Hematology/Oncology CM and CA
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
Percentage of RBCs in blood
41%
Percentage of WBCs in blood
4%
Percentage of plasma
55%
Ratio of myeloblasts to erythrocyte progenitor cells
2:1 up to 4:1
What progenitor cell develops into neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells
Granulocyte macrophage progenitor --> myeloblast
What is a reticulocyte?
immature RBC
what differentiates into platelets?
Megakaryocytes
What type of hemoglobin chains are found in fetal hemoglobin (HGB F)?
2 alpha, 2 gamma
What type of hemoglobin chains are found in adult hemoglobin?
2 alpha, 2 beta
At what age does hemoglobin turn from fetal to adult?
6 months
What does high Hgb/Hct indicate?
dehydration, polycythemia
What does low Hgb/Hct indicate?
anemia
What does MCV refer to?
Mean corpuscular volume - average size of RBC (Hct/RBC count)
What is the normal range of MCV?
81-100fL
What does high MCV indicate?
macrocytic; liver disease, chemo, alcoholism, B12, folate deficiency
What does low MCV indicate?
microcytic; iron deficiency, thalassemia, chronic illness
What does MCH indicate?
Mean corpuscular height; average amount of Hgb in RBCs
What does low MCH indicate?
Hypochromic; microcytic anemia
What is the normal range of MCH?
26-34pg
What does high MCH indicate?
Hyperchromasia; macrocytic anemia
what does MCHC indicate?
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
what is the normal value of MCHC?
31%-36%
what does high MCHC indicate?
hereditary spherocytosis, cold agglutinins, intravascular hemolysis
What does low MCHC indicate?
severe iron deficiency, thalassemia
What does RDW indicate?
Red cell distribution width, variation in size of RBC
What is the normal value for RDW?
11.5%-14.5%
What does high RDW indicate?
many different sized RBCs present due to large immature RBCs (reticulocytes); iron deficiency anemia, B12/folate deficiency, hemoglobinopathies, sickle cell anemia, hemolytic anemias, posthemorrhagic anemias
What is the normal range for RBC count, male and female
Male: 4.35-5.65 trillion cells/L
Female: 3.92-5.13 trillion cells/L
What is the normal range of hemoglobin for males and females?
Male: 13.2-16.6 g/mL
female: 11.6-15 g/mL
What is the normal range of hematocrit for males and females?
Male: 38.3%-48.6%
Female: 35.5%-44.9%
What does a low reticulocyte count indicate?
aplastic anemia, vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, depletion of iron stores, chronic infection, cirrhosis, cancer, radiation
What is the normal WBC count?
3.4-9.6 billion cells/L
What is the normal platelet range for males and females?
Male: 135-317 billion/L
Female: 157-371 billion/L
What is the normal range for serum iron levels for males and females?
Male: 80-180mcg/dL
Female: 60-160mcg/dL
what does high serum iron indicate?
hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis, hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, lead toxicity, iron poisoning, massive transfusion
What does low serum iron indicate?
insufficient dietary iron or absorption of iron, chronic blood loss, late pregnancy, iron deficiency anemia, cancer, chronic GI/urinary blood loss
What is the normal range of ferritin in males and females?
Male: 12-300mcg/dL
Female: 10-150mcg/dL
What does high level ferritin indicate?
hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis, hemolytic anemia, megaloblastic anemia, liver disease (alcohol or inflammatory)
What does low ferritin levels indicate?
severe protein deficiency, iron deficiency anemia, hemodialysis
What is the normal range for transferrin saturation in males and females?
Male: 20-50%
Female: 15-50%
What does high transferrin saturation indicate?
iron overdose, hemolytic anemia, hemosiderosis, acute iron overload
What does low transferrin saturation indicate?
iron deficiency anemia, chronic illness
What is the normal range for total iron binding capacity?
250-460mcg/dL
What does high TIBC indicate?
oral contraceptives, late pregnancy, polycythemia vera, iron deficiency anemia
What does low TIBC indicate?
hypoproteinemia, inflammatory diseases, cirrhosis, hemolytic anemia, pernicious anemia, sickle cell anemia
What is the normal level of serum B12?
160-950pg/mL
What does high serum B12 indicate?
leukemia, polycythemia vera, severe liver dysfunction, myeloproliferative disease
What does low serum B12 levels indicate?
pernicious anemia, malabsorption, IBD, intestinal worms, achlohydria
What is the normal serum folate level?
5-25ng/mL
What is the normal RBC folate level?
360-14nMol/L
What does high folate levels indicate?
pernicious anemia, vegetarianism, recent blood transfusion
What does low folate levels indicate?
folic acid deficiency, hemolytic anemia, malnutrition, malabsorption, celiac disease, cancer, late pregnancy, alcoholism, anorexia, drugs
Anisocytosis
variation in RBC size
Poikilocytosis
variation in RBC shape
Rouleaux
RBCs arranged like "stacked coins"
Liver disease, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, chronic inflammatory disease
Agglutination
RBCs randomly clumped together
Howell-Jolly Bodies
Small, round remnants of nuclear material remaining in RBC
post-surgical splenectomy, functional asplenia, hemolytic anemia, megaloblastic anemia
Nucleated normoblasts
presence of immature RBCs
anemia, chronic hypoxemia, marrow-occupying neoplasm, fibrotic tissue
Basophilic stippling
bodies in cytoplasm of RBCs
lead poisoning, reticulocytosis
Siderocyte
RBC containing iron not bound by HGB
sideroblastic anemia, hemoglobinopathies, hemosiderosis, myelodysplastic syndrome, lead, ethanol
Eliptocyte/ovalocyte
severe iron deficiency, hereditary
Target cell/codocyte
thalassemia, liver disease, hemoglobinopathies, post-splenectomy
Tear drop
myelofibrosis, underlying marrow process
Schistocyte
fragmented RBCs
Hemolytic anemia, DIC, TTP, mechanical valve induced
What is leukocytosis? What are causes of it?
increased leukocytes
infections, leukemia, trauma, stress, tissue necrosis, inflammation
What is leukopenia? what are causes of it?
Decreased leukocytes
bone marrow suppression, infiltration, or failure
dietary deficiency, peripheral destruction, chemo, overwhelming infections, sequestration at site of infection, autoimmune disease
What is polycythemia? what causes it?
"thickening" of blood due to:
1. chronic hypoxia
2. dehydration, hemoconcentration
What is anemia? what causes it?
Decreased oxygen carrying capacity of blood
Hereditary hemoglobinopathies, hemorrhage, hemolysis, pregnancy, chemo, cancer, chronic illness, renal disease, inflammatory diseases, bone marrow failure, pernicious anemia, dietary deficiency, subacute endocarditis, prosthetic valves, overhydration
What is thrombocytosis? what causes it?
increased number of platelets
reactive: infection, cancer, blood loss, splenectomy
myeloproliferative disorders: polycythemia
Hemolysis, chronic myeloblastic leukemia, essential thrombocytosis
What is thrombocytopenia? what causes it?
Reduction of platelets
destruction from drugs (quinine, heparin), hypersplenism, DIC, autoimmune (ITP), thiazides, estrogen, etoh
What counts as low, very low, and critically low platelet levels?
Low: 10,000-50,000
Very low: 5,000-10,000
Critical: <5,000 ; WITHOLD SURGERY
What is lymphocytosis? what causes it?
Elevated levels of lymphocytes (B/T/NK)
chronic bacterial infection, viral infections (mumps, rubella, hepatitis, mono), ALL/CLL, multiple myeloma, radiation
What is lymphocytopenia? what causes it?
Reduction of lymphocytes (B/T/NK)
Leukemia, sepsis, infection, immunodeficiency (later stages of HIV, chemo, radiation), adrenocorticosteroids, Lupus
What is neutrophilia? What causes it?
Increased number of neutrophils
Physical/emotional stress, trauma, acute bacterial infection, AML/CML, cushing's, inflammatory disorder (RA, thyroiditis, rheumatic fever), metabolic disorders (ketoacidosis, gout)
What is neutropenia? What causes it?
Reduction of neutrophils
aplastic anemia, dietary deficiency, overwhelming bacterial infection (especially in elderly), viral infections (hepatitis, flu, measles), radiation therapy, chemo, addison's
What is monocytosis? what causes it?
Increased number of monocytes
chronic inflammatory disorders, viral infections (EBV/TB/UC), malaria
What is monocytopenia? what causes it?
Reduction of monocytes
aplastic anemia, hair-cell leukemia, prednisone
What is eosinophilia? What causes it?
increased number of eosinophils
parasitic infection, allergic reaction, eczema, leukemia, autoimmune disorders
What is eosinopenia? What causes it?
Decreased eosinophil count
increased adrenosteroid production
What is basophilia? what causes it?
increased number of basophils
myeloproliferative disease, leukemia, uremia
What is basopenia? What causes it?
Reduction of basophils
acute allergic reaction, hyperthyroidism, stress reaction
What is a tiger or gold top used for?
Gel substance to separate cells from liquid and clot activator -- chemistries
What is a red top used for?
serum on top without additives for anticoagulation; chemistries, drug levels, blood banking
What is a light blue top for?
plasma on top with sodium citrate anticoagulant
PT/INR, PTT, coagulation studies, hematology labs
What is a lavender top used for?
plasma on top with EDTA anticoagulant
CBC, hematology labs
What is a green top used for?
plasma on top, heparin anticoagulant to be analyzed quicker than red tube
chemistries, blood gases, ammonia
What is a yellow top used for?
Citrate dextrose to preserve RBC
blood grouping, typing, cultures
What is navy blue top used for?
EDTA, one without
Trace metals (arsenic etc)
What is a gray top used for?
sodium fluoride oxalate preventing glycolysis
glucose tolerance, lactose tolerance
What is a black top used for?
plasma on top, sodium citrate anticoagulant
ESR
Target Cell
What RBC morphology is this?
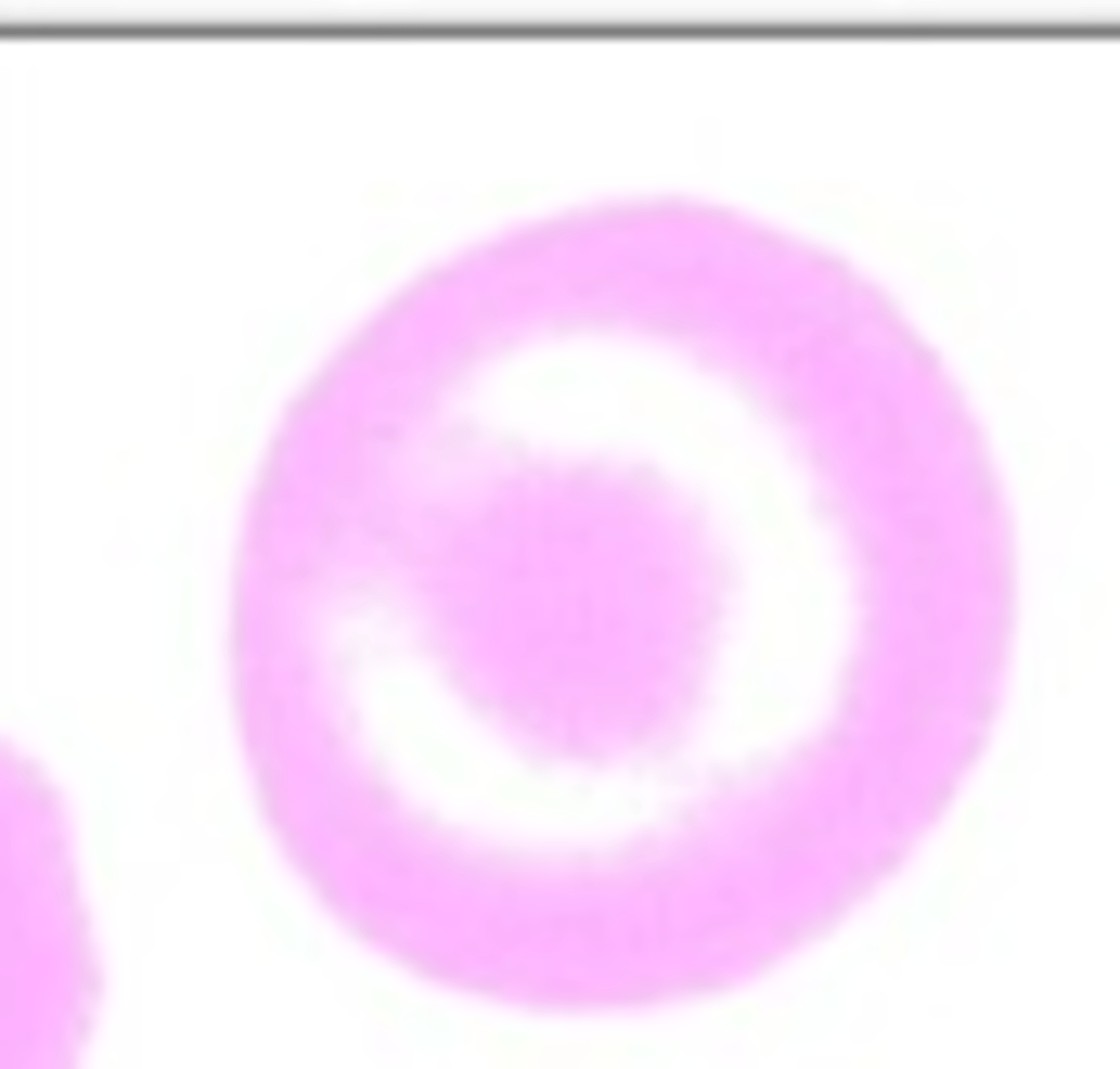

Acanthocyte
What RBC morphology is this?
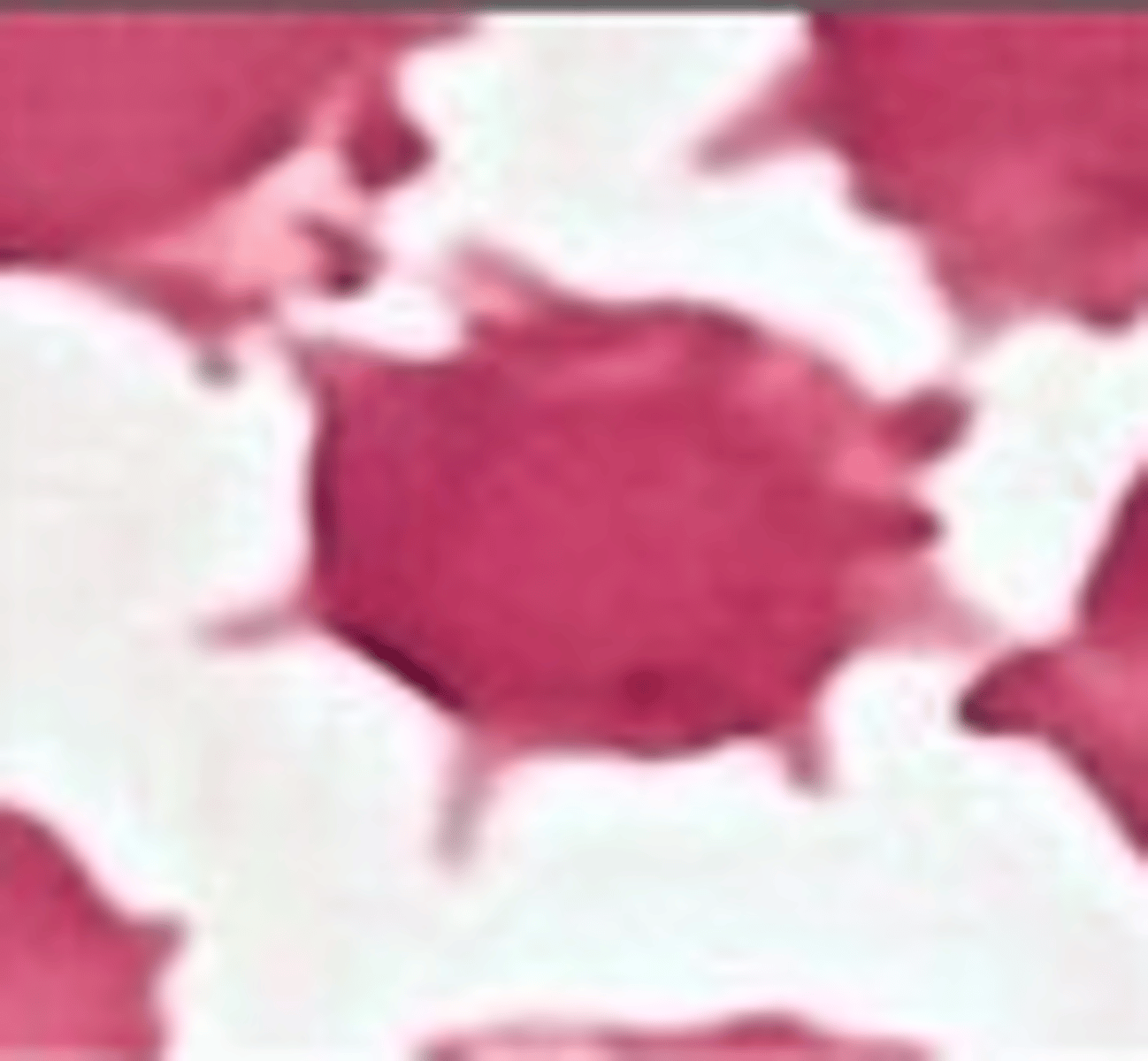

Echinocyte (Burr cell)
What RBC morphology is this?
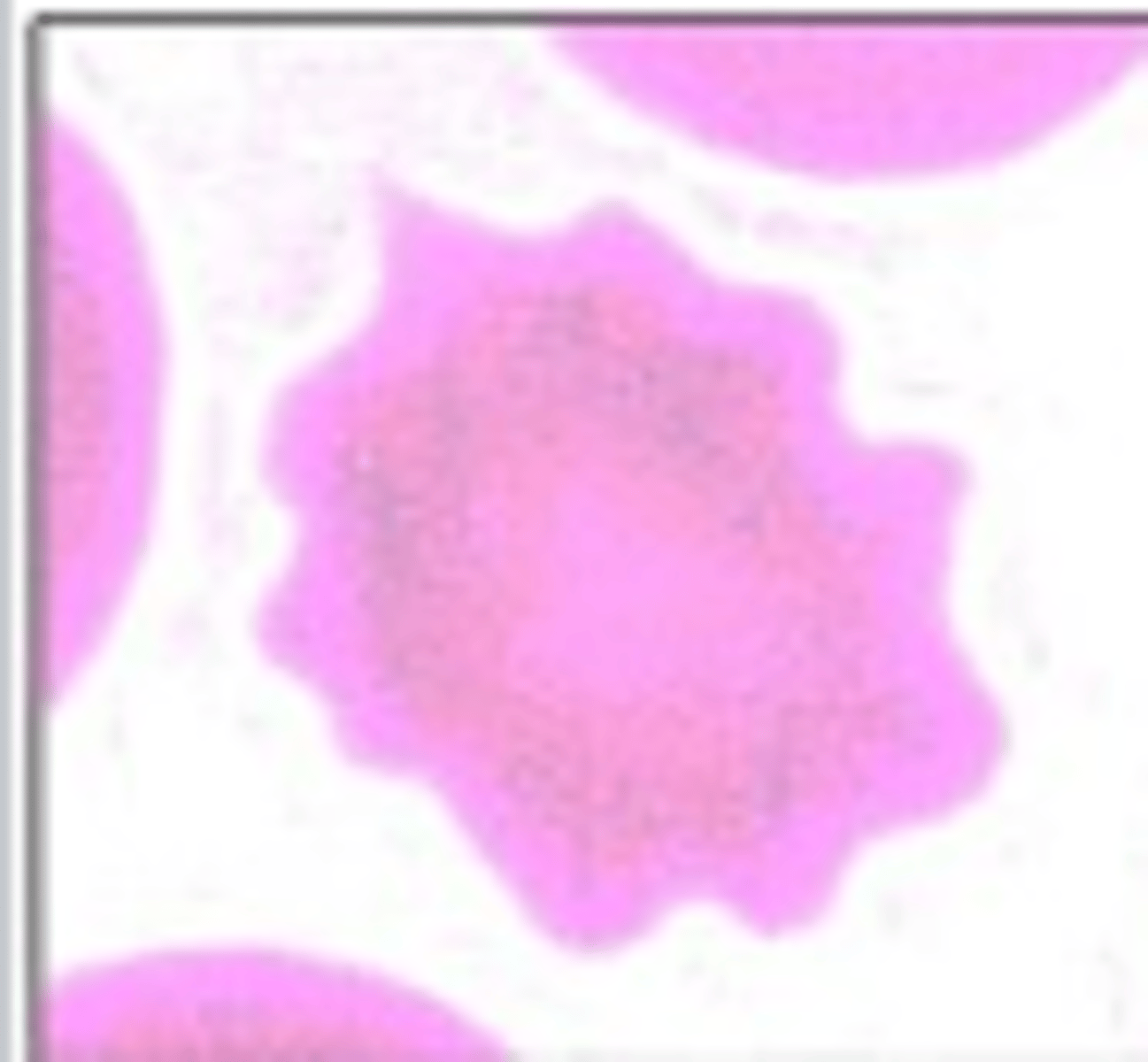
Sickle Cell (drepanocyte)
What RBC morphology is this?
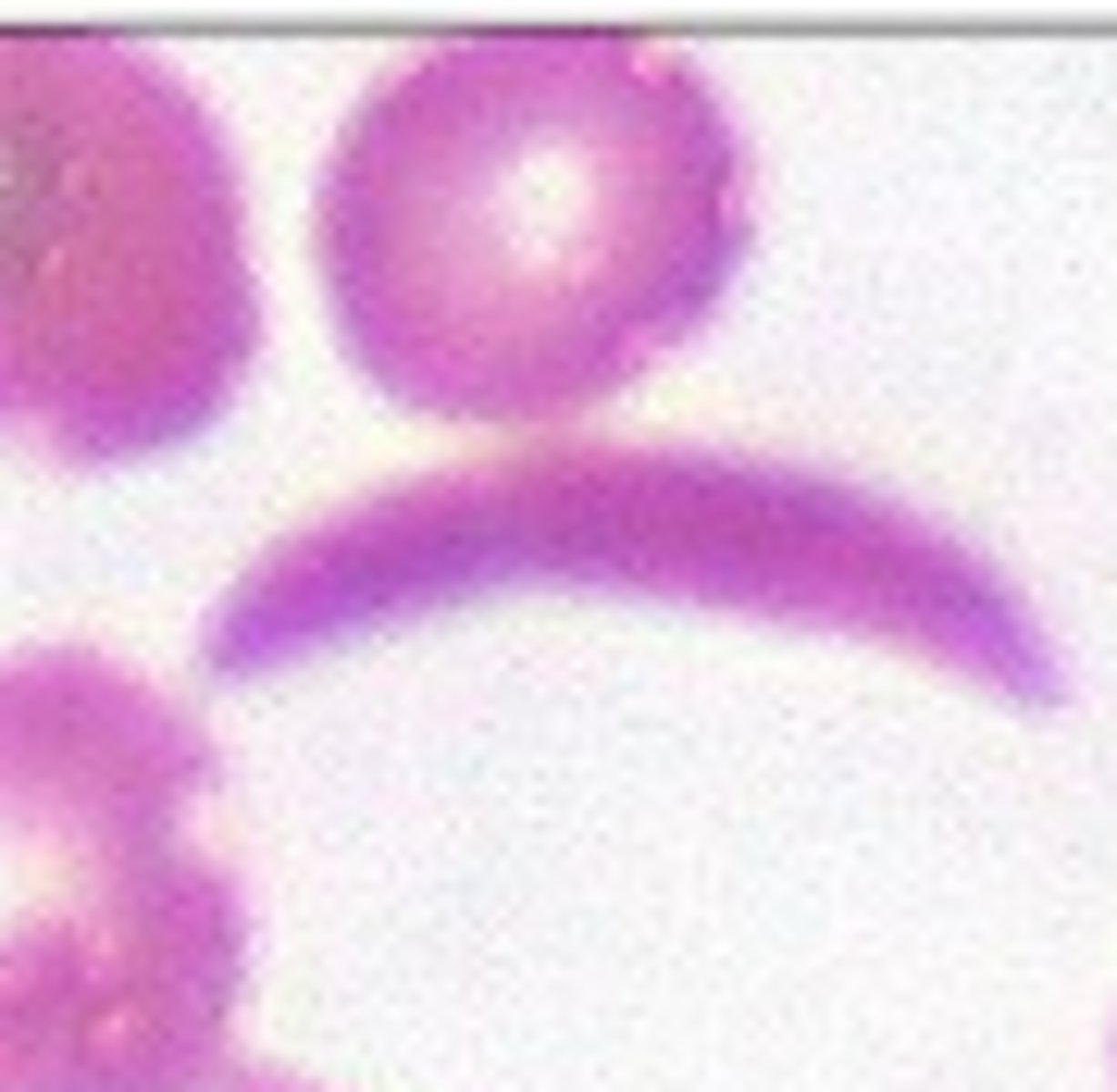
Dacrocyte (Tear drop cell)
What RBC morphology is this?
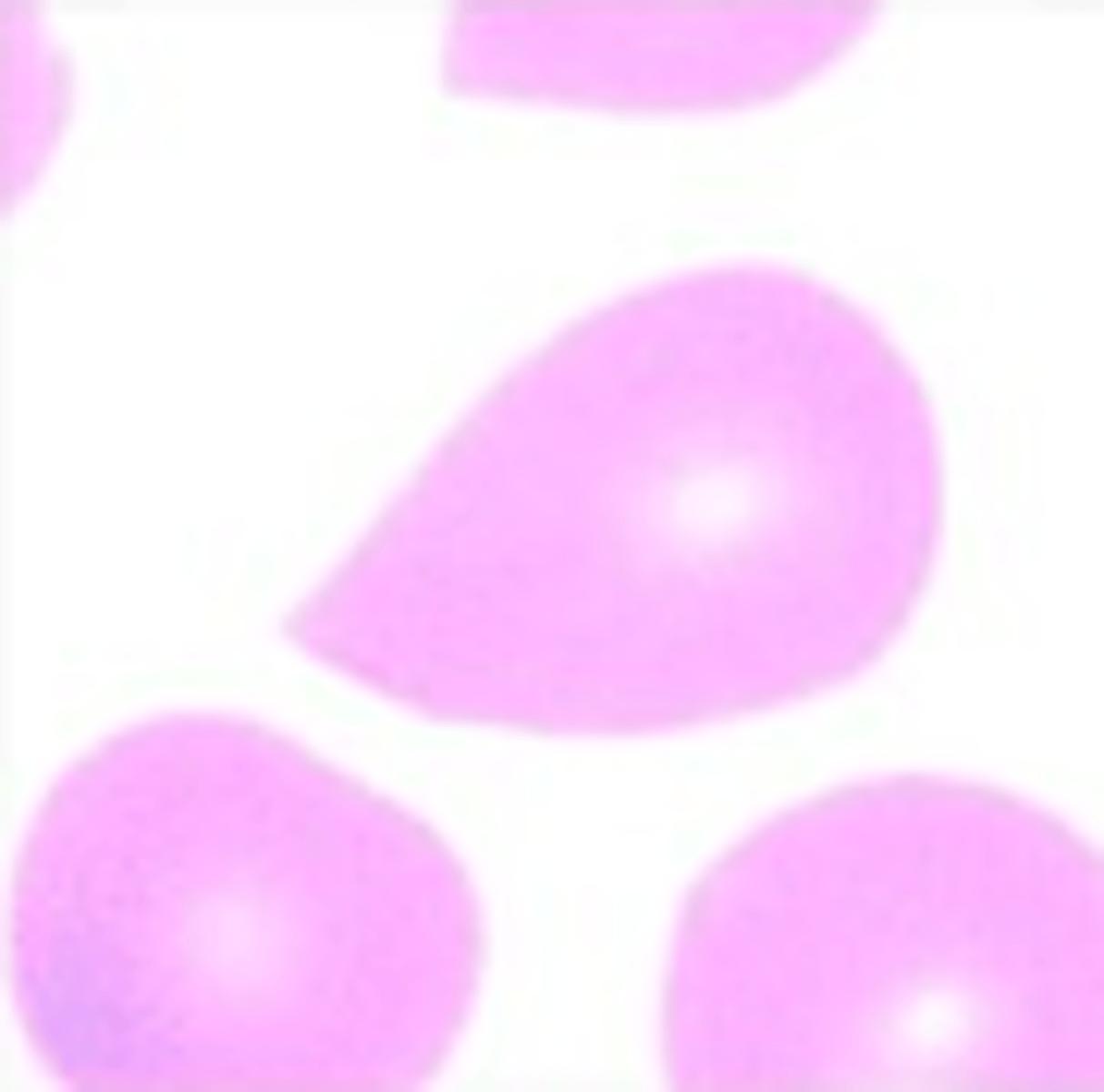
Stomatocyte
What RBC morphology is this?
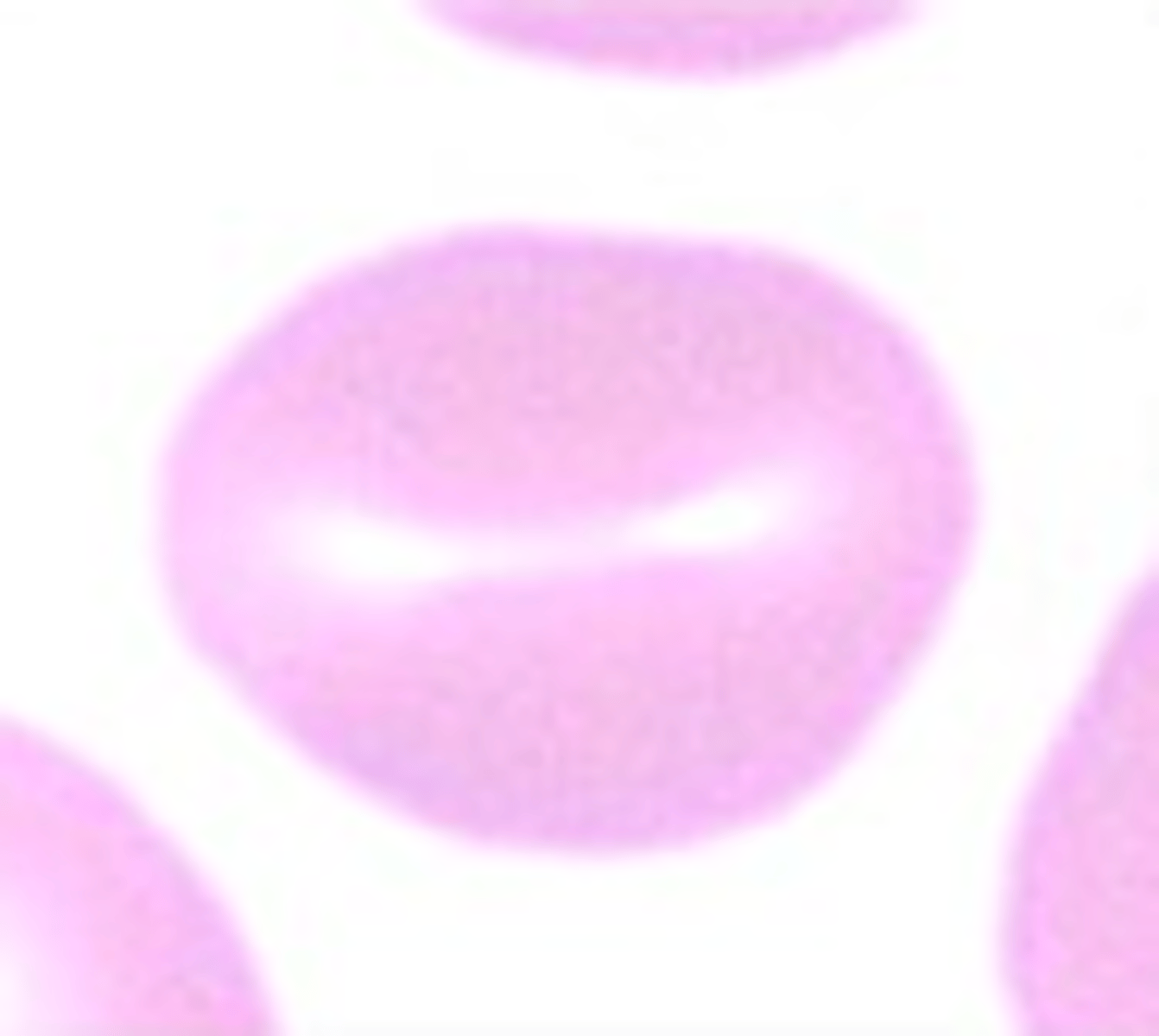

Spherocyte
What RBC morphology is this?
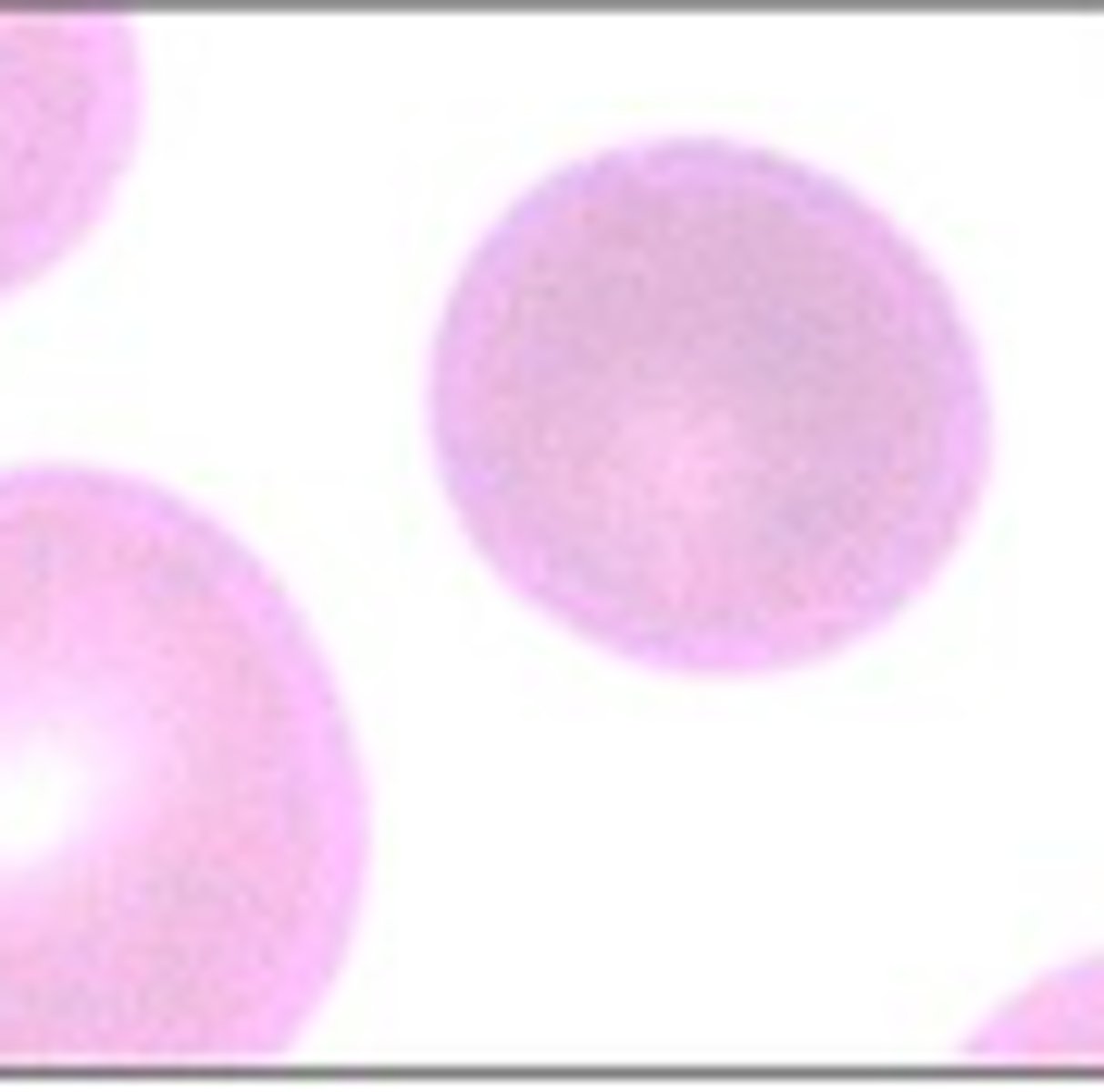
Schistocyte
What RBC morphology is this?
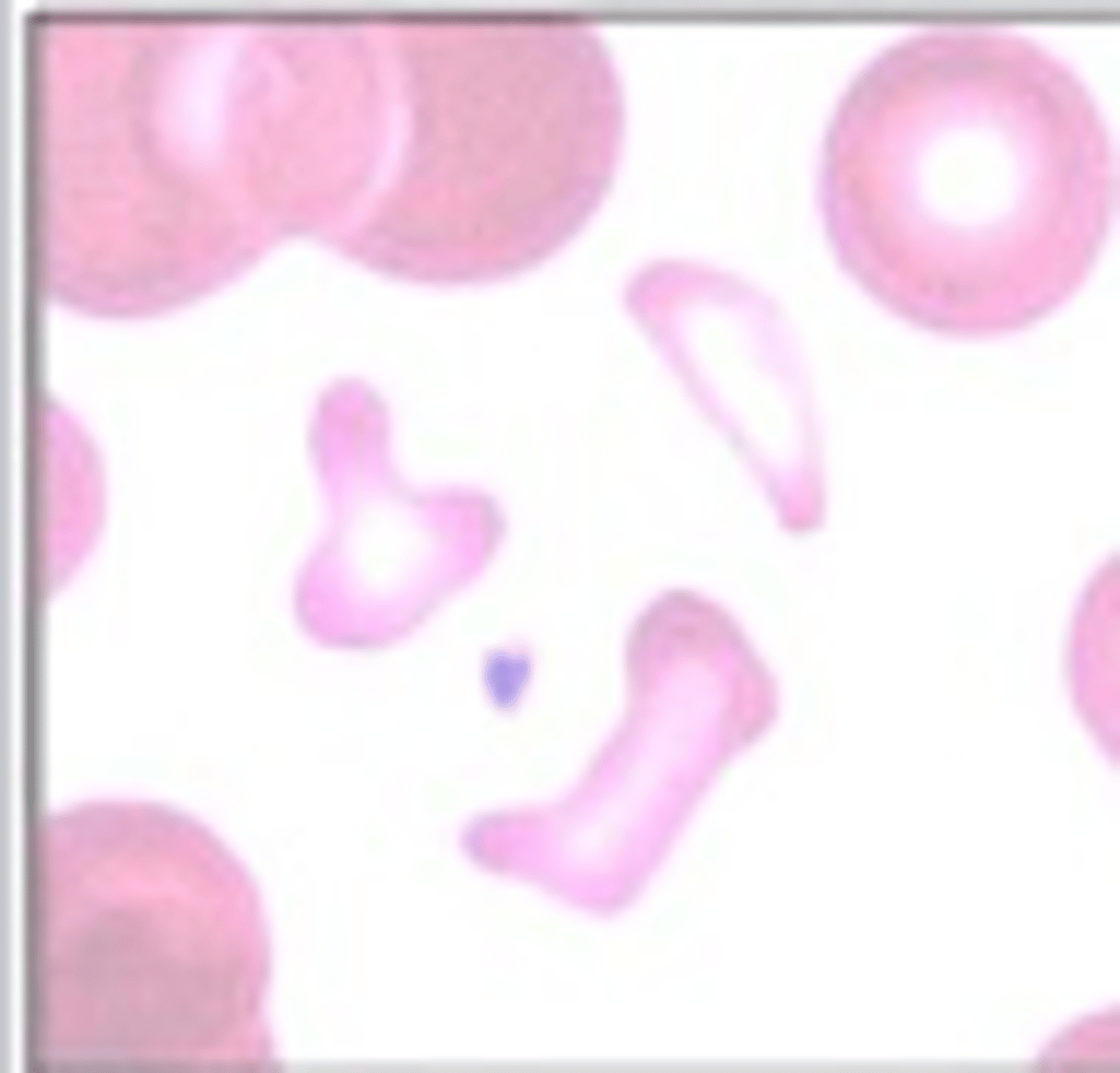
Elliptocyte
What RBC morphology is this?
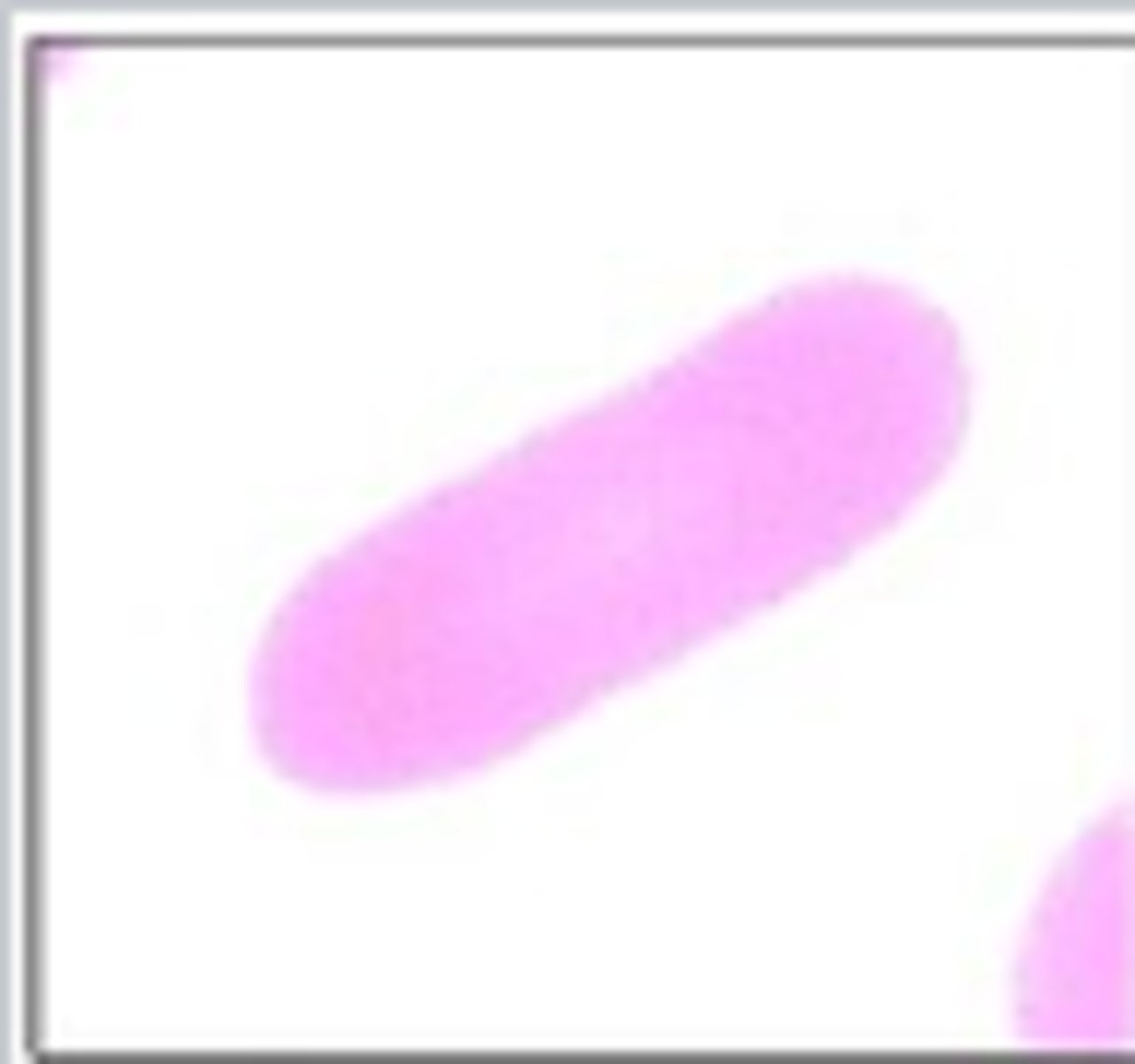
Basophilic Stippling
What RBC morphology is this?