Measurements, uncertainties and SI units
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
How do you find Absolute uncertainty?
Range/2
How to fin the percentage uncertainty?
Range/2 x mean value
What is the total percentage uncertainty of the value of velocity when distance has 5% and time has 0.43% percentage uncertainties? And what is the absolute uncertainty of v if v= 8.7 ms
v=dxt
Has both so add them together
5.43% percentage uncertainty
Absolute uncertainty= 8,7×0.0543= +-0.5 ms
Why are log graphs better than regular graphs?
Log graphs are better because they are better at displaying data that is spread over multiple orders of magnitude.
Which part of y=mx+c is the gradient
M
If f²=T/4L²u what is the gradient?
m= 1/4L²u
Accuracy
How close a measurement is to its true value, influenced by the systematic and random errors of that measurement.
Precision
How close a set of repeated measurements are to one another but not the true value, influenced by the measurement’s random errors.
Random Error
The unpredictable variation in a measurement. These can be reduced by taking many repeated measurements and calculating their mean.
Zero error
when a measuring instrument shows a non-zero reading when the actual quantity being measured is zero, leading a systemic error in all readings.
Systematic Error
A constant shift in readings causing a deviation from the true value, due to the equipment or method being used and cannot be reduced by repeated measurements.
Repeatable
When the same person with the same equipment obtains the same result when doing the same experiment.
Reproducible
When different people with different equipment, measuring the same quantity, get a similar result.
Resolution
The smallest interval that a measuring device can measure.
What are the six SI units?
Kilogram
Kelvin
Candela
Metres
Moles
Seconds
Amps
When you calculate and uncertainty. When do you combine uncertainties?
ADDING and SUBTRACTING
A thermometer with an uncertainty of ±0.5 K shows the temperature of water falling from 298 ±0.5 K to 273 ±0.5K, what is the difference in temperature?
0.5 + 0.5 = 1K
= 25 +-1 K
a force of 91 ±3 N is applied to a mass of 7 ±0.2 kg, what is the acceleration of the mass? and it’s percentage uncertainty?
= 3.3% + 2.9%
= 6.2%
6.2% of 13 is 0.8
=13 ±0.8 m s-2
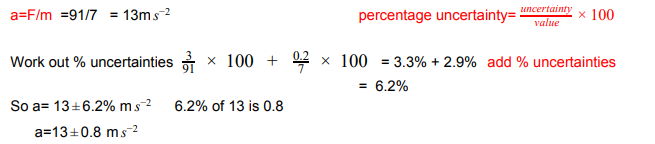
What is the forumal for percentage uncertainty?

The radius of a circle is 5 ±0.3 cm, what is the percentage uncertainty in the area of the circle?
0.3/5 × 100= 6
6 × 2= 12cm3

When mutiplying or dividing uncertainties
add the percentage uncertainties
then work out the absolute uncertainty
suggest one way for experimental evidence to become valid
through peer reviewing
suggest 2 ways the application of science can be beneficial
developing medical treatments
carrying out research on prior knowledge
what does an application of science mean?
a use of scientific knowledge to carry out a specific action