✔️✔️17 & 18 - Surgery of Bladder & Urethra I & II 🟢
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
LECTURES 17 & 18 POWERPOINT INFO
LECTURES 17 & 18 POWERPOINT INFO
A surgical incision into the urinary bladder
What is a cystotomy?
The creation of an opening into the bladder
What is a cytostomy?
Removal of a portion of the urinary bladder
What is a cystectomy?
An incision into the urethra
What is a urethrotomy?
Urinary bladder calculi
What is cystolithiasis?
Removal of urinary bladder calculi
What is cystolithetomy?
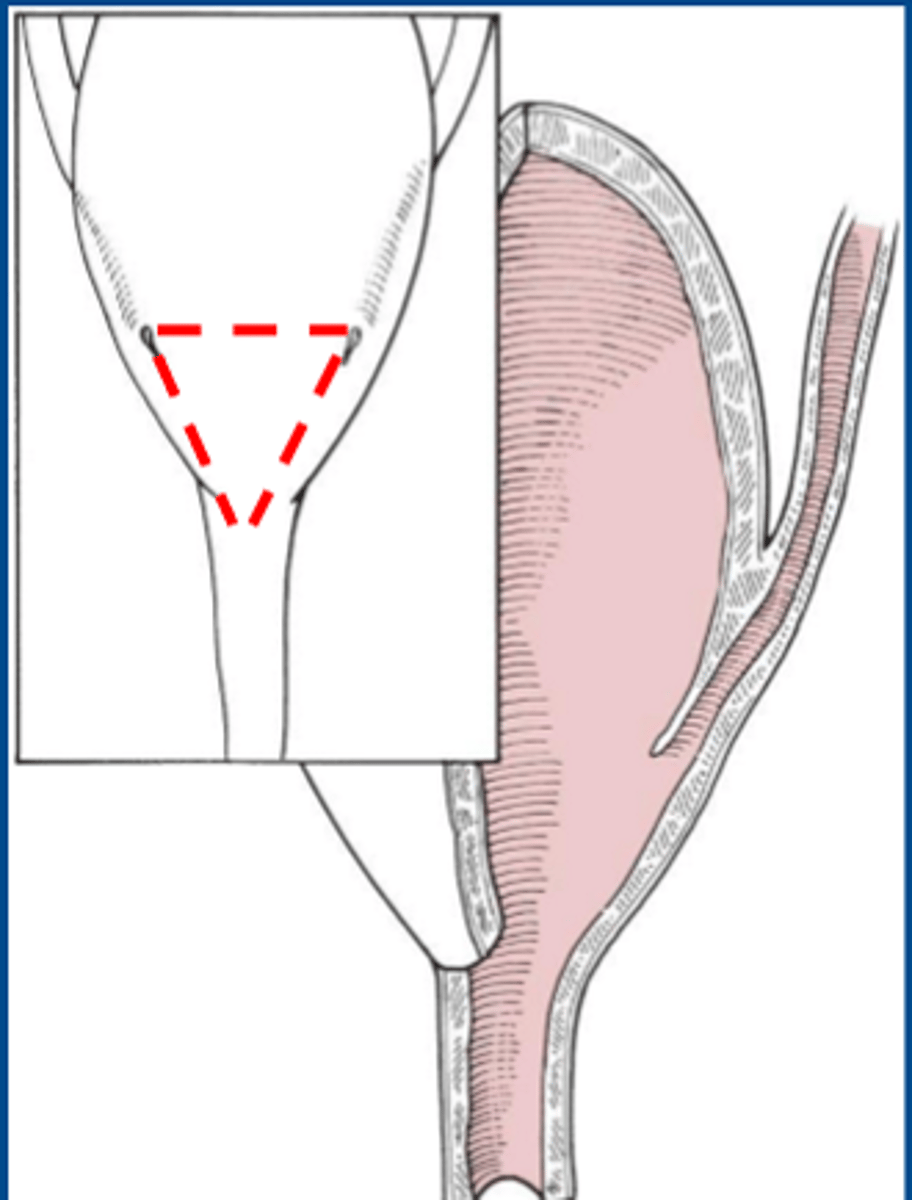
Trigone
What is the area of the bladder that is a smooth triangular portion of the mucous membrane at the base of the bladder where the ureters empty?
Prepubic catheterization
What is usually performed to provide cutaneous urinary diversion in animals with urethral obstruction or trauma?
Presence of urine in the abdominal cavity
What is uroabdomen?
Creation of permanent fistula into the urethra
What is a urethrostomy?
Trigone
What is this?
-Remove calculi
-Repair trauma
0Resect or biopsy neoplasms
-Correct congenital abnormalities
-Evaluation of urinary tract infection resistant to treatment
What are the indications for cystotomy?
-Struvite
-Calcium oxalate calculi
What are the most common canine uroliths?
Struvite calculi
What type of urolith in dogs is most frequently associated with infection?
Cystotomy
What surgery is used to treat urinary calculi?
Retrihydropropulsion
What is used to propel urethral stones back into the bladder?
Failure to remove all stones
What is the most common complications for cystotomy?
Hemorrhage
What is the main complication of urethrotomy?
Lithotripsy
What uses shock waves to break up stones in the kidney, bladder, or ureter?
-Provide cutaneous urinary diversion in animals with urinary obstruction, traumatized urethra, and surgically repaired urethra
-Bladder atony secondary to neurologic disease
-Prevention of overdistention of bladder after surgery
When is cystotomy indiciated?
-Male dogs to remove urethral calculi that cannot be retrohydropropulsed into the bladder
-Facilitate placement of catheters into the bladder
-Occasionally biopsy of obstructive lesion
What are the indications for urethrotomy?
-Remove calculi from distal penile urethra
-Place foley catheters into urinary bladder
What are the indications for prescrotal urethrotomy?
-Removal calculi lodged at ischial arch
-Place catheters into bladder of large male dogs
What are the indications for perineal urethrotomy?
-Recurrent obstructive calculi that cannot be managed medically
-Calculi that cannot be removed by retrohydropropulsion or urethrotomy
-Urethral stricture
-Urethral or penile neoplasia or severe trauma
-Preputial neoplasia requiring penile amputation
What are the indications for urethrostomy?
If castration is an option
When is scrotal urethrostomy preferred?
Perineal urethrostomy
What type of urethrostomy is routinely performed in cats?
Scrotal urethrostomy
What type of urethrostomy in dogs are preferred because the urethra is wider and more superficial and is surrounded by less cavernous tissue?
-Prevent recurrence of obstruction in male with feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC)
-Treat obstruction that cannot be eliminated by catheterization
-Treat strictures secondary to urethral obstruction and catheterization
What are the indications for feline perineal urethrostomy?
Urethral opening of insufficient diameter and predispose your patient to urinary tract blockage
In feline perineal urethrostomy, you pass a closed halsted mosquito hemostat up the urethra and passed to level of boxlocks without resistance. What could happen is you failed to perform this step?
LECTURES 17 & 18 NOTES
LECTURES 17 & 18 NOTES
removal of calculi
What is the most common reason for a cystotomy?
can seed the cancer into the abdominal wall if going through body wall rather than a catheter
If you suspect that there is transitional cell carcinoma, do not do a cystocentesis. Why?
apex
Which part of the bladder is good for placing stay sutures?
ventral
_____ approach is often prefered for a surgical approach for a cystotomy
tough
Is the bladder a delicate or tough organ?
simple continuous
What pattern do we use to close the bladder?
1. express - but be careful as you can push stones down the urethra
2. place catheter - can help push stones back up into the bladder, which may be helpful
3. intraoperative cystocentesis - come through the wall with a needle with/without suction
What can we do to empty the bladder if its too full?
stone formation
If there is any type of foreign body in the urinary bladder, there is propensity for _____
simple continuous on the mucosa & then the outer layer
How can we suture a very inflamed bladder, with potentially severe hemorrhage?
true
T/F - We always need to look at/analyze the stones themselves, not just the urine
cats
In [dogs/cats], struvite formation is not associated with infection
obstruct
In male dogs especially, if you get the stone too small and they push it down the urethra, they can _____
shorter
The female urethra is [longer/shorter] than a males
true
T/F - The urachal diverticula can be removed during cystotomy
didn't get all the stones
What is the #1 complication with stone removal surgery?
hemorrhage
What is the main complication of urethrotomy?
opening the abdomen, making a hole in the bladder, & placing device, suturing the bladder to body wall with device in place
Describe prepubic catheterization
getting the stones back into the bladder
What is our first "choice"/course of action when doing a urethrotomy?
urethra
The _____ really likes to hemorrhage!
yes - can use #15
Is it recommended to change the blade when cutting into the urethra?
boxlocks
During a feline perineal urethrostomy, the hemostat should be able to be passed to the level of the _____ without resistance (~5mm diameter)
skin
During a feline perineal urethrostomy, suture the urethral mucosa to the _____