Chapter 1 - Introduction to the Human Body (multiple choice)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Metabolism
The sum of all the chemical process that occurs in the body
Responsiveness
Body's ability to detect and respond to external and internal changes
Movement
E.g., movement of the body, organs, tissues, cells, and subcellular structures
Growth
Increase in body size that results from an increase in the size of the existing cells and/or an increase in the number of cells
Differentiation
The development of a cell from an unspecialized to a specialized state
Reproduction
Formation of new cells for tissue growth, repair, or replacement; the production of a new individual
Intracellular fluid
The fluid within body cells
Extracellular fluid
The fluid outside body cells
Receptor
A sensor or structure that detects changes in the internal or external environment (ex. themoreceptors in the skin)
Stimulus
A change in the environment that disrupts the controlled condition (ex. hot weather causes an increase in body temperature)
Controlled condition
A monitored variable that is being regulated to stay within a normal range (ex. body temperature, normally around 37°C)
Control Center
Processes input from receptors, compares it to a set point, and sends output signals to effectors (ex. brain)
Effector
A body structure that receives output signals from the control center and produces a response (ex. sweat glands and blood vessels)
Response
The action taken by the effector that alters the controlled condition (ex. sweating helps to cool down the body)
Positive feedback system
A system where the body's response will amplify the initial change
Negative feedback system
A system where the body's response will counteract the initial change
Aging
A progressive decline in the body's ability to restore homeostasis
Disorder
Any abnormality of structure or function
Disease
Illness characterized by a recognizeable set of signs and symptoms
Symptoms
Changes in body functions that are felt or reported (ex. headache)
Signs
Changes in body functions that can be measured or observed
Blood plasma
The fluid component of blood
Lymph
The fluid inside of lymph vessels
Anatomical position
To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
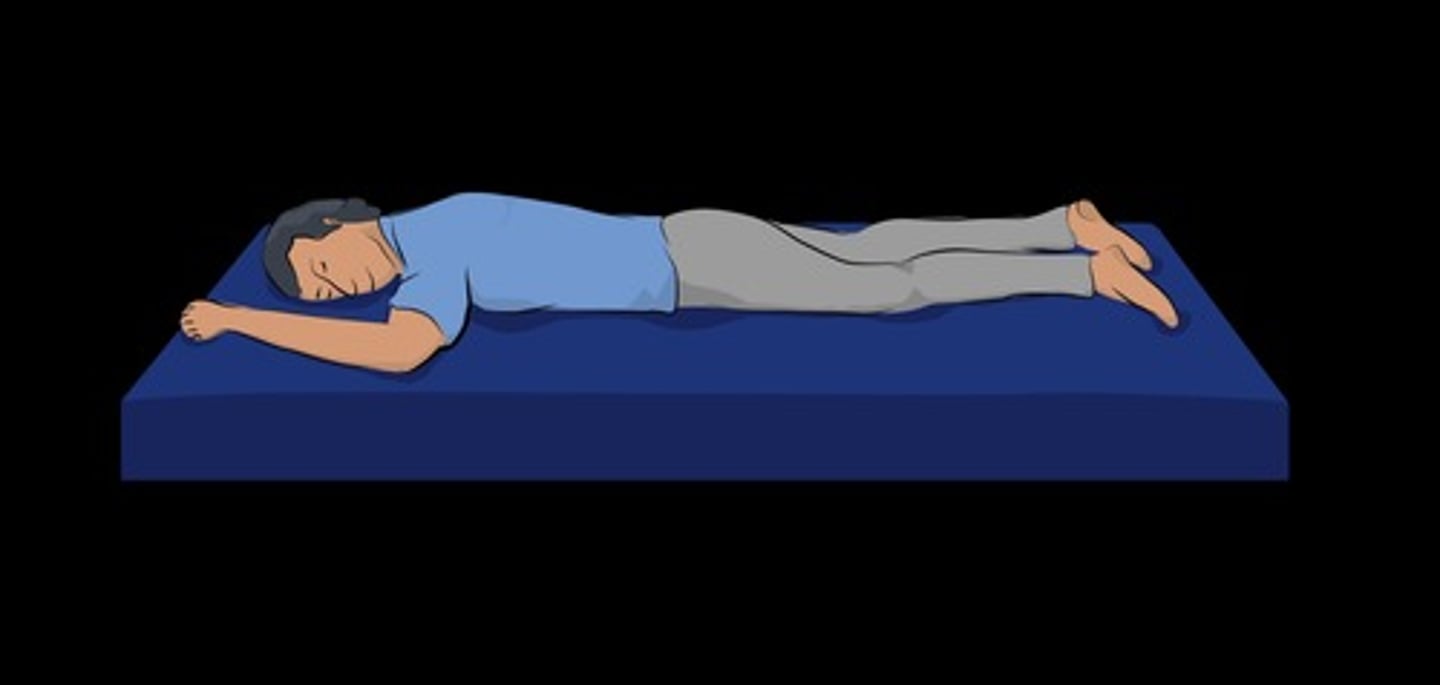
Prone position
Lying face down
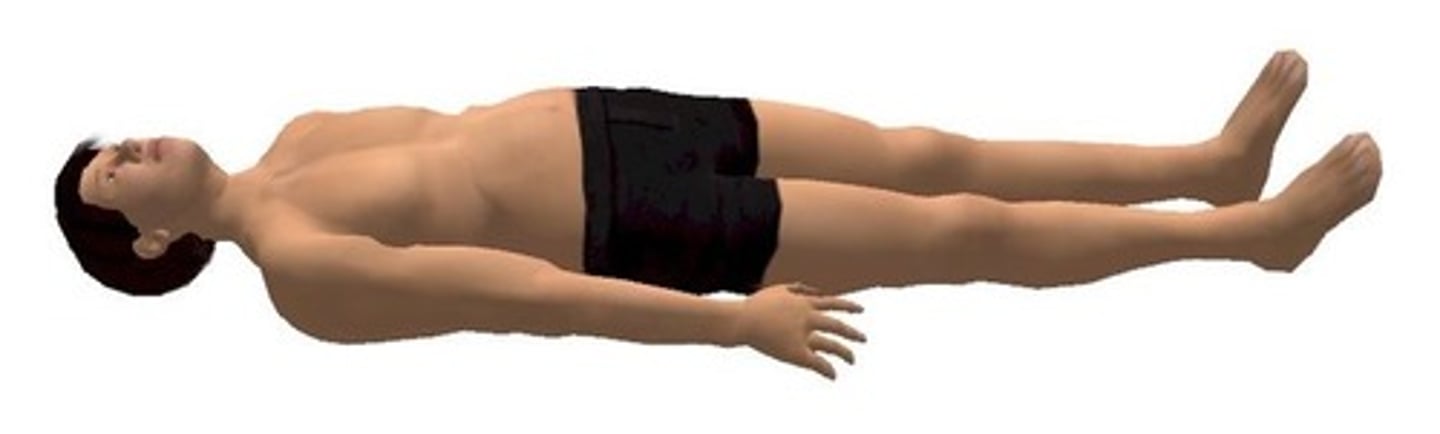
Supine
Lying face up
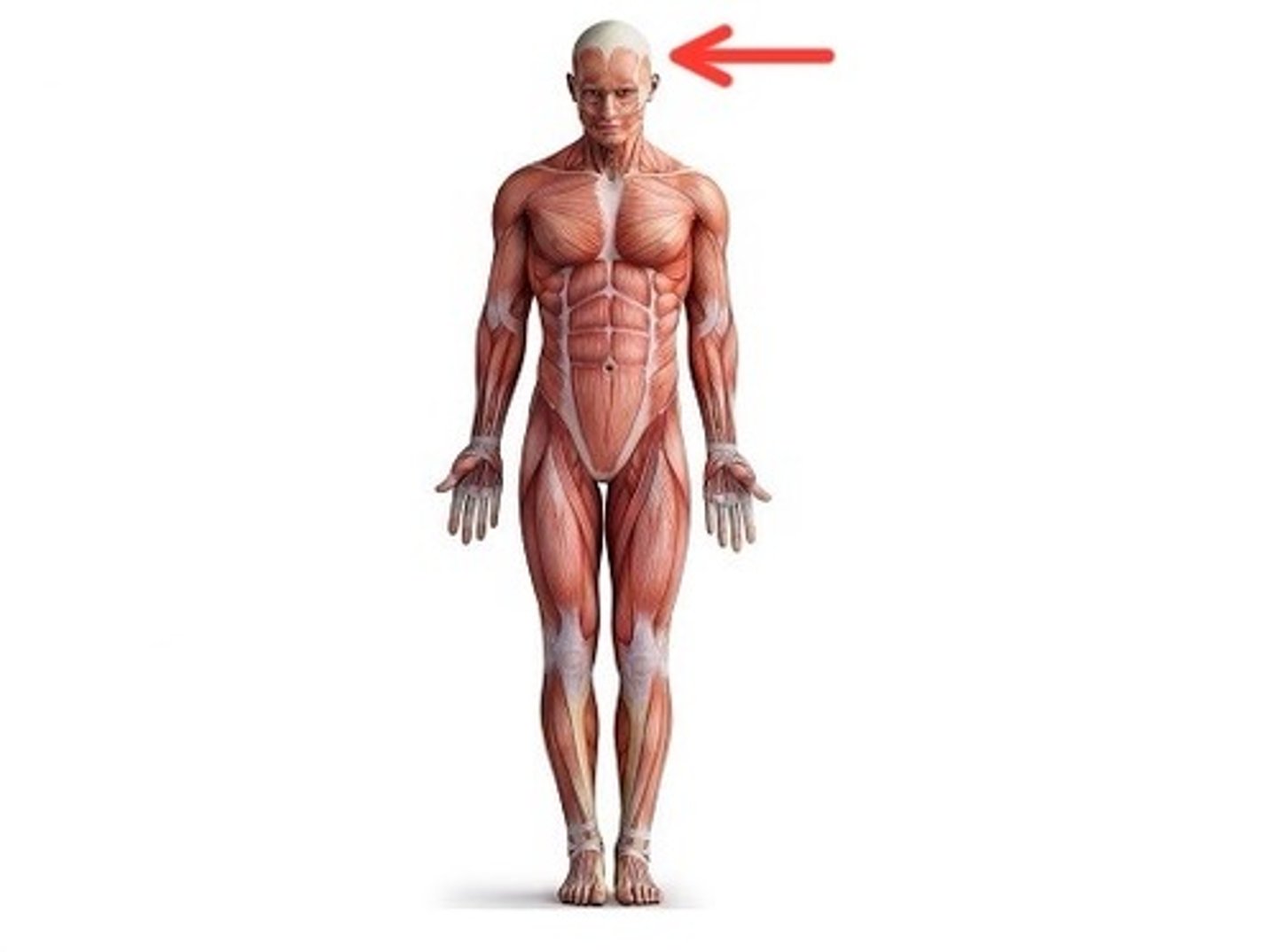
Cephalic
Head region
Cervical
Neck region
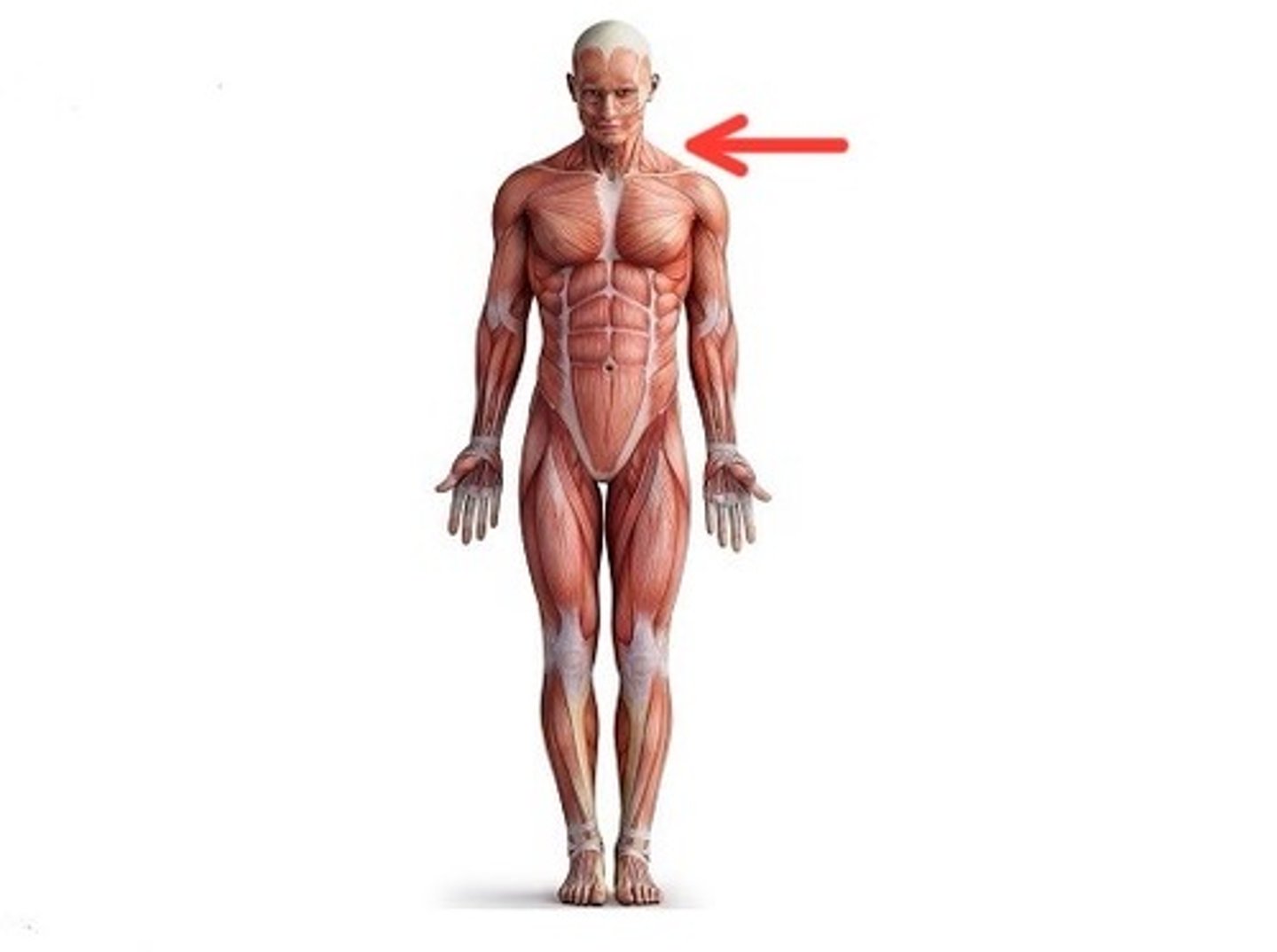
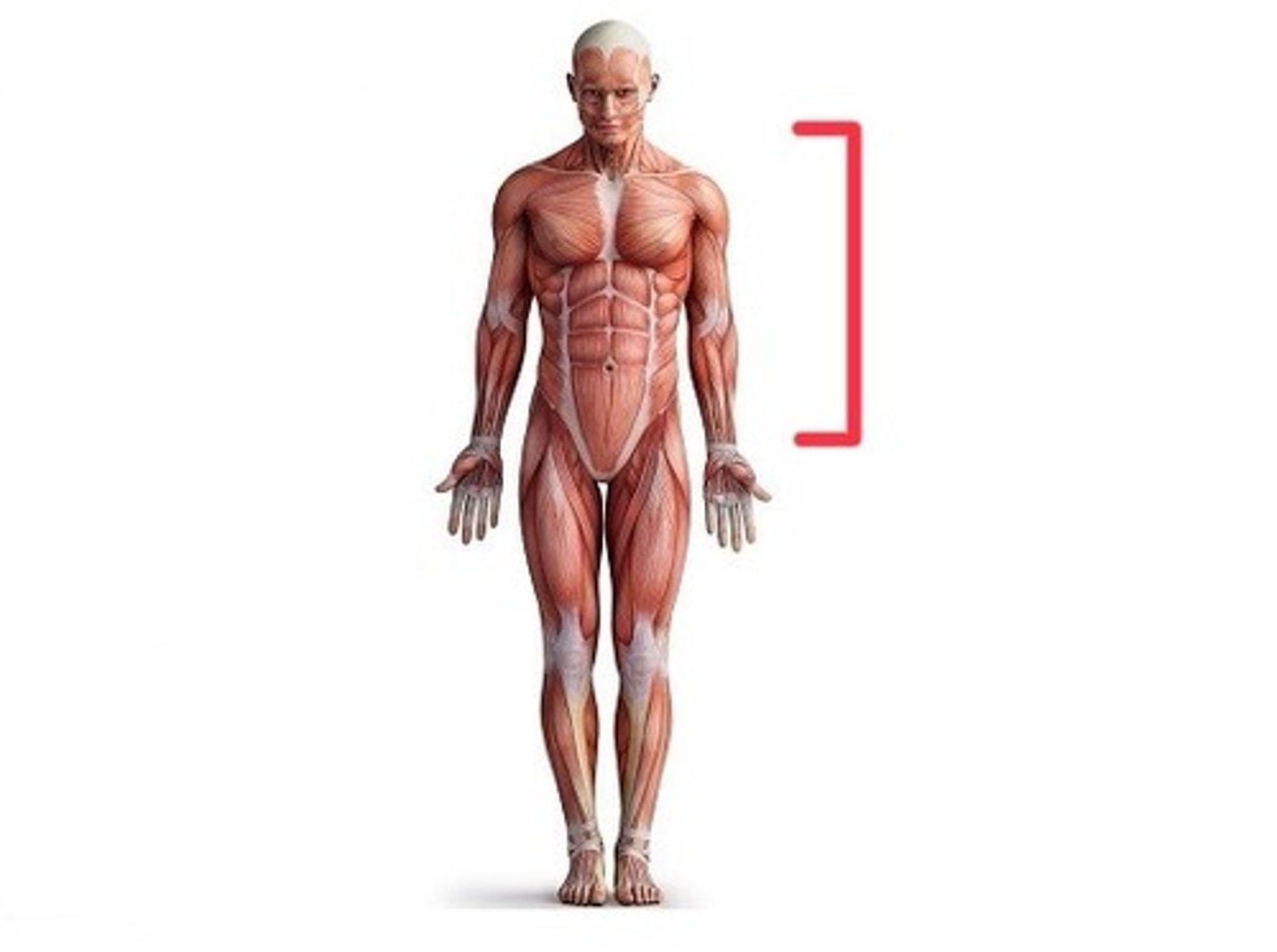
Trunk
Chest, abdomen, and pelvis region (base of the head to hips)
Directional terms
Used to precisely locate one part of the body relative to another
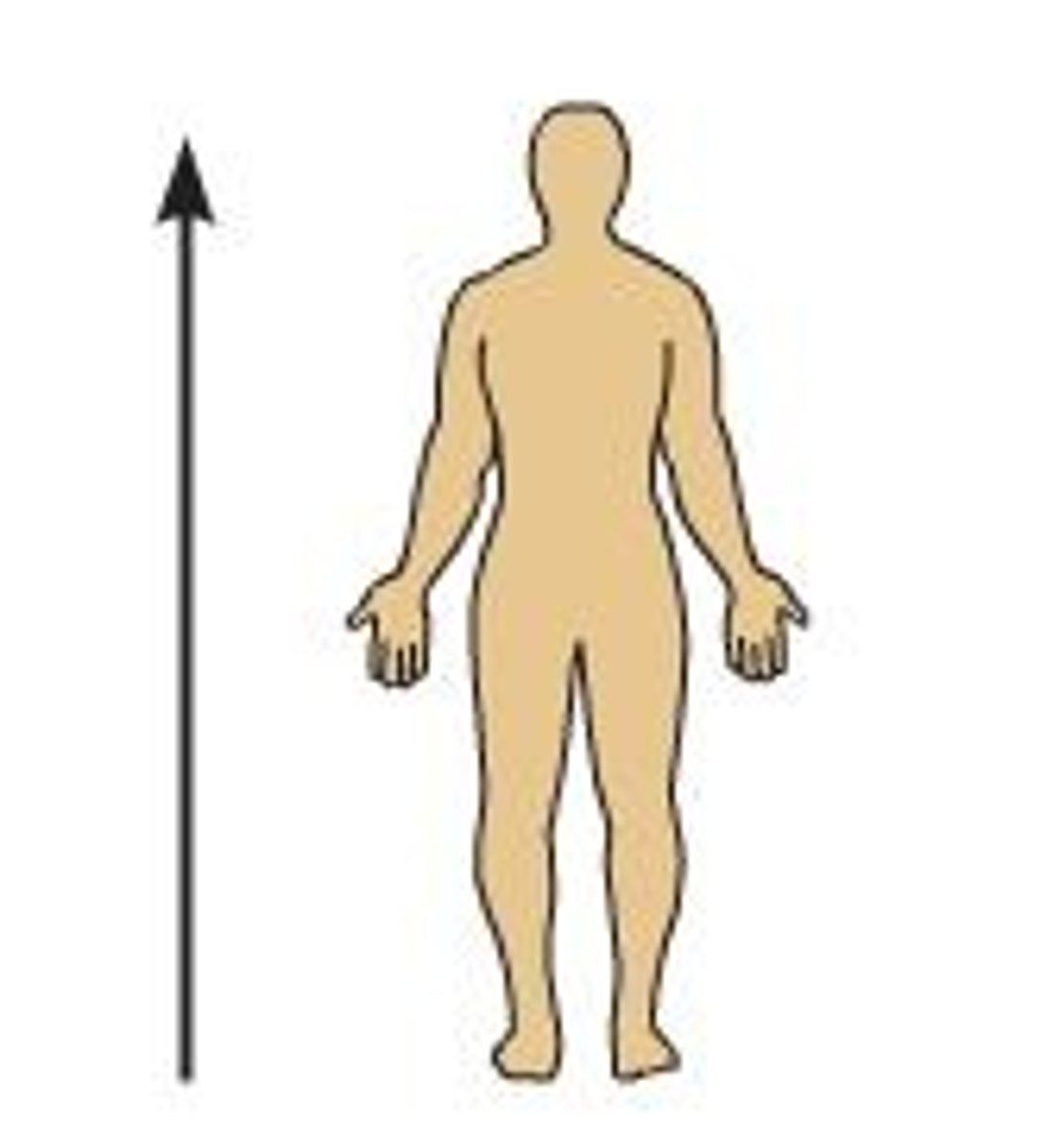
Superior
Higher on the body, towards the head (ex. the heart is ________ to the liver)
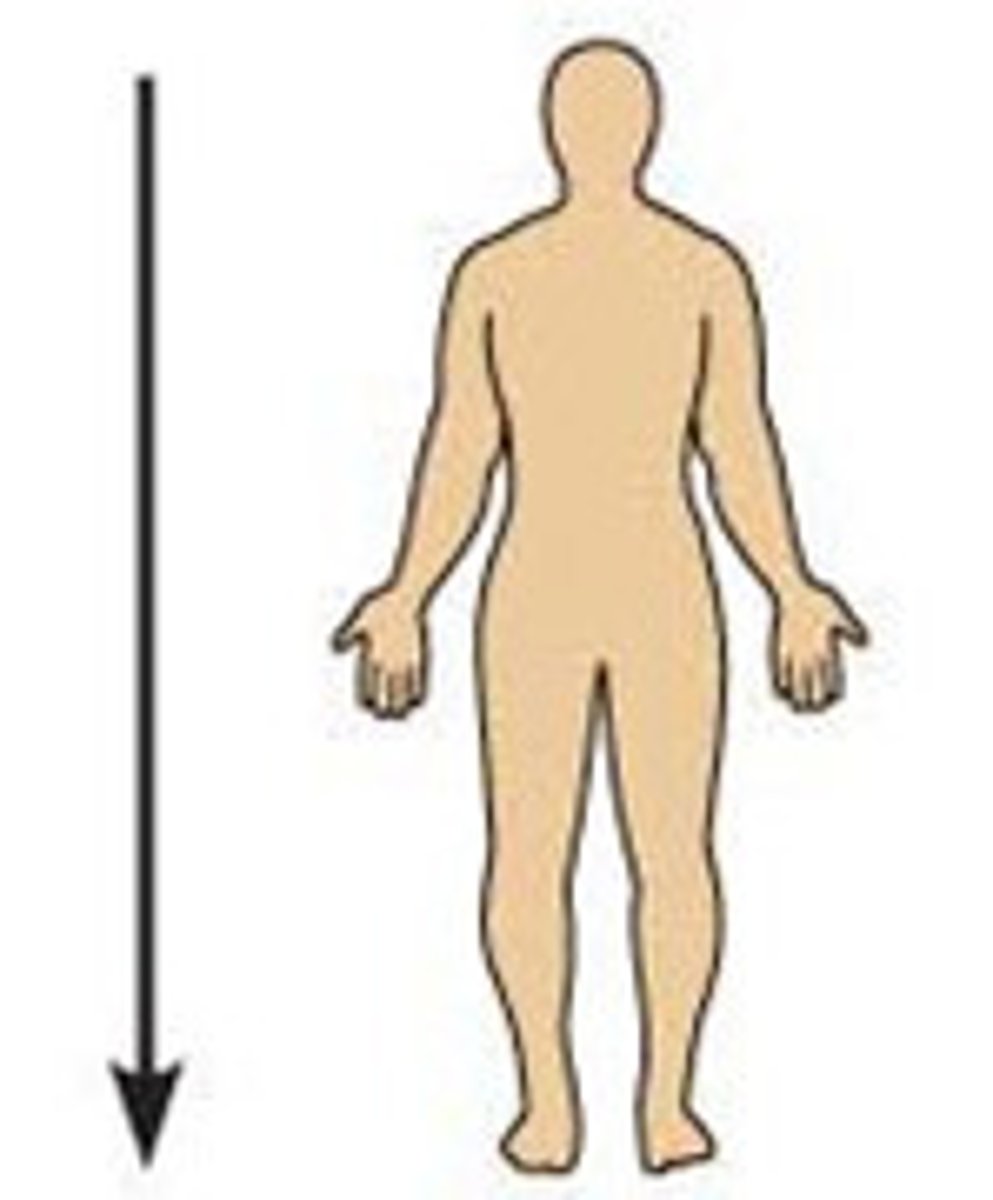
Inferior
Lower on the body, farther from the head (ex. the stomach is ________ to the lungs)
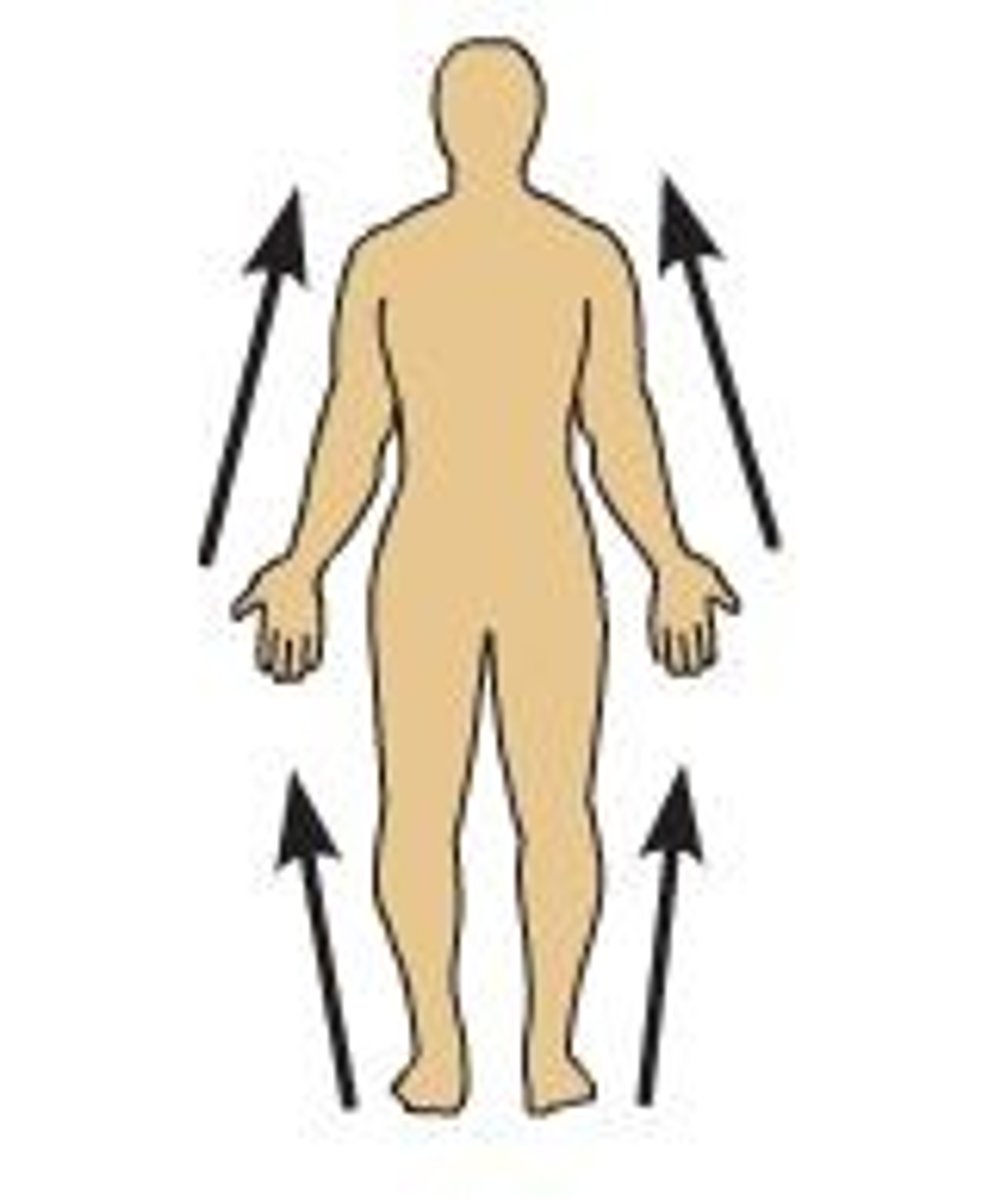
Proximal
Closer to the attachment of a limb to the trunk (ex. the bicep is ________ to the forearm)
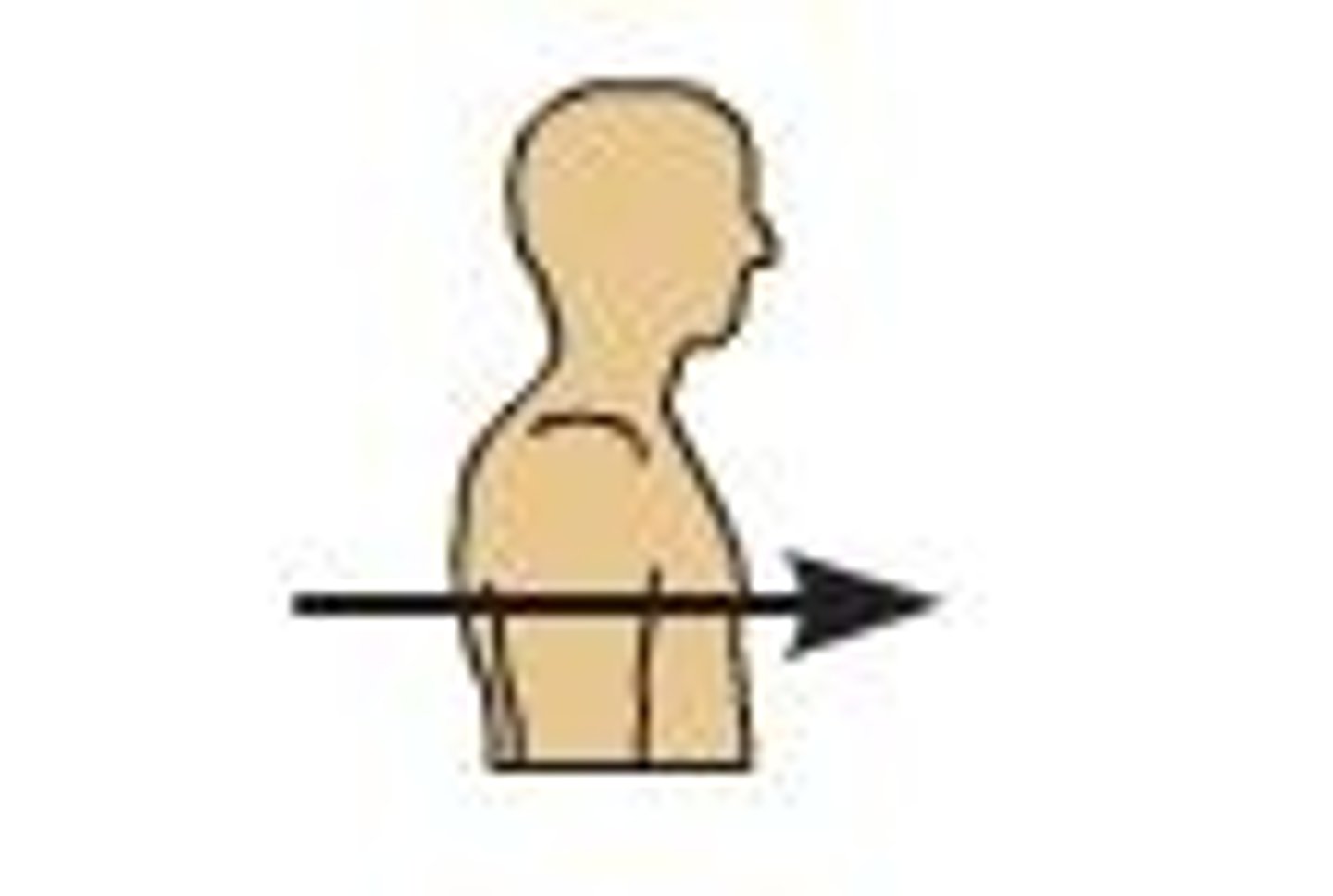
Anterior (ventral)
Nearer to or at the front of the body (ex. the sternum is ________ to the heart)
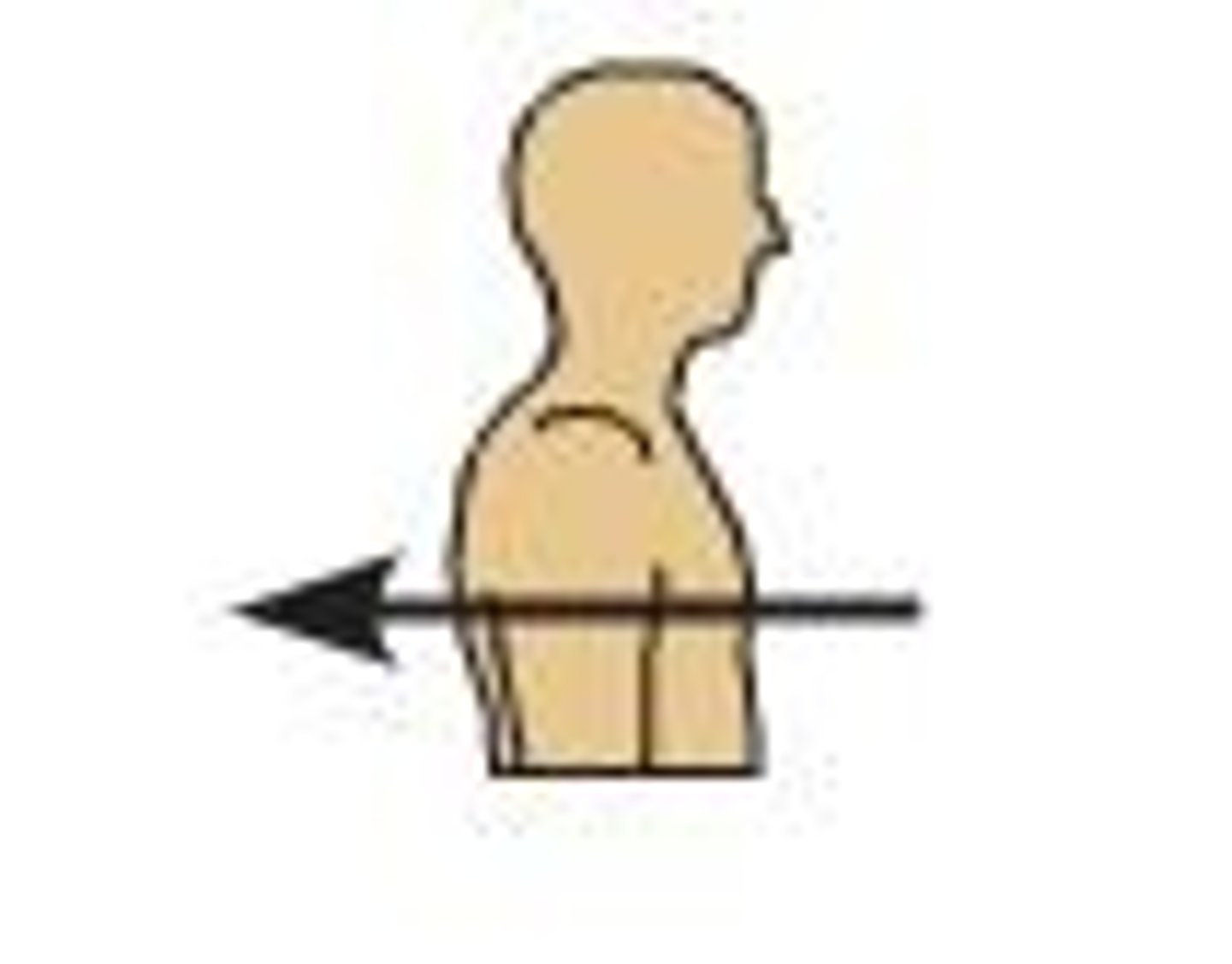
Posterior (dorsal)
Nearer to or at the back of the body (ex. the esophagus is ________ to the trachea)
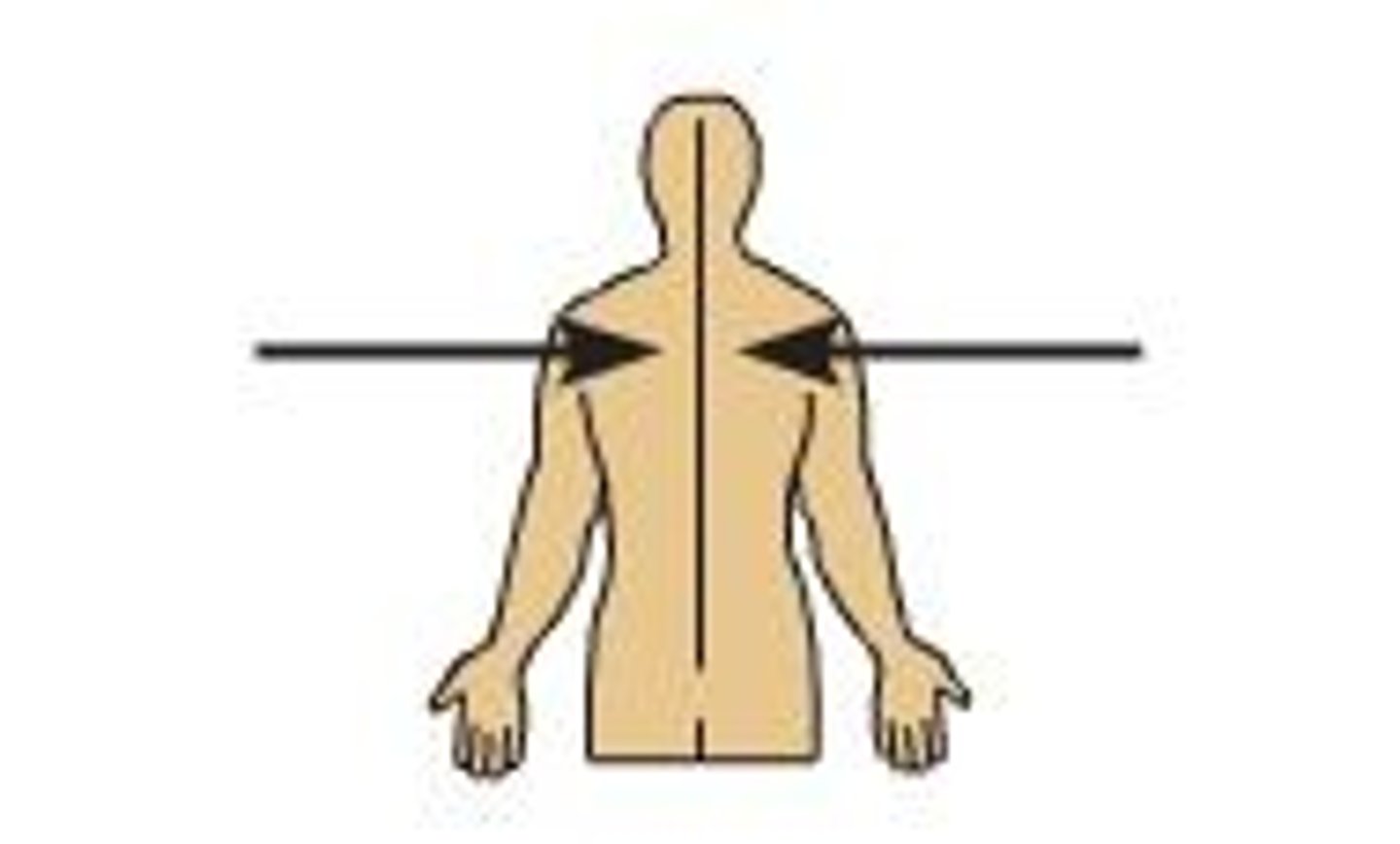
Medial
Nearer to the midline (ex. the heart is _________ to the lungs)
Lateral
Farther from the midline (ex. the lungs are ________ to the heart)
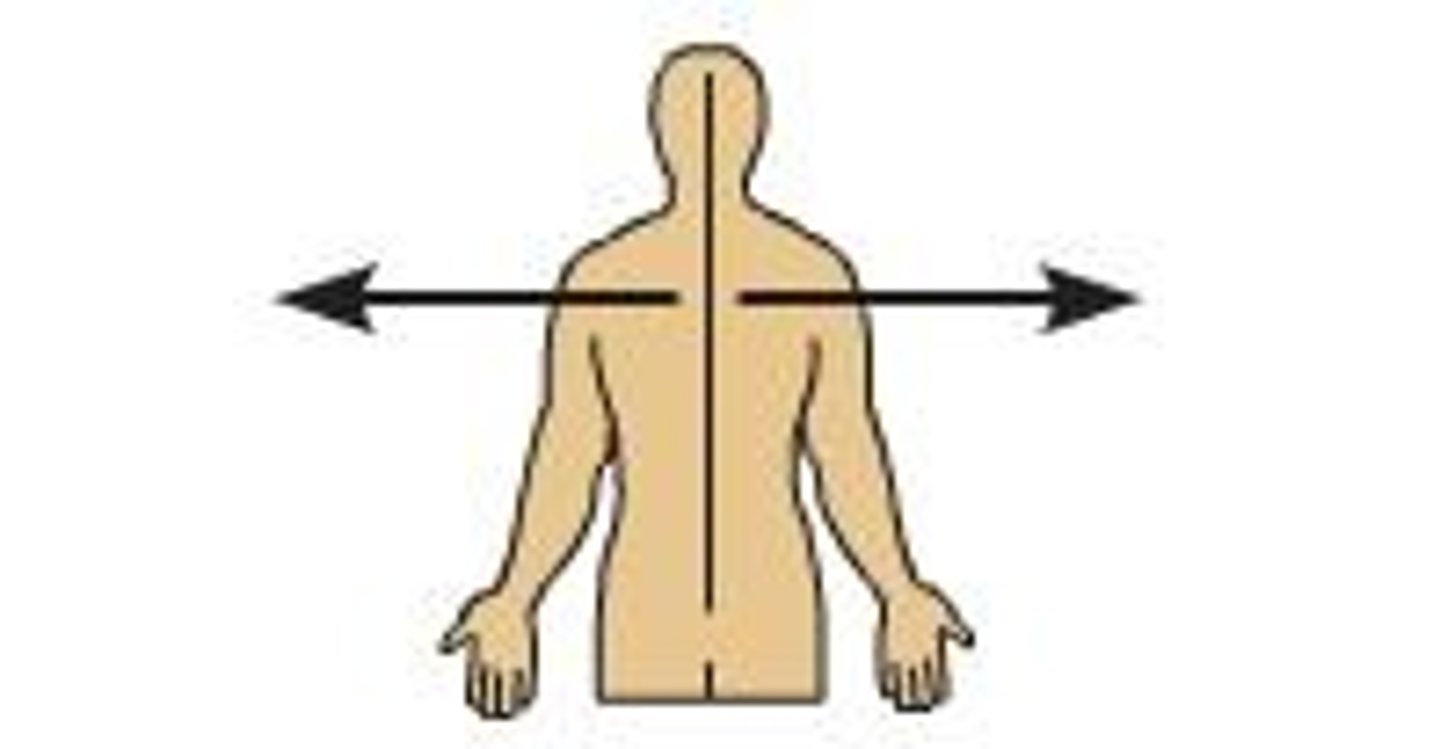
Intermediate
Between two structures (ex. the heart is __________ to the left and right lungs)
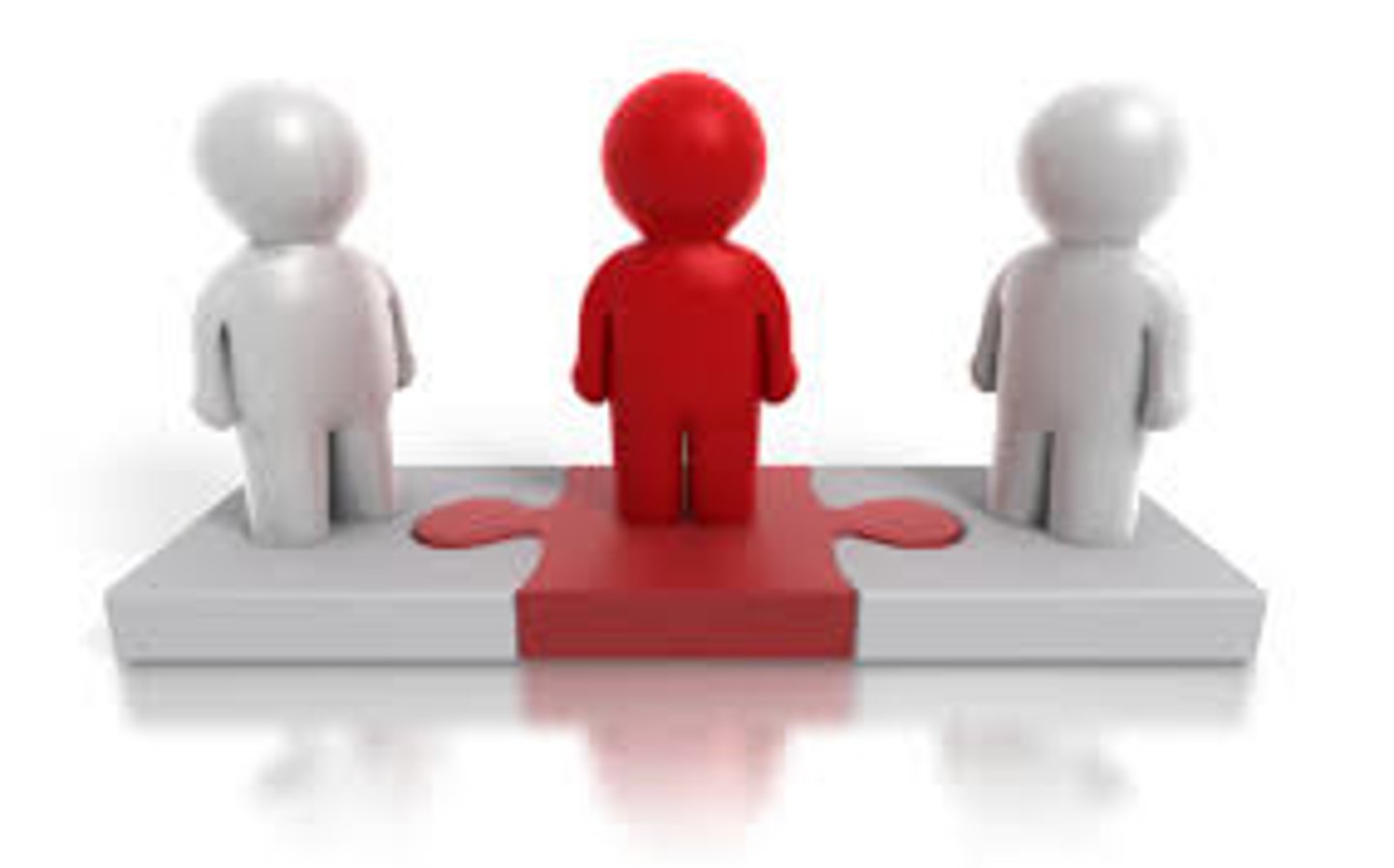

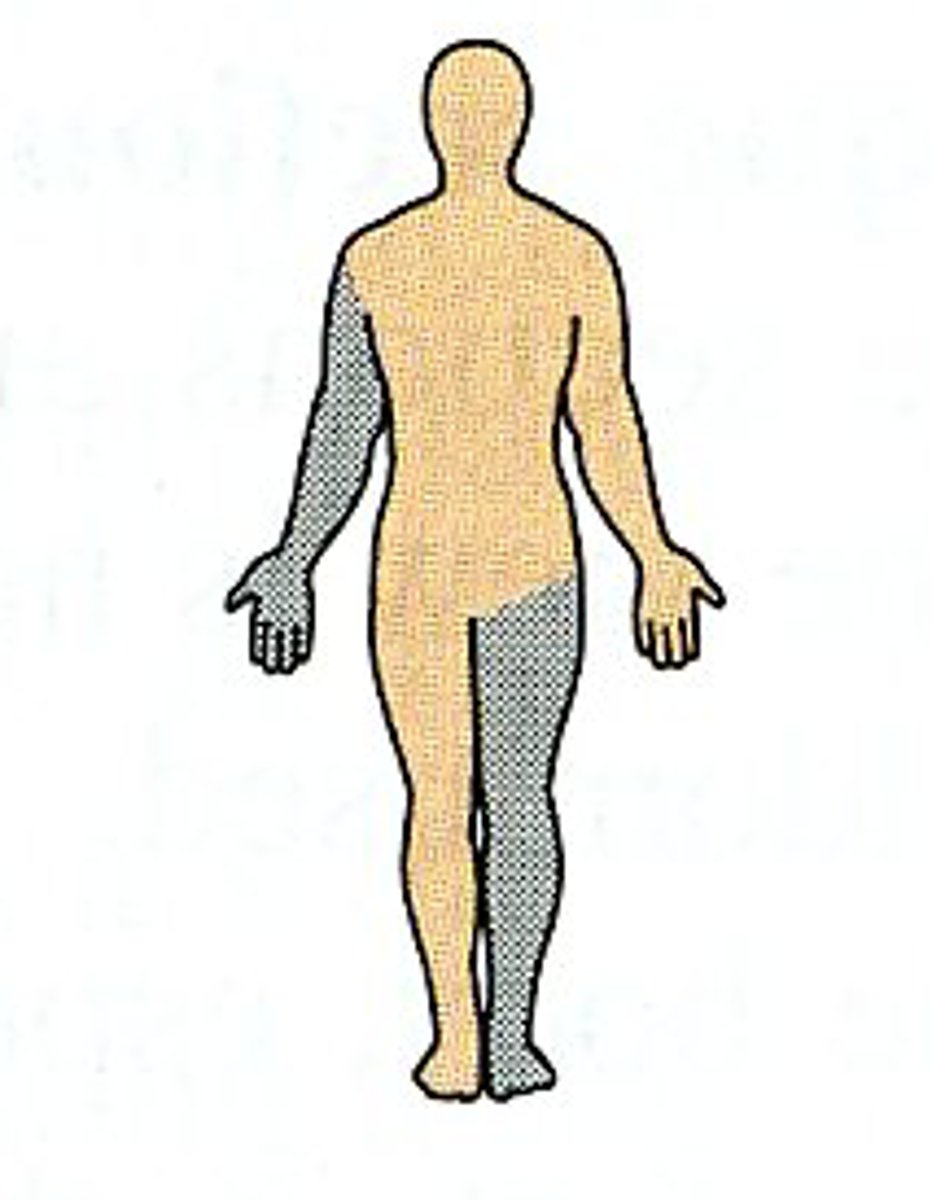
Ipsilateral
On the same side of the body as another structure (ex. the right arm and right leg are __________)
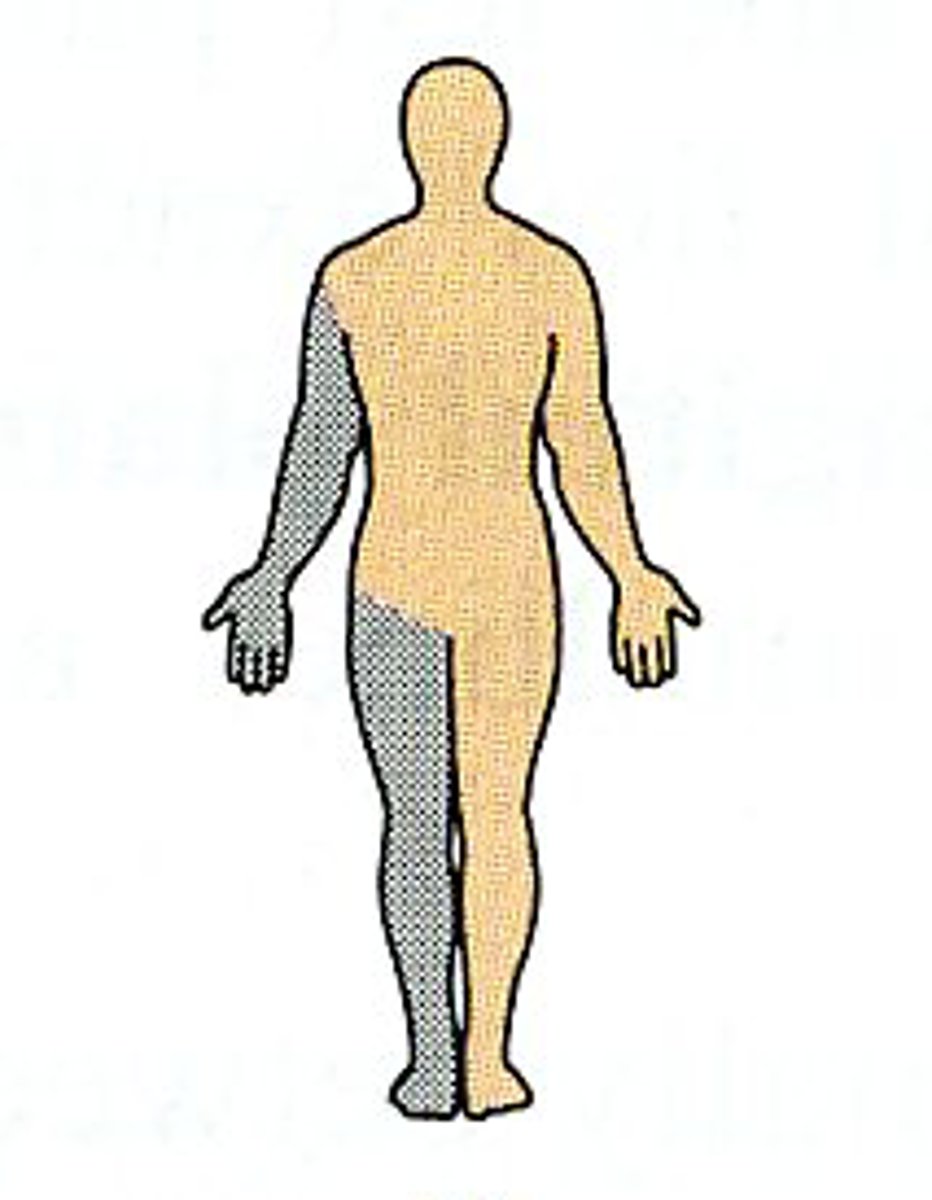
Contralateral
On the opposite side of the body from another structure (ex. the right arm and left leg are ___________)
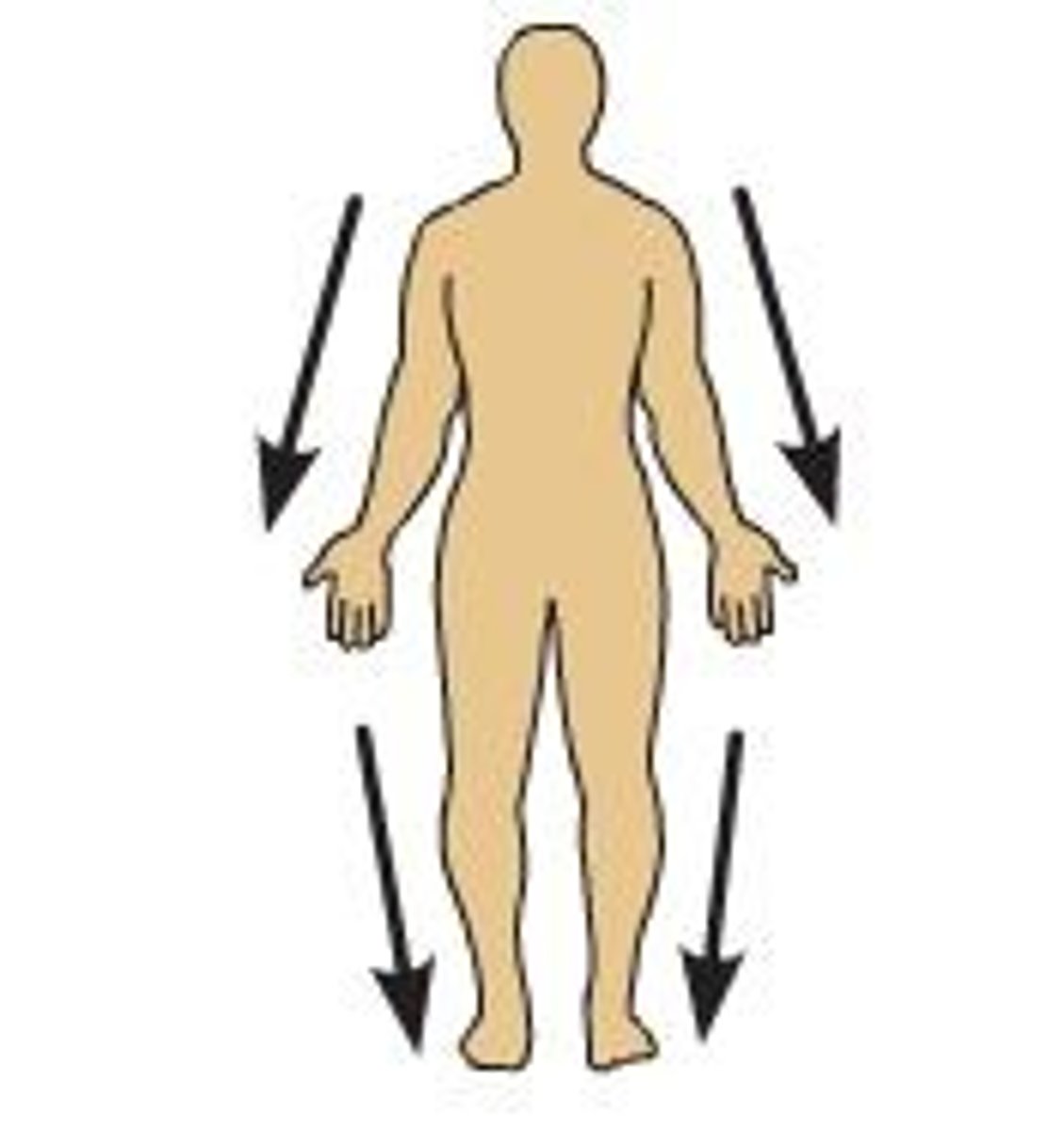
Distal
Farther from the attachment of a limb to the trunk (ex. the fingers are _________ to the wrist)
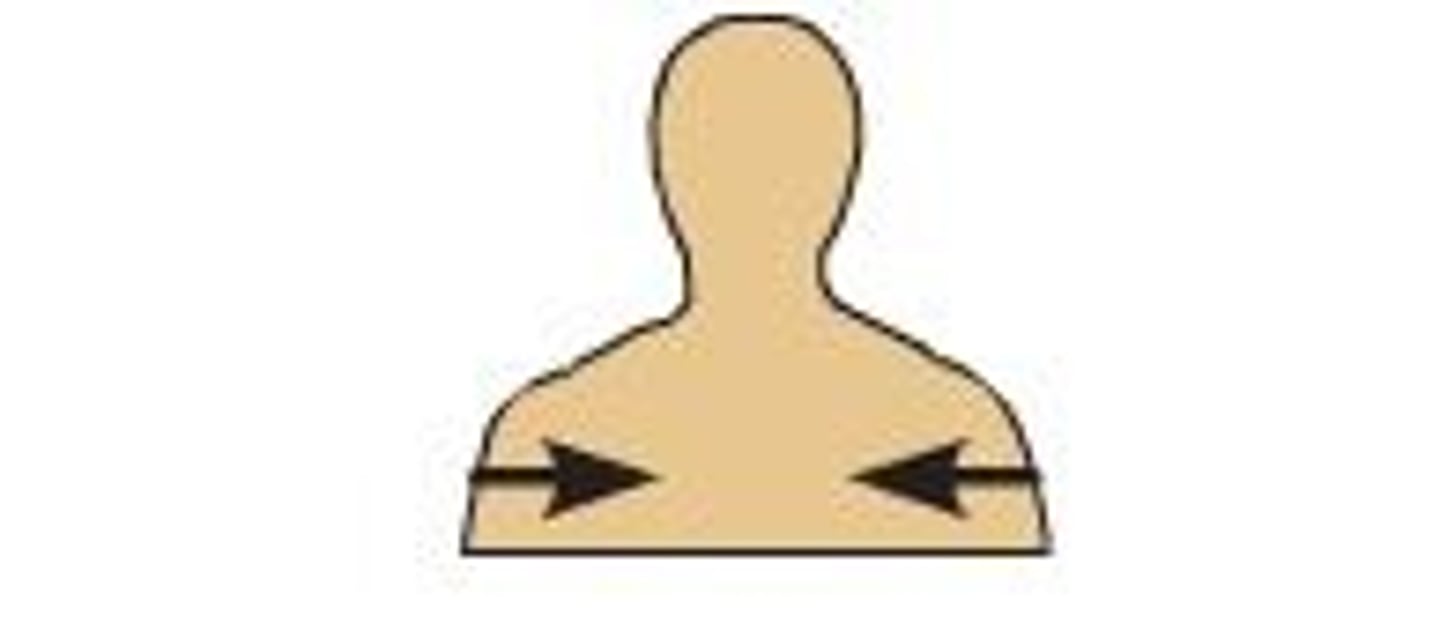
Superficial
Toward or on the surface of the body (ex. the ribs are _________ to the lungs)
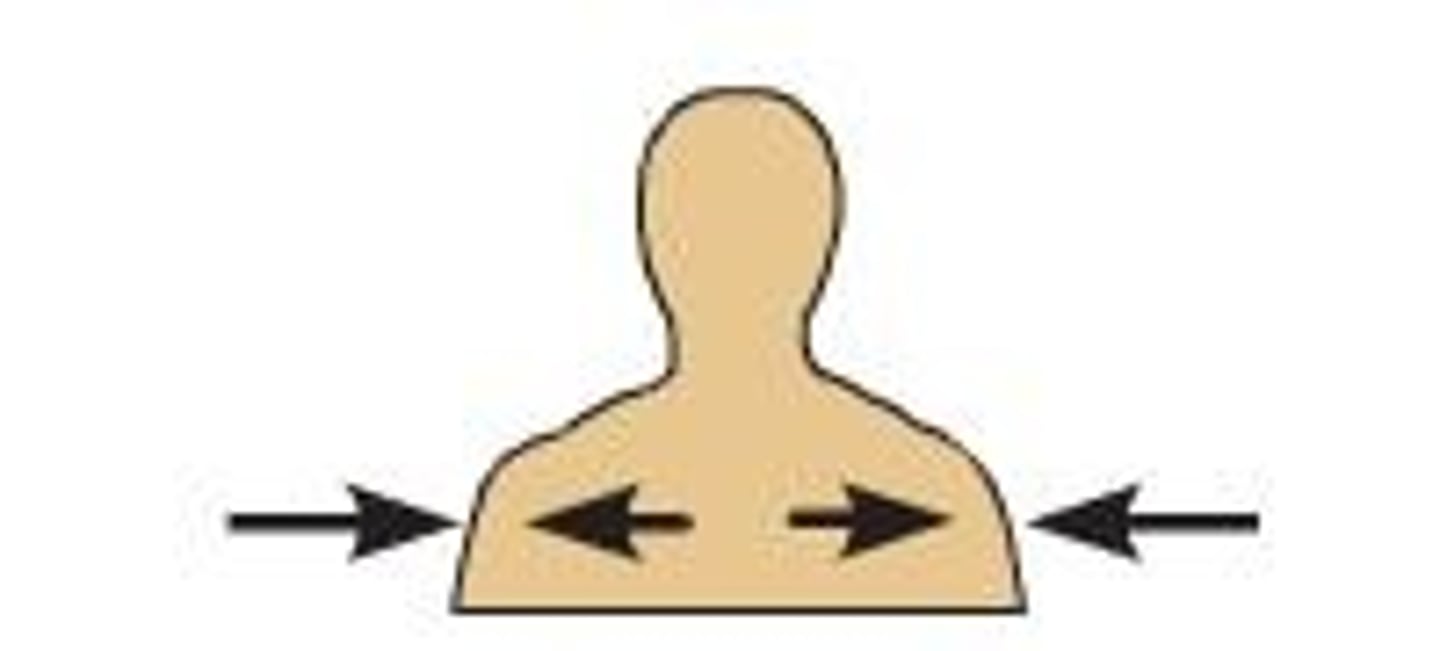
Deep
Away from the surface of the body (ex. the heart is ________ to the ribs)
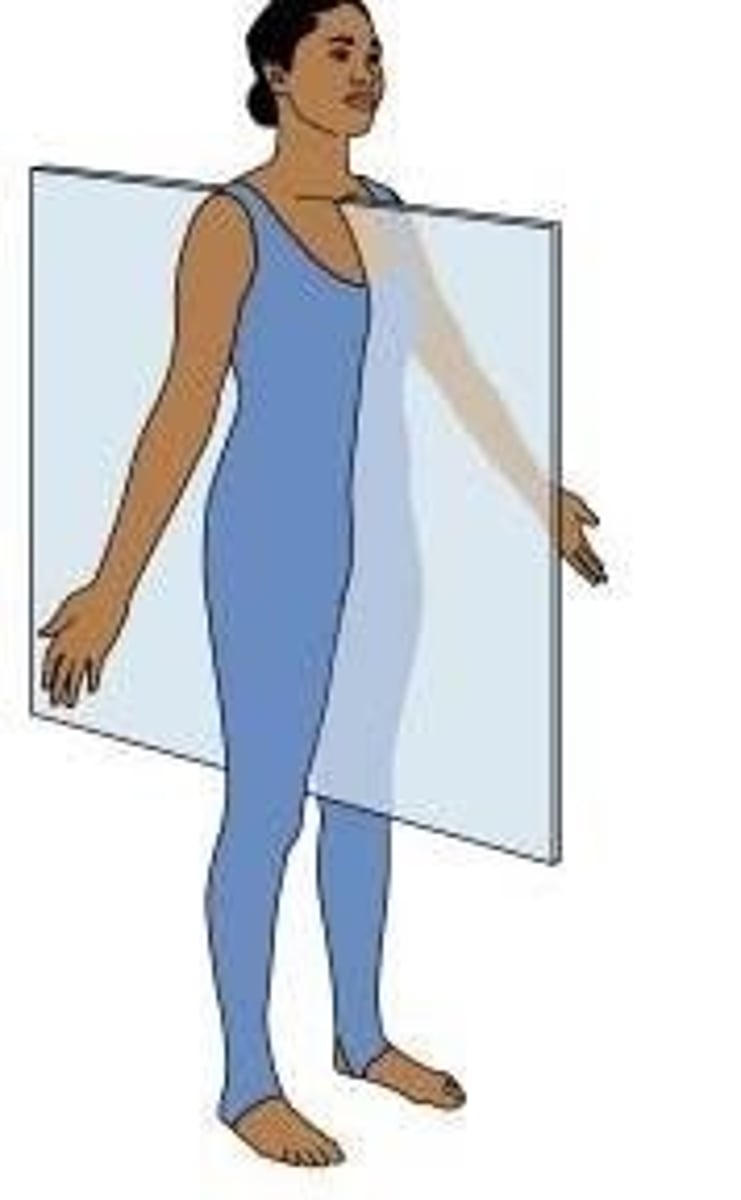
Planes
Imaginary flat surfaces that are used to divide the body
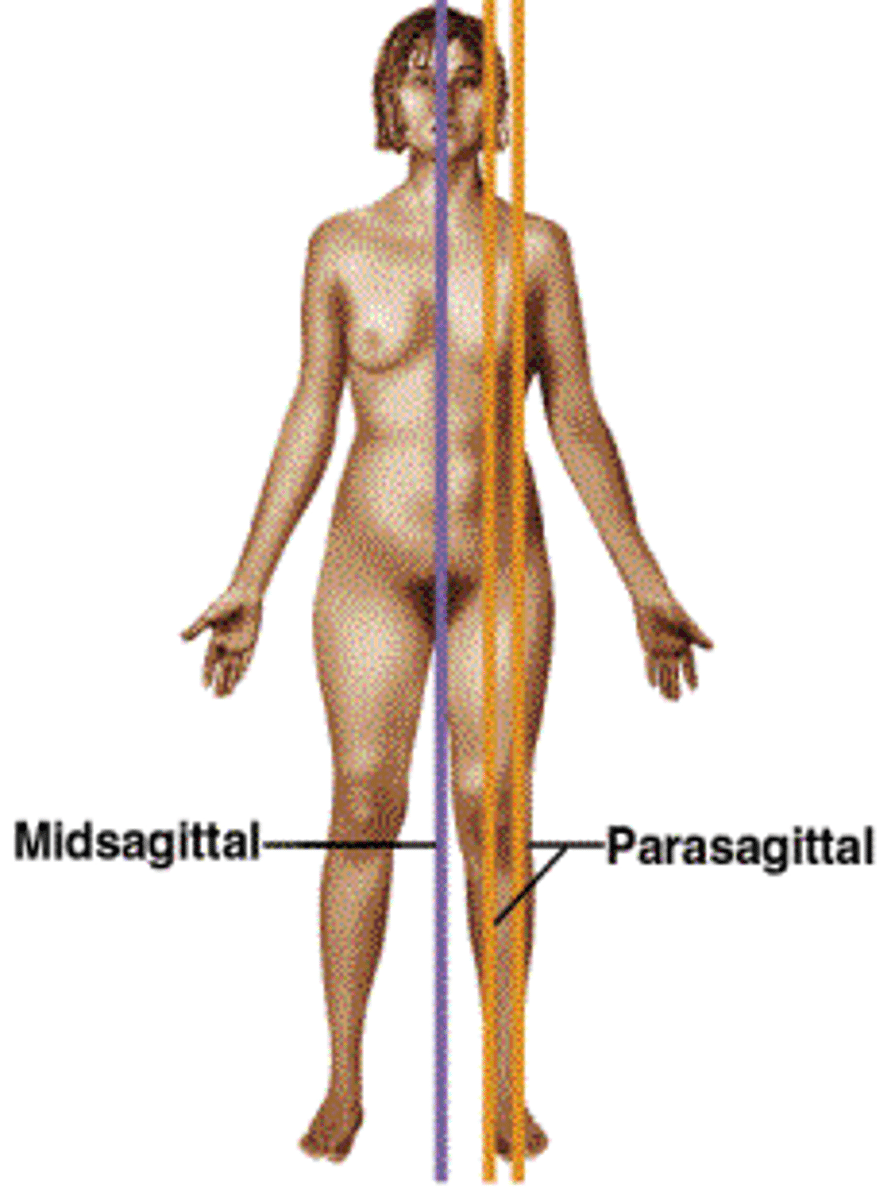
Midsagittal (median) plane
Divides the body into equal right and left sides (passes through the midline)
Parasagittal (paramedian) plane
Divides the body into unequal right and left sides (does not pass through the midline)
Frontal (coronal) plane
Divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
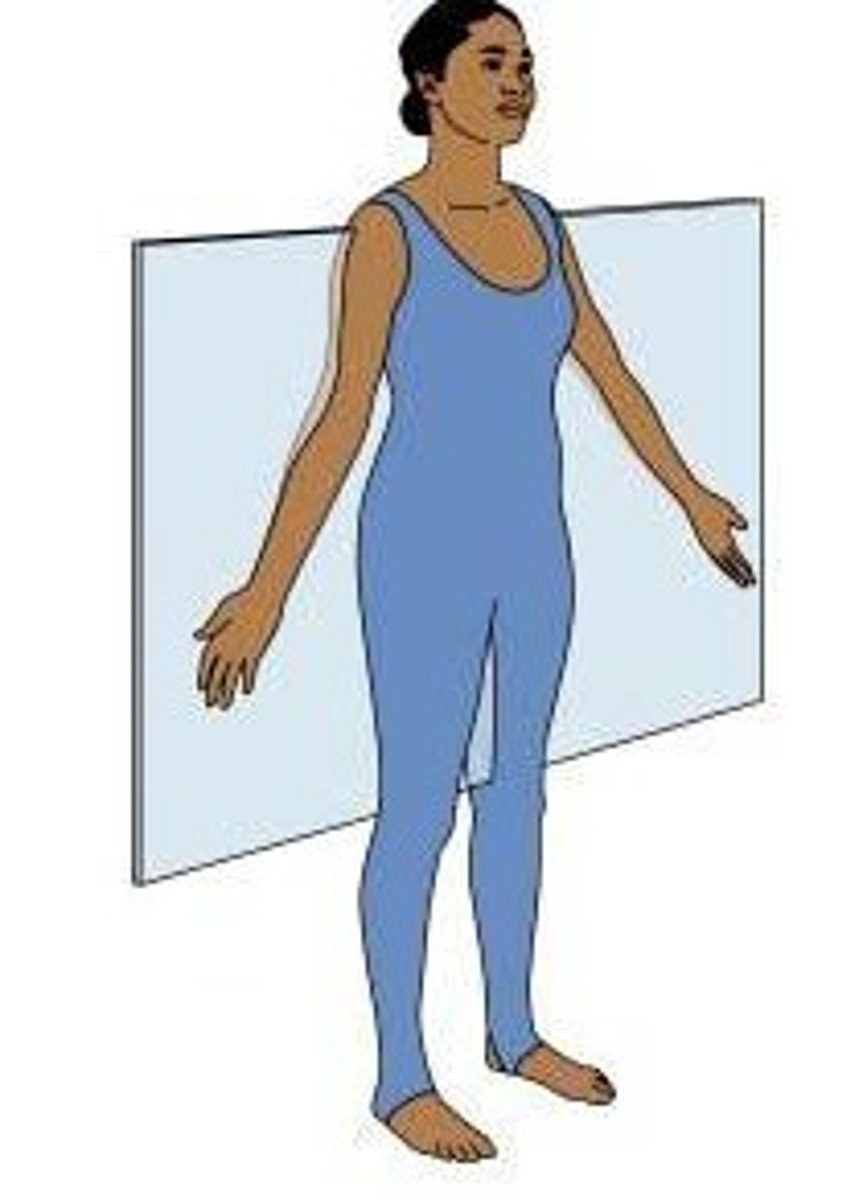
Transverse (axial) plane
Divides the body into top and bottom parts
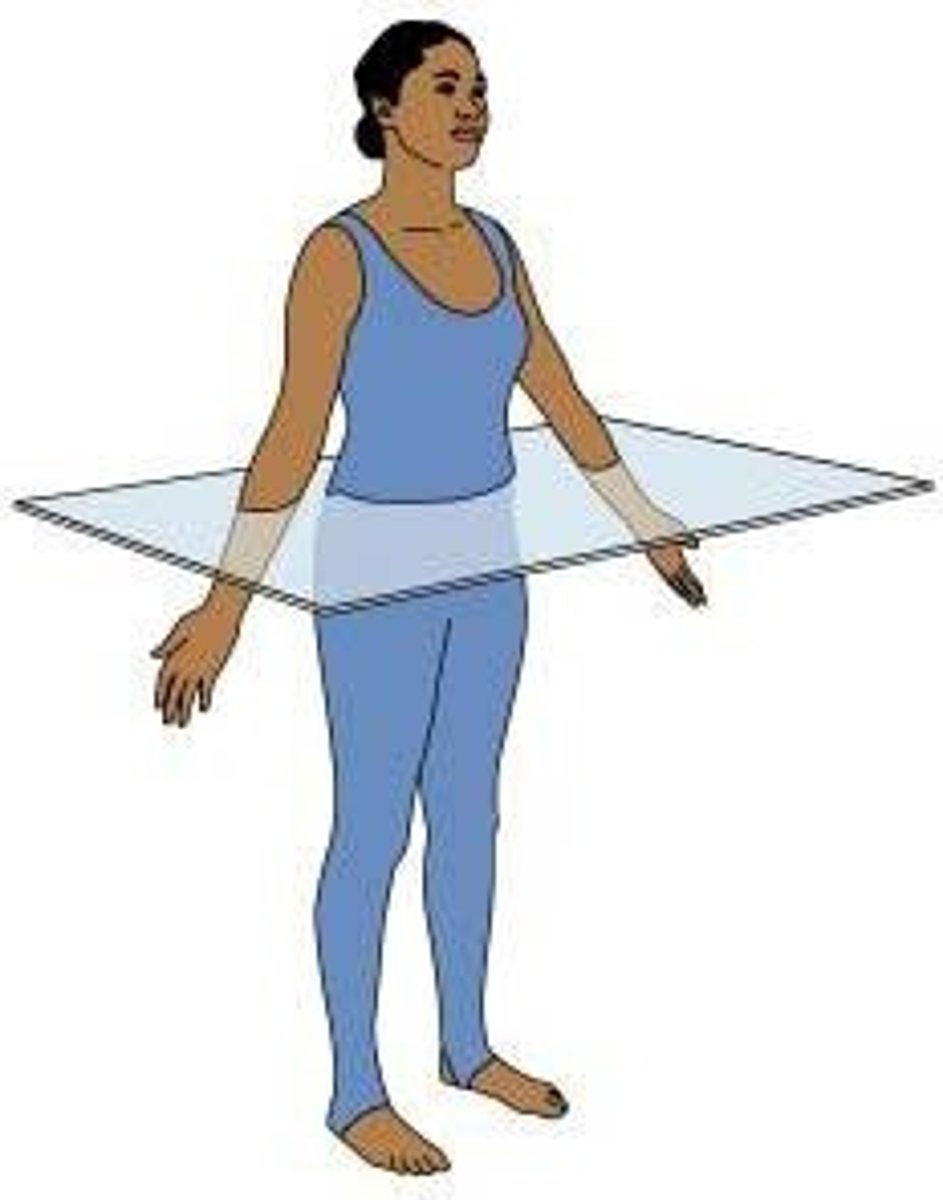
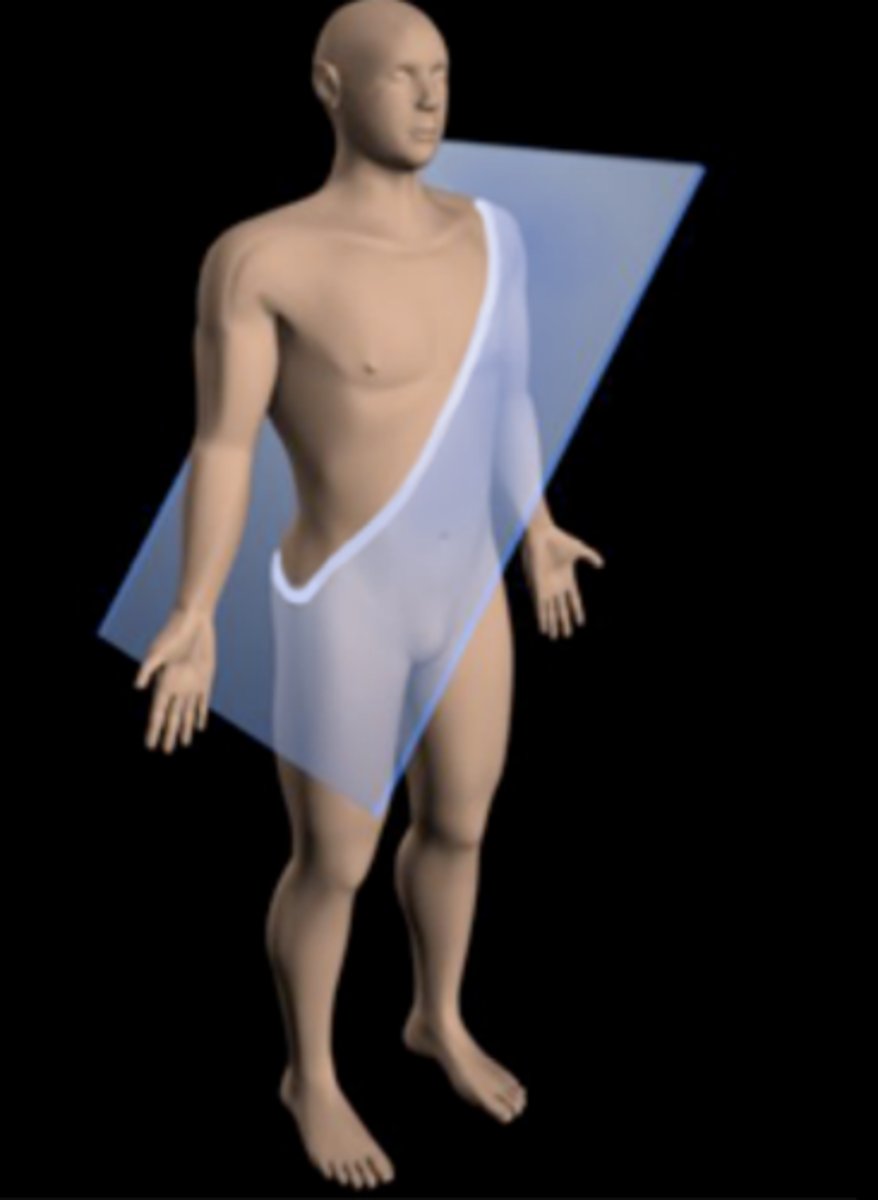
Oblique plane
Passes through the body at an angle

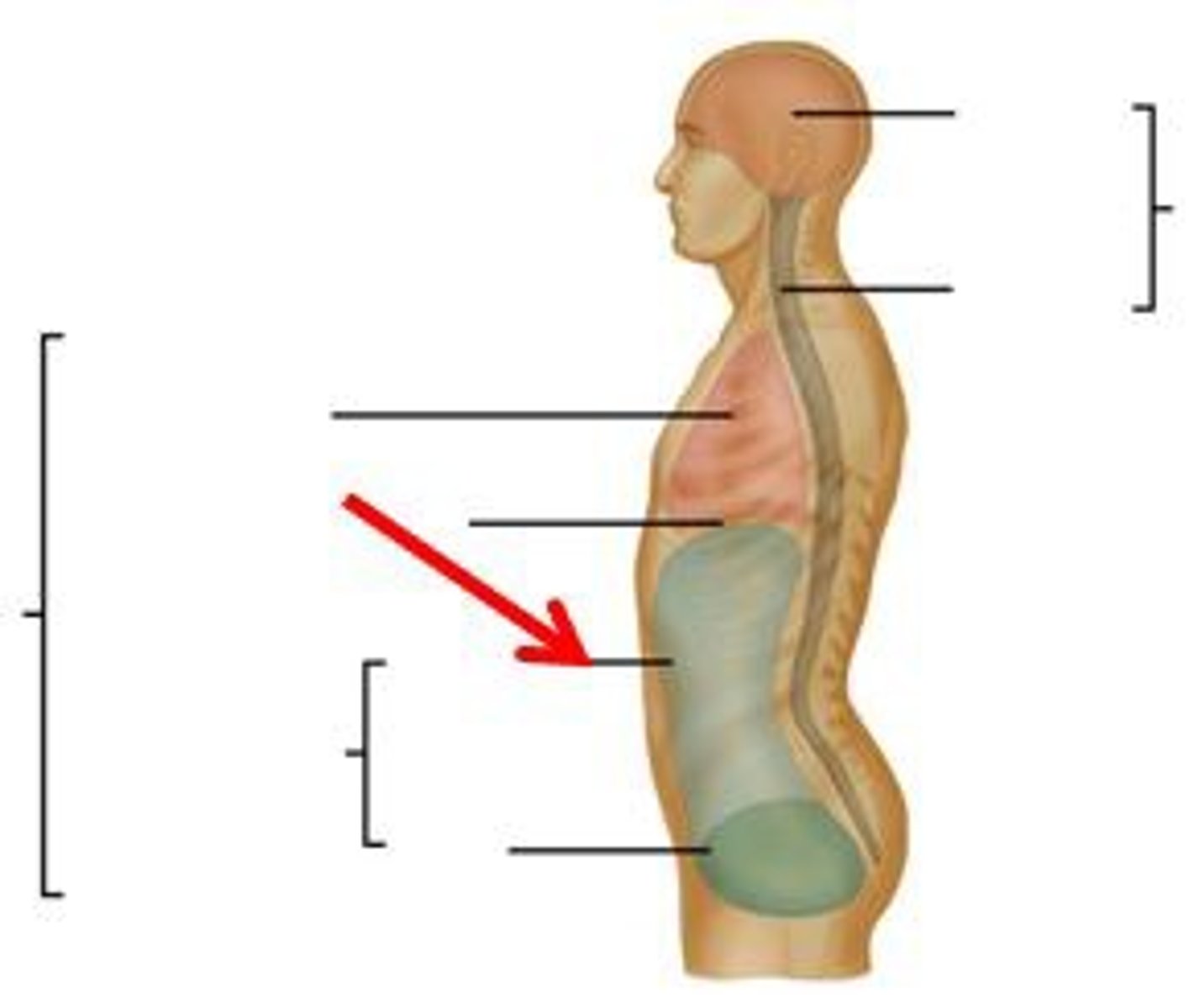
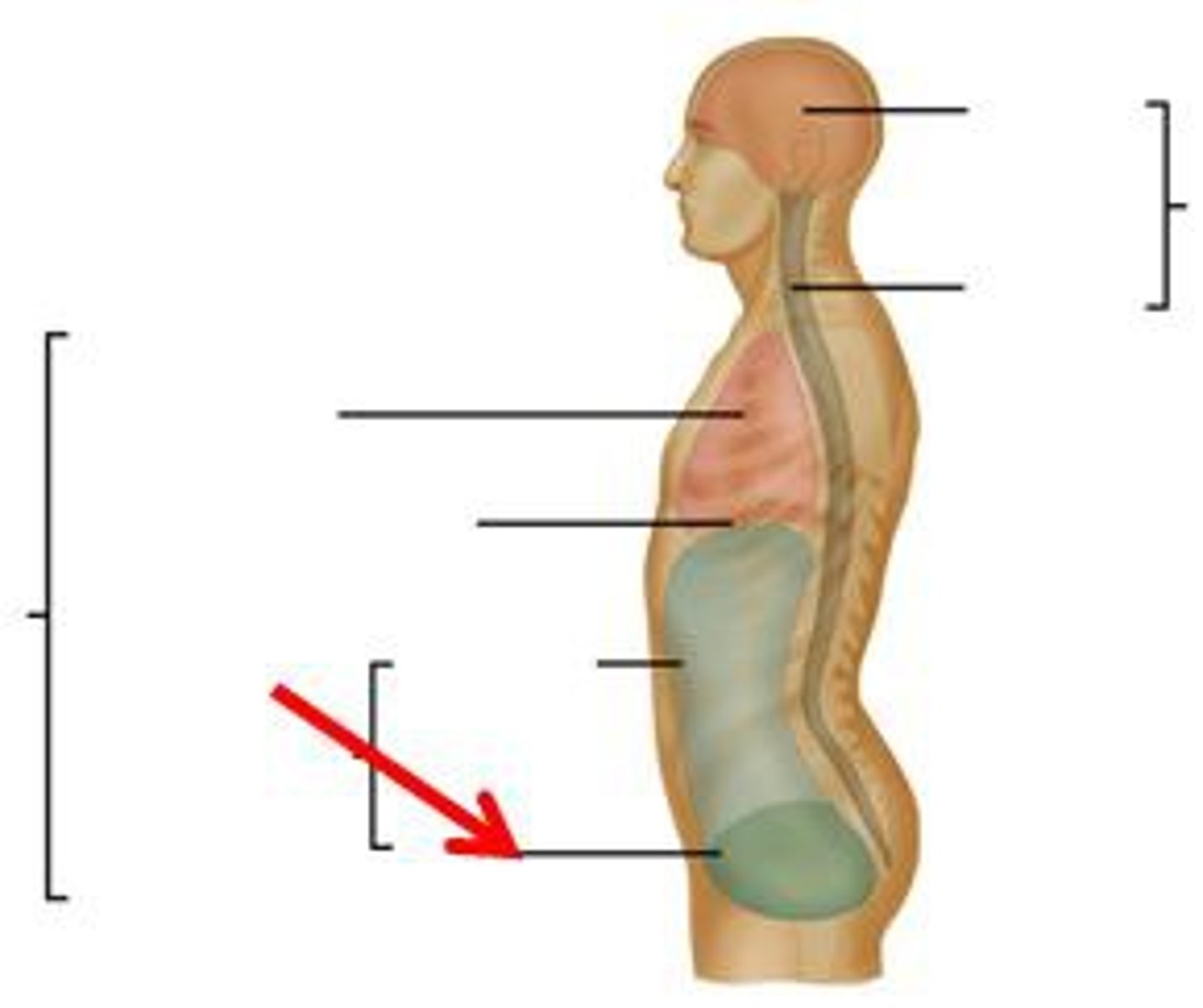
Body cavities
Spaces within the body the help protect, separate, and support internal organs
How are homeostatic imbalances related to disorders?
They can occur due to disruptions from the external or internal environments
Homeostasis
The condition of equilibrium
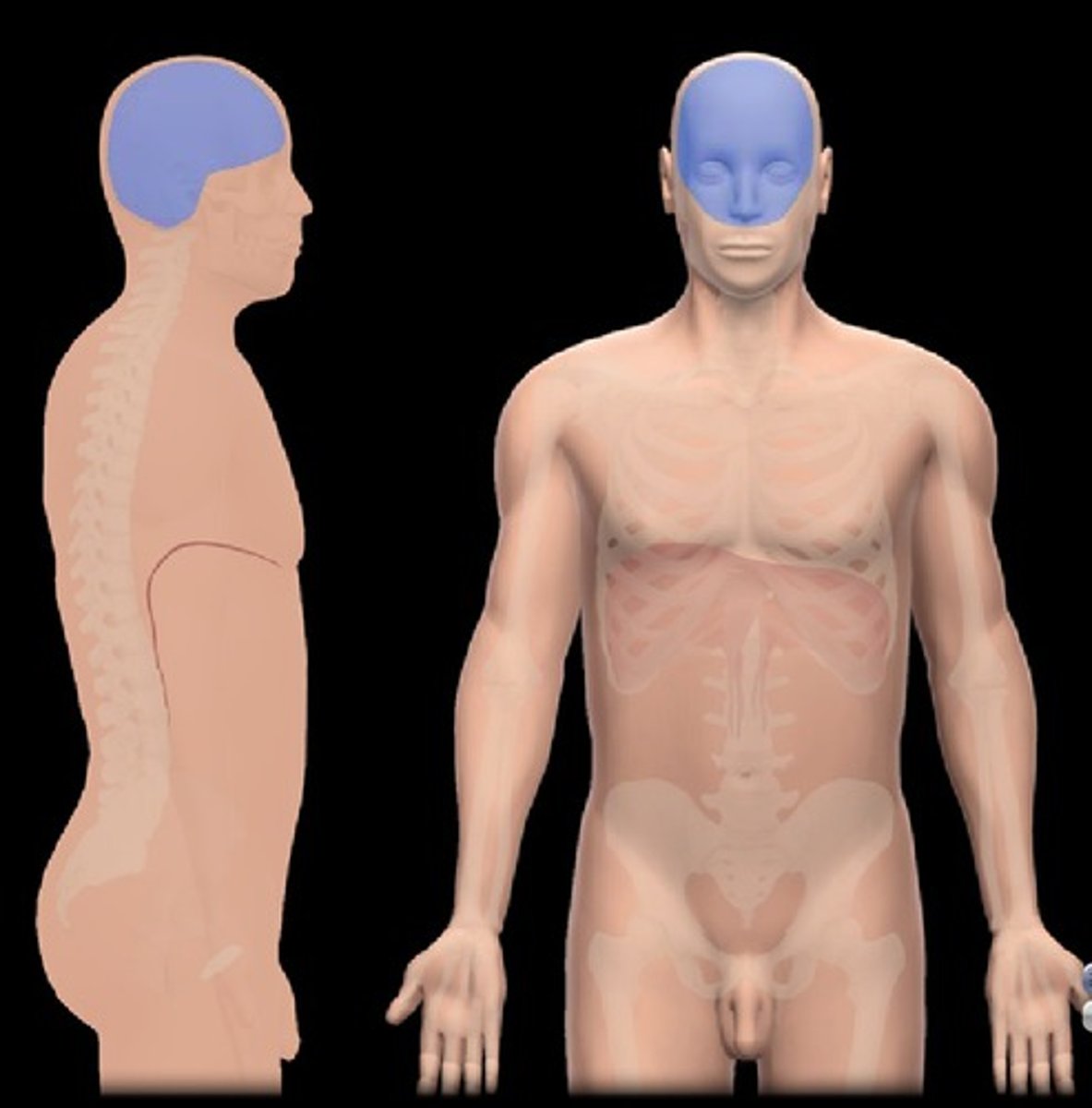
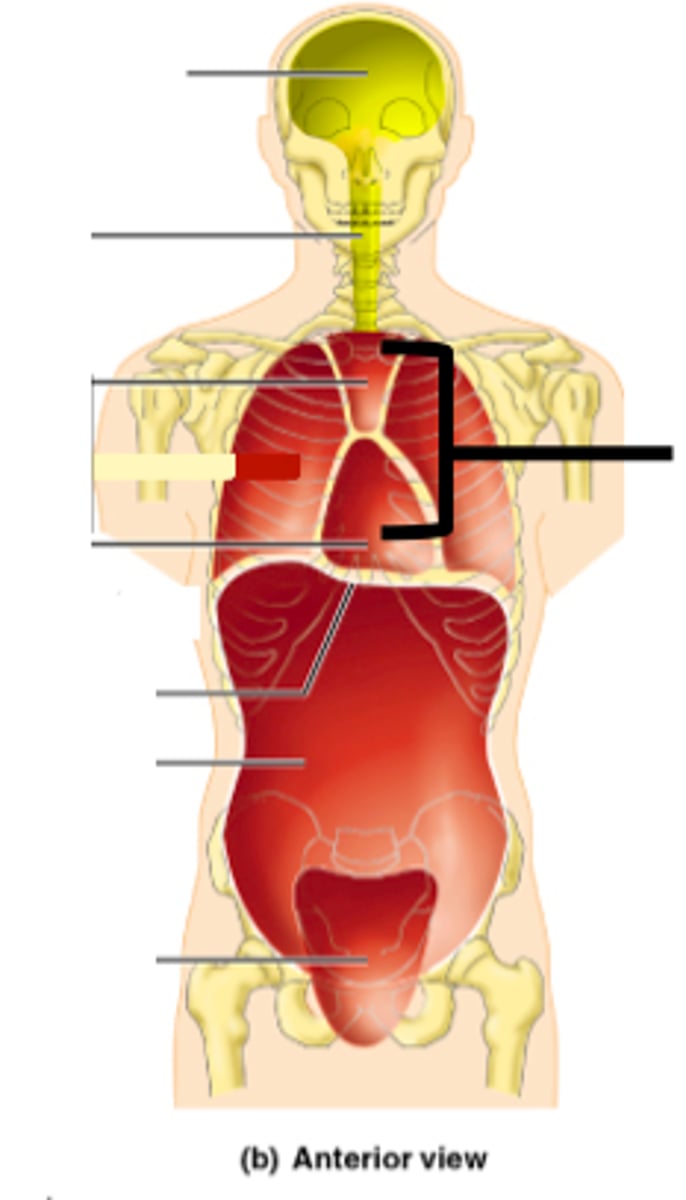
Cranial cavity
Formed by cranial bones and protects the brain
Vertebral canal
Formed by vertebral column and protects spinal cord and the beginnings of spinal nerves
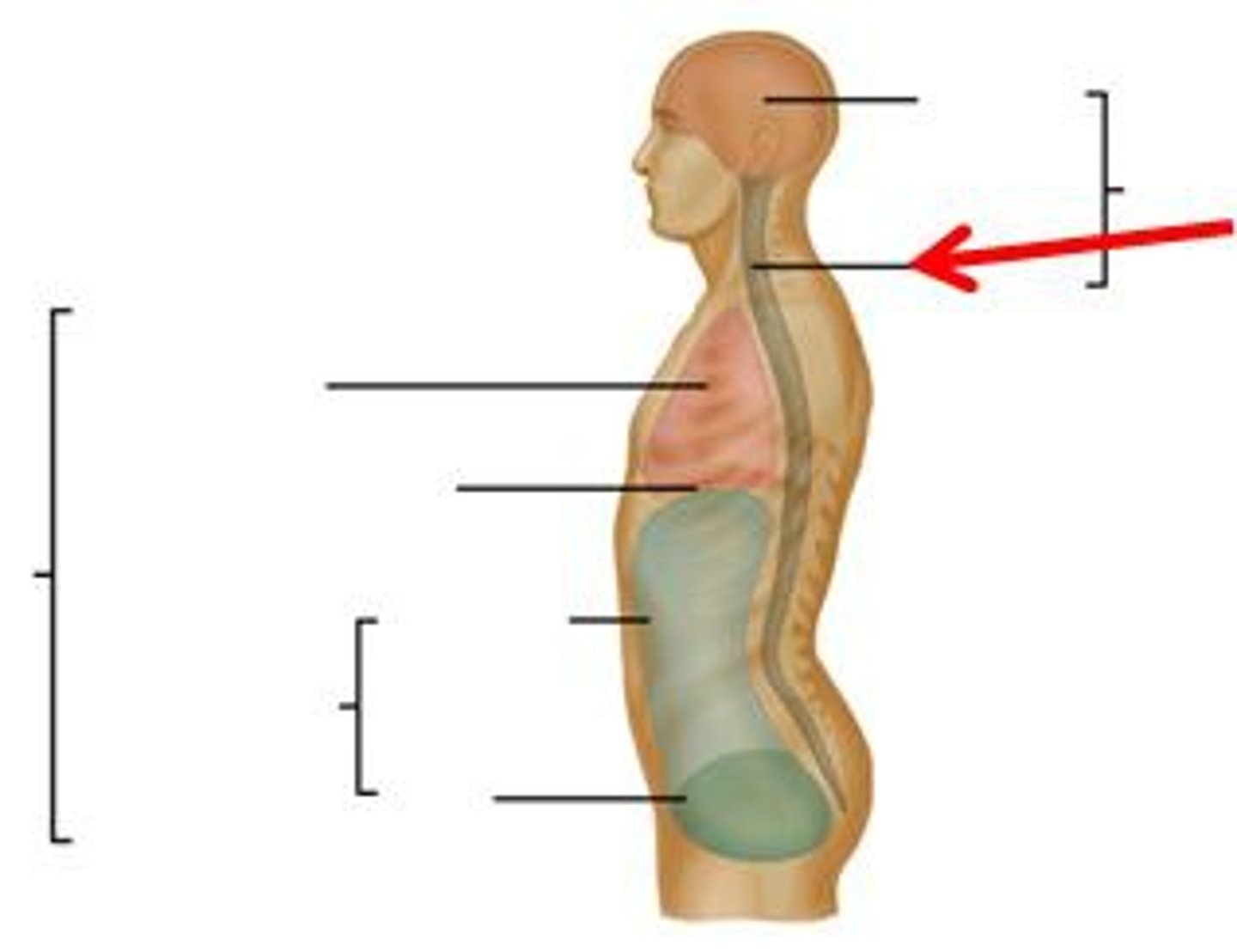
Thoracic cavity
Chest cavity that protects the heart and lungs and contains pleural and pericardial cavities and the mediastinum
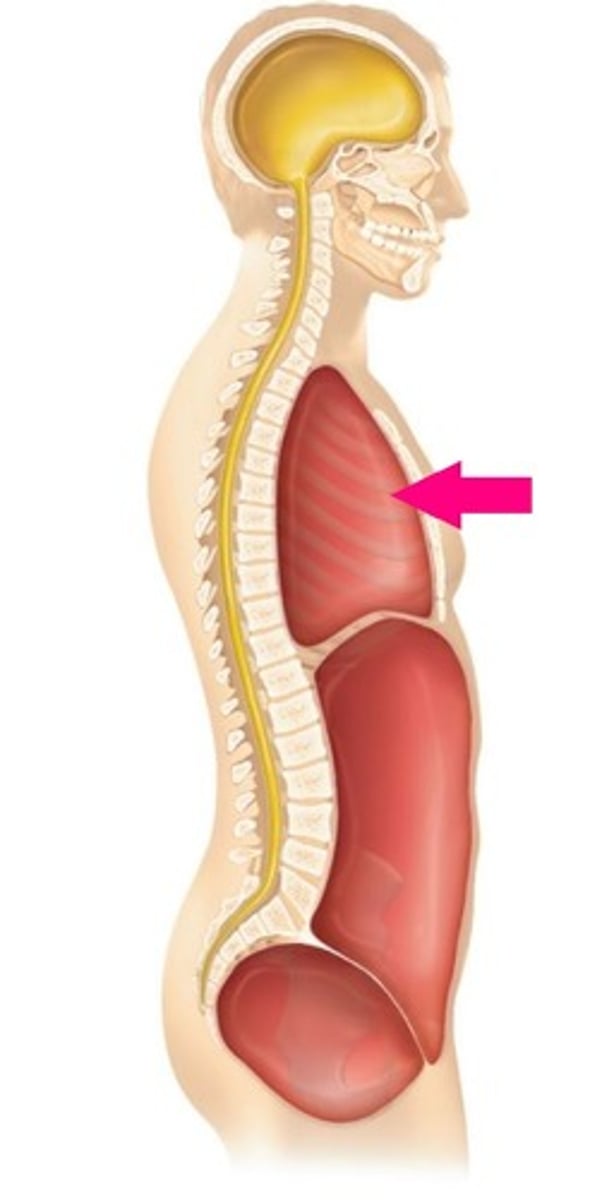
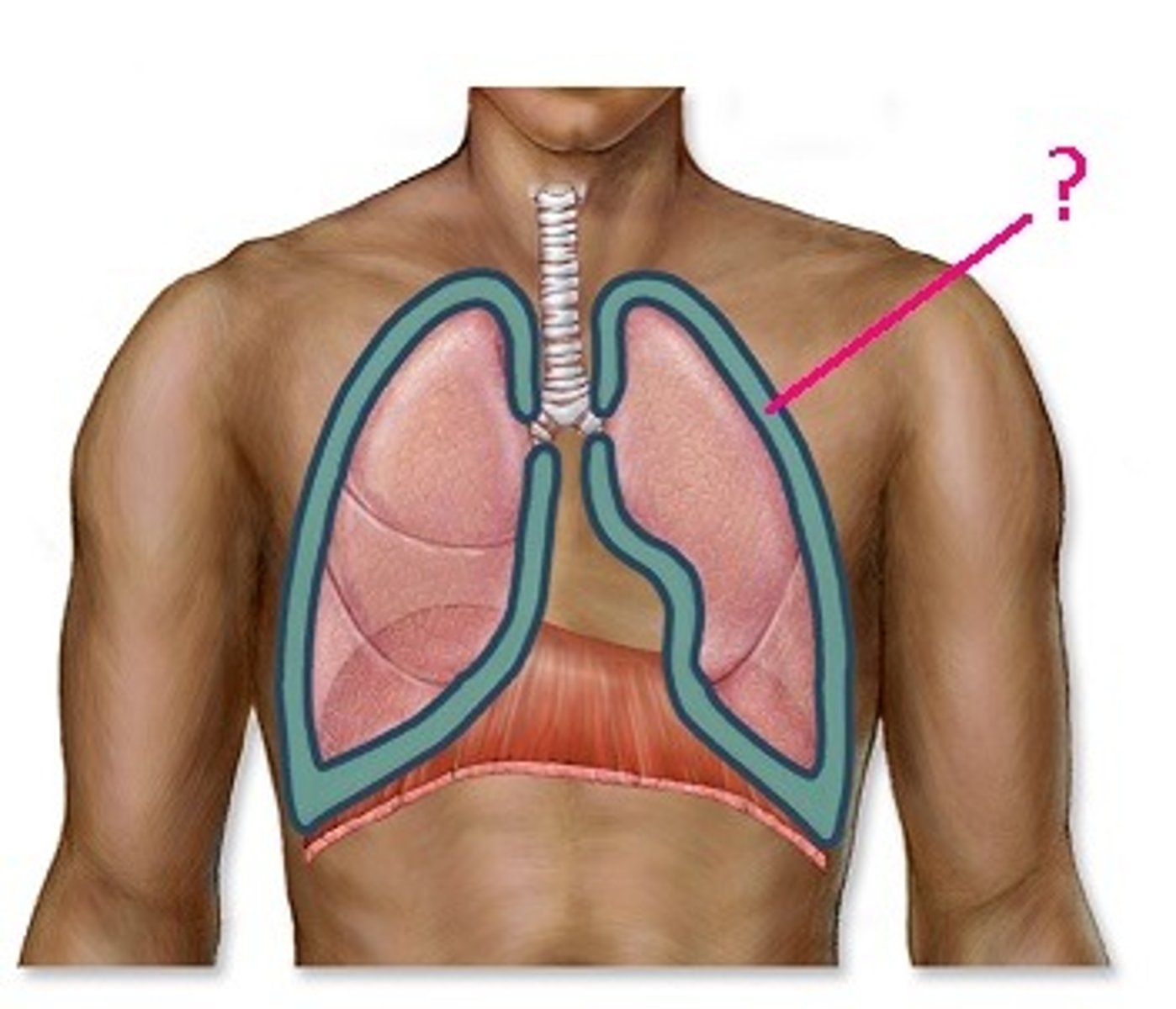
Pleural cavity
A space between the layers of the pleura that surrounds a lung
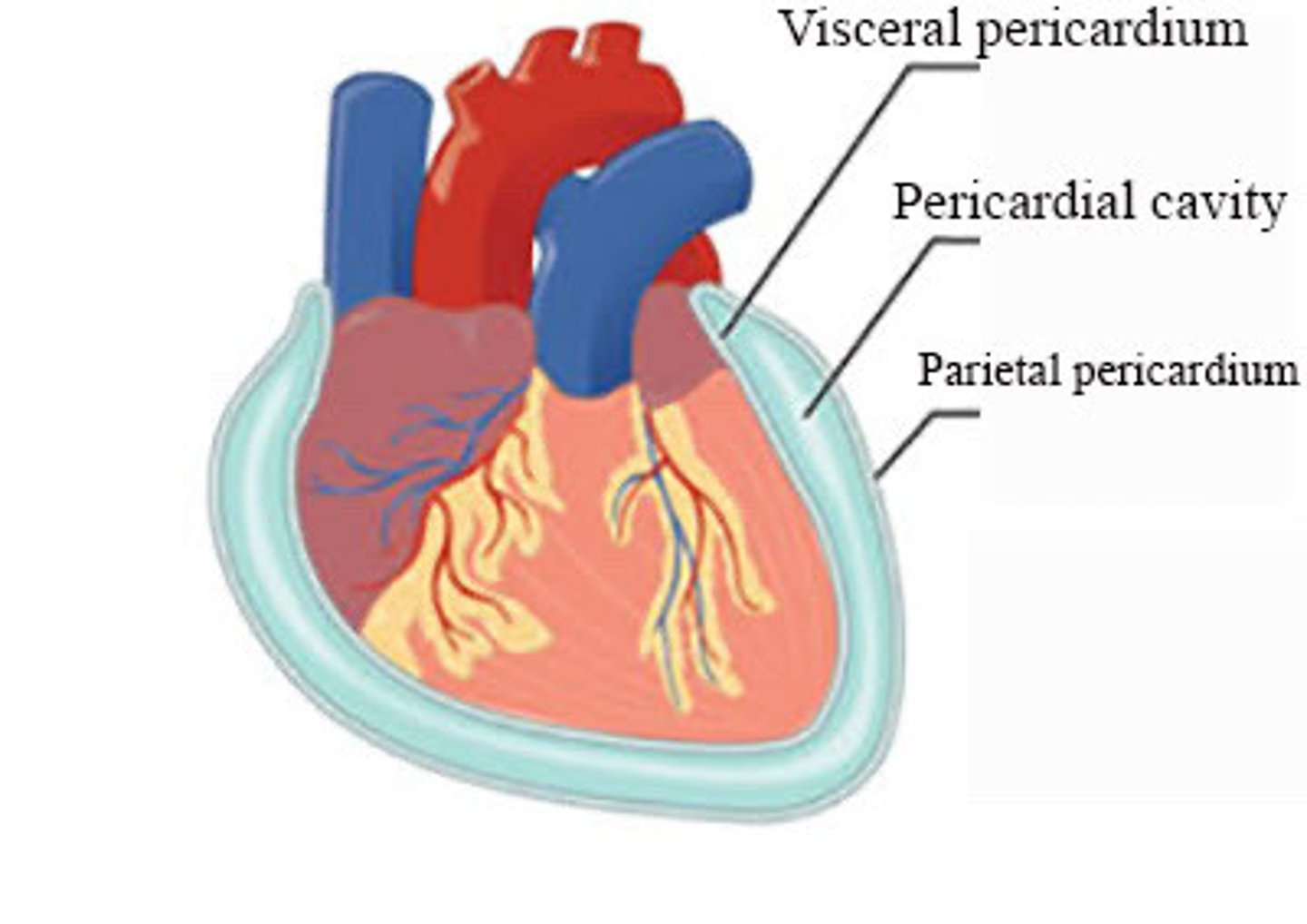
Pericardial cavity
A space between the layers of the pericardium that surrounds the heart (ex. visceral pericardium)
Mediastinum
Central compartment of the thoracic cavity that encloses the heart, esophagus, trachea, and other organs
Abdominopelvic cavity
Contains both the abdominal and pelvic cavities
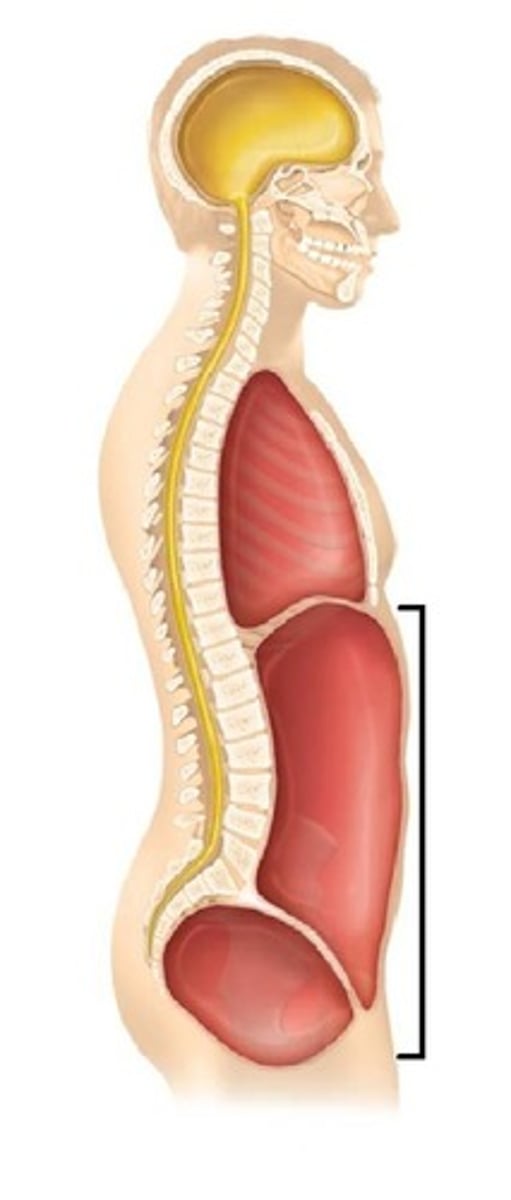
Abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs with the peritoneum as its serous membrane
Pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
Peritoneum cavity
Serous membrane of the abdominal cavity
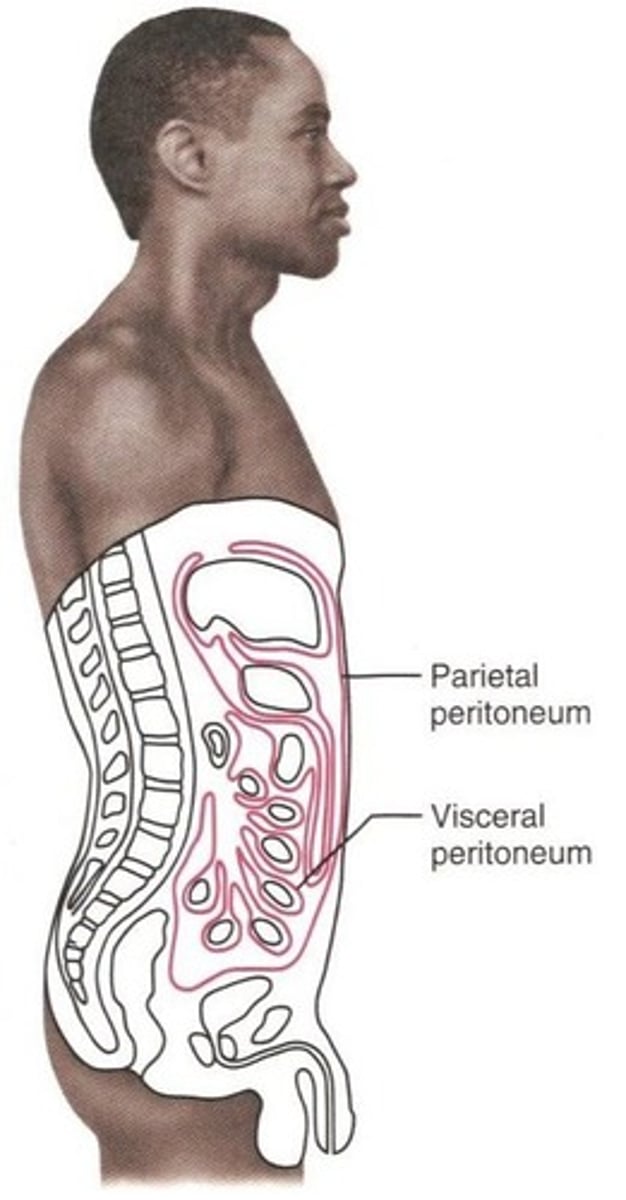
Retroperitoneal
The classification some organs are given because they are not surrounded by the peritoneum, rather, they are posterior to it
Inspection
To visually look at someone
Palpation
To use hands to feel parts of the body
Ausculation
To use a stethoscope to listen to body cavities
Percussion
To use hands or instruments to listen to sounds (ex. tapping the patient)
Symptoms of aging
Wrinkled skin, decreased lung capacity, decreased kidney function, increased susceptibility to infections and cancer, decreased production of some hormones, etc.
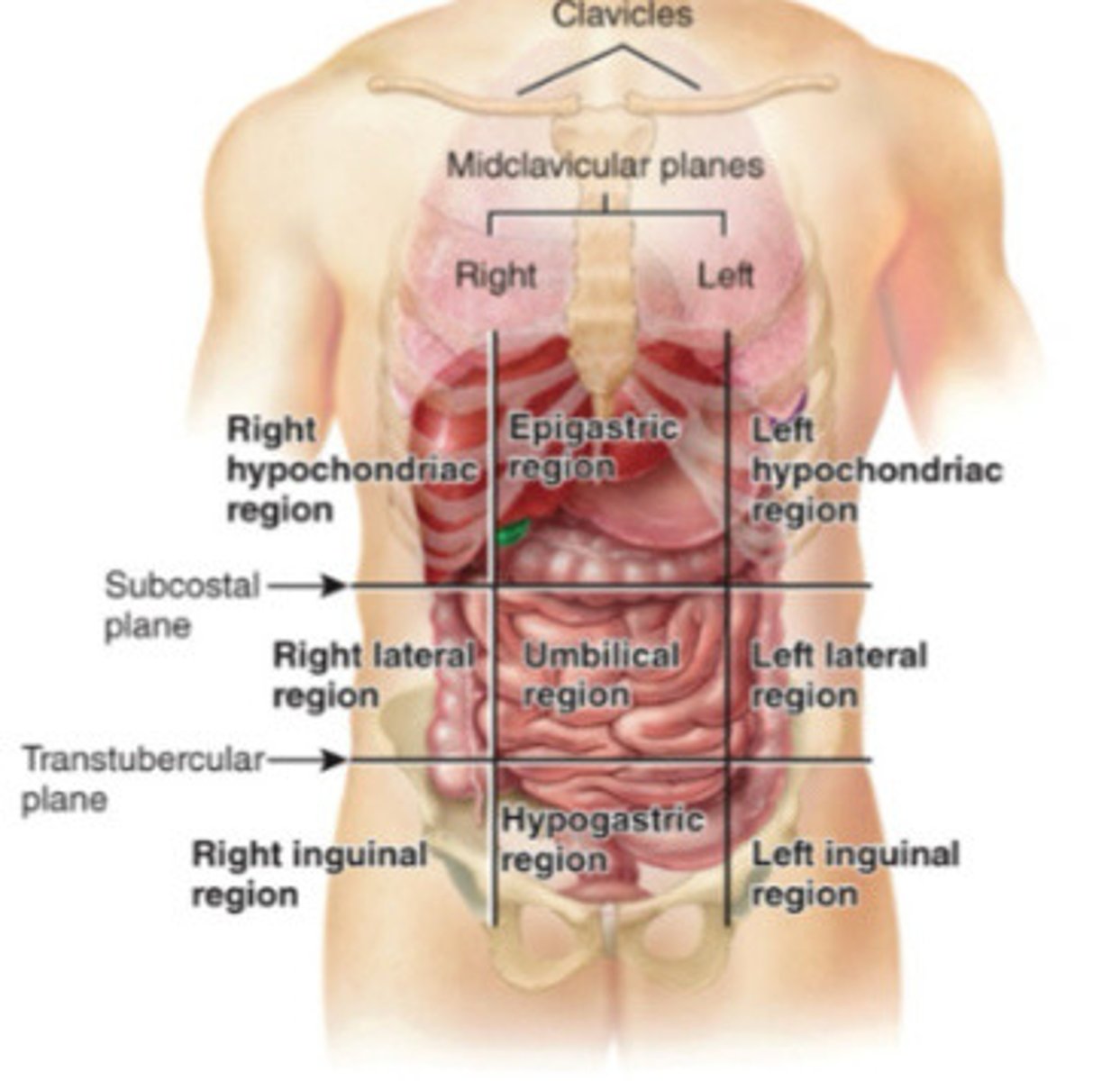
Midclavicular lines
Clavicle lines that divide the abdominopelvic cavity into three columns
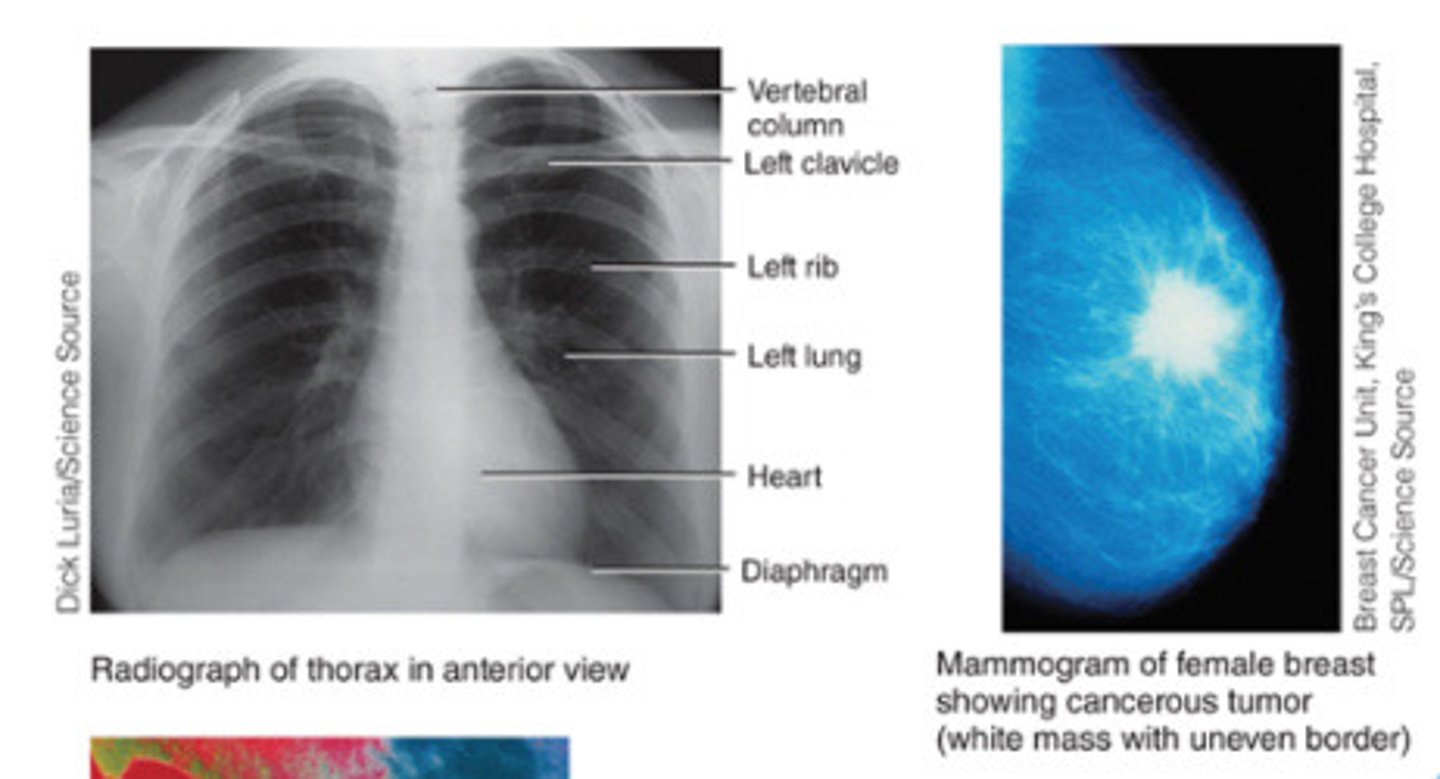
Radiography
A single barrage of x-rays used to produce images through the body, useful for examining the breast and for determining bone density
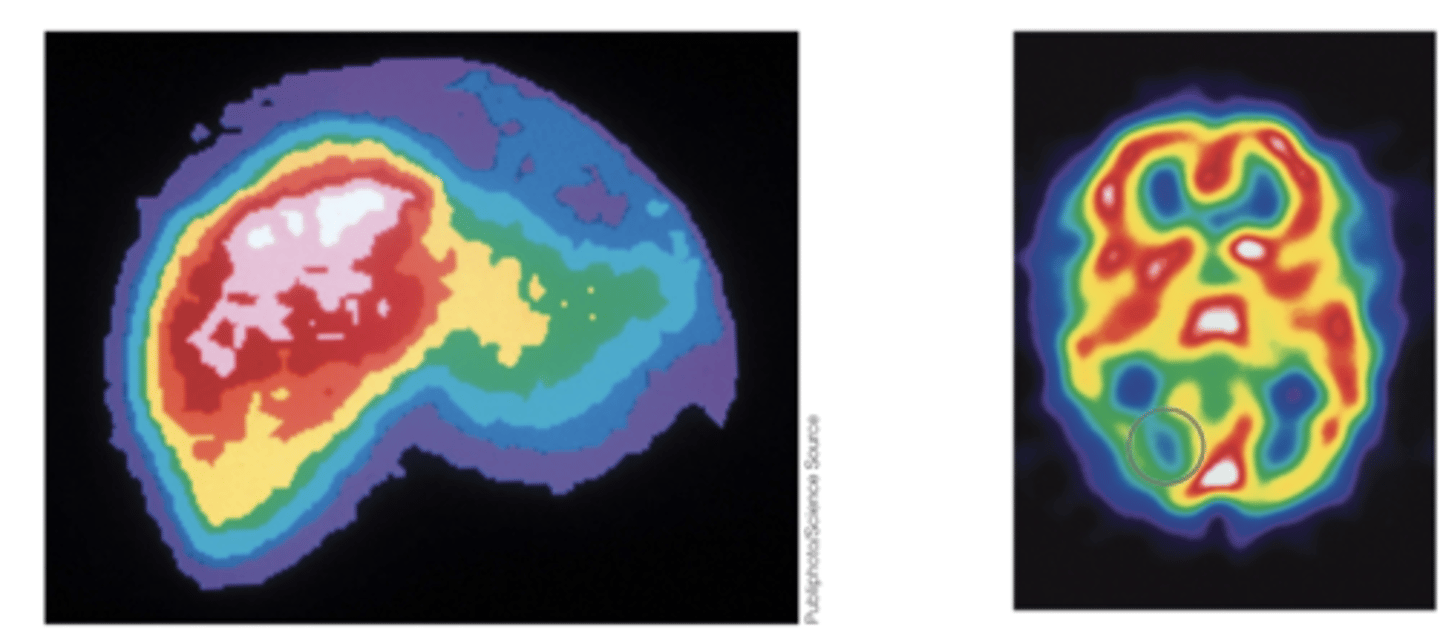
MRI
Usually used to look at the brain, kidney, or liver to detect tumors, abnormalities and measure blood flow
CT scan
A series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and assembled to look for lung cancers, coronary artery disease and kidney cancers
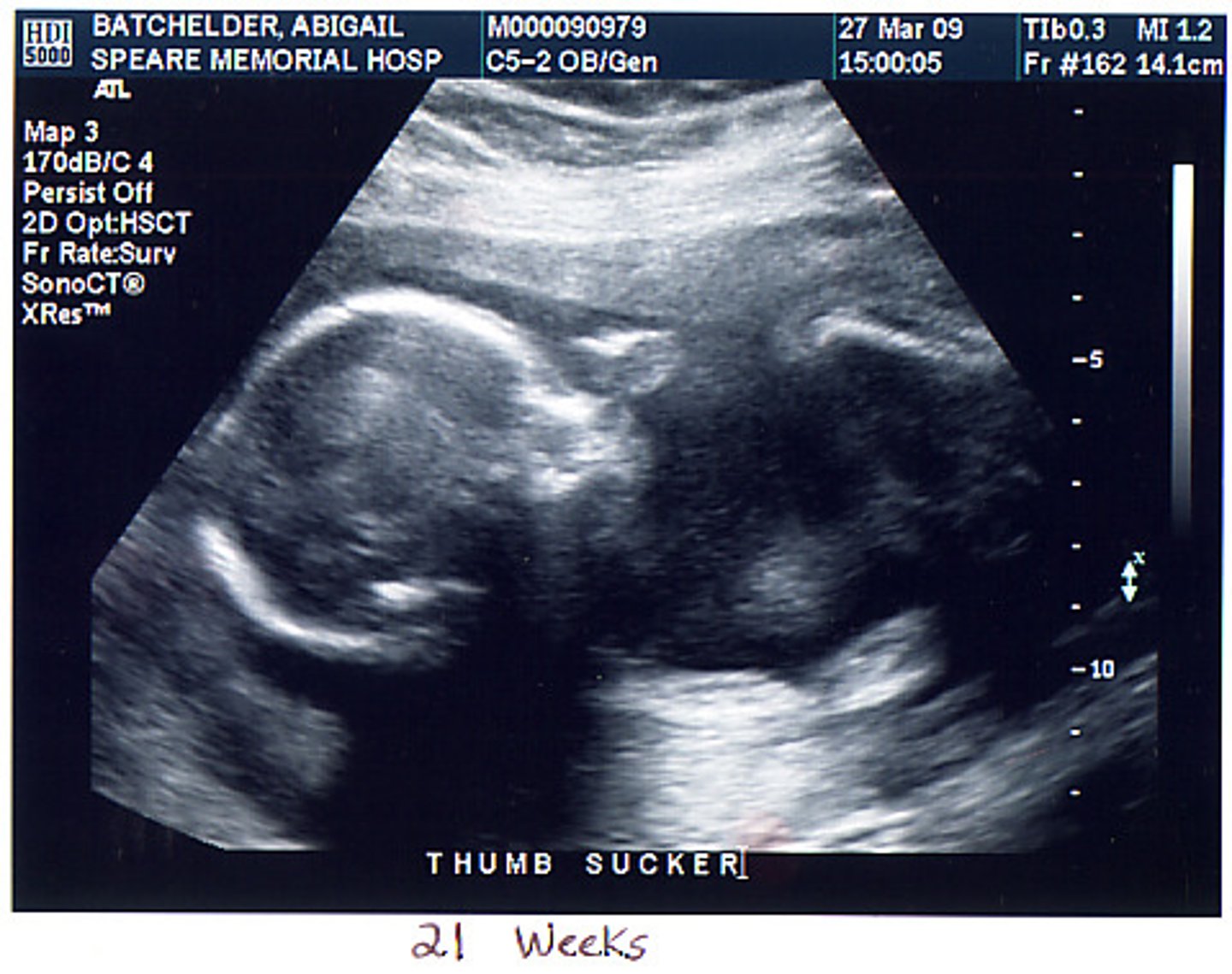
Ultrasound
High-frequency sound waves used to create an image of a developing fetus and can check the size, location, and actions of organs and blood flow through blood vessels
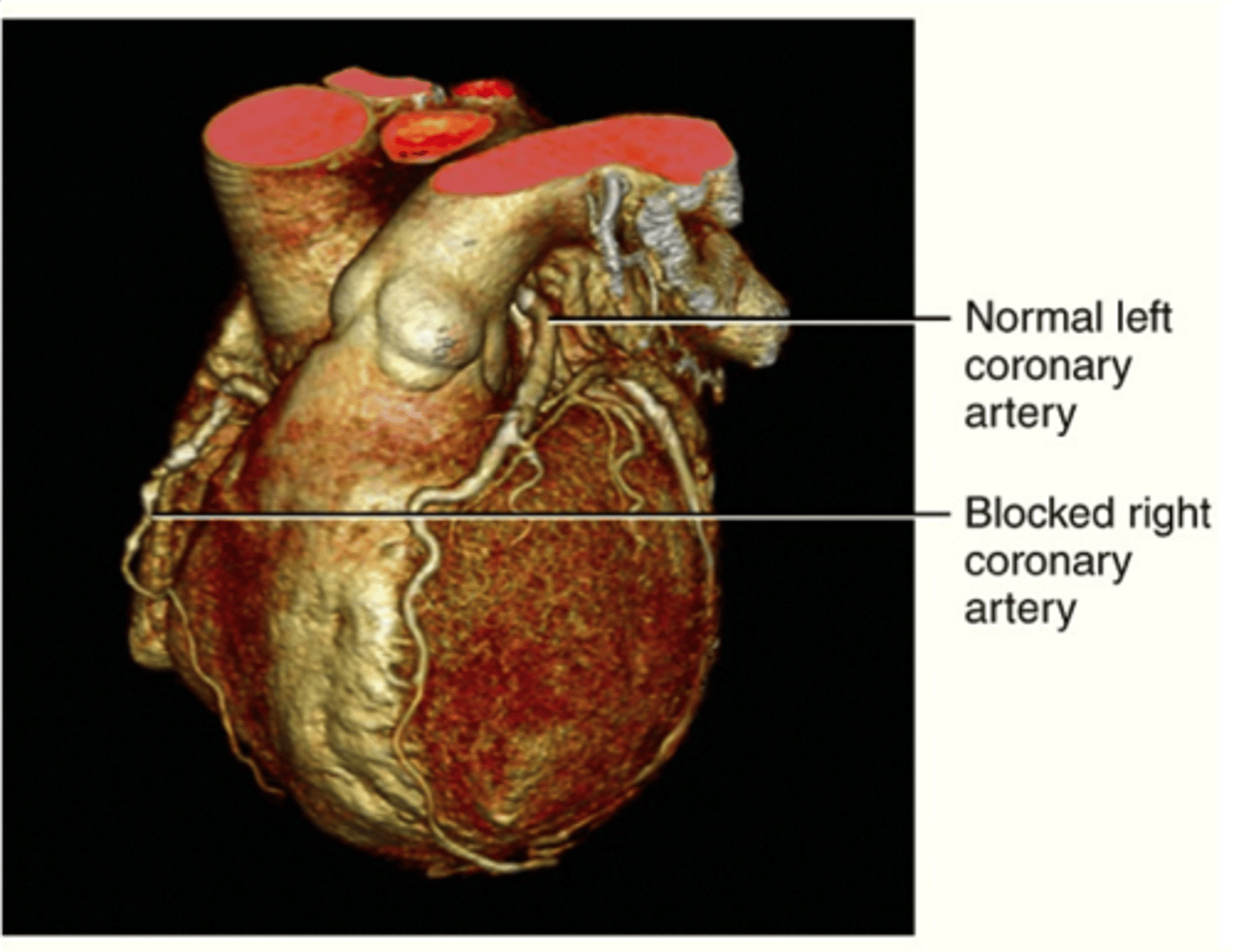
CCTA scan
A contrast medium is injected into a vein, numerous x-ray beams use to look at the heart which is used to study the blood vessels and check for any coronary artery blockages
PET scan
The patient is injected with a radioactive substance which can create gamma rays to study the physiology of body structures (ex. metabolism in brain/heart)
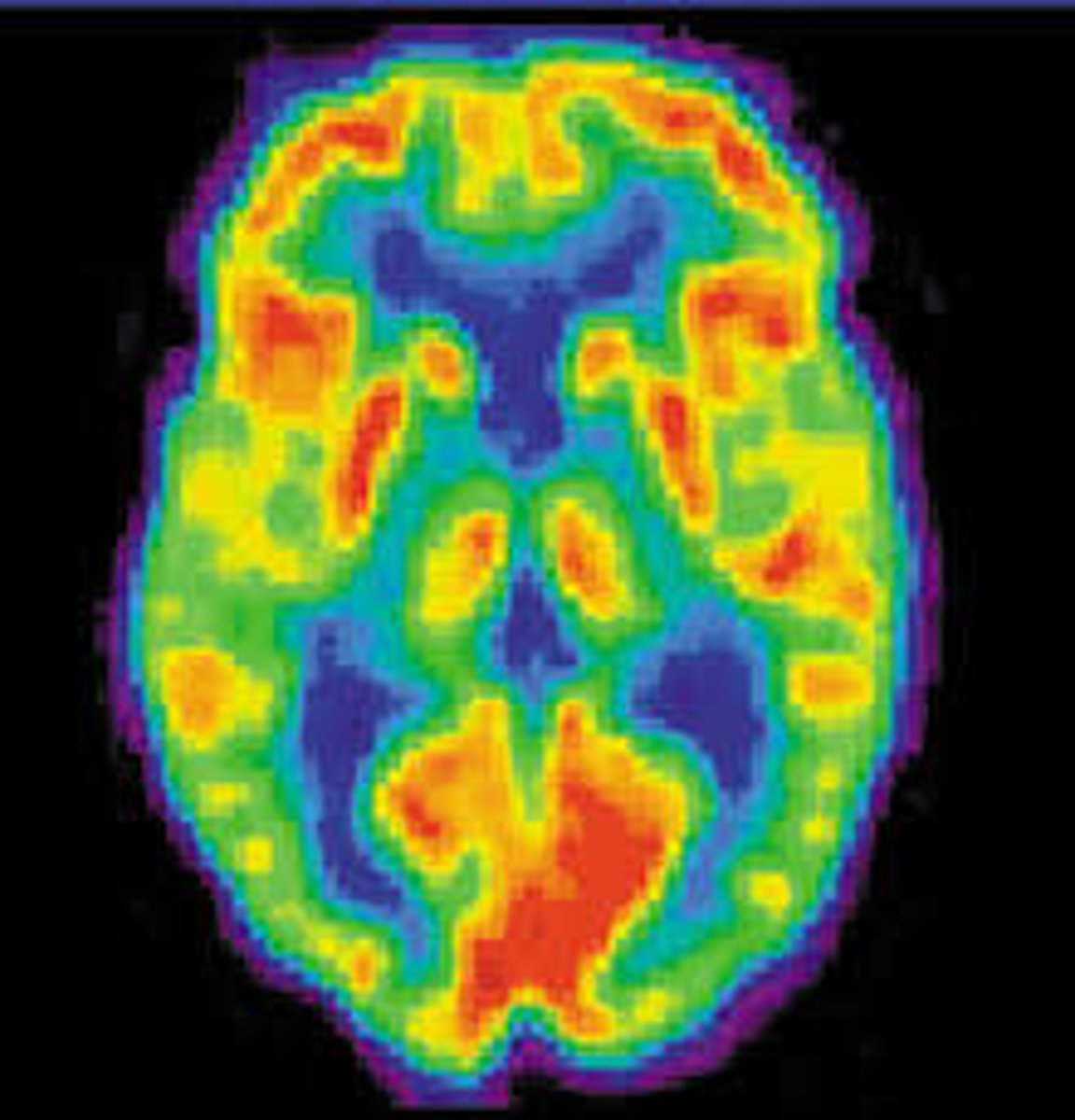
Radionuclide scan
The patient is injected with a radioactive substance that directly emits gamma rays that are detected to study activity of a tissue or organ such as tumors in body tissue
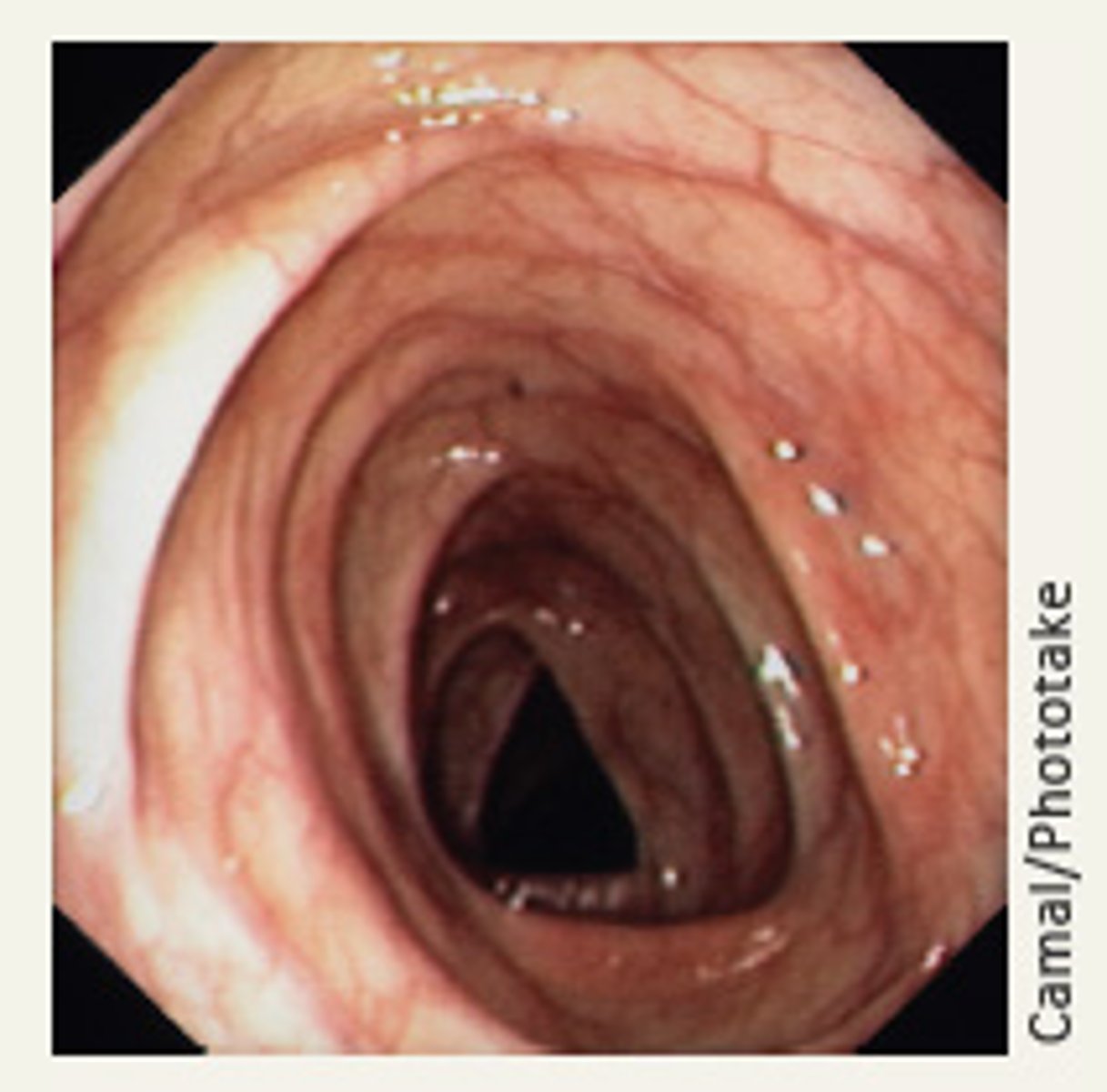
Endoscopy
Visual examination of a body cavity or canal using a specialized lighted instrument called an endoscope
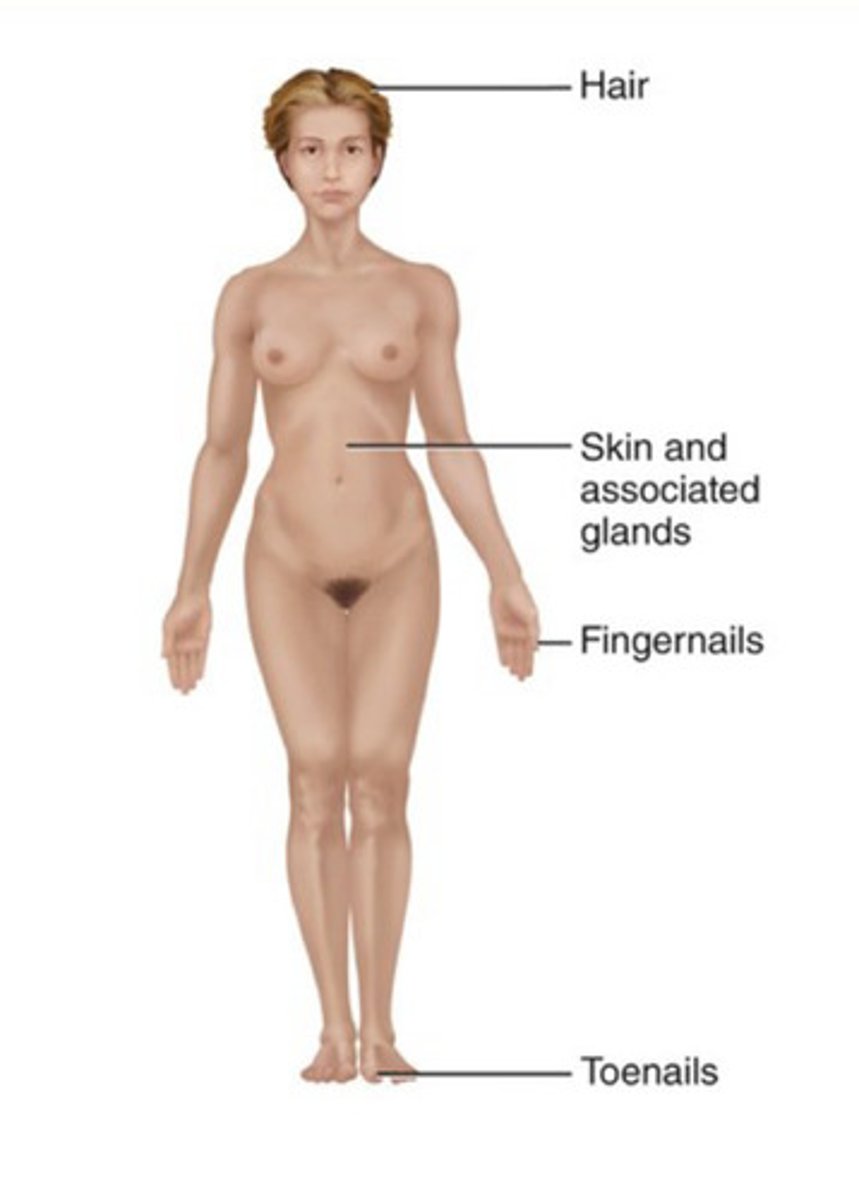
Components of the integumentary system
Skin, and associated structures ex. hair and fingernails
Components of the skeletal system
Bones, joints, and cartilages
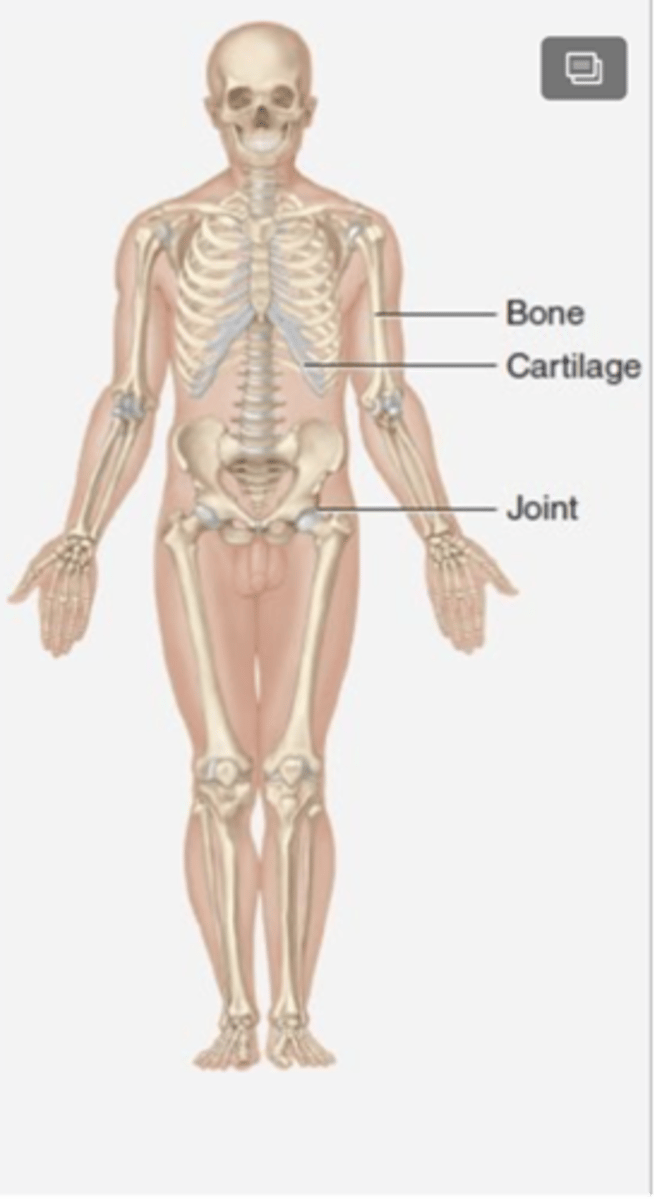
Functions of the skeletal system
Supports and protects the body, and aids body movements
Components of the muscular system
Skeletal muscles
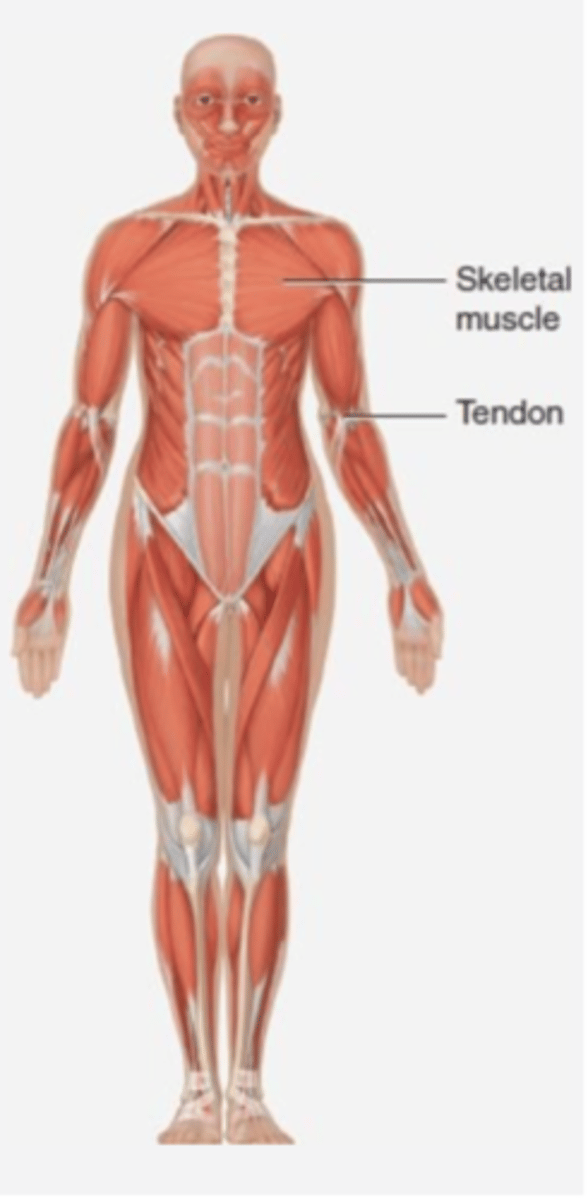
Functions of the muscular system
Movement and body heat
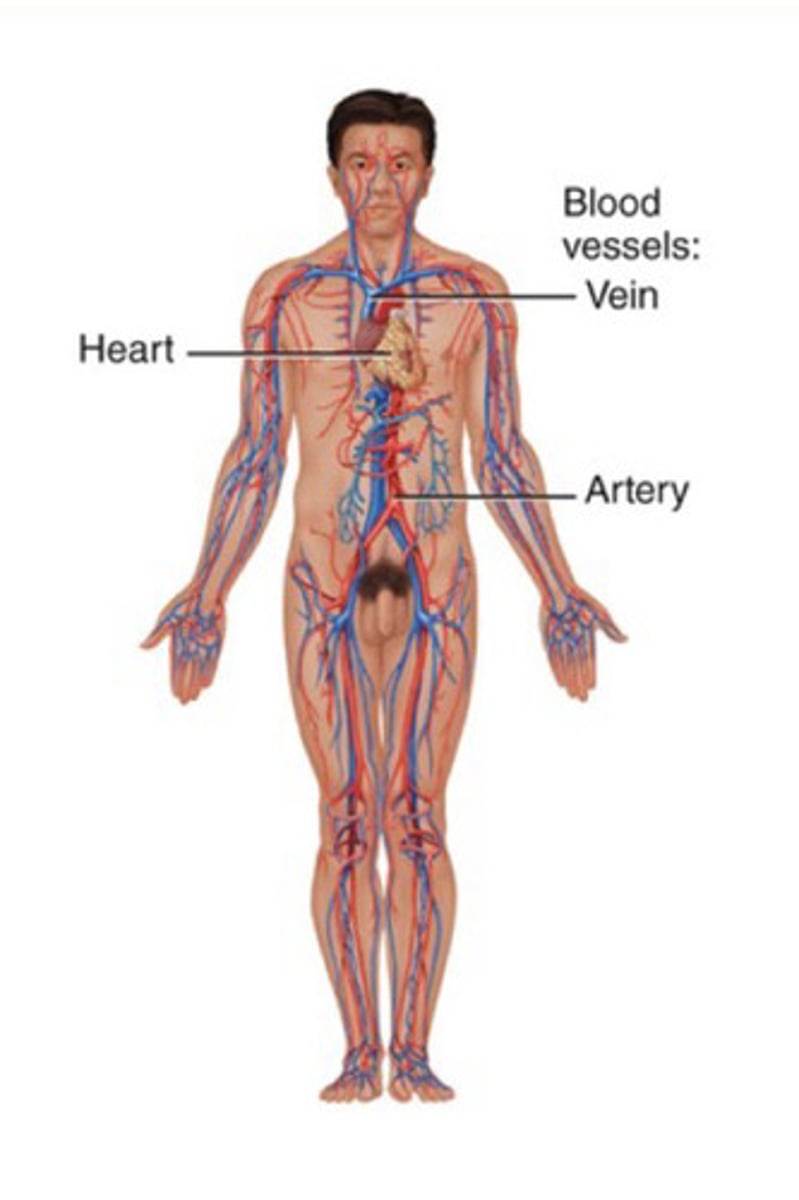
Components of the cardiovascular system
Blood, heart, and blood vessels
Functions of the integumentary system
Protects the body and helps regulate body temperature
Functions of the cardiovascular system
Transports blood, nutrients, and gases throughout the body
Components of the lymphatic and immune system
lymph, thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, and tonsils
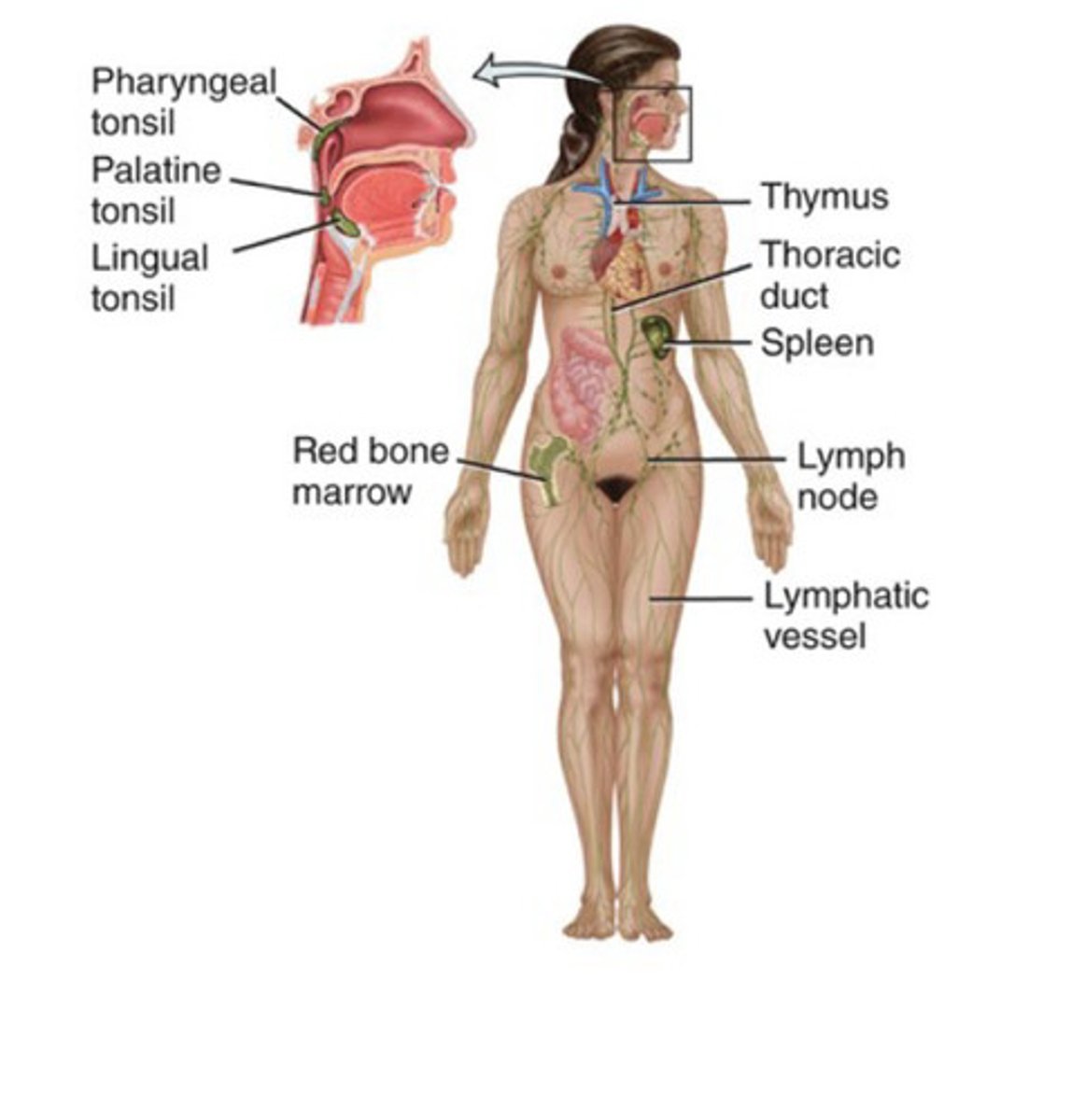
Functions of the lymphatic and immune system
Filters body fluids and molecules and defends the body from invaders
Components of the respiratory system
Lungs, trachea, pharynx, larynx, and bronchial tubes
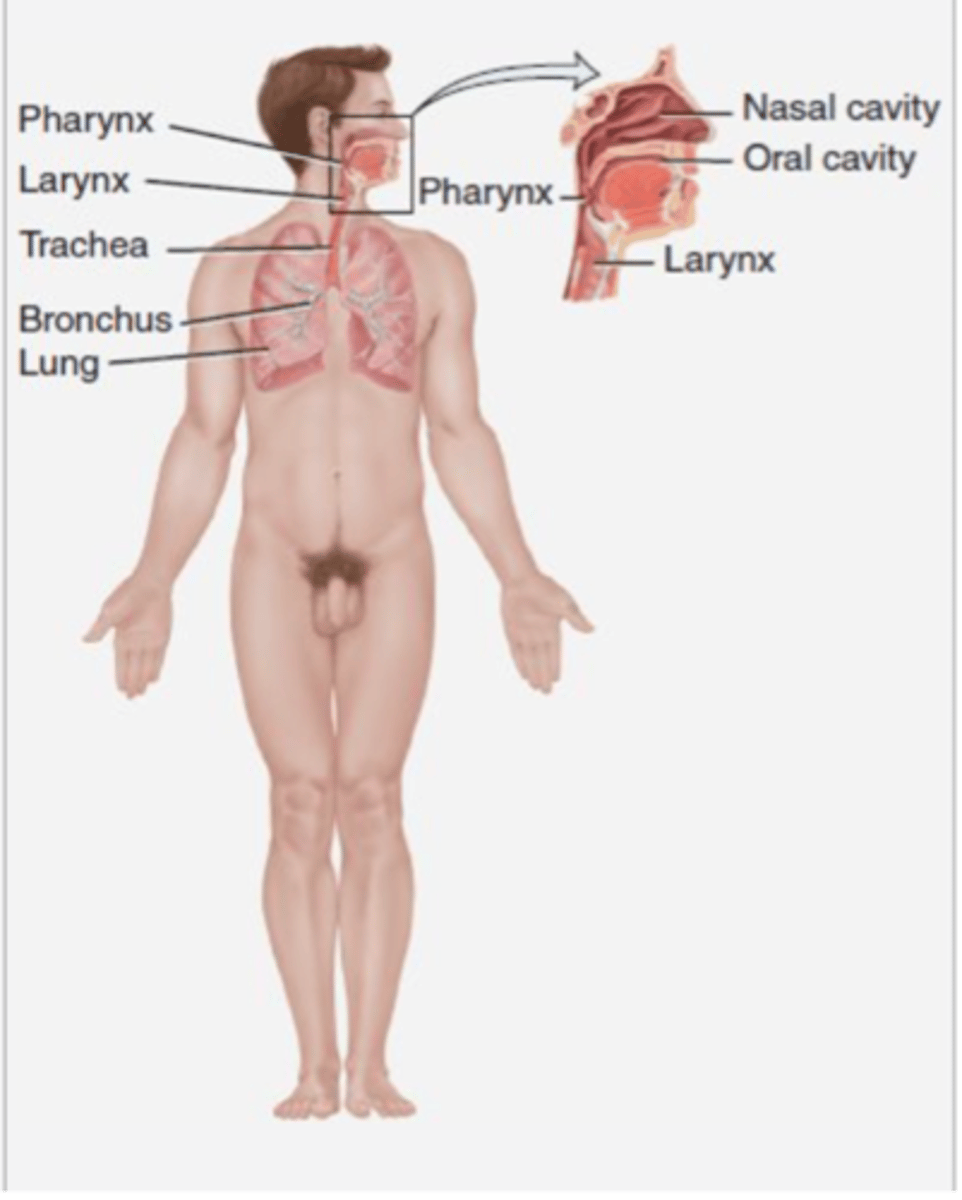
Functions of the respiratory system
Exchange gases between the body and the environment; disposes carbon dioxide waste
Anatomy
Study of structure
Physiology
Study of how body parts function
Anabolism
building up simple molecules into more complex molecules
Basic life processes
Metabolism, responsiveness, movement, growth, differentiation, and reproduction
Catabolism
breaking down of more complex molecules into simpler molecules
Levels of Structural Organization
chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, system, and organismal
Angiogram
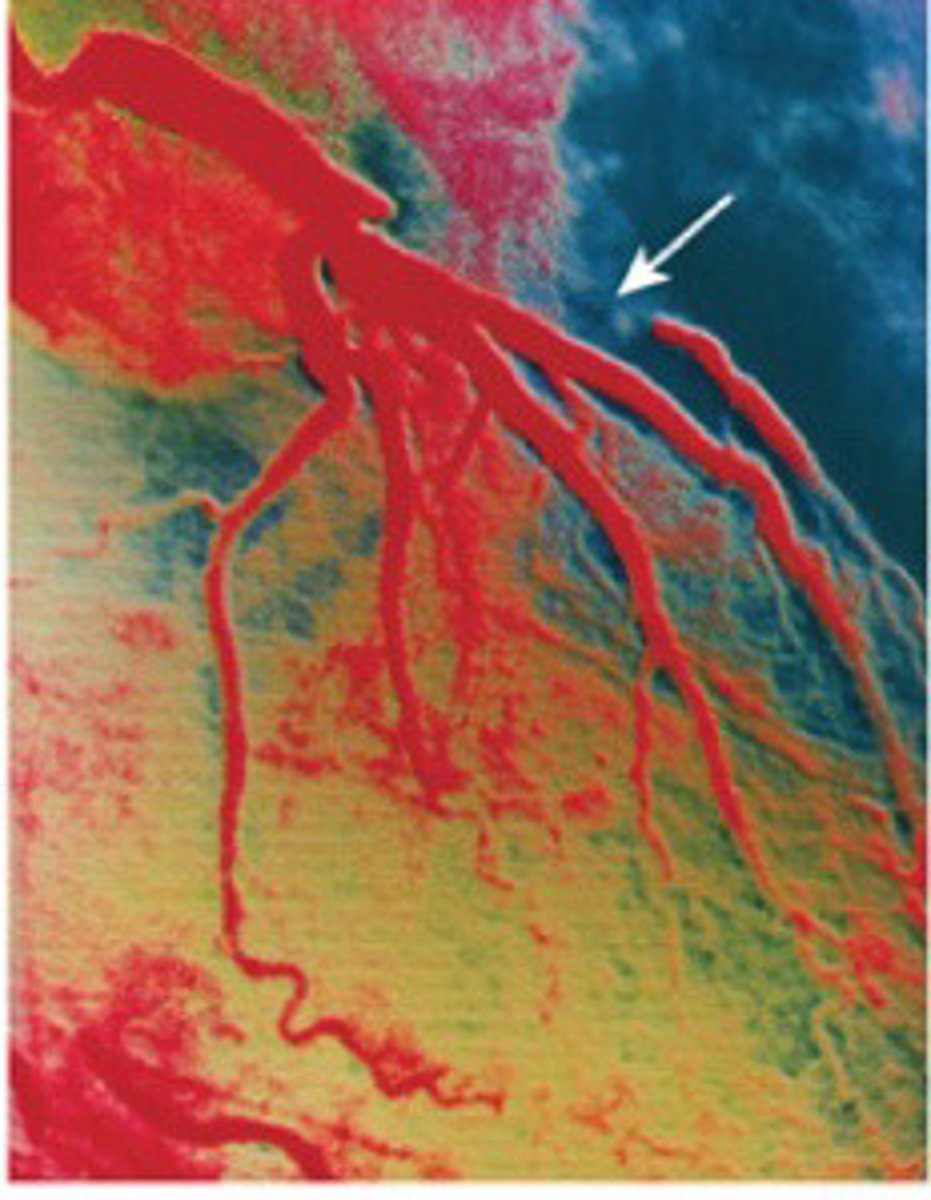
Intravenous urogram