SiR - Lecture 5
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What are interlocutors? (definition)
The people involved in the conversation (dyadic vs multi-party, children vs adults, cultural background, relationship roles).
What is conversational context? (definition)
The environment where the conversation happens (public vs private, social rules, etiquette, role relationships).
What are conversational goals?
The purposes of the interaction—service, educational, social support; often multiple and conflicting.
What is conversational initiative?
Who leads or controls the conversation (human-led, robot-led, mixed-initiative).
What is turn-taking? (definition)
Managing when each participant speaks using multimodal cues (gaze, prosody, pauses).
Why is good turn-taking important for HRI?
Bad timing causes frustration, lowers sociability, and reduces effectiveness.
What is repair in conversation? (definition)
Fixing misunderstandings using clarifications, rephrasing, or other modalities (gesture, display).
What is the Grice's Cooperative Principle?
A theory saying conversation works best when speakers cooperate using the four maxims.
List Grice’s four maxims.
Quantity (say enough, but not too much)
Quality (be truthful and avoid misleading statements)
Relation (make your contribution relevant to the ongoing conversation)
Manner (be clear, avoid ambiguity)
What is personalization? (definition)
Dynamic tailoring of robot behavior based on user characteristics, context, emotions, and history.
What aspects of a robot can be personalized?
Behavior, communication, appearance, functionality, interface.
What information can personalization be based on?
Demographic, physiological, behavioral, cognitive, social/context, explicit user input.
Why is personalization important?
Improves performance, engagement, trust, accessibility, comfort, and long-term bonding.
What is a design pattern? (definition)
A reusable solution to a recurring design problem.
What is the Undo pattern?
A pattern allowing the user to correct or revert mistakes.
What is the “Specifications” design pattern?
Pair a closed question with an open follow-up to avoid interrogation and encourage self-disclosure.
Example of closed + open question pairing?
“What is your favorite season?” → “Why is that your favorite?”
What is the relationship building pattern?
Robot must be reciprocal, socially responsive, reduce uncertainty, and acknowledge user attempts.
What is Social Penetration Theory?
Relationships deepen through self-disclosure and reciprocity.
What is social responsiveness in HRI?
Robot must acknowledge every attempt, respond in relevant and timely ways.
What is memory-based personalization? (definition)
Robot uses stored memories (name, preferences, past dialogs) to personalize future conversations.
What are memory references?
Robot recalls name, past topics, personal preferences.
What is content selection?
Robot chooses topics based on user interests and avoids repetition.
What is content augmentation?
Robot enriches dialog with personalized details (e.g., “Let’s talk about [risotto] next time”).
Why is cross-session memory important?
Builds long-term relationship, reduces novelty effect, increases engagement.
Describe the Ligthart et al. study.
46 children, 5 sessions over 2 months, personalized vs non-personalized robot.
What is a flow diagram? (definition)
A visual structure showing conversational logic: user inputs, robot actions, branches, fallbacks.
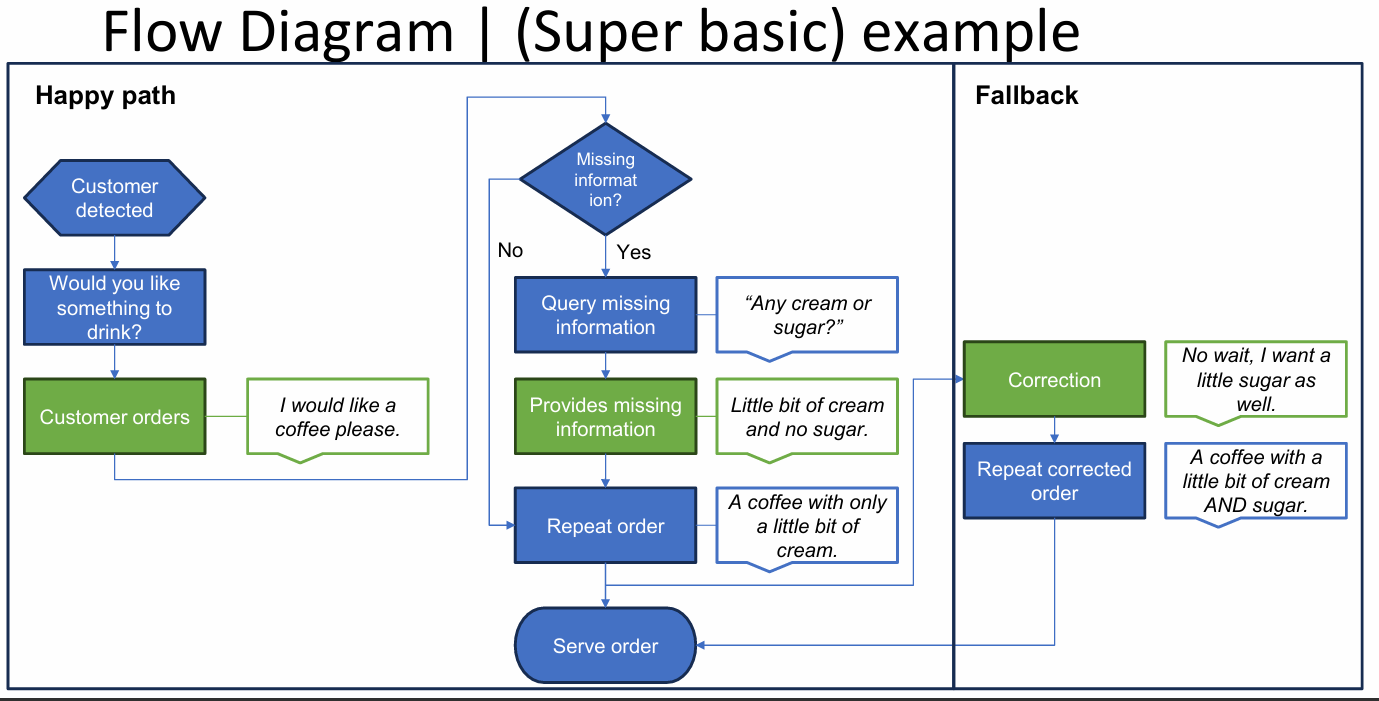
What are the key flow diagram nodes?
Start, user input, system response, decision points, end nodes.
In the diagram flow, what is a fallback?
A recovery path when user input is unexpected or missing.
What is a narrative dialog? (definition)
A multi-session storytelling conversation where robot drives the story and user influences it.
Why are narratives helpful in HRI?
Novel content, continuity, shared interest, common ground → stronger relationships.
Name three types of minidialogs.
Narrative, Chitchat, Functional (greetings/goodbye).
What are the four move types?
Say, Ask, Do, Generate.
What is dynamic compilation of minidialogs?
Robot chooses dialogs based on history, user model, interests, and dependencies.
What is robot identity? (definition)
A designed persona with consistent traits, behavior, voice, gestures, and fictional + real goals.
Why create a robot persona?
Enhances engagement, improves communication, reduces uncanny valley, builds trust.
What is a storyworld?
A fictional narrative universe connecting robot personality, goals, and behavior.
What must be considered when designing a robot persona?
NVC impact, voice/language, gestures, ethics, privacy, cultural sensitivity.