Chemistry - Topic 1 Stoichiometric relationships
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
What do the coefficients in a balanced equation mean?
Normally, we read the coefficients as moles. However, if all the substances are in gaseous form (g), you can read the coefficients as dm3.
What are the three gas laws?
The pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume, given temperature is constant.
The volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, given pressure is constant.
The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, given that the volume is constant.
The three gas laws can be summarized in the following equation:
T has to be in Kelvin!
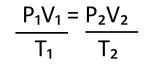
What is the conversion factor for pressure?
1,000 Pa = 1 kPa
What is the conversion factor for temperature?
Add 273.15 to a given Celsius value in order to make it Kelvin.
What is the ideal gas equation?
PV = nRT
Be careful with units!
P: must be in Pa
V: must be in m3
N: the amount in moles of the element
R: the constant 8.31
T: must be in K
What does the kinetic-molecular theory of gases assume?
The kinetic-molecular theory of gases assumes that:
Ideal gas molecules are constantly moving.
Ideal gas molecules have negligible volume.
Ideal gas molecules have negligible intermolecular forces.
Ideal gas molecules undergo perfectly elastic collisions.
Ideal gas molecules have an average kinetic energy proportional to their absolute temperature.