Lecture 5: Biological Targets and Their Modulation 2
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Types of protein Targets for drugs
Enzymes
Drugs usually inhibit the enzyme
Effect: block or reduce formation of the enzyme product
Receptors:
Drugs can activate (agonist) or block (antagonist) the receptor
Some drugs can act as both
Effect: amplify or suppress receptor signaling
Ion channels
Drugs can open or close the channel
Some drugs can perform both functions
Effect: amplify or suppress channel activity
Structural proteins (less common)
Drugs interfere with assembly or disassembly of protein structure
Biological mechanism of top 50 drugs
Enzyme inhibitors: 38%
Receptor antagonists: 24%
Receptor agonists: 12%
Ion channel modulators: 8%
Unknown/miscellaneous: 18%
Enzymes catalyze reactions
Provide a designer solvent for the transition state of a reactions
Enzymes bind very tightly to transition states
Designer solvent for Transition state
Enzymes stabilize the reaction transition state
Best binding occurs at the transition state, not the substrate or product
Enzyme Active site is Relatively small
The active site is a tiny pocket where catalysis occurs
The rest of the enzyme functions mainly as a scaffold
Only a small part of the enzyme touches the substrate
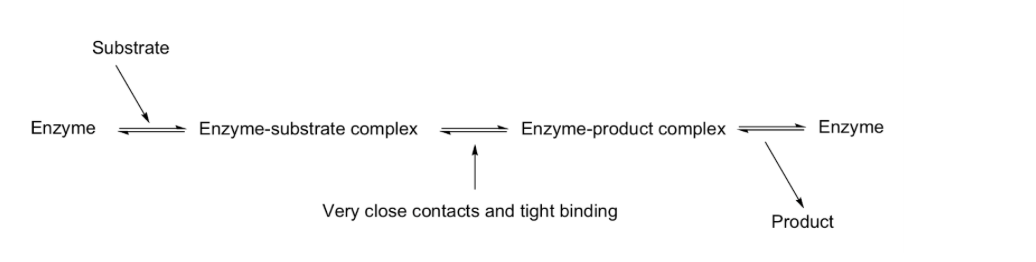
Enzyme (E) binds to substrate (S)
Binding forms the enzyme-substrate complex (ES)
The process is reversible (equilibrium)
Enzyme changes shape to better fit the substrate
The substrate also adjusts its shape during binding
Reaction occurs
In the enzyme-substrate complex (ES), the substrate is positioned correctly for reaction
The substrate is converted into product within the active site
The enzyme may undergo shape changes during catalysis
Product is released
After catalysis, the product is formed in the active site
The product has lower affinity for the enzyme that the transition state or substrate
Product is released from the enzyme
The enzyme returns to its original form, ready to catalyze another reaction
THeories of Enzymatic conformational change
Lock and key (older model)
Active site is a rigid picket already shaped to fir the substrate exactly
Induced fir(current model)
Substrate binding causes the enzyme to change shape
Conformational change can “activate” or “deactivate” the enzyme
Remember that the substrate is also flexible and will change conformation during binding
Molecules are not static
Often drawn as fixed shapes, but this is an oversimplification
Enzymes and substrate are constantly moving and flexing
Shape changes are gradual, not instant and often asymmetrical
Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
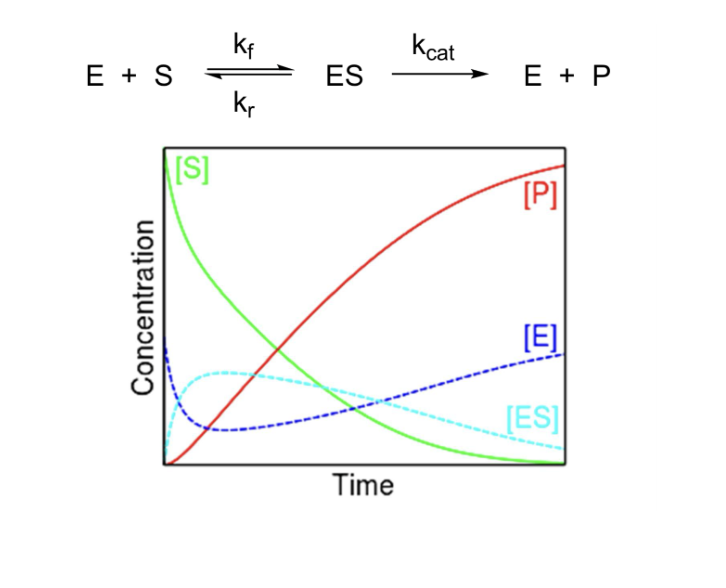
Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
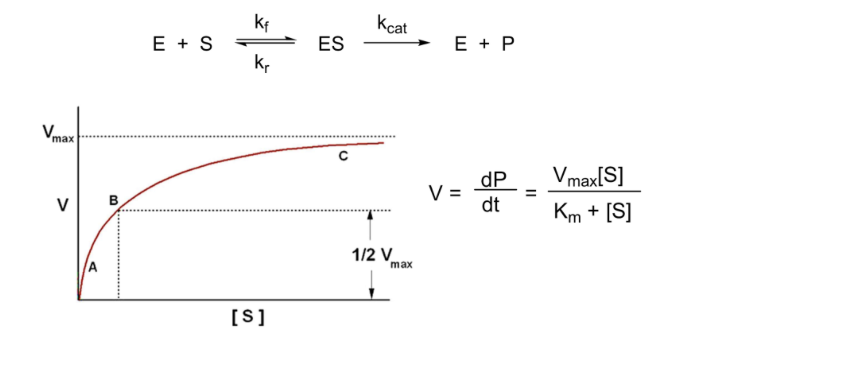
Kcat and Km
Kcat = turnover rate
Measure of how efficiently ES complex produces product
Larger Kcat = easier reaction
Km= [S] at 1/2 Vmax
Ratio of Kcat/Km used to index enzyme efficiency
High ratio = more efficient enzyme
Also used as a specificity constant
Compare ration for different substrates
Kd = dissociation constant = Kr/kf
Measure of binding between E and S
Small Kd = tight binding
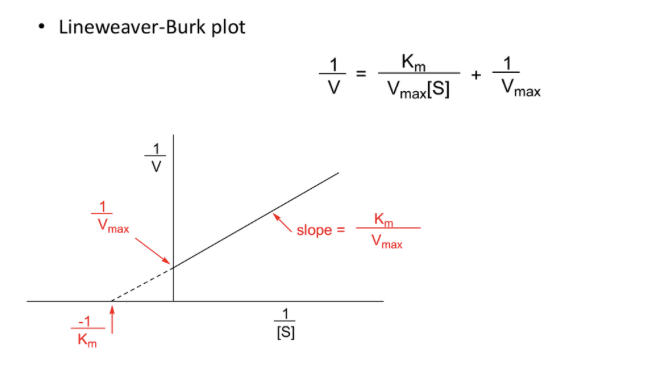
Rearranging the equation gives a linear relationship
Enzyme inhibition
Competitive inhibition
Inhibitor competes with substrate for the active store
Binding occurs at the active site
Substrate is blocked from binding
Non-competitive inhibition
Inhibitor binds to enzyme but not at the active site (allosteric site)
Substrate may still bind to the active site
Inhibitor binding prevents catalysis (disrupt enzyme function or conformation change)
Uncompetitive inhibition (very rare)
Inhibitors binds only to ES complex
Binding prevents the reaction (destroys catalytic ability)
Competitive inhibitor
Inhibitor molecule competes with substrate molecule for active site
Bindind is in the active site
Substrate cannot bind
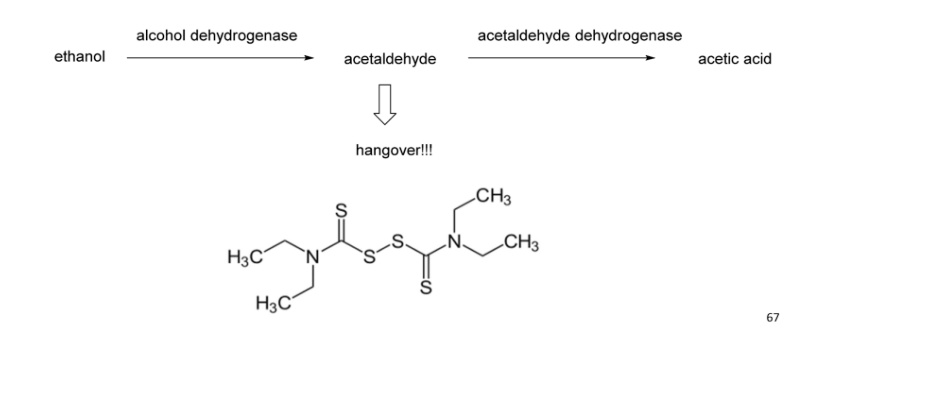
Disulfiram(Antabuse) Is competitive
Blocks aldehyde dehydrogenase
Generates rapid and severe hangover when drinking
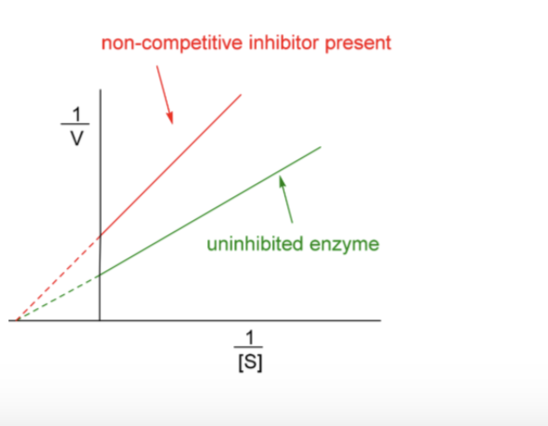
Non- Competitive Inhibitor
Inhibitor binds to enzyme but not in active site
Substrate binds to active site
Inhibitor binding preventing ES complex from forming (prevents or alters conformational change)
Non-competitive inhibitor changes the slope and intercept
Km appears unaltered
Slope and intercept change
Fluconazole is non-competitive
Blocks cytochrome P450
Does not bind to active site
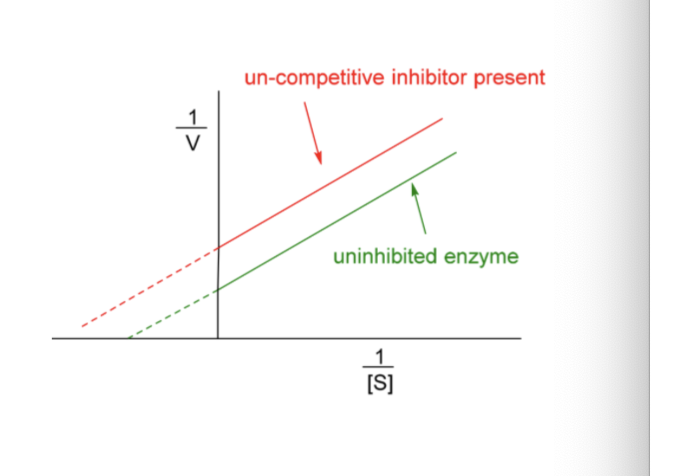
Uncompetitive Inhibition (very rare)
Inhibitor binds to ES complex
Binding destroys catalytic ability of ES complex
Un-competitive inhibitor changes the intercept
Vmax and Km decreased
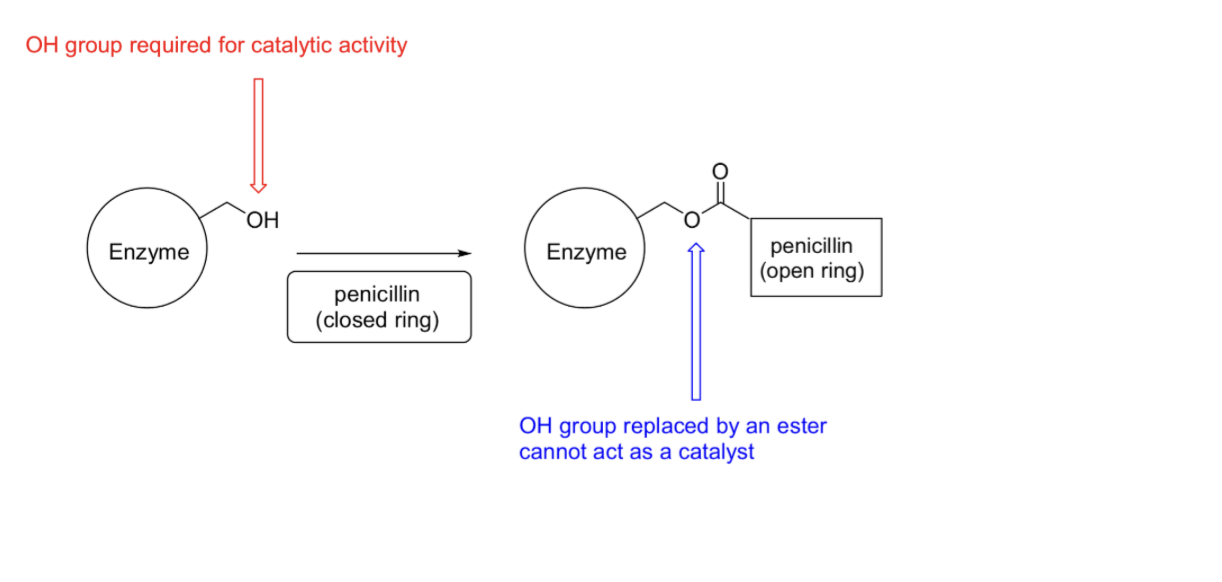
Irreversible inhibitors
Also known as suicide inhibtors
Bond covalent to enzyme
Inhibit by altering conformational or disabling functional groups
Specific inhibitors usually bond in active site
Penicillin is an irreversible inhibitor
Blocks transpeptidase, enzyme used to finish cell wall construction
Penicillin reacts covalently with transpeptidase
Messengers work by inducing shape changes
Chemical interactions between messenger(ligand) and receptor change the shape of the receptor
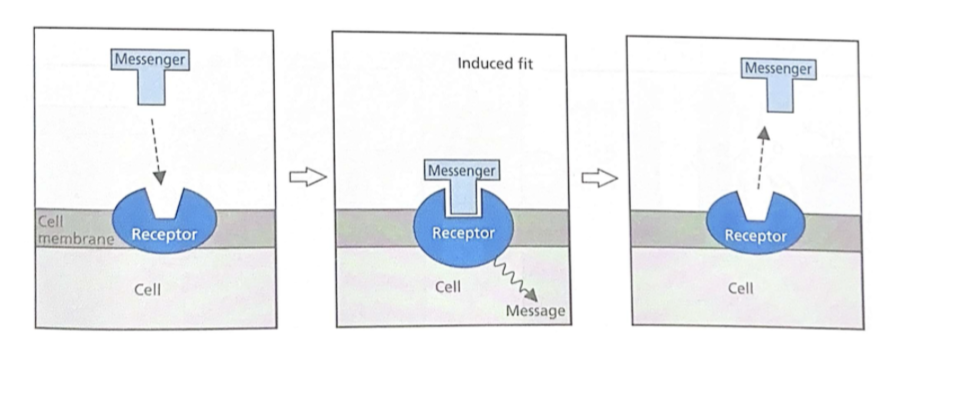
Chemical messaging via binding
Chemical interactions between messenger and receptor change the shape of the receptor
Shape change allows a second messenger to bind or to be released
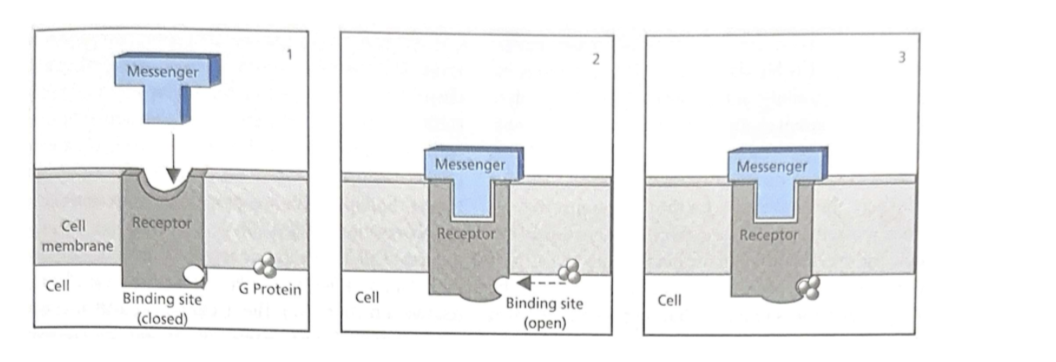
Chemical messaging via catalysis
Chemical interactions between messenger and receptor change the shape of the receptor
Shape change allows creates/destroys catalytic function
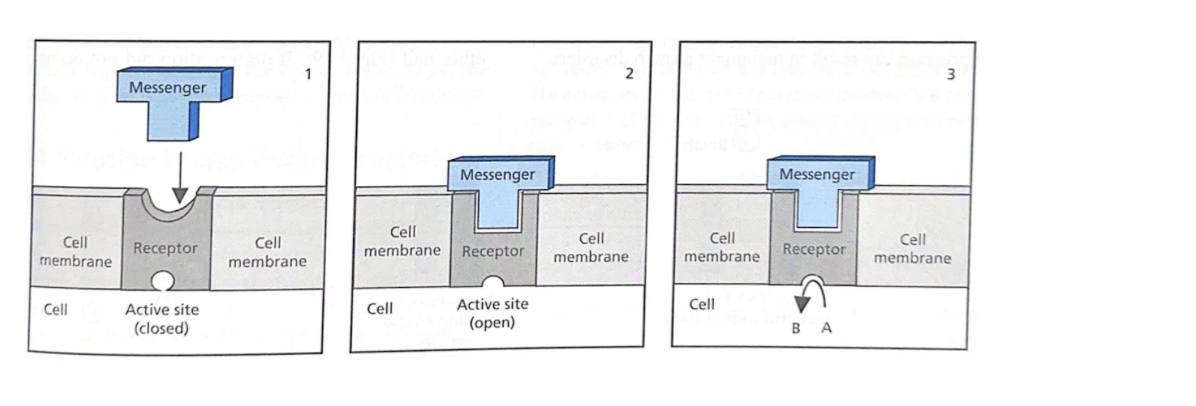
Agonists “SImulate” The normal messenger
Agonist binding induces shape change that results in transmission of a signal
Usually bind at same location (Active site) as messenger
Some agonists bind to other locations (allosteric sites)
Allosteric modulators
Asthma drugs are adrenaline agonists
Adrenaline receptors in lungs stimulate bronchial opening when activated
Bing to active site of the noradrenaline receptor
Benzodiazepines are Allosteric Modulators
Binds allosterically to GABA ion channel
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter
In presence of benzodiazepines the channel opens more readily and stays open longer )lower concentration of GABA opens the channel)
Antagonists block normal receptor function
Antagonist binding induces abnormal shape change that results in no signal transmission
May bind at same location (active site) as messenger
May bind at other locations (allosteric sites)
Tagamet is an active site antagonist
Binds to histamine binding site
Distance between main binding domains is larger in histamine
Stretches the active site and produces antagonism
Allosteric Antagonists
Can bind near or even partly inside the active site
Can bind in a distal location
Partial agonists (2 possibilities)
Agonist binds to receptor and produces non-ideal conformational change
Weak signal is sent (short duration)
Agonist capable of binding to receptor in more than one way
One binding mode gives agonism
Other binding mode gives antagonism
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist of opioid receptor
Used to block the effects of opioid poisoning
Inverse agonist
Some receptors have a background activity
Receptor shows weak function in absence of messenger
Antagonist changes normal confirmation, shutting off this background activity
GABA agonists produce relaxation
GABA inverse agonists produce agitation
Clozapie shows inverse agonist behaviour
Originally thought to be a weak D2 (dopamine receptor) antagonist
Recently found to be an inverse agonist of D2
Measuring drug beahviour
Use a biological assay
Qualitative (yes/no)
Quantitative (number)
In vitro
Using biological chemicals, cells or tissues
In vivo
Tests done in living animals
In vitro methods are ALWAYS preferred
General Assay types
HTS (qualitative)
Routine SAR (quantitative)
Kinetics or special studies (quantitive)
Cell based
Antibiotics, antivirals, anti-cancer, metabolism studies
Result of several properties
Tissue based
Permeability
Complex
HTS
Emphasis on speed
Usually qualitative (yes/no at set concentration)
Fully automated
Preferred detection method is fluorescence
Some assays may use radioactivity to measure effects
Usually performed on 384 or 1536 well plates
Assays for routine work
Emphasis on accuracy
Usually quantitative (concentration or rate)
Semi-automated or manual
Preferred detection method is fluorescence
Some assays may use radioactivity to measure effects
Cell-based assays
Usually quantitative
Required skilled technicians
Usually slow
SOmetimes difficult to interpret results
Black box
Industry uses some standardized cell-based assays