AP Human Geography Unit 1 Vocabulary Notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1: Thinking Geographically- Different types of maps and what they tell you. How geographers collect and use data. Spatial relationships and patterns. Data analysis at different scales (for example, global, national, local)
Last updated 2:31 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
**Human Geography**
The study of the interrelationships between people, place, and environment, and how these vary spatially and temporally across and between locations
2
New cards
**Scale**
Generally, the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and the Earth as a whole
3
New cards
**Place**
A specific point on Earth distinguished by a particular characteristic
4
New cards
**Region**
An area distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features
5
New cards
**Vernacular Region**
A place that people believe exists as part of their cultural identity
6
New cards
**GPS**
This system uses data from satellites to pinpoint a location on earth and help people find their way to a destination
7
New cards
**GIS**
A computer system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth's surface. It may show many different kinds of data on one map, such as streets, buildings, or vegetation
8
New cards
**Diffusion**
The spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time
9
New cards
**Sustainability**
The use of Earth’s renewable and nonrenewable natural resources in ways that do not constrain resource use in the future
10
New cards
**Physical Systems**
The processes shaping the earth's climate; soils; distributions of plants and animals; landforms, including caves and glacial landscapes; and water, including rivers, lakes, and aquifers
11
New cards
**Distribution Features**
Patterns in data or features, spread over a designated geographic area
12
New cards
**Geospatial Data**
Information that describes objects, events or other features with a location on or near the surface of the earth
13
New cards
**Quantitative Data**
Any pieces of information that can be displayed using numbers, such as populations, distances, prices, and other measurements
14
New cards
**Absolute Location**
A place's absolute location is its exact place on Earth, often given in terms of latitude and longitude
15
New cards
**Relative location**
A description of how a place is related to other places
16
New cards
**Agricultural Density**
The number of farmers per unit of farmland
17
New cards
**Arithmetic Density**
The total number of people divided by the total land area. This is what most people think of as density; how many people per area of land
18
New cards
**Cartography**
The science of map-making
19
New cards
**Projection**
The scientific method of transferring locations on Earth's surface to a flat map
20
New cards
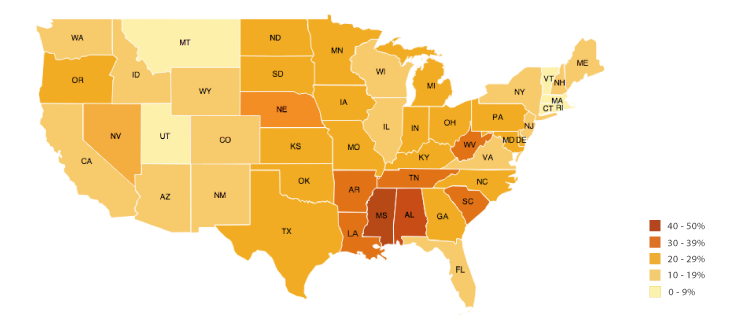
**Choropleth Map**
A map that uses shading to show a pattern of a variable (the darker the shading, the higher the concentration of the variable)
21
New cards
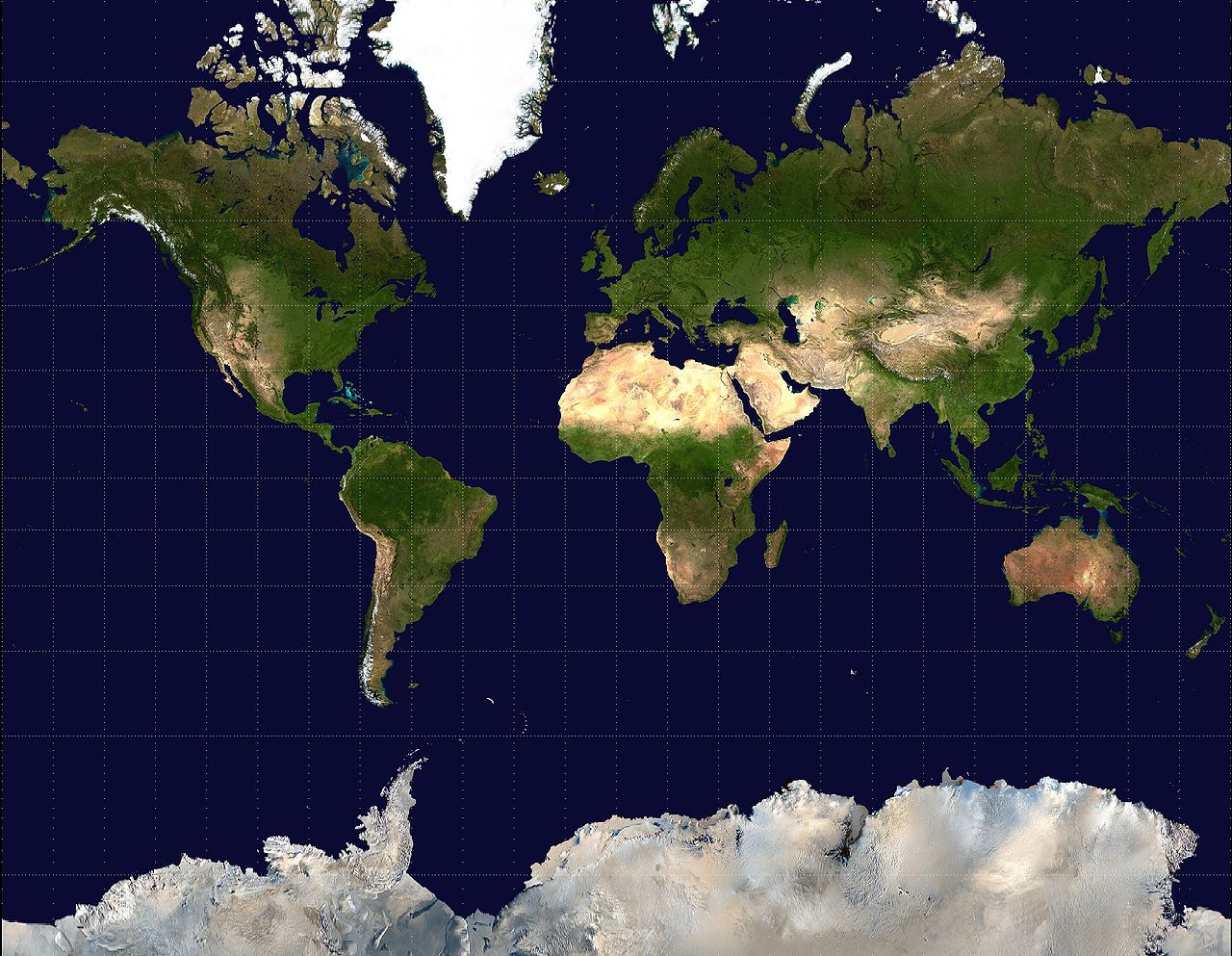
**Mercator Map**
A map projection that fairly accurately shows shape and direction, but distorts distance and size of land masses
22
New cards
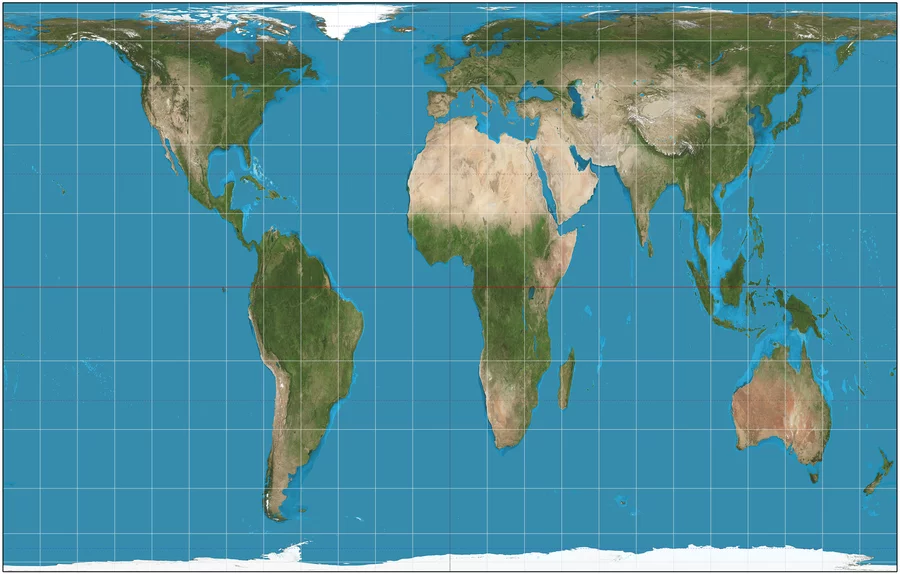
**Gall-Peters Map**
A rectangular, equal-area map projection. The map shows the correct sizes of countries, but it also distorts their shape
23
New cards
**Robinson Map**
A map projection showing the poles as lines rather than points and more accurately portraying high latitude lands and water to land ratio
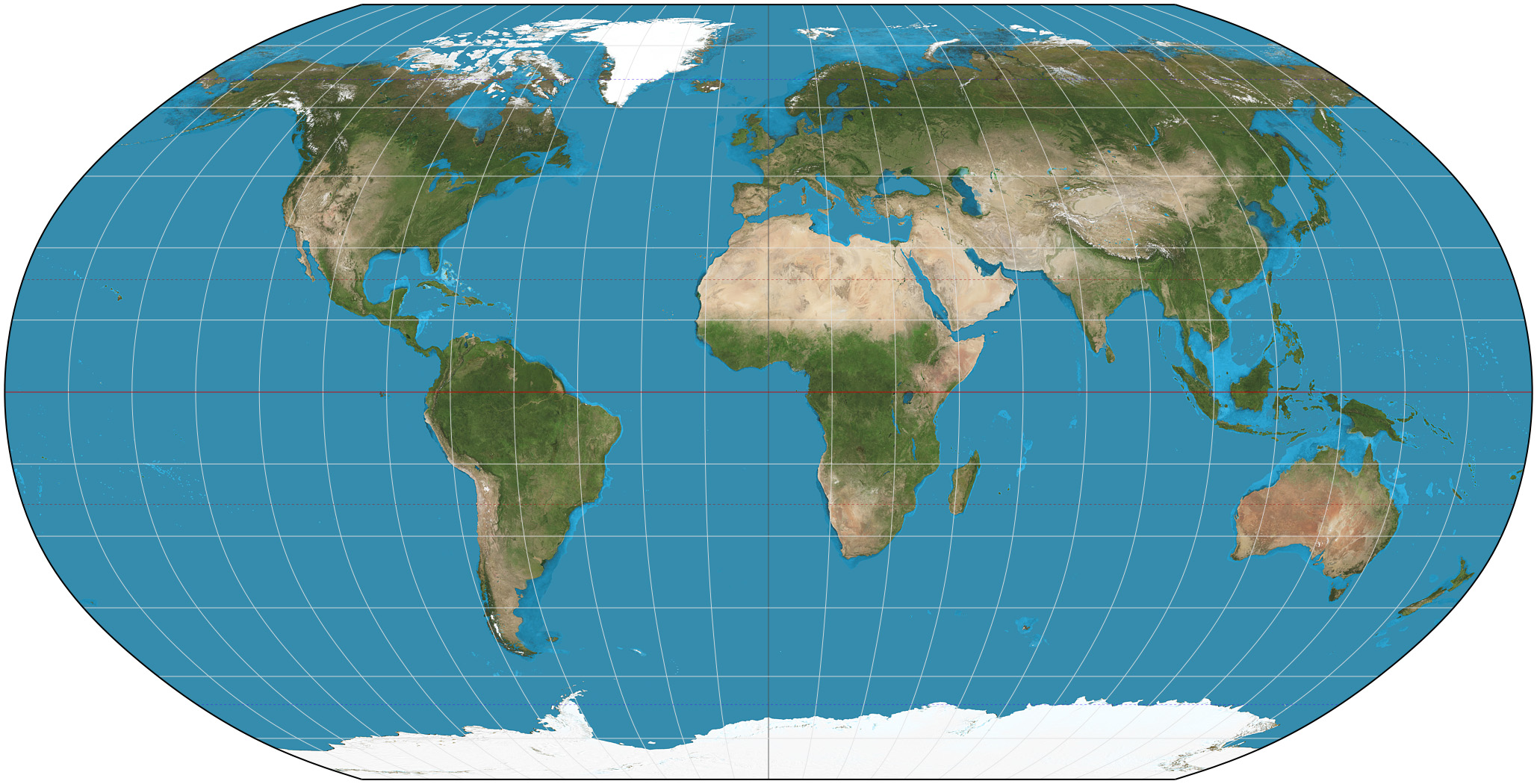
24
New cards
**Dymaxion /** **Fuller Map**
A map only intended for representations of the entire globe. When presented as a flat map, the land masses are unbroken. The flat map is heavily interrupted in order to preserve shapes and sizes
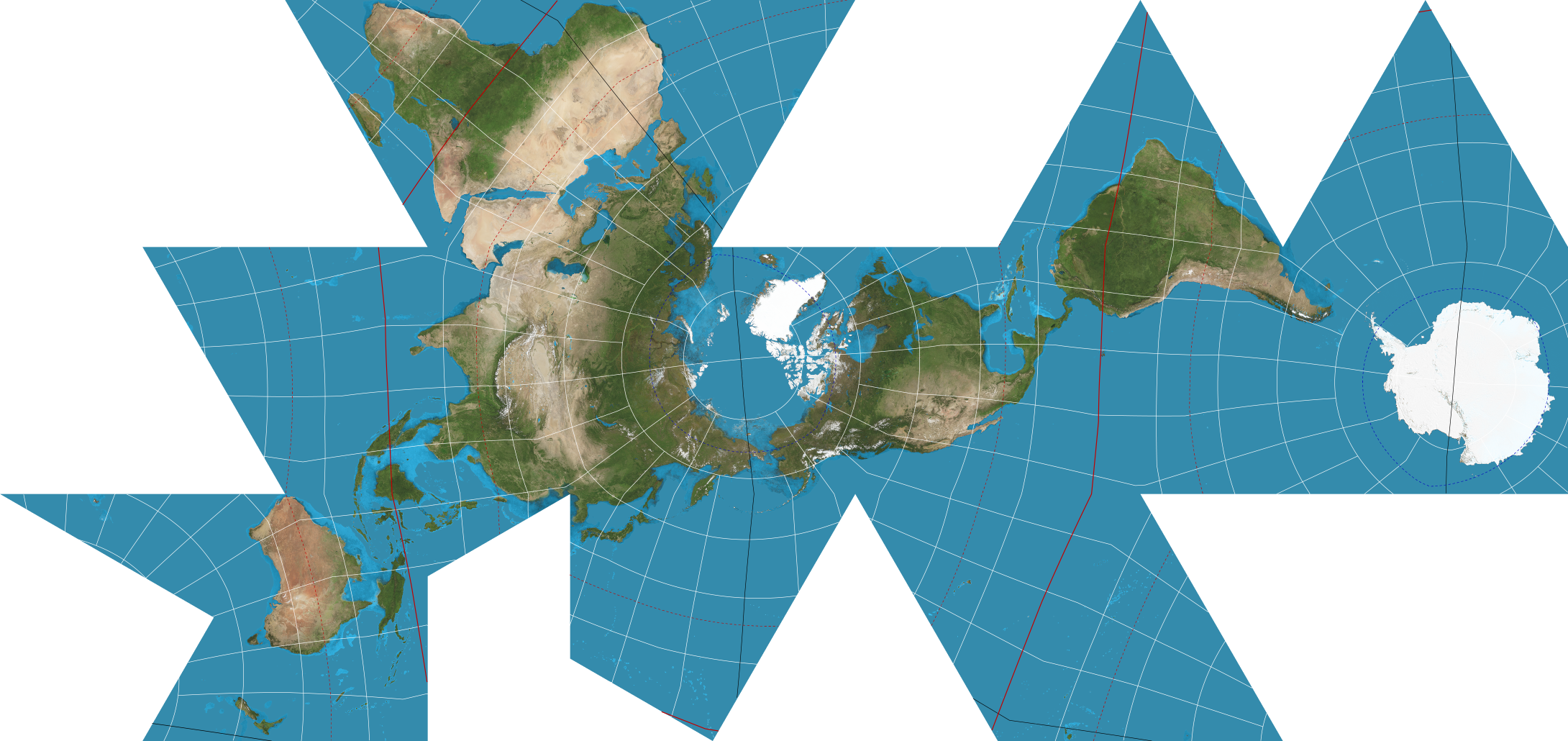
25
New cards
**Goode Homolosine Map**
It shows the continents proportionally sized to each other, however its use of distances, directions, and angles are not accurately shown because of distortion
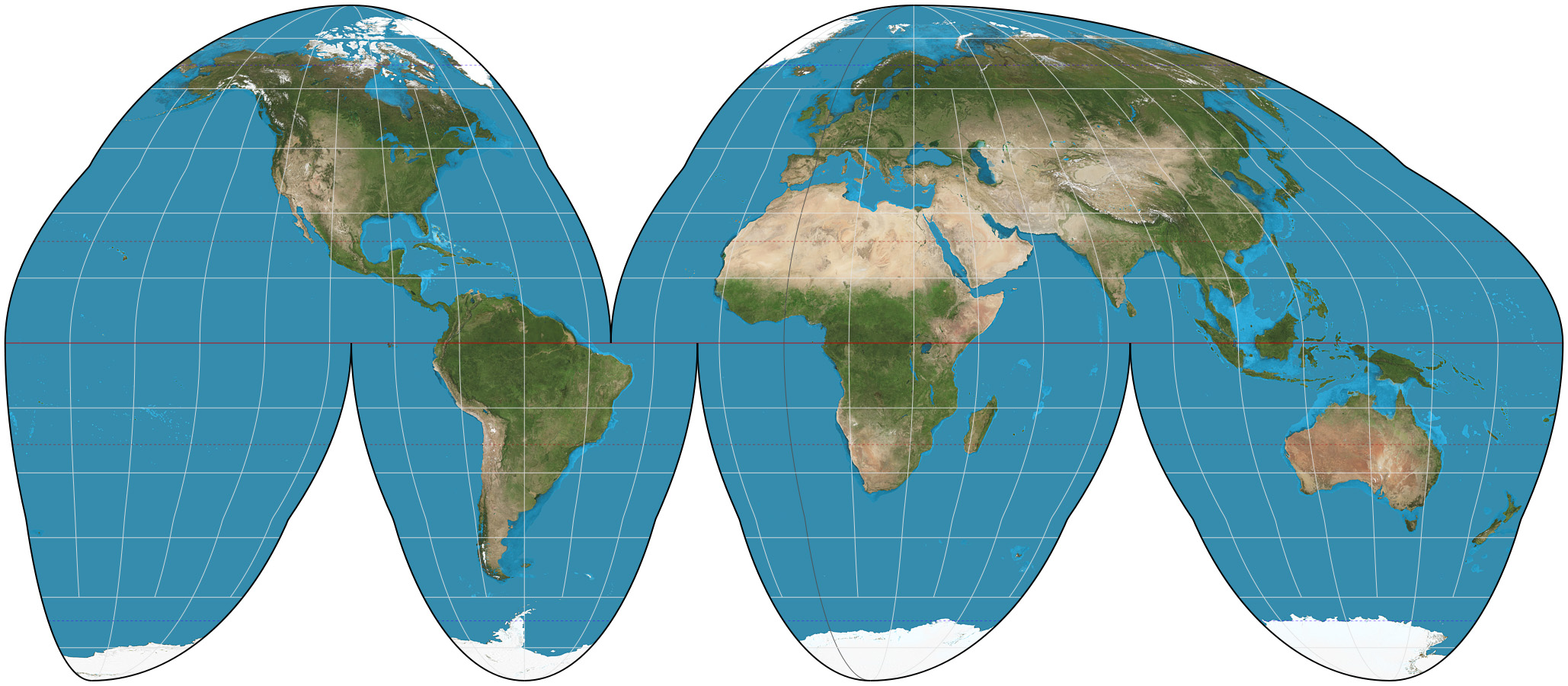
26
New cards
**AuthaGraph Map**
It is considered the most accurate projection for its way of showing relative areas of landmasses and oceans with very little distortion of shapes
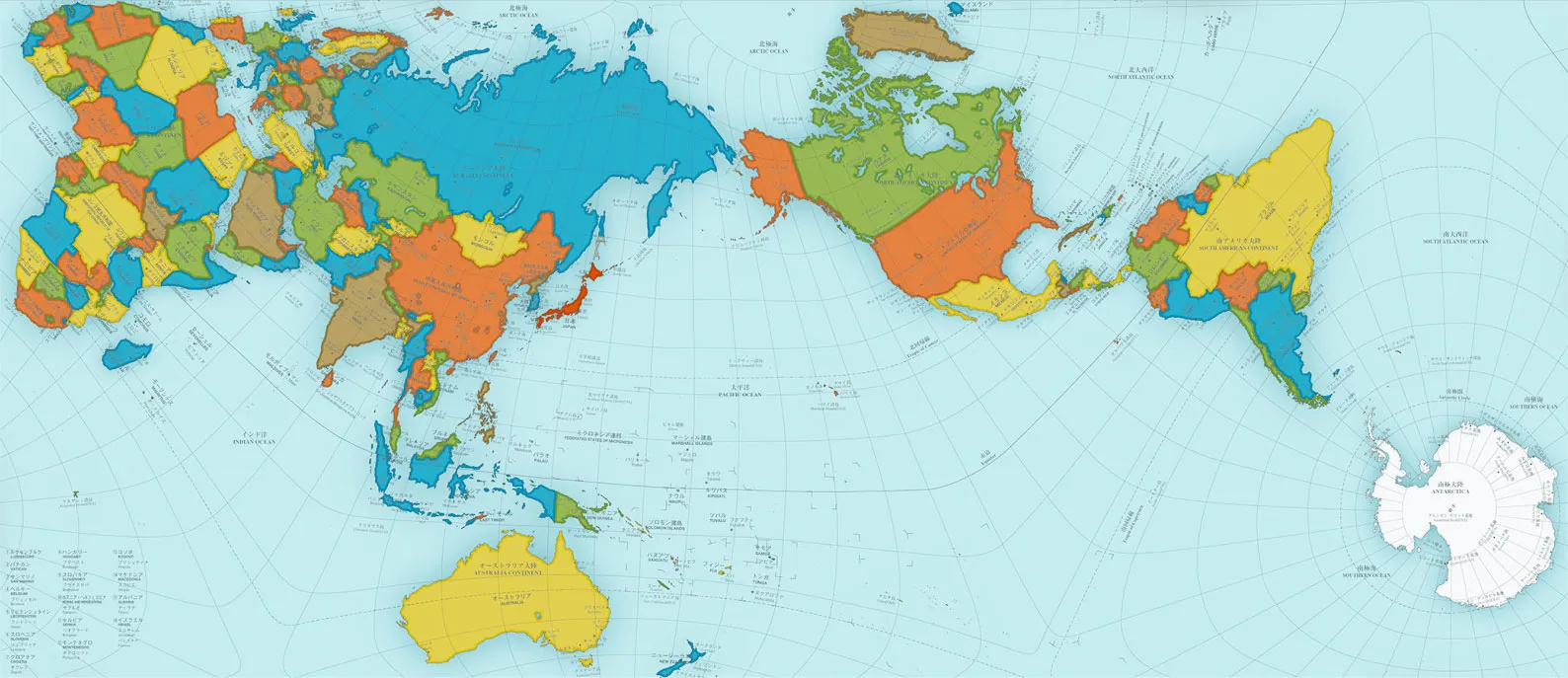
27
New cards
**Thematic Map**
A map that shows the spatial distribution of one or more specific data themes for selected geographic areas (Ex: Weather maps, population density maps, geology maps)
28
New cards
**Isoline Map**
A map type that has lines drawn on it connecting data points of the same value
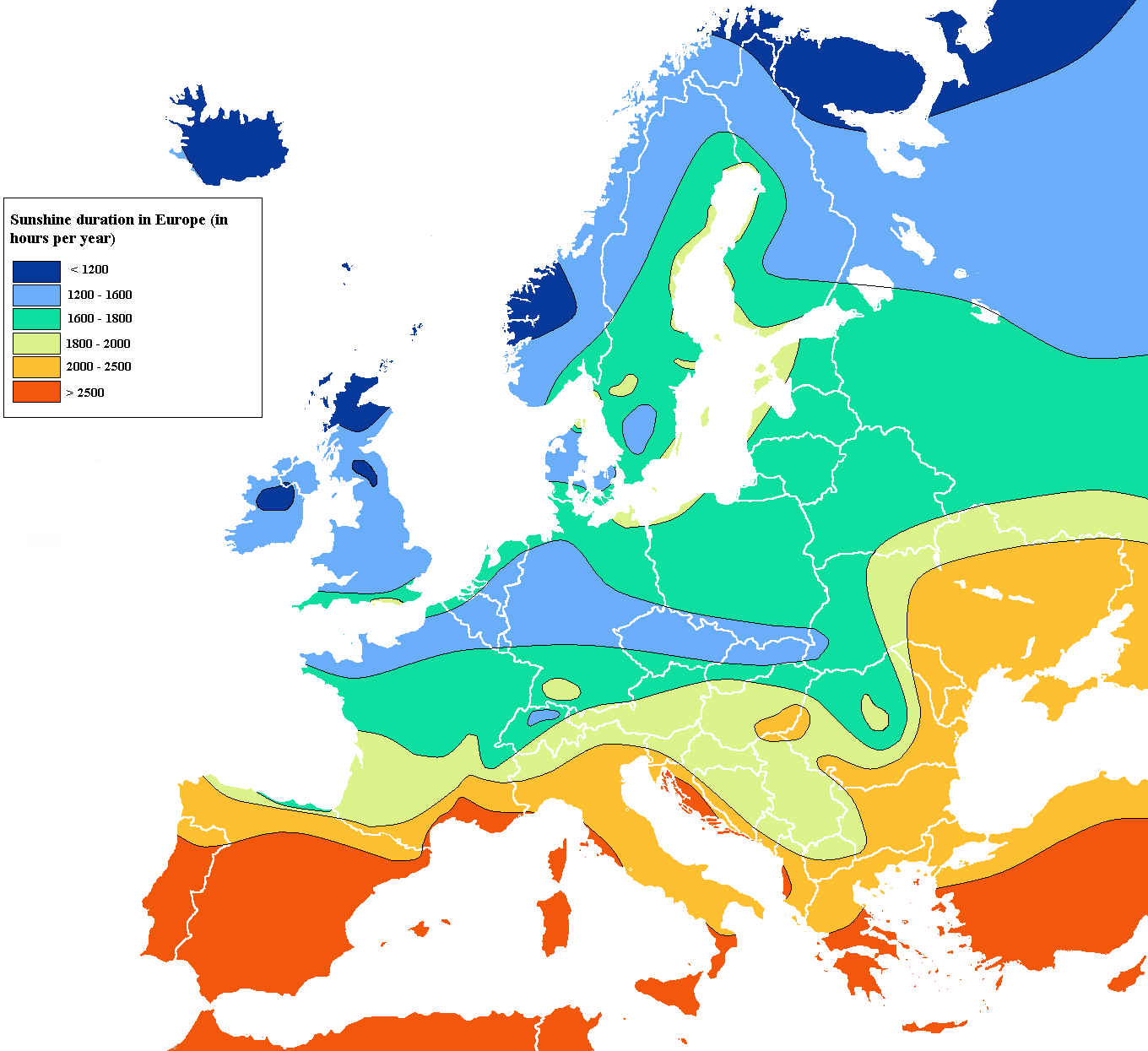
29
New cards
**Dot Distribution (Density) Map**
A type of thematic map that uses a point symbol to visualize the geographic distribution of a large number of related phenomena
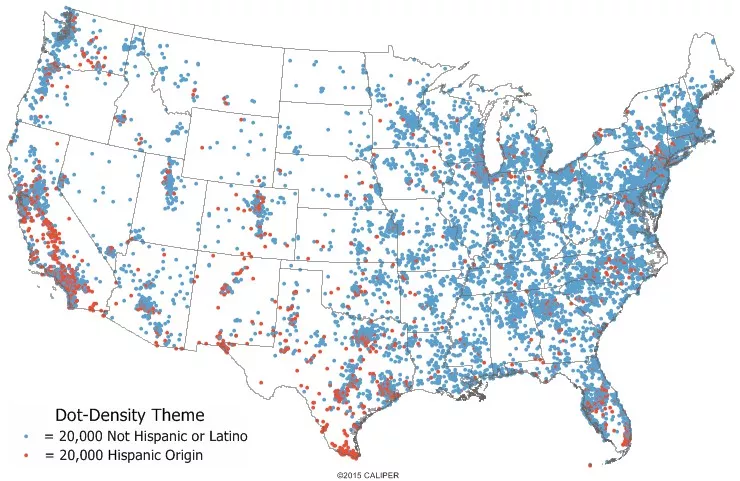
30
New cards
**General Reference Map**
A map that focuses on the location and names of features, like a political map, road map, or topographic map
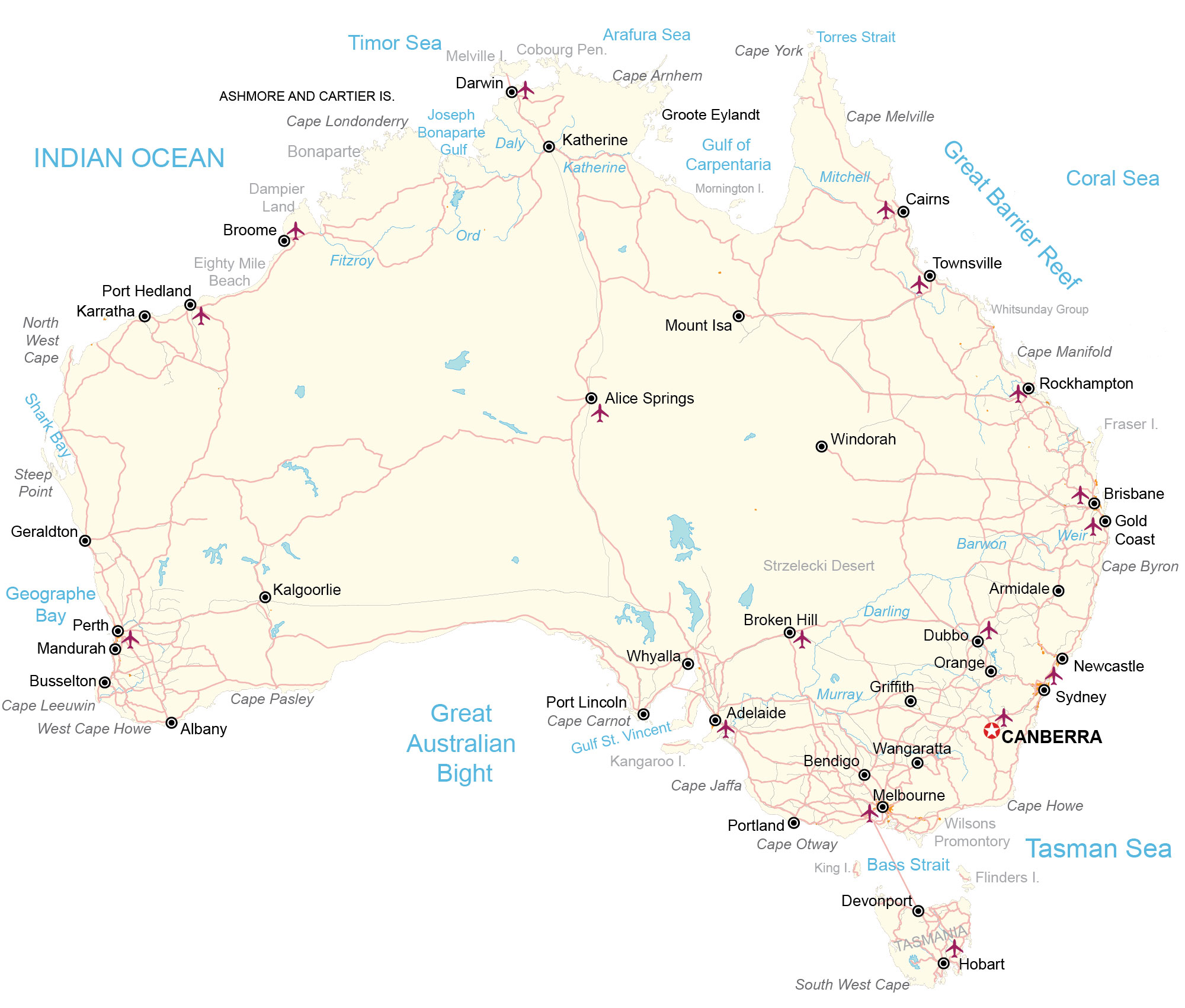
31
New cards
**Cartogram Map**
A map that distorts the shape of geographic region so that the area directly shows a specific data variable
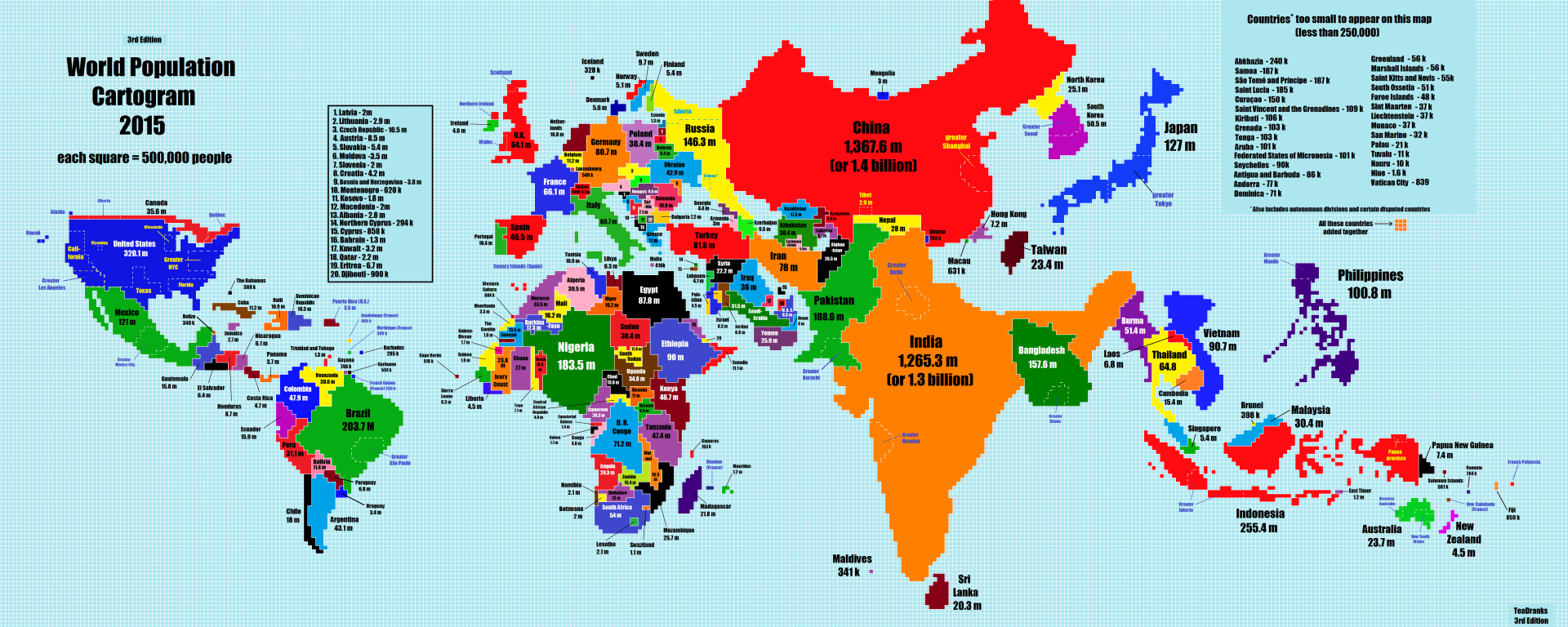
32
New cards
**Graduated / Proportional Symbol Map**
A type of thematic map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent.
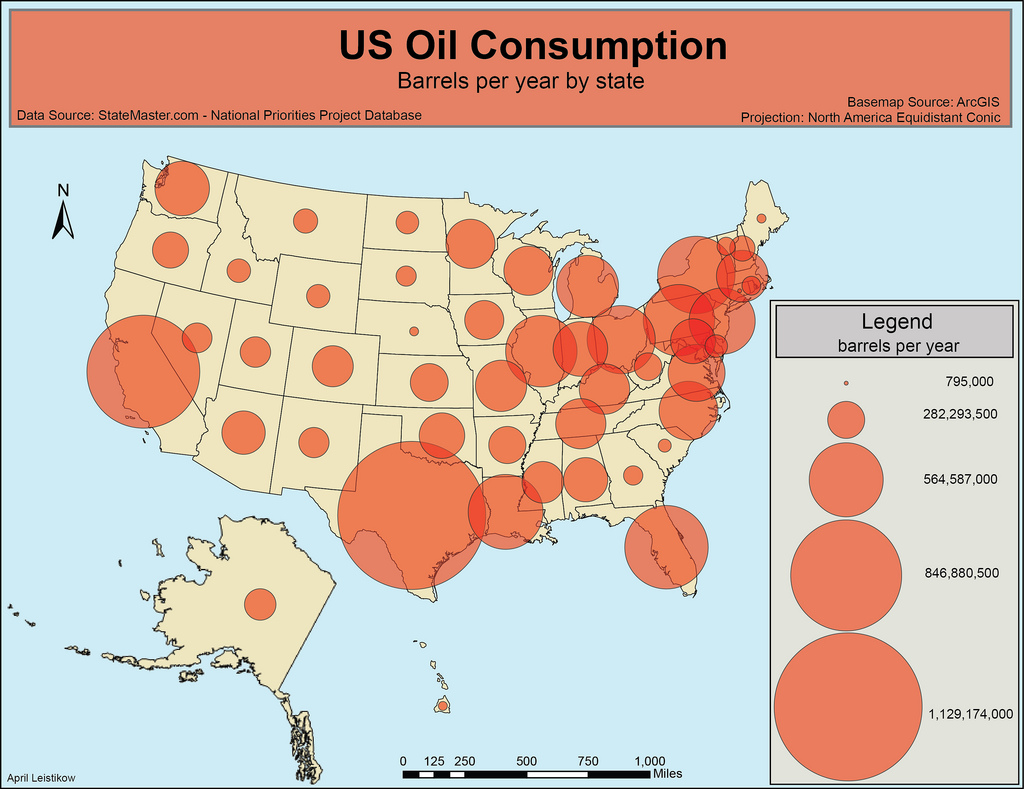
33
New cards
**Contagious Diffusion**
The rapid, widespread diffusion of a characteristic throughout the population
34
New cards
**Core-periphery**
Central, wealthy, technologically advanced countries vs. less-developed, poor, and dependant countries
35
New cards
**Cultural Ecology**
The geographic study of human-environment relationships
36
New cards
**Cultural Landscape**
Forms superimposed on the physical environment by humans Cultural attributes of an area often used to describe a place (Ex: buildings, theaters, places of worship)
37
New cards
**Natural Landscape**
The physical landscape or environment that exists before it is acted upon by human activities
38
New cards
**Distance Decay**
The theory that states that as the distance between two places increases, the interaction between those two places decreases
39
New cards
**Environmental Determinism**
The theory that the physical environment controls human growth, development, and activities
40
New cards
**Environmental Possibilism**
The theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives
41
New cards
**Formal Region**
An area within which everyone shares in a common one or more distinctive characteristics
42
New cards
**Function Region**
An area organized around a node or central point
43
New cards
**Expansion Diffusion**
The spread of a feature from one place to another in a snowballing process
44
New cards
**Stimulus Diffusion**
The spread of an underlying principle, even though a characteristic itself apparently fails to diffuse
45
New cards
**Globalization**
A force or process that involves the entire world and results in making something worldwide in scope
46
New cards
**Hearth**
The place from which an innovation originates
47
New cards
**Hierarchical Diffusion**
The spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority to other persons or places
48
New cards
**International Date Line**
A line following the 180 degree latitude that runs between the South and North Poles and serves as the boundary between one calendar day and the next
49
New cards
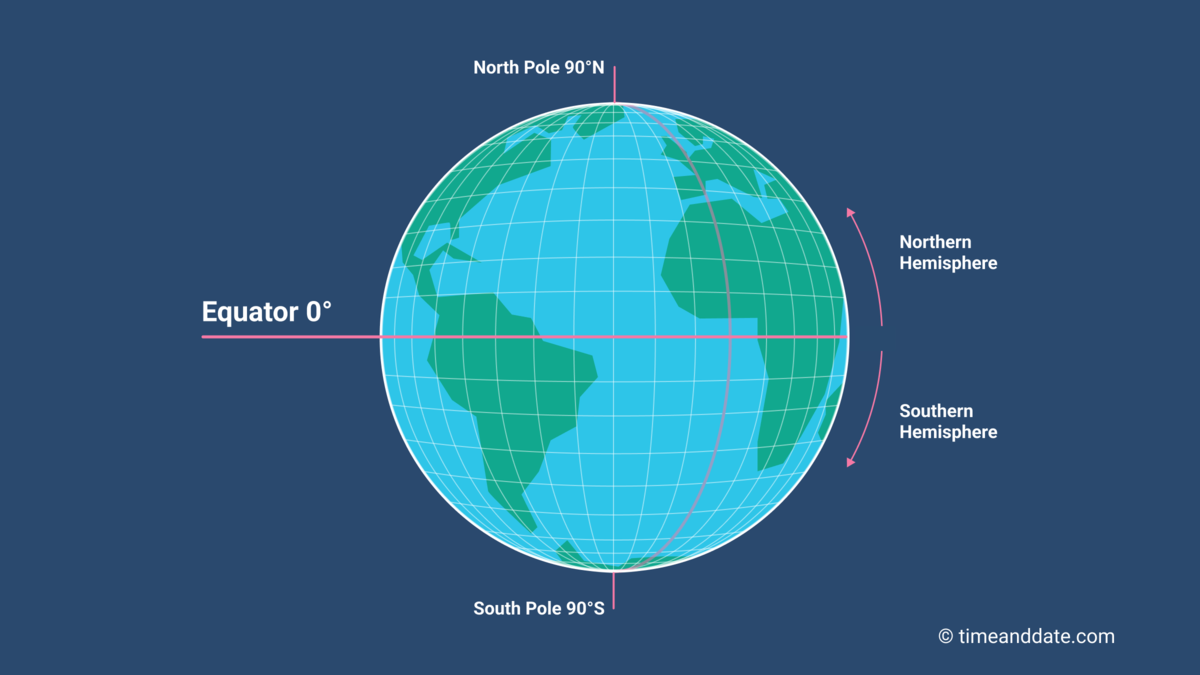
**Latitude**
The numbering system used to indicate the location of parallels drawn on a globe and measuring distance north and south of the equator
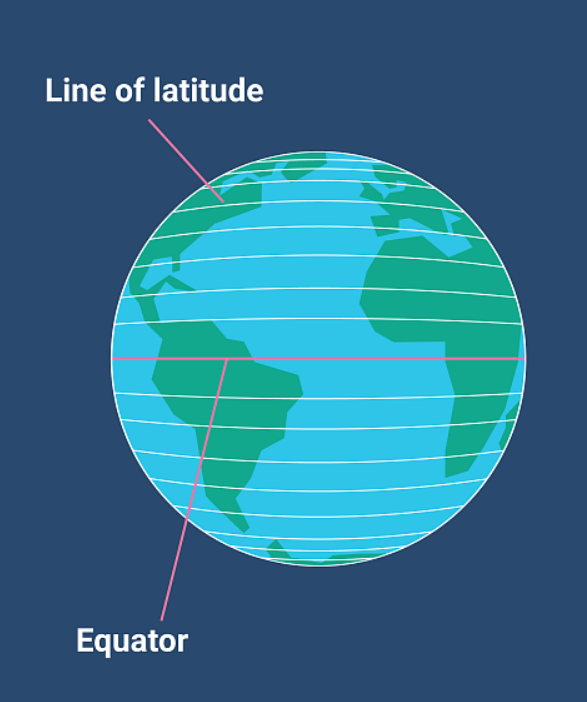
50
New cards
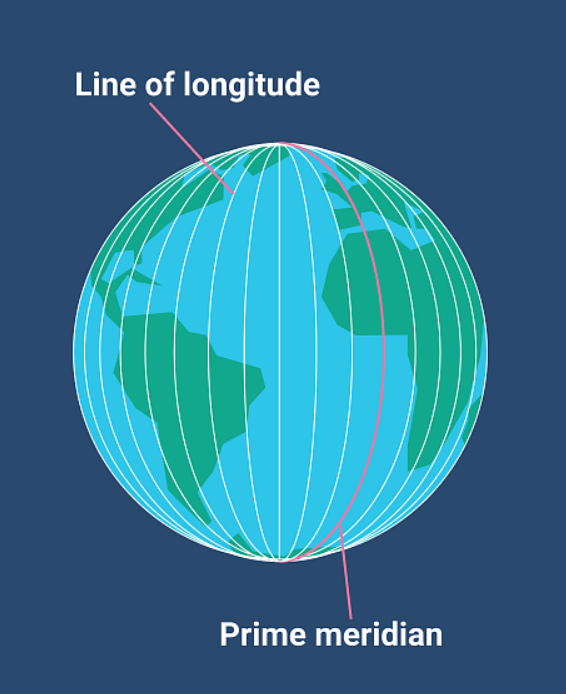
**Longitude**
The set of curving imaginary lines that run North-South, coming together at the poles. They measure distance (degrees), east or west of the Prime Meridian
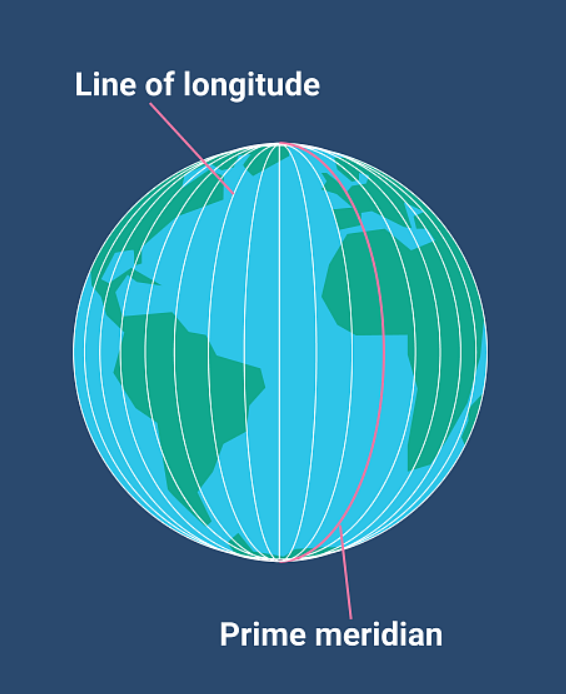
51
New cards
**Prime Meridian**
A line of 0° longitude that is the starting point for measuring distance both east and west around Earth
52
New cards
**Equator**
A line that runs through the middle of the Earth horizontally, separating the Earth into North and South