AP Psych Unit 1-A: Biological Bases of Behavior
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Nature
how much of human experience is biological/genetic
Nurture
how much of human experience is built by our environment
Twin Studies
comparing MZ and DZ twins
Monozygotic (identical) twins
a fertilized egg splits into two; twins share 100% of genes
Dizygotic (fraternal) twins
two eggs are fertilized by two different sperm cells; share 50% of genes (no more similar than any pair of siblings)
Adoption Studies
comparing adoptive children and their biological and adoptive families; investigate role of nurture
Family Studies
Comparison of parents, their children, and their sibling; investigate role of genetics
Neurons
neural cells that transmit signals throughout the body; collect, process, and respond to info
Glial Cells
non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that support neuron structure and function
Reflex Arc
simple neural circuits; input, integration, output; bypass brain for quicker reaction time
Sensory neurons
Afferent neurons, detect sensory information like needle on skin
Motor neurons
efferent neurons, output, muscle or gland activity
S.A.M.E
Sensory=Afferent; Motor=Efferent
Interneurons
integrate information, communicate with (or bypass) brain
Dendrites
receive messages from other cells
Soma (Cell Body)
the cell’s life support center including the nucleus which contains DNA
Axon
Passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
Myelin Sheath
Covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulse; the fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons for insulation
Terminal Branches
form junctions with other cells
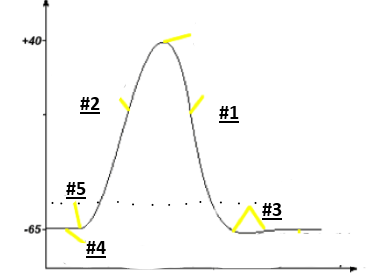
Action potential
an electrical charge that travels down a neuron (dendrite → terminal branches)
Resting potential
A neuron at rest has a voltage of approximately -65 mV
Threshold
minimum voltage needed to fire an action potential; if not strong enough, no signal is passed along
All-or-none response
If threshold is met neuron fires a full response; if threshold is not met no response
Depolarization
increasing membrane potential (mV); neuron becomes positive; Na+ in (+40 mV)
Repolarization
Decreasing membrane potential; neuron returns to negative voltage; K+ out
Hyperpolarization
overshoots resting potential, neuron becomes negative; lag on K+ channels
Refractory period
created by hyperpolarization; brief period which another action potential cannot be produced in that region; ensures signal in one direction
Myelination
Speeds things up; messages passed quicker
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
damaged myelin → increased reaction time; auto immune disorder in which immune cells attack and destroy myelin on nerve cells in the central nervous system
Synapse
the space between adjacent neurons; chemical signal is passed across to the next neurons
Neurotransmitters
chemicals in synaptic vesicles; release triggered by action potential
Diffusion
neurotransmitters simply diffuse out of the synapse
Reuptake
Neurotransmitters are taken back up by a neuron recycling channel
Digestion
broken down by enzymes and no longer binding to postsynaptic neuron
Excitatory NT
depolarizes neuron; encourages an action potential; membrane voltage becomes more positive; approaches threshold → more likely to fire
Inhibitory NT
further polarizes neuron; discourages an action potential; membrane voltage becomes more negative; moves away from threshold
Acetylcholine
enables skeletal muscle movement; enhances learning, memory, and attention
Norepinephrine/noradrenaline
Influences alertness and arousal; active in the fight or flight response
Serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, and psychological arousal
Dopamine
Reward pathways; enhances muscle movement, emotion, attention, and more
GABA
major inhibitory neurotransmitter; important role in learning and memory
Glutamate
major excitatory neurotransmitter; important role in learning and memory
Endorphins
Natural pain relivers and mood boosters; modulate pain response and replace with pleasure (ex. runners high)
Substance p
Role in pain perception and activating immune response
Myasthenia gravis
Chemical signal impacted; causes muscle weakness and fatigue; antibodies block receptors → neuron to neuron communication; auto immune disease where antibodies block acetylcholine receptors
Endocrine system
a collection of glands that produce hormones; chemicals that are released directly into the circulatory system (often activated by nervous system)
Adrenaline
Adrenal glands (pancreas: regulate blood glucose level) cortisol; fight or flight response horomones
Oxytocin
Pitutary gland which can release into the blood stream; love hormone, facilitate childbirth, sexual excitement
Drugs
interrupts neurons
Narcotics (opiates)
Binds endorphin receptors → pain relief euphoria/dopamine release (ex. opium, morphine, heroin)
Stimulants
Stimulate neural activity; excitatory NT (ex. caffeine, nicotine, methamphetamine, cocaine)
Depressants
Depress neural activity → can stimulate the release of GABA (inhibitory NT) (ex. Alcohol, barbiturates)
Hallucinogens
Distorts sensory perception or cognition (ex. LSD/Acid, MDMA/Ecstasy/Molly, Marijuana/THC)
Agonists
A drug molecule that binds receptor sites and increases a neurotransmitter’s action (ex. marijuana)
Antagonist
A drug molecule that binds receptor sites and inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter’s action (ex. pain killer and caffeine)
Reuptake Inhibitors
a drug molecule that prevents reuptake of a neurotransmitter; increases NT’s action (ex. cocaine and antidepressants)
Tolerance
drug’s effect lessens after repeated use → takes larger doses to feel high
Dependence
Physiological and/or psychological need to use a drug
Addiction
compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse consequences
Withdrawal
the discomfort and distress that follow discontinued use of an addictive drug
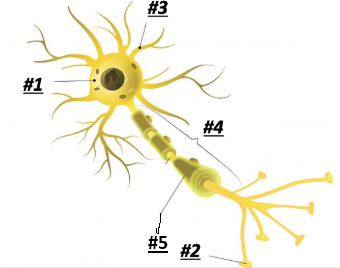
Soma/Cell Body
1
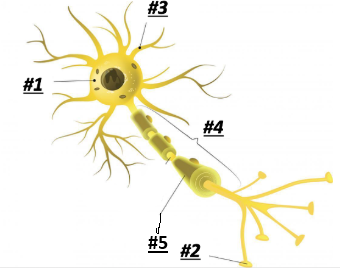
Terminal Branches
2
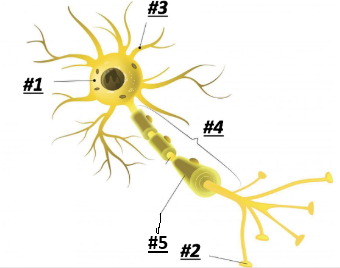
Dendrites
3
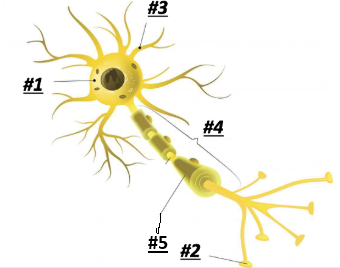
Axon
4
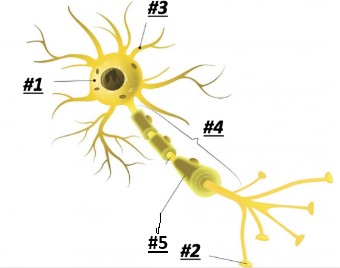
Myelin
5
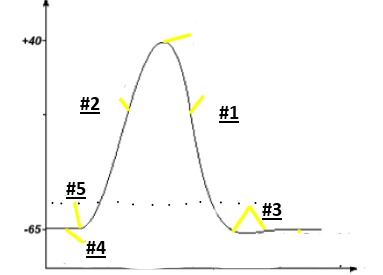
Repolarization
1
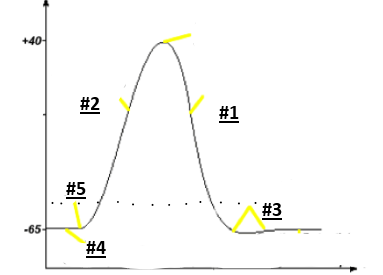
Depolarization
2
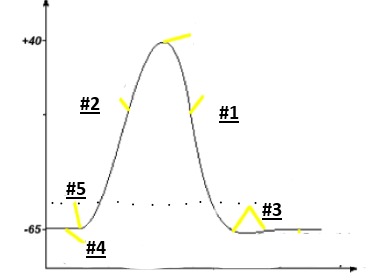
Hyperpolarization
3
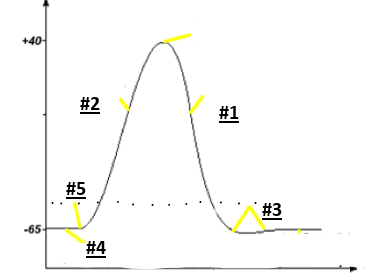
Resting potential
4
Threshold
5
Central Nervous System
Brain spinal cord; integrate signals from various regions of the body, includes interneurons
Peripheral Nervous System
Outside of brain and spinal cord; carries info into/out of the CNS; Afferent/efferent neurons
Somatic
controls the body’s skeletal movement; voluntary control
Autonomic
controls the glands and muscles of internal organs; operates automatically
Sympathetic
Fight or flight; arouses the body, mobilizing it’s energy
Parasympathetic
Rest and digest; calms the body, conserving it’s energy
Lesions
areas of the brain tissue that are damaged or deteriorating; can be natural
CAT/CT Scan
computerized tomography; uses a series of x-rays (radia
MRI
uses magnetic fields to visualize the brain’s structure; expensive and detailed
EEG
measures electrical activity in the brain; fast but not location specific
fMRI
measurement of oxygen use by brain cells; visualize what areas of the brain are involved in different tasks
PET
monitor circulation of radioactive tracers; visualize glucose, metabolism, and oxygen/blood flow
Brainstem (reptilian)
Medulla oblongata, Reticular activating system, cerebellum
Medulla oblongata
control of heart rate and breathing
Reticular activating system
some motor function, breathing, eye movement, arousal, sleep/wake cycle
Cerebellum
coordinates voluntary movement and balance
Limbic system (feeling)
Thalamus, Amygdala, Hippocampus, Hypothalamus, Pituitary gland
Thalamus
Sensory relay station; directs sensory info (touch, vison, hearing, taste) to other parts of the brain
Amygdala
Response to strong emotion trending negatively (ex. fear)
Hippocampus
encoding and processing memory
Hypothalamus
governs pituitary gland; feeding, fighting, fleeting, “mating”
Pituitary gland
Regulated by hippocampus; releases hormones (ex. appetite)
Cerebral cortex (neocortex)
Frontal lobe, Parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe
Frontal lobe
higher order thinking, language processing, judgment, and decision making
Motor cortex
initiates motor movement; within frontal lobe
Broca’s area/aphasia
language center located in the left frontal lobe, involved in expressive language (speech)
Parietal lobe
processes sensory input for touch and body position
Somatosensory
touch sensitivity
Temporal lobe
auditory information and linguistic processing; primarily from opposite ear
Wernicke’s area/aphasia
language center located in the left temporal lobe; involved in language comprehension/coherence