Learning and Memory II
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:03 PM on 5/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
what were the results from Thorndike’s puzzle box experiment??
2
New cards
what is the law of effect?
behaviour that leads to a positive outcome is more likely to occur in the future
3
New cards
what is the law of exercise?
connections between responses and outcomes are strengthened by repetition
4
New cards
what is the law of readiness?
learning is motivated by an internal state
5
New cards
what is response-outcome learning?
associations between response/behaviour and outcome
6
New cards
what is learning of adaptive behaviour?
learning through experience of success and failure (trial and error learning)
7
New cards
what is a reinforcer?
a stimulus/event that increases the likelihood of the preceding behaviour to occur
8
New cards
what is a positive reinforcer?
stimulus (usually positive) produced by the behaviour that increases the likelihood of the preceding behaviour to occur
9
New cards
what is a negative reinforcer?
Stimulus (usually negative) eliminated by the behaviour that increases the likelihood of the preceding behaviour to occur
10
New cards
what is a punishment?
Negative stimulus/event that decreases the likelihood of the preceding behaviour to occur
11
New cards
what is omission?
Elimination of positive reinforcer decreases the likelihood of preceding behaviour
12
New cards
what is a reinforcement schedule?
a rule that dictates when a reward is given
13
New cards
what are the two types of reinforcement?
* continuous reinforcement: each behavioural response is reinforced
* partial reinforcement: behaviour is reinforced only part of the time
* partial reinforcement: behaviour is reinforced only part of the time
14
New cards
what is a ratio schedule?
reinforcement is given after every *n*th response
* fixed = response is always constant
* variable = response requirement varies around the average
* fixed = response is always constant
* variable = response requirement varies around the average
15
New cards
what is an interval schedule?
reinforcement is given after a certain amount of time
* fixed = reward intervals are constant
* interval = reward interval varies around mean time
* fixed = reward intervals are constant
* interval = reward interval varies around mean time
16
New cards
what are the principles of associative learning?
* Learning through reinforcement
* Association by ***contiguity***
* Co-occurrence in space and time
* Arbitrariness
* We can learn associations between any stimuli and between any response and outcome
* Empty organism
* Organism is black box – collection of associations
* Passive organism
* Learning happens TO the organism
* Association by ***contiguity***
* Co-occurrence in space and time
* Arbitrariness
* We can learn associations between any stimuli and between any response and outcome
* Empty organism
* Organism is black box – collection of associations
* Passive organism
* Learning happens TO the organism

17
New cards
what is taste aversion learning?
a learned association between the taste of a food and illness
(causes subject to avoid eating that food)
(causes subject to avoid eating that food)
18
New cards
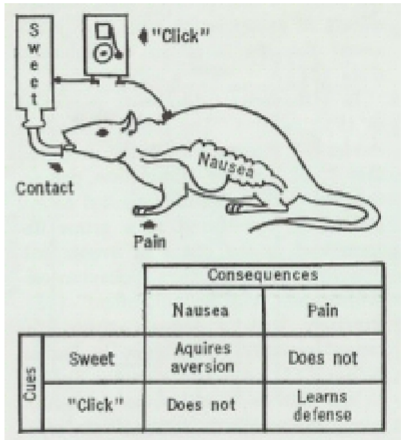
describe Garcia and Koelling’s (1966) taste aversion learning study
* created a compound conditioned stimulus (bright, noisy + sweetened water)
* the unconditioned stimulus was wither a mild foot shock (immediate discomfort) (group 1) or X-rays (delayed illness) (group 2)
* split the conditioned stimulus into two (bright/noisy water and sweetened water)
* the unconditioned stimulus was wither a mild foot shock (immediate discomfort) (group 1) or X-rays (delayed illness) (group 2)
* split the conditioned stimulus into two (bright/noisy water and sweetened water)
19
New cards
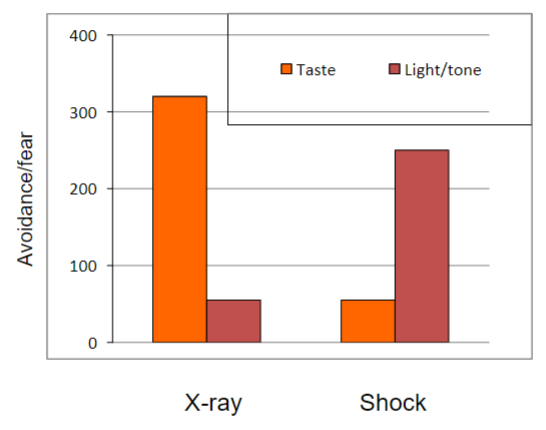
what were the results of Garcia and Koelling’s (1966) taste aversion learning study?
* the rats that were made ill avoided the sweet water
* the rats that received a shock avoided the bright/noisy water
* the rats that received a shock avoided the bright/noisy water
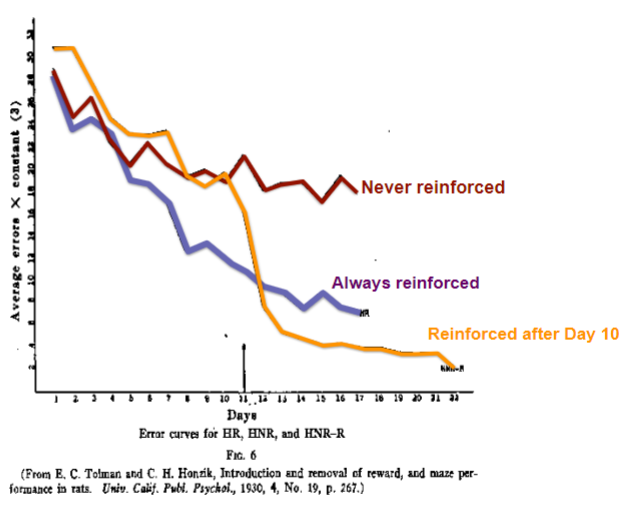
20
New cards
describe Tolman’s Latent learning effect study
* had rats try to complete a maze
* some received food rewards (always reinforced), others didn’t (never reinforced) and some given were rewarded after day 10
* the group that was always reinforced learnt faster and made fewer mistakes by day 17
* however learning occurred at a faster rate in the group receiving a delayed reward (learning was ‘dormant’)
* some received food rewards (always reinforced), others didn’t (never reinforced) and some given were rewarded after day 10
* the group that was always reinforced learnt faster and made fewer mistakes by day 17
* however learning occurred at a faster rate in the group receiving a delayed reward (learning was ‘dormant’)