DANB RHS review + practice
1/43
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
When taking an occlusal radiograph, the PSP packet should extend from the patient's mouth by approximately.
1/2 - 5/8 inches.
1/8 -1/4 inches.
1 1/8 - 1 1/4 inches.
3/4 - 1 inches.
1/8 - 1/4 inches
Which radiograph is used to diagnose interproximal caries?
bitewing
Phosphor plates are processed by using
laser beam technology
Impacted third molars are best seen with what type of radiograph?
Bitewing
Periapical
Panoramic
Cephalometric
panoramic radiograph
How do most carious lesions appear on an image?
Undetectable
Radiopaque
Radiolucent
Mixed density
radiolucent
The most common radiographic exposure used to evaluate a dental implant on an adult is
periapical
occlusal
bitewing
panoramic
panoramic radiographs
Paralleling technique requires the image receptor be placed
against the occlusal surface of the tooth.
against the lingual surface of the tooth.
away from the tooth, toward the middle of the oral cavity.
toward the tooth, away from the oral cavity.
away from the tooth, toward the middle of the oral cavity
On an anterior image, the anterior alveolar crest normally appears
pointed and sharp
as a dense radiopaque line
as a triangular-shaped radiopacity
flat and smooth
pointed and sharp
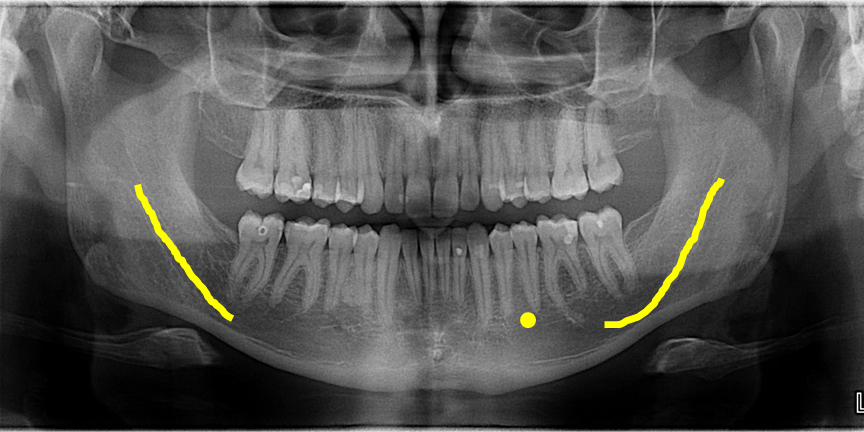
The dense radiopaque band that outlines the edge of a mandibular image is the
Mental protuberance
Inferior border
Mylohyoid ridge
Oblique ridge
inferior border
What is the most common radiographic exposure used to detect periodontal disease?
bitewing.
periapical.
occlusal.
panoramic.
bitewing
which term is used to describe abscess or pulp on a radiograph
radiopaque
radiolucent
density
contrast
radiolucent
Which device is a disposable intraoral PSP holder?
Rinn XCP®
Endoray®
Eezee grip®
Stabe®
stabe®
double ended film holder
Rinn XCP®
Endoray®
Eezee grip®
Stabe®
Eezee grip®
What influences the sharpness of a radiograph?
X-ray beam angulation
Object-receptor alignment
Focal spot size
kVp and mA
focal spot size
Impacted third molars are best seen with what type of radiograph?
Panoramic
Periapical
Bitewing
Cephalometric
panoramic
Which landmark is seen in a maxillary anterior periapical image?
Genial tubercule
Incisive foramen
Zygomatic process
Mental foramen
incisive foramen
Which extraoral radiograph is used to evaluate impacted teeth, large lesions and fractures of the mandible?
Lateral jaw projection
Waters projection
Posteroanterior projection
Reverse Towne projection
Lateral jaw projection
Supernumerary teeth are best detected using what type of image receptor?
Cephalometric
Periapical
Bitewing
Panoramic
panoramic
Which image would be used to see the relationship of the alveolar bone?
Occlusal
Horizontal bitewing
Vertical bitewing
Periapical
vertical bitewing
The most radiolucent area on an anterior image is the
maxillary sinus
maxillary tuberosity
nasal fossa
nasal spine
nasal fossa
The edentulous radiographic series may include all the following EXCEPT
bitewings.
occlusals.
panoramic.
periapicals.
bitewings
What radiographic technique is recommended for a patient with a shallow palate?
Periapical
Paralleling
Occlusal
Bisecting
bisecting
The BEST radiograph to evaluate a suspected salivary stone in the submandibular gland is a/an
periapical.
panoramic.
cephalometric.
occlusal.
occlusal
Which of the following will best protect the dental assistant from cross-contamination while exposing radiographs?
a. Film holding devices
b. barriers on PID
c. Patient bib
d. Gloves
gloves
After the completion of a radiographic procedure, the PID should be
a. disinfected
b. dried
c. exposed
d. sterilized
disinfected
The primary disadvantage of the bisecting technique is:
a. Longer exposure time
b. Dimensional distortion of the teeth
c. Requirements of a receptor holder
d. Greater magnification
dimensional distortion of the teeth
In bisecting technique, which angle is being bisected?
a. The angle between the image receptor and the long axis of the tooth
b. The angle between the central ray and the long axis of the tooth
c. The angle between the image receptor and the central ray
d. The angle that is perpendicular to the image receptor
The angle between the image receptor and the long axis of the tooth
The dentist says that the image has too much density. What adjustment would you make?
a. Increase mA.
b. Increase kVp
c. Decrease kVp
d. Decrease mA
Decrease mA
Which appears most radiopaque on a dental image?
a. pulp
b. enamel
c. dentin
d. sinus
enamel
The difference in the degrees of blackness between adjacent areas on a dental radiograph is termed
a. contrast
b. density
c. distortion
d. penumbra
contrast
To produce ionizing radiation, an atom must
lose a proton
add a proton
lose a neutron
add an electron
add an electron
Contrast in a digital image primarily controlled by
mA
kVp
Exposure time
Size of sensor
Kvp
According to the inverse square law, when changing the PID length from 8 to 16 inches, the beam's intensity is
¾ as intense
4 times as intense
2 times as intense
¼ as intense
¼ as intense
Leakage radiation is any radiation that is
From the primary beam
From the secondary beam
Received from the operator
Received from the patient
Primary beam
Somatic effects (effects only the individual) of radiation do NOT have damaging effects on
Bone marrow
Offspring
Blood cells
The patient
Offspring
What is the thickness of the collimator?
1.75 inches
1.25 inches
2.75 inches
2.25 inches
2.75 inches
What is the thickness of aluminum filtration?
1.5 mm
2.5 mm
3.25 mm
2.25 mm
2.5 mm
What is the purpose of aluminum filtration?
removes low energy, long-wavelength x-rays
An instrument that contacts mucous membranes but does not penetrate soft tissues or bone is considered __
Semi-critical
You are using a complete series of dental images to educate your patient on the value of radiography. According to HIPAA, what should not be present in or on the film mount?
The patient’s name.
Which of the following statements about the panoramic dental radiography is FALSE?
a. The vertical angulation of the panoramic tube head is not adjustable
b. The tube head of the panoramic unit always rotates in front of the patient's head
c. Screen type film must be used during panoramic radiography
d. intensifying screens must be used during panoramic radiography
b. The tube head of the panoramic unit always rotates in front of the patient's head
All of the can be adjusted prior to exposing a panoramic radiograph EXCEPT:
a. milliamperage
b. kilovoltage
c. exposure time
d. patient positioning
exposure time
Which of the following causes overlapping?
a. Inadequate vertical angulation
b. Decreased vertical angulation
c. Central ray not perpendicular to the teeth
d. Patient movement
Central ray not perpendicular to the teeth
Which of the following will cause foreshortening?
a. Inadequate vertical angulation
b. Inadequate horizontal angulation
c. Too much vertical angulation
d. Incomplete coverage of the image receptor
too much vertical angulation