism that increases the chance that the plant will access light.
14
New cards
Gibberellins
plant hormones that promote stem elongation thus mimicking the etiolation response.
15
New cards
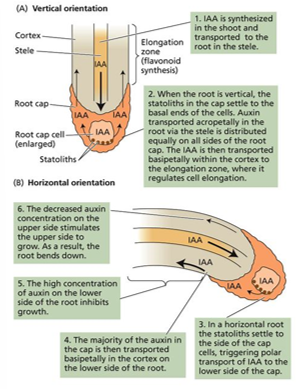
Gravitropism (geotropism)
occurs when a plant is placed on its side and the roots are elongated
16
New cards
Statoliths
organelles containing starch grains
17
New cards
Bottom of the cells in the root tip
Where does the statolith settle by gravity?
18
New cards
auxin (IAA)
What is pumped outside of the cell when pin proteins are redistributed?
19
New cards
under side of the root
Where does auxin accumulates during gravitropism?
20
New cards
inhibit root cell elongation
What does auxin cause during gravitropism?
21
New cards
Nastic movement
non-directional responses to stimuli
22
New cards
Tropic movement
the movement of the plant in response to the stimulus present in the environment
23
New cards
Independent
Nastic - growth
24
New cards
Dependent
Trophic - growth
25
New cards
Immediate
Nastic - time of action
26
New cards
Slow
Tropic - time of action
27
New cards
Non-directional
Nastic - response to stimulus
28
New cards
Directional
Tropic - response to stimulus
29
New cards
Change in turgor
Nastic - reason for action
30
New cards
Cell division
Tropic - reason for action
31
New cards
Sensence
Term relating to "ageing"
32
New cards
Fruit ripening
ethylene stimulates the conversion of starch and acids to sugars
33
New cards
abscission
natural detachment of parts of a plant
34
New cards
Senescence and cell death
What happens to when ethylene when auxin level decline?
35
New cards
Giberellin, auxin, cytokinin, ethylene, abscisic acid
Five common gases in plants
36
New cards
expansin
What is activated when pH level is decreased?
37
New cards
geotropism - (plant part - shoot) In the light it is
positive
38
New cards
geotropism - (plant part - root) In the light it is
negative
39
New cards
geotropism - (plant part - root) In the gravity it is
positive
40
New cards
geotropism - (plant part - shoot) In the gravity it is
negative
41
New cards
Hydrotropism
Growth/movement in response to **water**
42
New cards
responsible for the response to hydrotropism, which induces differential growth in plant parts/ in response to water
Abscisic Acid (ABA)
43
New cards
Thigmotropism
Growth/movement in response to **touch/contact**
44
New cards
It is also called Haptotropism
Thigmotropism
45
New cards
Auxin -> Growth -> Ethylene -> Changed in Turgidity
Mechanism of Thigmotropism
46
New cards
It changes turgidity (movement) of stem
Ethylene
47
New cards
Growth/movement in response to **heat**
Thermotropism
48
New cards
Some plants protect leaves during periods of high irradiance by sunlight or from cold temperature (tumitiklop ang mga leaves)
Thermotropism
49
New cards
Growth/movement of in response to **chemical stimuli**
Chemotropism
50
New cards
51
New cards
52
New cards
53
New cards
54
New cards