Physics AQA Topic 2 (Current, potential difference and resistance)
1/28
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is the circuit symbol for a cell
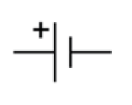
What is the circuit symbol for a battery
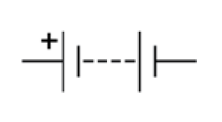
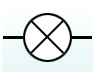
What is the circuit symbol for a lamp
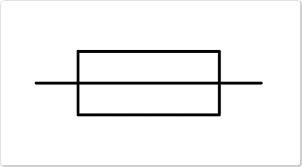
What is the circuit symbol for a fuse
What is the circuit symbol for a voltmeter
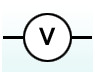
What is the circuit symbol for an ammeter
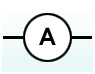
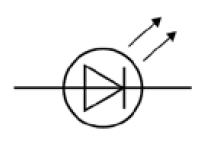
What is the circuit symbol for a diode
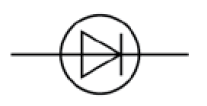
What is the circuit symbol for a resistor
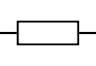
What is the circuit symbol for a thermistor
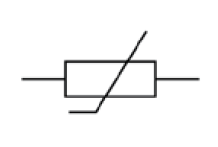
What is the circuit symbol for a variable resistor
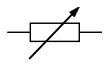
What is the circuit symbol for an LDR
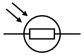
What is the circuit symbol for an LED
What is electric current
The flow of electrical charge
What must the circuit include for electrical charge to flow through a closed circuit
A source of potential difference
What is the equation linking charge, current and time
Q = It (Charge = current x time)
What are the units for the equation linking charge, current and time
Charge = coulombs (C), current = amperes (A) and time = seconds (secs)
What can be said about the value of current at any point in a single closed loop
Current is the same at all points in a closed loop
What two factors does the current in a circuit depend on
Potential difference and resistance
What equation links potential difference, current and resistance
V = IR (Voltage = current x resistance)
What are the units for the equation linking potential difference, current and resistance
Potential difference = volts (V), current = amperes (A) and resistance = ohms (Ω)
What is an ohmic conductor
A conductor for which current and potential difference are directly proportional - resistance remains constant as current changes (temperature must be constant)
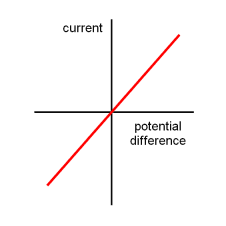
List 4 components for which resistance is not constant as current changes
Lamps, diodes, thermistors and light dependant resistors
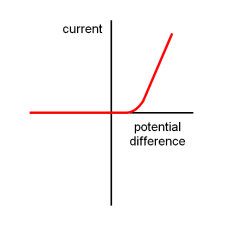
What happens to the resistance of a filament bulb as current increases
Resistance increases, increased current heats up the filament so ions in metal have more energy and vibrate more, causing more collisions with the electrons as they flow through the metal, creating greater resistance to the flow of current
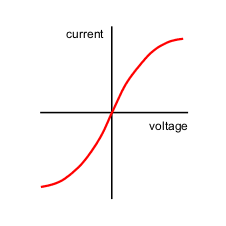
What is different about current flow through a diode
The current only flows through the diode in one direction so the resistance is very high in the other direction, preventing the current from flowing through
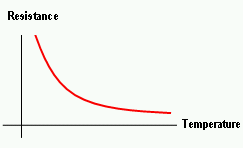
State what happens to the resistance of a thermistor as temperature increases
The thermistor's resistance decreases
Give two examples of when a thermistor may be used
In a thermostat to turn a heater on below a certain temperature, or in a freezer to turn on a cooler when the temperature becomes too high
State what happens to the resistance of an LDR as light intensity decreases
The LDR's resistance increases
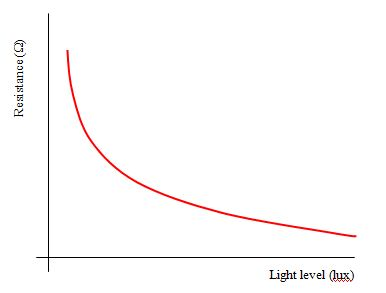
Give an application for an LDR
Street lights
How does using LDRs in a street lamp work
LDR is in a parallel circuit with the bulb so when the resistance of the LDR is high (light intensity is low), more current will choose to flow down the wire with the bulb in it so the bulb will get brighter when the light intensity is lower (when it is night)