Adrenergic Antagonists
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What are the key features of nonselective adrenergic antagonists?
phenethylamine backbone
any non-hydroxy substitution → antagonist
Labetalol HCl → Normodyne
nonselective adrenergic antagonist
blocks A1 = vasodilation
blocks B1 = decreased CO
blocks B2 = bronchoconstriction
asthma is a contraindication
What are the key features of nonselective alpha antagonists?
imidazoline ring = increased affinity to alpha
CH2 - imidazoline and a heavily subbed benzene ring indicates…
alpha 1 agonist
NH2-imidazoline indicates…
alpha 2 agonist
tolazoline - Priscoline
nonselective alpha antagonist
antagonist structure where it is less lipophilic than the agonist
indication: pulmonary HTN
IV administration
phentolamine - Oraverse, Regitine
nonselective alpha antagonist
indication: pheochromocytoma
tumor of adrenal medulla → increased release of NE → HTN
What is the effect of alpha 1 selective antagonists?
dilate blood vessels
What are key features of alpha 1 selective antagonists?
quinazoline nucleus (benzene + pyridine)
all have amino group
6,7 dimethoxy
2-piperazine ring system
carbonyl
NOT a phenethylamine backbone
prazosin - Minipress
alpha 1 selective antagonist
blocks BOTH A1A + A1B
furan group
piperazine
quinazoline
indication: HTN
terazosin - Hytrin
alpha 1 selective antagonist
indication: HTN
doxazosin - Cardura
alpha 1 selective antagonist
indication: BPH, CHF, HTN

trimazosin
alpha 1 selective antagonist
OH group → short acting
metabolizeddirectly to phase II conjugation
tamsulosin - Flomax
alpha 1 selective antagonist
has a phenethylamine backbone
no affinity to BVs
more selective to alpha 1A
sulfur group
drug goes directly to kidneys
indication: BPH
alfuzosin - Uroxatral
alpha 1 selective antagonist
quinoline nucleus
NO piperazine → less affinity to circulatory alpha 1 → increased selectivity to alpha 1A
indication: BPH
Which of the alpha 1 selective antagonists does NOT have a quinoline backbone?
tamsulosin - Flomax
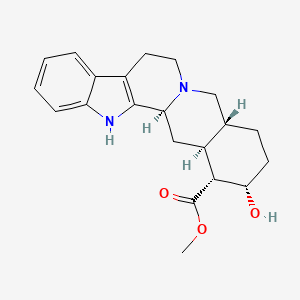
yohimbine
alpha 2 selective antagonist
indication: sexual dysfunction
What are the indications for nonselective beta antagonists?
CV disease
glaucoma
What are the effects of nonselective beta antagonists?
B1 = renin release → angiotensin II (powerful vasoconstrictor)
B2 = liver, skeletal muscle, uterus, vascular SM, eye, bronchi
What are the contraindications of nonselective beta antagonists?
diabetes
asthma
What are the key features of nonselective beta antagonists?
NE but without OH → antagonist
nonhydroxyl sub
OH-CH2 b/w ethylamine + phenyl
additional ring → increases lipophilicity
A tertbutyl structure in nonselective beta antagonists increases selectivity for which receptor?
beta 2
An isopropyl structure in nonselective beta antagonists increases selectivity for which receptor?
BOTH B1 and B2
fused rings usually indicate
nonselectivity
propranolol - Inderal
nonselective beta antagonist
isopropyl group
naphthalene (fused benzene rings) → very lipophilic!
indication: angina, HTN, arrhythmia
What is the contraindication to propranolol?
cirrhosis
How is propranolol metabolized?
aromatic hydroxylation by CYP in liver
pindolol - Visken
nonselective beta antagonist
indole nucleus
lipophilic → metabolized by liver
indication: angina, HTN, arrhythmia
What is a contraindication of Visken?
cirrhosis
nadolol - Corgard
nonselective beta antagonist
tertbutyl group
NOT a catechol since OH isn’t in position 3,4
indication: angina, HTN, arrhythmias
What is a contraindication of Corgard?
cirrhosis
drug will be conjugated in phase II
timolol - Timoptic, Istalol
nonselective beta antagonist
thiadiazole group
tertbutyl group
more polar
hydrophilic side chain
will not cross BBB
indication: glaucoma
What are the indications for selective beta 1 antagonists?
HTN
arrhythmia
angina
What are the key features of selective B1 antagonists?
isopropyl N-substitution
O-CH2 spacer
single benzene ring w/ substitution at position 4
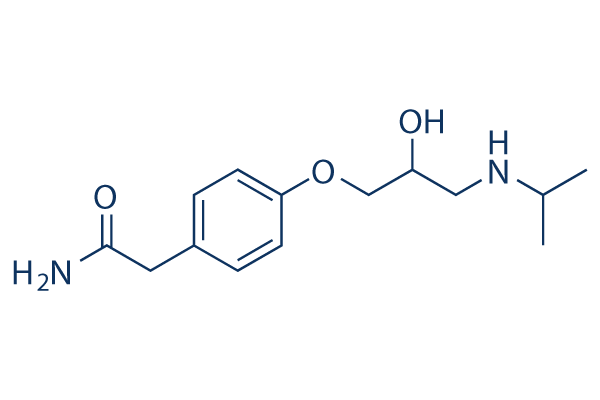
atenolol - Tenormin
B1 selective antagonist
amide group
isopropyl → increased selectivity to B1
How is atenolol metabolized?
amidases
result: NH4 + COOH

esmolol - Brevibloc
B1 selective antagonist
short acting due to ester group being easily hydrolyzed
indication: acute MI, HTN, arrhythmia
injection (HCl)
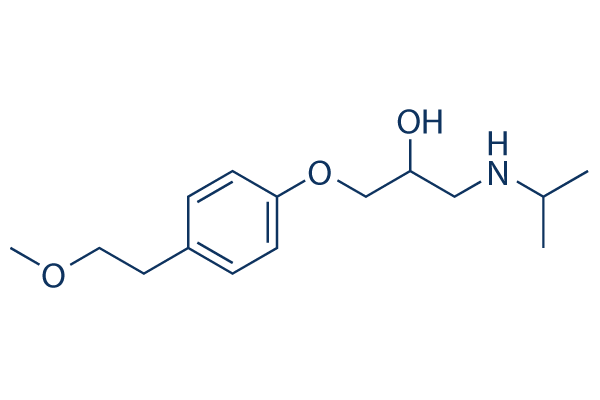
metoprolol succinate - Toprol Xl
metoprolol tartrate - Lopressor
B1 selective antagonist
indication: angina, HTN, arrhythmia
How is Toprol XL/Lopressor metabolized?
O demethylation by CYP in liver
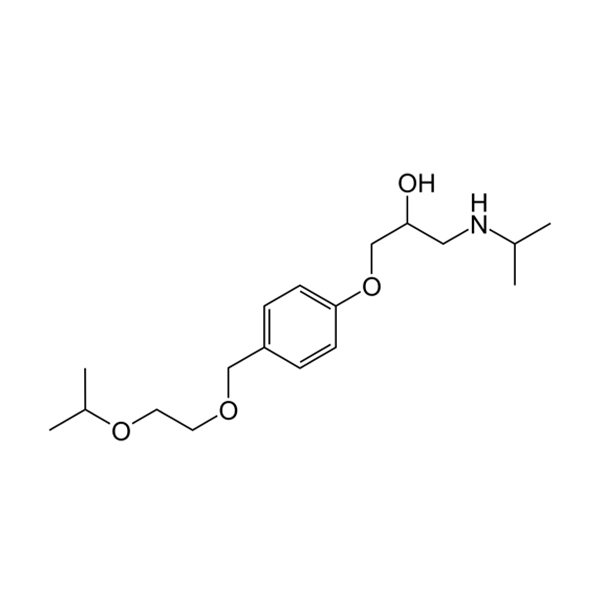
bisoprolol fumarate - Zebeta
B1 selective antagonist
isopropyl group on ether → less likely to be metabolized by O-demethylation
longer duration of action than metoprolol
indication: CHF, HTN
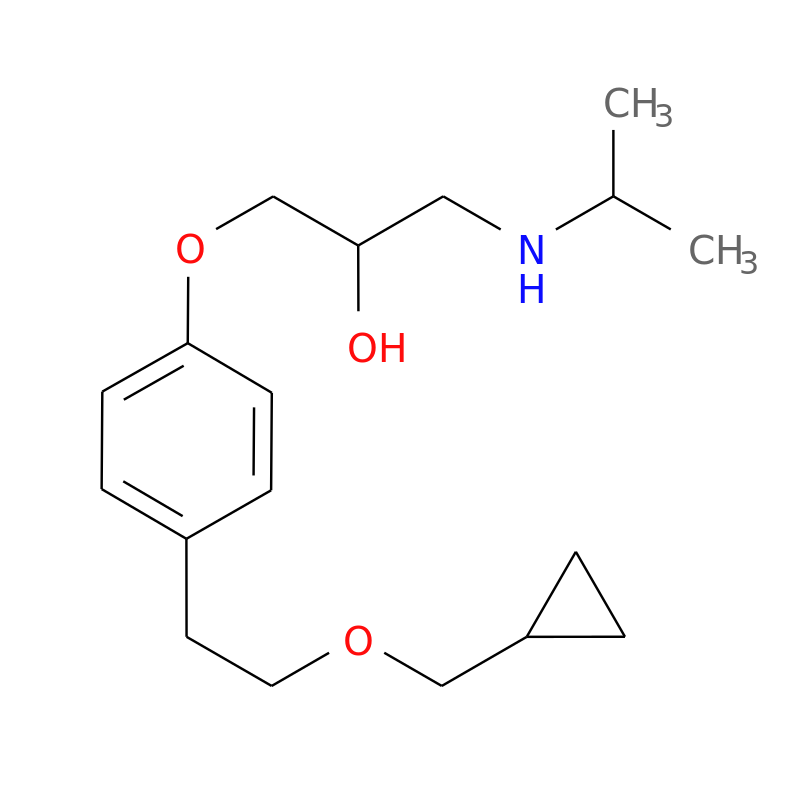
betaxolol - Betoptic S/Kerlone
B1 selective antagonist
less likely to be metabolized by O-demethylation
longer duration of action than metoprolol
indication: glaucoma, HTN, angina