Biochem Sept. 8th
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering energy changes (ΔG), the central dogma, and fundamental concepts about amino acids, peptide bonds, and protein structure.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What way is a sequence of amino acids read?
The sequence of amino acids in a protein is read from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
Usually methionine (Met) initiates the chain
What determines the proteins chemical properties and folding behaviour?
The R group side chain of amino acids
What are amino acids made of?
Amino acids are made of an amino group(NH3+), a carboxyl group (COO-), and an R group side chain, all attached to a central carbon atom.
What do mutations or DNA damage do?
Mutations and DNA damage can alter the sequence of amino acids in proteins, changing protein structure and function, which underlies many diseases.
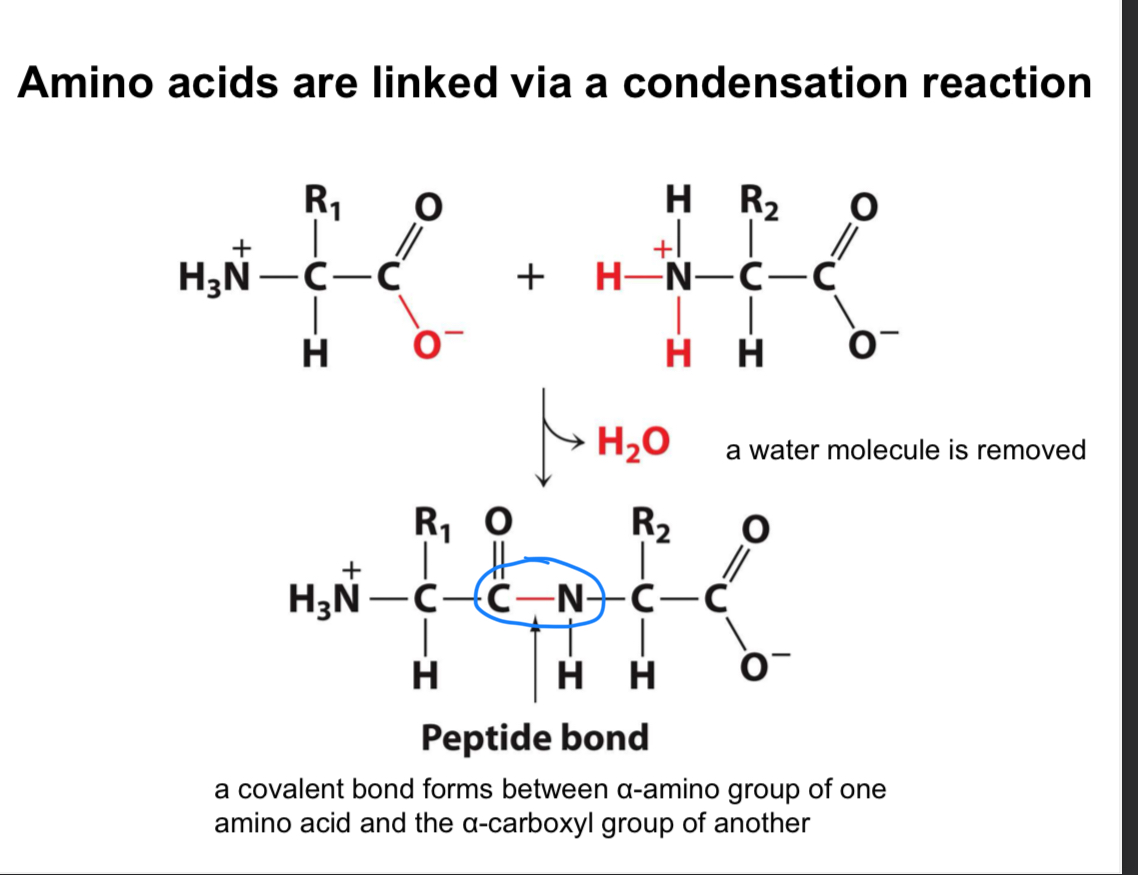
What is a peptide bond?
A peptide bond is a covalent bond that links amino acids together, formed through a dehydration (removal of water) reaction between the amino group (NH3+) of one amino acid and the carboxyl group (COO-) of another.
What are the amino acids that have hydrophobic R groups
Alanine, Valine, Proline, Leucine, Isoleucine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, and Methionine
What are the amino acids with polar R groups?
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine, Tyrosine, and Histidine. These amino acids can form hydrogen bonds and interact with water, making them hydrophilic.
What are the amino acids with charged R groups?
Lysine, Arginine, Aspartate, and Glutamate. These amino acids have side chains that can gain or lose protons, thus acquiring a charge and affecting their behavior in a protein's structure and function.
What amino acids have ionizable groups?
lysine, arginine, glutamate, aspartate, cystine, histidine and tyrosine. Obvi all do with the C-terminus and N-terminus groups being ionizable)
What is the Ka?
The acid dissociation constant, a measure of the strength of an acid in solution.
What is the pKa?
The negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka), which indicates the pH at which an acid is half dissociated.
Lower the pKa ..
The stronger the acid
What does it mean when the pH of a solution is equal to the pKa of that acid (pH = pKa) ?
Half of the molecules are in the protonated form (HA) and half are deprotonated (A-)
(Charge is either 0.5 or -0.5)
pH = pKa + 1
~91% in A⁻
~9% in HA
pH = pKa - 1
~9% in A⁻
~91% in HA
(Ex. Tyrosine has a pKa of 10 and the pH is 9, what’s the average net charge? Answer = -0.1 because 0.09 is basically 0.1)
-0.1 because 10% of it is in the deprotonated form and 90% is the neutral form -0.1 + 0 = -0.1
pH = pKa + 2
~99% in A⁻
~1% in HA
pH = pKa - 2
~1% in A⁻
~99% in HA
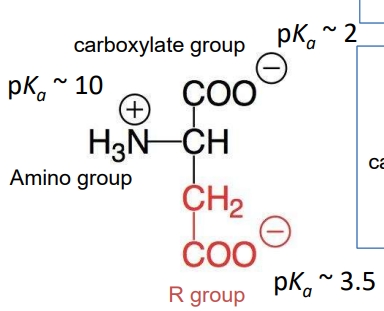
Net charge of amino acids
Ex. Asp at pH 7