Information Systems, Risk, Threat Landscape
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
The protection of information systems (hardware, software, and associated infrastructure), the data on them, and the services they provide from unauthorised access, harm, or misuse.
This includes harm caused intentionally by the operator of the system, or accidentally, as a result of failing to follow security procedures.
Information systems, consisting of
People (operator)
Physical (infrastructure)
Technical (hardware, software)
Data, and services of the system
To analyze cybersecurity problems.
The threat landscape (what to protect):
e.g., what’s happening around the world, which industry and what industry-specific attacks are there.
How do we design cybersecurity?
Incorporate within the system architecture.
How do we implement cybersecurity?
Physical (data center security access cards), electronic, administrative.
What are the risks, impacts, and controls?
e.g., implementing a data center, risk analysis before, impact of attacks, and control includes prevention and response.
Business continuity:
Competitive advantage:
Reputation:
Return on investment:
Shareholder value:
Privacy:
Legal obligation:
Intellectual property (IP).
We are living in an increasingly digital world, with handheld devices, cars, and healthcare.
The more we have digitally, the more criminals have access to move around and attack us.
It maintains business continuity and viability by ensuring its goals are achieved.
Protects assets by ensuring they aren’t impacted by realised threats.
Helps ensure they are following laws, regulations, and security policies.
Different organizations have different risk tolerances, so information security needs to be tailored to each business.
Safeguard: planned security measures to protect assets.
Countermeasure: response actions to mitigate security risks and issues.
Administrative control: policy development and enforcement.
Technical control: preventing data loss, firewalls.
Physical control: CCTV, locks.
Cyber-physical security: consider both network and real-world implications.
Must understand business risk exposure and risk appetite when implementing controls.
what are the main principles / concepts of information security
CIA triad
authentication
authorization
non-repudiation
audit
Authentication verifies identity through methods like passwords, smart cards, biometric devices, and one-time passwords (OTPs).
Authorization determines access rights once identity is verified, such as server permissions and physical access control.
Non-repudiation ensures that actions taken by users or systems are recorded and cannot be denied later, providing accountability.
Auditing captures information that can be troubleshooted later, helping to monitor actions and trace security issues.
Accountability ensures that individuals are responsible for their actions, helping to enforce security protocols and avoid breaches.
what makes up the CIA traid
confidentiality
integrity
availability
what is the CIA triad
a model that describes the 3 goals of information security, and guides policy development within organisations - any cybersecurity attack can be classified under this model
what is confidentiality
preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure, including means for protecting personal privacy and proprietary information
what is integrity
guarding against improper information modification or destruction and ensuring information non-repudiation and authenticity
what is availability
ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of information
ensures the core principles of protecting data and information systems.
It helps maintain trust, functionality, and security of the system.
what is the threat landscape
the overall picture of potential cyber threats and risks facing individuals, organizations, or systems
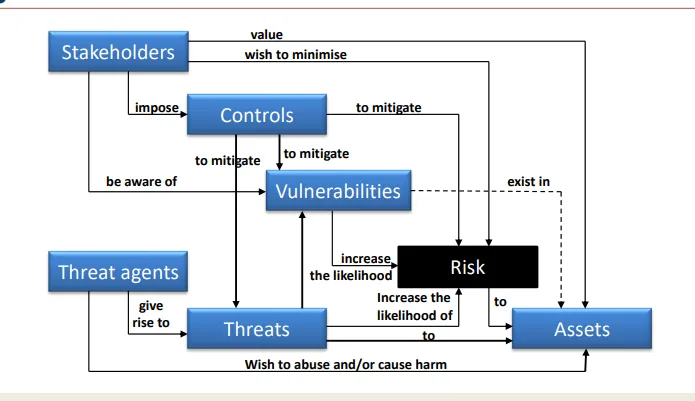
Stakeholders
Controls
Vulnerabilities
Risk
Threat Agents
Threats
Assets
Silly Cats Visit Real Trees To Admire.
Companies can use frameworks to understand the threat landscape and mitigate threats.
what are stakeholders
Any person with a vested interest in the business who want to minimise risk including management or government
what are the links between stakeholders in the threat landscape
Stakeholders value [[Assets]]
Stakeholders want to minimise [[Risk]]
Stakeholders impose [[Controls]]
Stakeholders need to be awake of [[Vulnerabilities]]
what are controls
Any controls and policies implemented need to be anchored to [[CIA Triad]]
what are the links between controls and the threat landscape
Controls are used to mitigate [[Risk]]
Controls are used to mitigate [[Vulnerabilities]]
Controls are used to mitigate [[Threats]]
what are vulnerabilities
A weakness that leaves you exposed to a threat, can cause legal liabilities and software vendors need to protect themselves from their own liabilities
what are the links between vulnerabilities and the threat landscape
Vulnerabilities exist within [[Assets]]
Vulnerabilities increase the likelihood of [[Risk]]
what is risk
The possibility that a given threat will exploit a vulnerability to harm an asset or organisation
what is the link between risk and the threat landscape
Risk impacts [[Assets]]
The process of understanding and responding to factors that may lead to a failure in the CIA Triad of an information system, to ensure the business’s longevity.
By following a Risk Management Framework.
Businesses need to align their risk management activities with their goals and objectives.
Need to build a bridge between business and technology risks, as businesses might not understand them.
Risk management language needs to be consistent across the business.
Use of resources to map potential vectors and vulnerabilities creates a better risk assessment.
what are threat agents
The individuals or entities who have the capability to exploit vulnerabilities and pose threats
what are the links between threat agents and the threat landscape
Threat agents want to abuse and cause harm to [[Assets]]
Threat ages give rise to [[Threats]]
what are threats
Natural or human induced event that could take advantage of a vulnerability to damage an asset e.g. floods that need planning to ensure business ops can continue, and viruses. Threats have the potential to harm.
what are the links between threats and the threat landscape
Threats exploit [[Vulnerabilities]]
Threats affect [[Assets]]
Threats increase the likelihood of [[Risk]]
what are assets
Anything of value that needs to be protected, can be a person or a system
what is risk tolerances
the amount of [[Risk]] that the organization can actually cope with per individual risk, and the acceptance of specific risk outcomes should they occur
what is risk appetite
the general type and amount of [[Risk]] that an organisation is willing to take in order to meet their strategic objectives without needing to take action to reduce the risk- variable depending on an organisation’s sector, culture, and objective
Technology weakness
Configuration weakness
Security policy weakness
Protocol weaknesses which exist in the design of the protocol, making them very hard to change since protocols are dependent on each other.
Examples: TCP/IP protocol, HTTP, FTP, ICMP, ARP.
Software vulnerabilities (see SSDF for reference):
Common deficiencies in the software code itself,
e.g., buffer overflow as a result of poor memory management.
The system/software is not set up properly, creating more weaknesses, e.g.
Weak or default passwords.
Misconfigured firewall.
Leaving ports open.
Weak security policy or policy enforcement/implementation.
Software and hardware installations and changes not following policy.
Lack of 2-factor authentication.
Using the CVE framework:
Notify the vendor of the software/protocol/device so they can fix it.
Assign the vulnerability to a unique CVE identifier.
Patches refer to the CVE, and once the fix has been made (not before), the vulnerability is announced (e.g., Sims 4 patch notes).
what are CVEs
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposure system
acts as a reference dictionary of publicly known information security [[Vulnerabilities]] and exposures
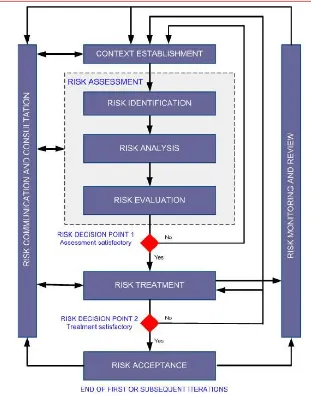
A set of guidelines and processes used by companies to identify, eliminate, and minimise risk.
Context Establishment
Risk Assessment
Risk Treatment
Risk Acceptance
Risk Communication and Consultation
Risk Monitoring and Review
They help organisations weather negative realised risks and capitalise on positive realised risks.
Minimise negative effects and maximise positive effects.
The difference between the security controls in place and the controls necessary to address all vulnerabilities.
Through a gap analysis.
what is context establishment
sets criteria for how risks are identified, risk ownership, how risks impact [[CIA]], and how risk impact and likelihood will be calculated
what is risk assessment
the actions from risk identification to prioritisation, frames how we implement the controls
what are the stages in the risk assessment process
risk identification
risk analysis
risk evaluation
To identify assets, threats, existing controls, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts.
Because when a threat is realised, the most important assets need to be restored first.
Because different threats impact different areas, e.g., infrastructure threats vs. pandemic threats affecting personnel and business operations.
It helps assess what protections are already in place and where gaps may exist.
To understand weaknesses in the system that could be exploited by threats.
It ensures planning for both widespread disasters and specific scenario impacts, often included in a Disaster Recovery Plan.
A risk register
a list of all identified risks with detailed information about each.
Because organisations can’t prepare for potential risks they aren’t aware of.
what are the aims of risk analysis
assessment of impact, likelihood, and level of risk determination
what methodologies can be used during the risk analysis stage
Quantitative Risk Methodology
Qualitative Risk Methodology
It uses numerically based (hard), objective data to measure risk.
It measures monetary units like expenses and return on security investments.
It relies on experts estimating risk in financial terms.
what calculations are done in the quantitative risk methodology
Asset Value
Exposure Frequency
Single Loss Expectancy
Annual Rate of Occurrence
Annualised Loss Expectancy
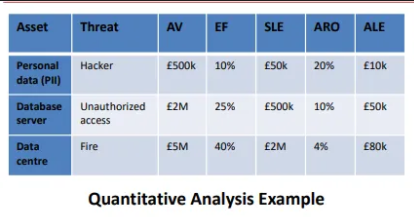
The value of the asset.
How often a threat may occur.
The financial loss if a threat is realised once.
The number of incidents expected per year.
The maximum amount worth spending to protect assets.
SLE = AV x EF

ALE = SLE x ARO

Value = ALE before control - ALE after control - annual maintenance cost of the control
If the value is positive, it’s financially worthwhile to implement the control.
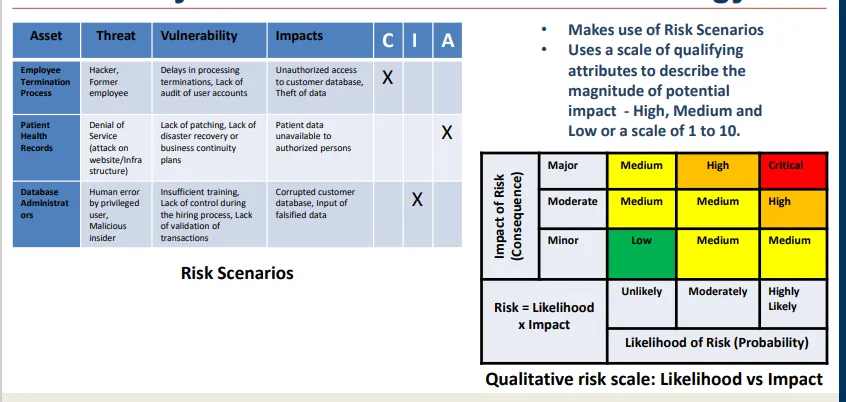
what is a qualitative risk methodology
uses scenario-based (soft), subjective data
gradual scale
based on risk perceptions by stakeholders
how does the qualitative risk methodology work
make use of risk scenarios - from a risk register, and risk scale, e.g. likelihood vs. impact, to describe the magnitude of impact and compare and prioritise the risks to see which needs dealing with first
what is risk evaluation
the evaluation of risk based on risk evaluation criteria like predetermined levels of acceptability. also deals with prioritising which risks need to be addressed (result of quantitative) and in which order (result of qualitative)
what is risk treatment
how the organisation responds to the identified risk (and as a result risk)
Inherent risk
Residual risk
The total currently existing risk, calculated as:
threats × vulnerabilities × asset value
The risk that remains after controls have been applied;
inherent risk - the cumulative effect of controls
Because it's impossible to eliminate all risk, so controls are used to reduce inherent risk to an acceptable residual level.
Risk mitigation
Risk acceptance
Risk avoidance
Risk transfer
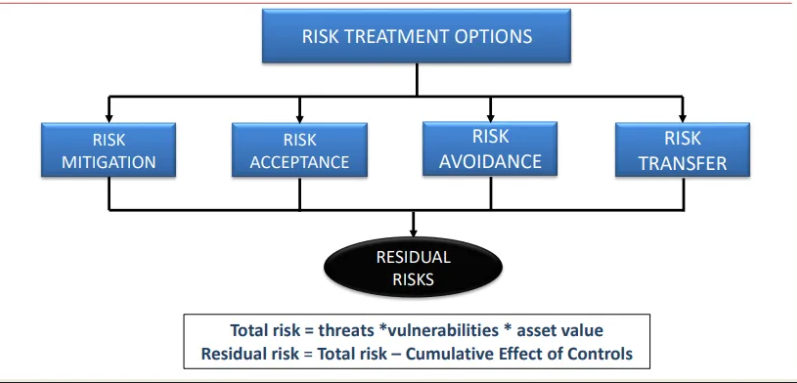
Actions taken to modify and reduce risk, typically through the application of administrative, technical, or physical controls.
What is risk acceptance? (as a risk treatment plan)
Accepting the risk as is, based on whether it falls within the established risk acceptance criteria determined by analysis.