Glycolysis pt1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Resolving the Equation of Glycolysis into Two Processes
the conversion of glucose to pyruvate is exergonic:
glucose + 2NAD+ ——>2 pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H+
∆G′°1 = −146 kJ/mol
the formation of ATP from ADP and Pi is endergonic:
2ADP + 2Pi ——→ 2ATP + 2H2O
∆G′°2 = 2(30.5 kJ/mol) = 61.0 kJ/mol
Standard Free-Energy Change of Glycolysis
under standard and cellular conditions, glycolysis is essentially irreversible because payoff phase is much higher in magnitude than investment
Energy Remaining in Pyruvate
energy stored in pyruvate can be extracted by:
aerobic processes:
oxidative reactions in the citric acid cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
anaerobic processes
reduction to lactate
reduction to ethanol
What is the Importance of Phosphorylated Intermediates
all nine intermediates are phosphorylated
functions of the phosphoryl groups:
prevent glycolytic intermediates from leaving the cell
serve as essential components in the enzymatic conservation of metabolic energy
lower the activation energy and increase the specificity of the enzymatic reactions
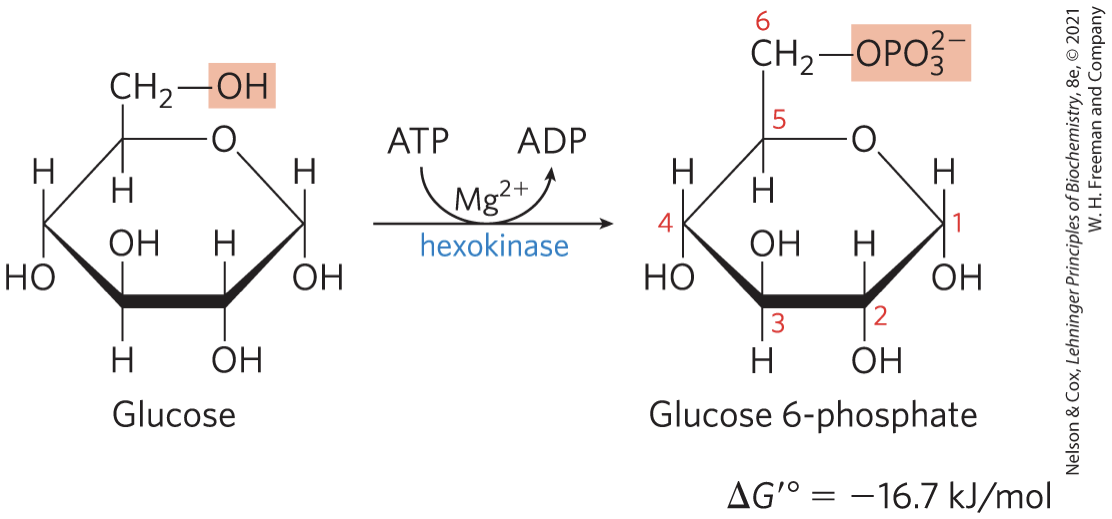
Phosphorylation of Glucose STEP 1
hexokinase activates glucose by phosphorylating at C-6 to yield glucose 6-phosphate
Mg2+ required
irreversible under intracellular conditions
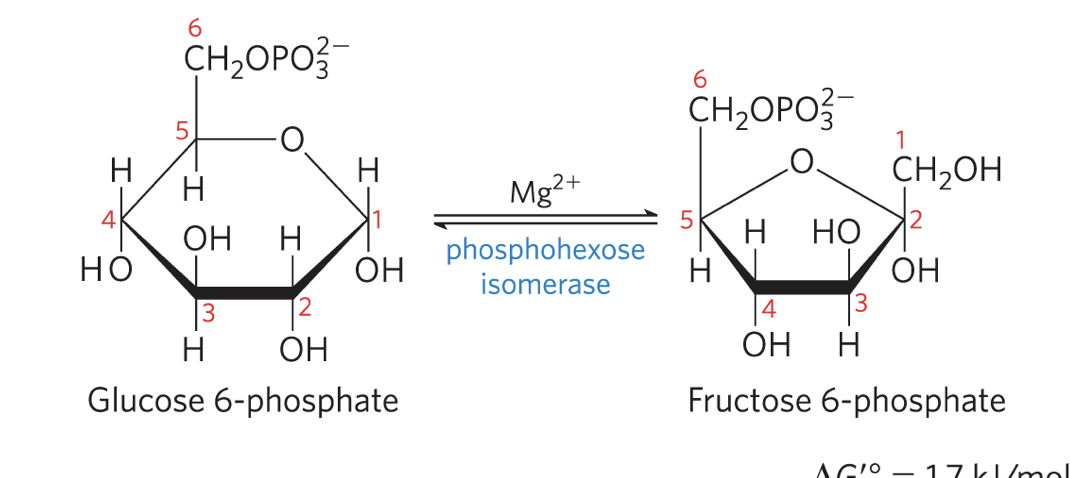
Conversion of Glucose 6-Phosphate to Fructose 6-Phosphate STEP 2
phosphohexose isomerase (phosphoglucose isomerase) catalyzes the reversible isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate
mechanism involves an enediol intermediate
reaction readily proceeds in either direction
reversible
Mg2+ required
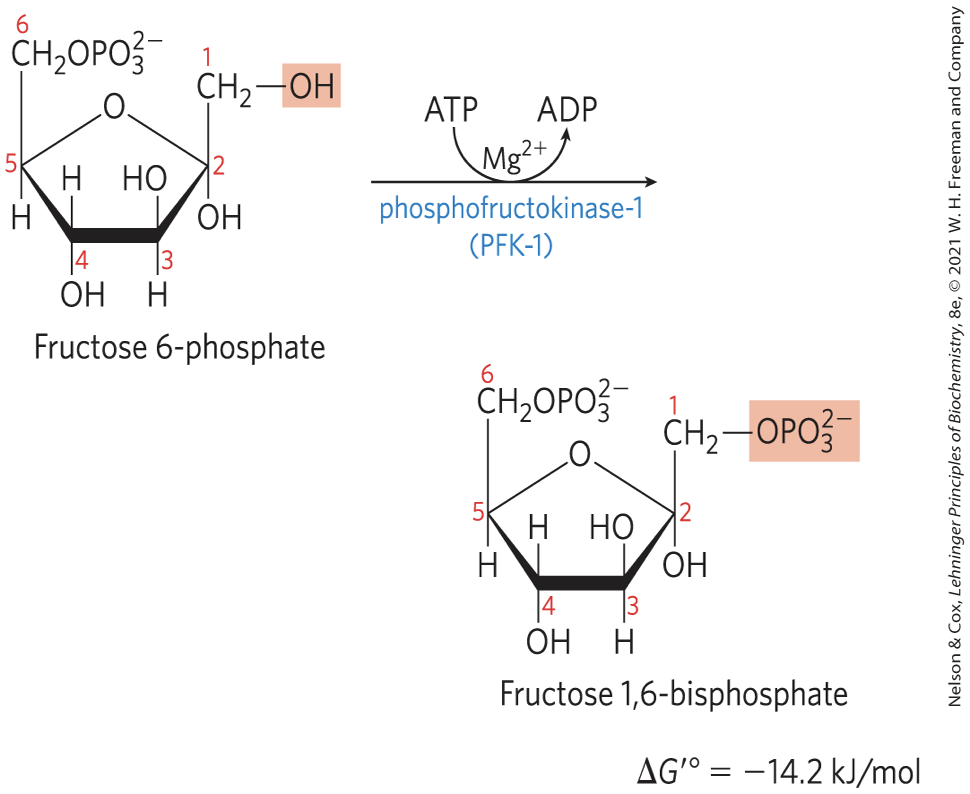
Phosphorylation of Fructose 6-Phosphate to Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate STEP 3
phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to yield fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
irreversible
Mg2+ required
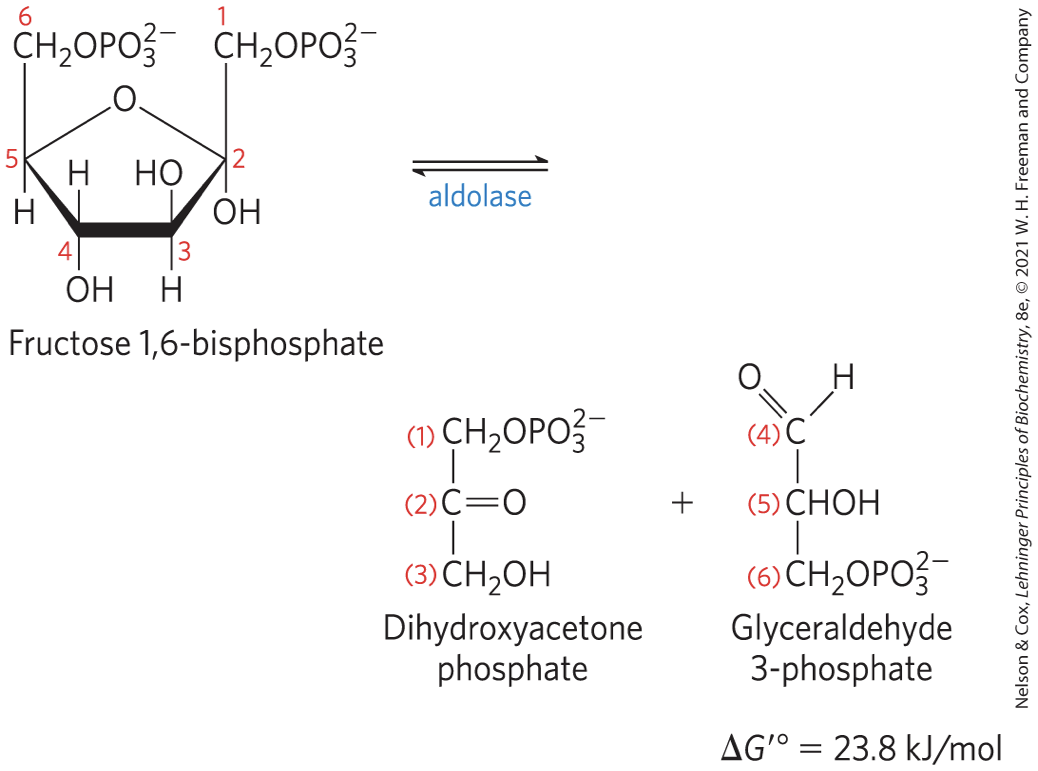
Cleavage of Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate STEP 4
aldolase
yield glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate
reversible because reactant concentrations are low in the cell
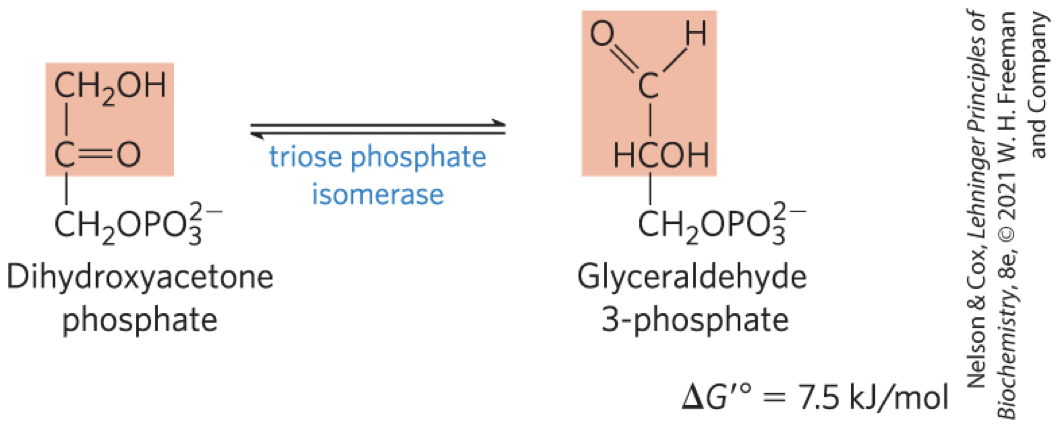
Interconversion of the Triose Phosphates STEP 5
triose phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
reversible
final step of the preparatory phase of glycolysis
in the payoff phase of glycolysis…
each of the two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate undergoes oxidation at C-1
some energy from the oxidation reaction is conserved in the form of one NADH and two ATP per triose phosphate oxidized
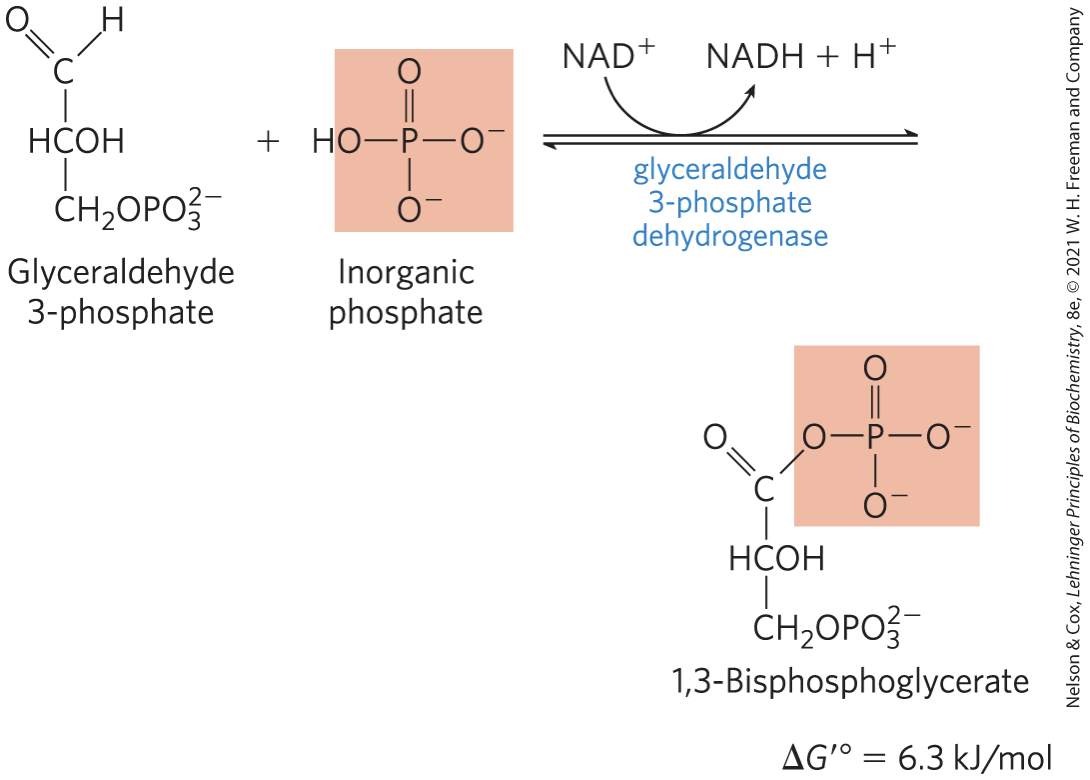
Oxidation of Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate to 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate STEP 6
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
energy-conserving reaction
The First Step of the Payoff Phase is an Energy-______ Reaction
Conserving
formation of the acyl phosphate group at C-1 of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate conserves the free energy of oxidation
acyl phosphates have a very high standard free energy of hydrolysis (∆G′° = −49.3 kJ/mol)
Phosphoryl Transfer from 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate to ADP STEP 7
phosphoglycerate kinase transfers the high-energy phosphoryl group from the carboxyl group of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP
forming ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate
requires Mg2+
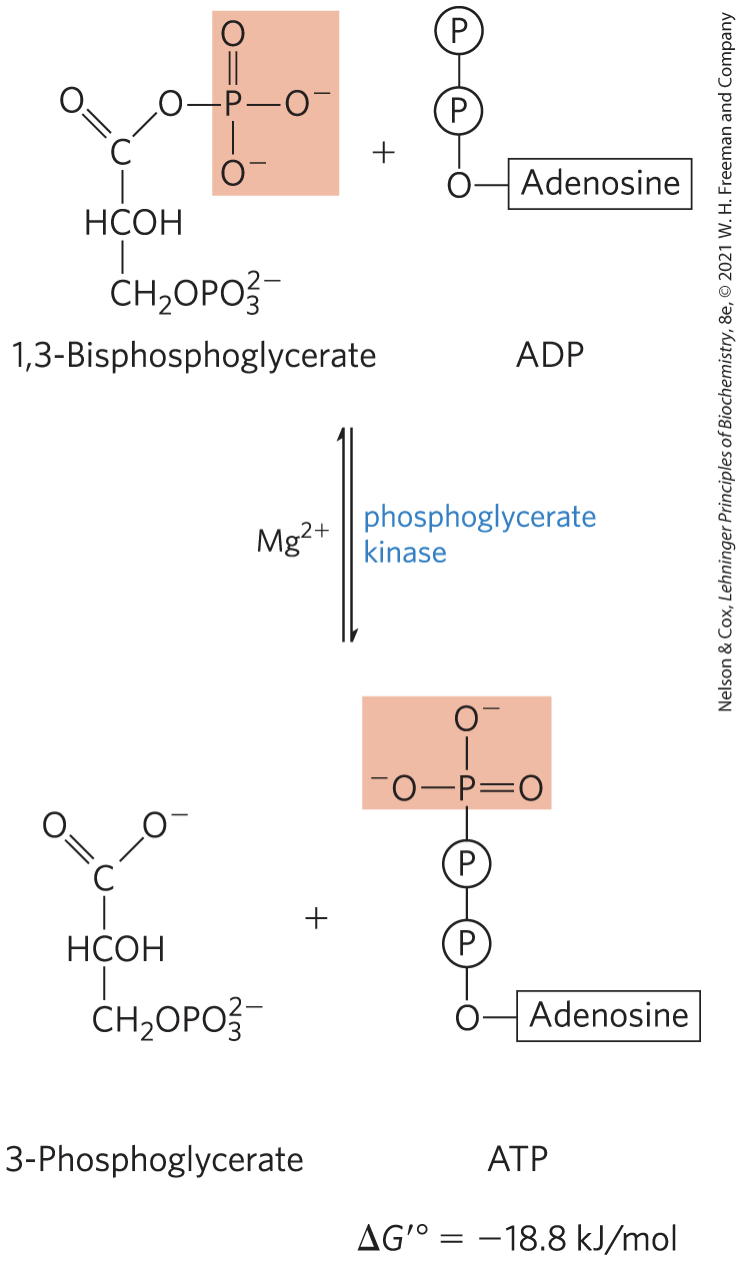
Steps 6 and 7 of Glycolysis Constitute an ______ Process
Energy coupling. deltaG 6-18
Conversion of 3-Phosphoglycerate to 2-Phosphoglycerate STEP 8
phosphoglycerate mutase catalyzes a reversible shift of the phosphoryl group between C-2 and C-3 of glycerate
requires Mg2+
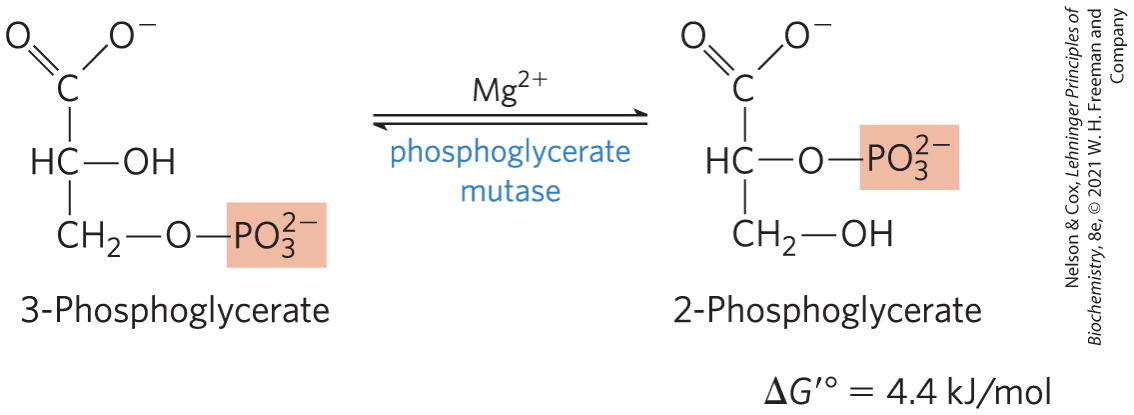
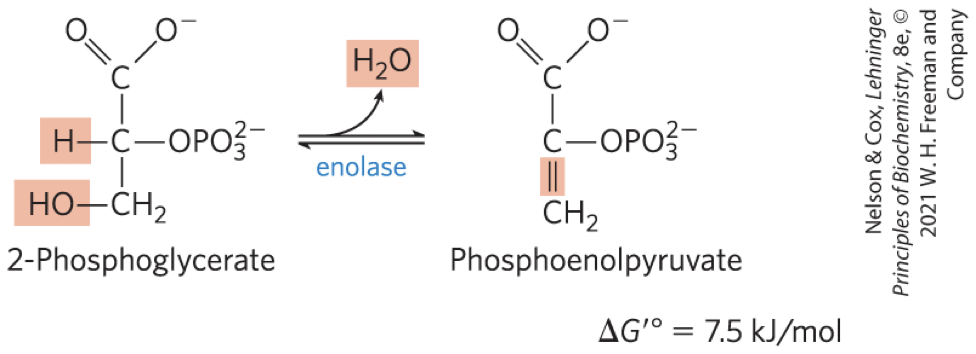
Dehydration of 2-Phosphoglycerate to Phosphoenolpyruvate STEP 9
enolase promotes reversible removal of a molecule of water from 2-phosphoglycerate to yield phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
energy-conserving reaction
Mg2+-stabilized enolic intermediate
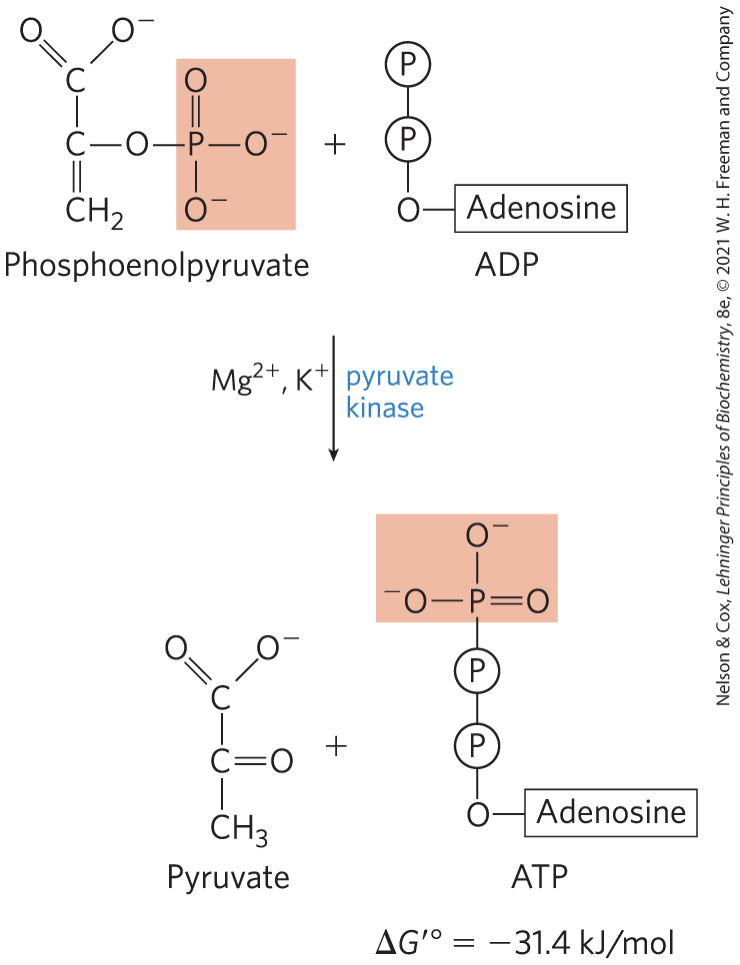
Transfer of the Phosphoryl Group from Phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP STEP 10
pyruvate kinase catalyzes the transfer of the phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, yielding pyruvate
requires K+ and either Mg2+ or Mn2+
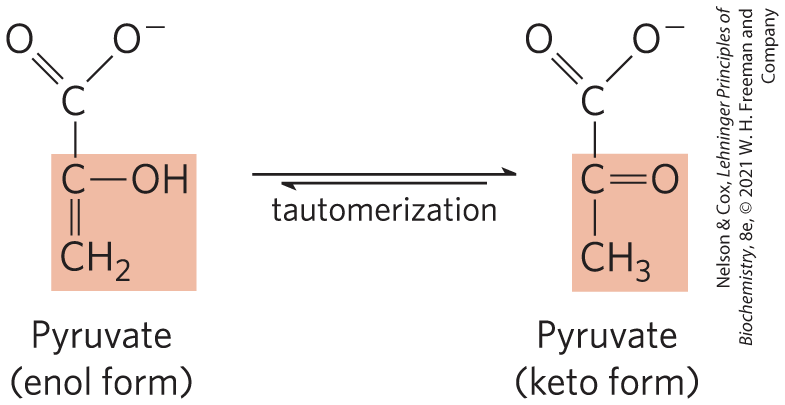
Pyruvate in its Enol Form Spontaneously
Tautomerizes to its Keto Form
Overall Reaction of Glycolysis
to Net Reaction
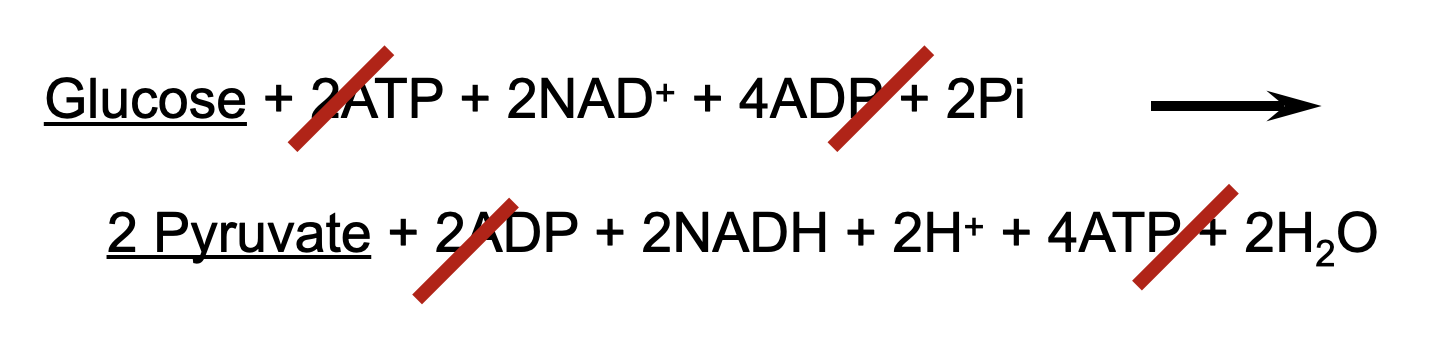
The Overall Balance Sheet Shows a Net ____
Gain of Two ATP and Two NADH Per Glucose
Endogenous Glycogen and Starch Are Degraded by Phosphorolysis
glycogen phosphorylase = mobilizes glycogen stored in animal tissues and microorganisms by a phosphorolytic reaction to yield glucose 1-phosphate
starch phosphorylase = mobilizes starch by a phosphorolytic reaction
Glycogen Breakdown Is Catalyzed by Glycogen Phosphorylase
glycogen phosphorylase = catalyzes phosphorolytic cleavage at the nonreducing ends of glycogen chains
requires pyridoxal phosphate
acts repetitively until it reaches a point four residues away from a (α1→6) branch point
Glycogen phosphorylase
catalyzes phosphorolytic cleavage at the nonreducing ends of glycogen chains
requires pyridoxal phosphate
acts repetitively until it reaches a point four residues away from a (α1→6) branch point
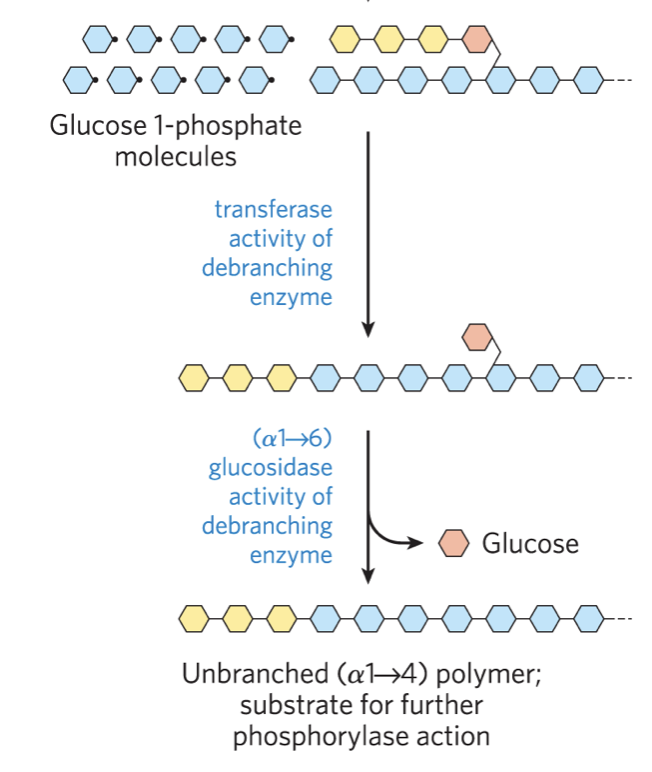
Glycogen Breakdown Mechanism
phosphorylase releases glucose-1-phosphate at non-reducing end until 4 residues away from branch
phosphoglucomutase isomerizes glucose-1-phosphate into glucose-6-phosphate
Debranching enzyme transferase branch onto main chain and exhibits glucosidase activity
α-amylase location, function, and products
salivary and small intestine enzyme that hydrolyzes the internal (α1→4) glycosidic linkages of starch and glycogen, producing di- and trisaccharides
pancreatic α-amylase yields mainly ____
maltose, maltotriose, and limit dextrins mmd (fragments of amylopectin containing (α1→6) branch points, which are removed by limit dextrinases)
Hydrolysis of Disaccharides
membrane-bound hydrolases in the intestinal brush border hydrolyze disaccharides:
monosaccharides pass through intestinal cells to the bloodstream, which transports them to the liver or other tissues

Cellulase
attacks the (β1→4) glycosidic bonds of cellulose
absent in most animals
microorganisms produce cellulase
Fructose and Mannose
fructose and mannose can be phosphorylated and funneled into glycolysis
hexokinase = phosphorylates fructose in the small intestine
fructose kinase = phosphorylates fructose in the liver
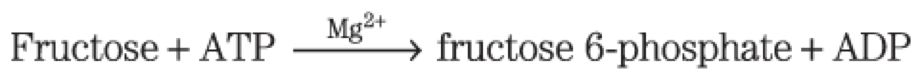
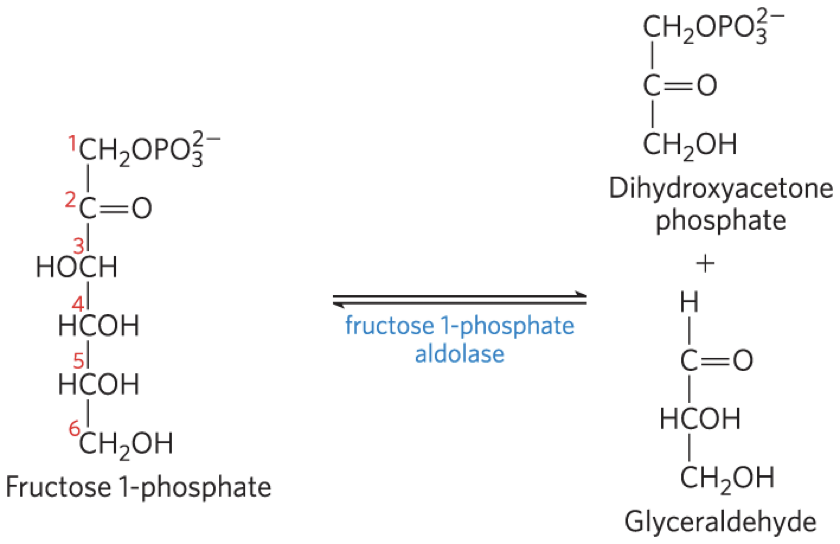
Fructose 1-Phosphate Aldolase
cleaves fructose 1-phosphate to glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Products of Fructose 1-Phosphate Hydrolysis Enter Glycolysis as
Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate
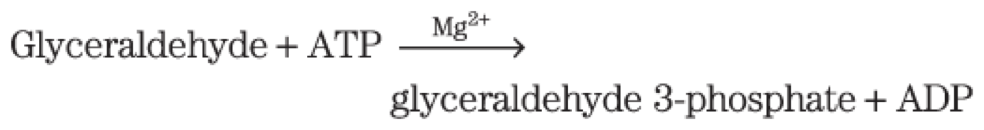
triose phosphate isomerase = converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
triose kinase = uses ATP to phosphorylate glyceraldehyde to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Mannose Enters Glycolysis as
Fructose 6-Phosphate
hexokinase = phosphorylates mannose at C-6
phosphohexose isomerase = converts mannose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate
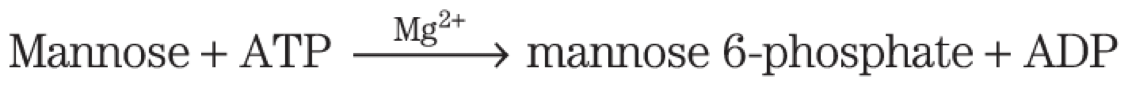
Regulation of irreversible reactions
Step 1: Hexokinase: product inhibition
Step 3: Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1): rate-limiting. Inhibited by HIGH ATP
Step 10: Pyruvate kinase: Inhibited by HIGH ATP
Fructose feeder pathway
in liver, fructose kinase phosphorylates to fructose-1-phosphate
in muscle and kidney, hexokinase to fructose 6 phosphate
Galactose feeder pathway
UTP phosphorylates galactose to glucose 1-phosphate
glucose 1-phosphate → phosphoglucomutase → glucose-6-phosphate