Waves
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what are waves
Waves transfer energy from one point to another through vibrations
what are transverse waves
in these waves the particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer .
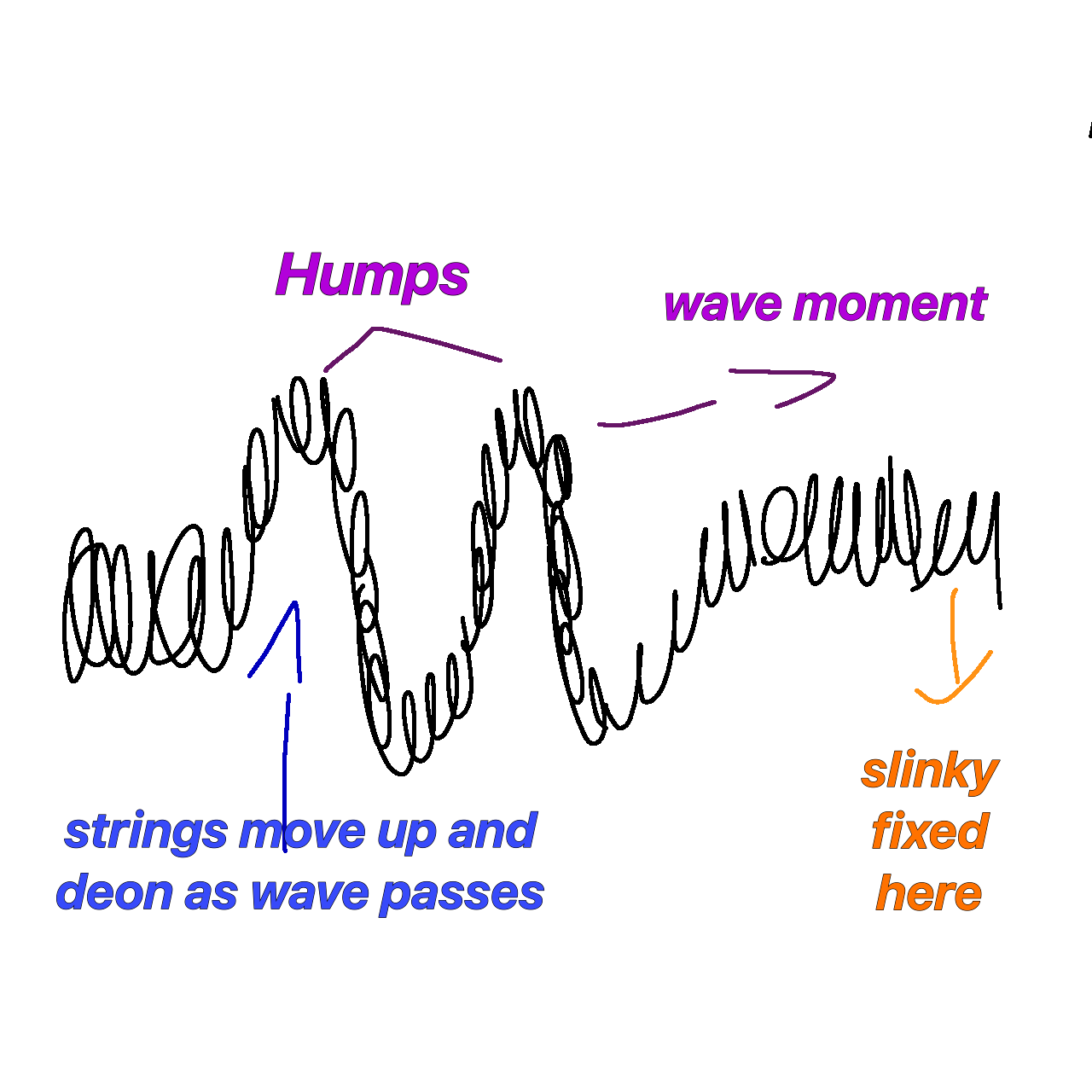

what are longitudinal waves
these are waves which the particles vibrate parallel to the direction of energy transfer

examples of transverse waves
Radio waves
Light rays
X rays
Water waves
Example of longitudinal
sound waves
Ultrasound waves (sound waves with a frequency greater than 20,000 hz)
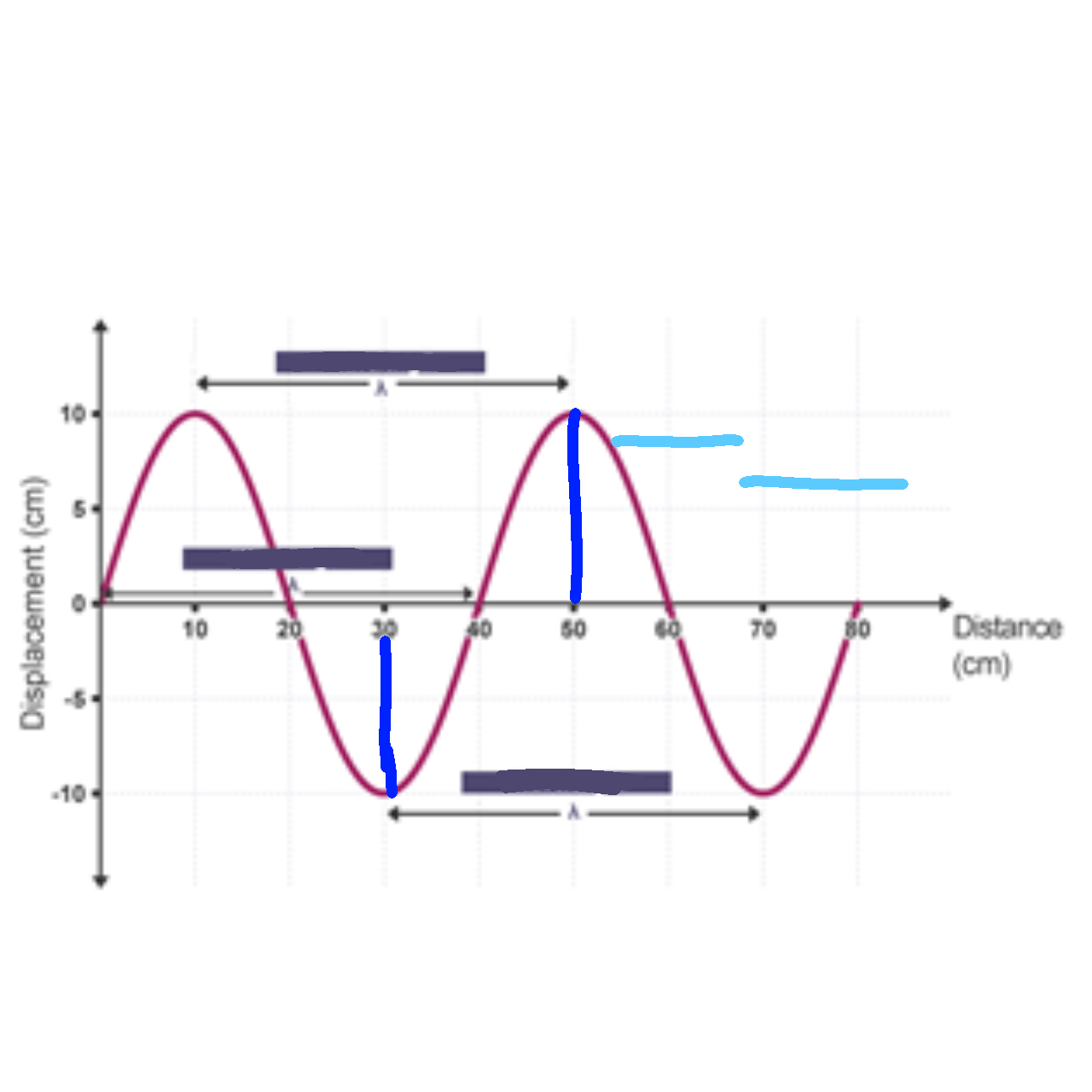
wave mechanics
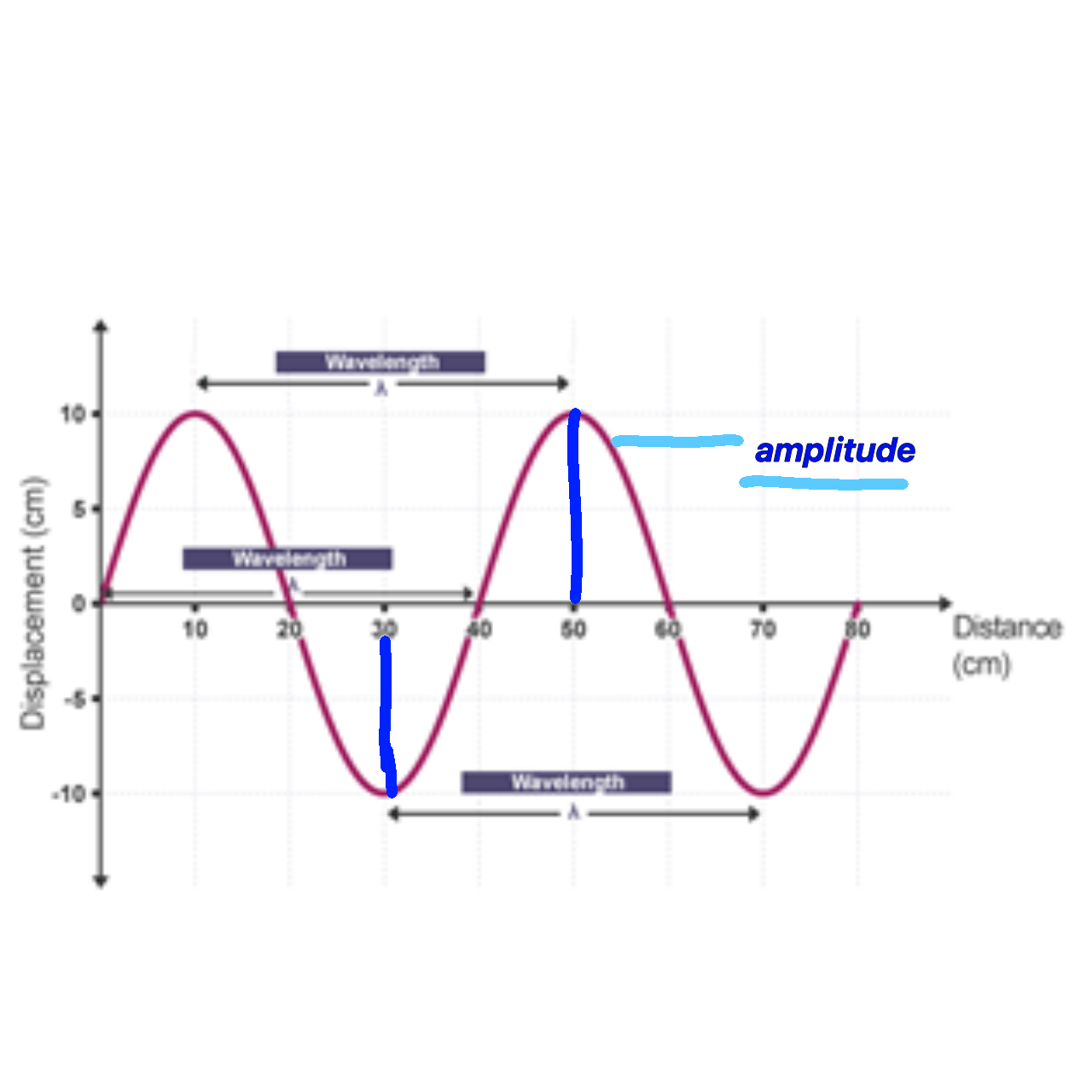
What is amplitude (m)
the maximum displacement of the particles from rest position
What is wavelength λ (m)
The distance between two identical points on the wave
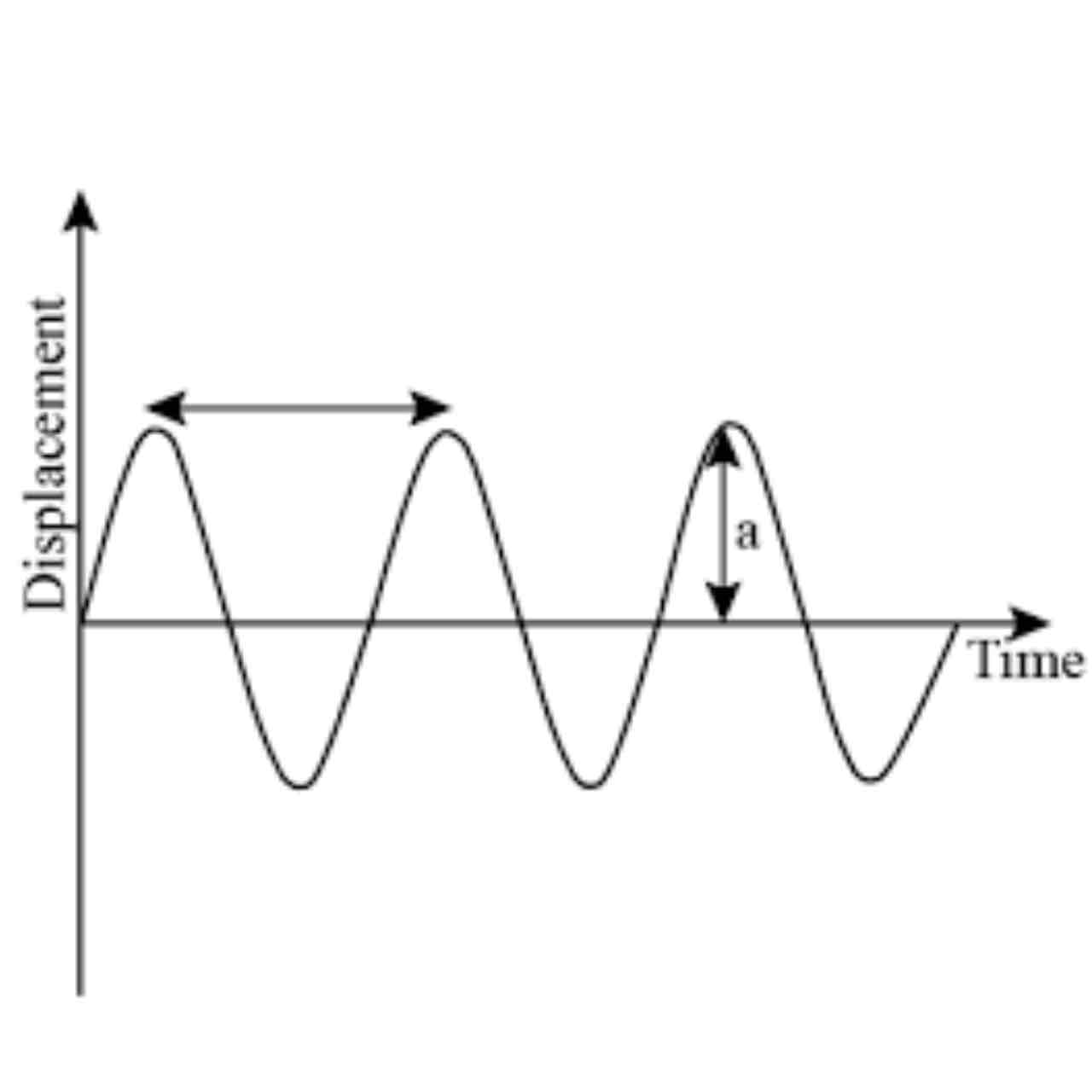
T = time period
The time taken for one complete wave and can only be found if time is on x axis
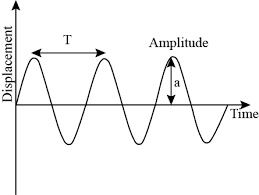
what is frequency -
Hz - the number of complete waves in one second
Wave equation
V = fλ
Velocity of wave (m-s)
Frequency (Hz)
wavelength (m)
Time period equation
f = 1 ➗T
Frequency’s
Time period
what is the human hearing range
20hz to 20,000hz
What is the an ultrasound
a frequency greater than 20,000hz
what is an ultrasound used for in medical uses
pre -natal scans
disintegrating kidney stones
process of prenatal scan
a pulse of ultrasound is directed toward the brain, this is absorbed and passes through the brain, it is then reflected at the far side of the brain and detected back from the sonographer, the equation distance = speed x time shows diameter of the brain
what are the industrial uses for ultrasound
determining the depth of an ocean
cleaning expensive jewellery
detect defects in metals
identify location of fish under boat, - ultrasound returns more quicker than expected
Echo
sonar use reflective soundwaves also known as echo
what is radar
a reflective radio wave . These are used to sims the location of planes approaching airports
properties of radar
travels very fast (3 × 108)
can travel through a vacum
Is transverse
what can sonar be used for
locating slow moving object e.g boats and submarines
fast moving objects e.g planes often travel faster than sound (super sonic) therefore sound waves travel too slow
what are the regions of the EM spectrum
Radio waves
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible light
Ultraviolet
X rags
Gamma rays
Longest wave length =
Smallest frequency , least dangerous : radio waves
smallest wavelength =
biggest frequency , most dangerous - gamma rays
Uses and Dangers of Radiowaves
Tv and Radio communication
No known risks
Uses and Dangers of Microwaves
phone calls, parking sensors, rapid heating of food.
Can cause tissue and cells to absrob microwaves and increase temperature
Uses and Dangers of Infrared
Remote control, night vision goggles, toasters and grills
Absorbed as heat energy by tissue/cells results in sun burn
Uses and Dangers of Visible Light
Photosynthesis, photography
Snow blindess, difficulty driving
Uses and Dangers of UV
Used to detect fake bank notes, kills bacteria in water
Absorbed by skin cells, dirsupts DNA causing cancer
Uses and Dangers of X rays
Detects fractures in broken bones, used in security scans at airports
Ionising radiation which dirsupts DNA - cancer
Uses and Dangers of Gamma Rays
based in chemotherapy and radiotherapy to kill cancerous cells
sterilise surgical equipment
highly ionising radiation which disrupt DNA