Chapter 3 - Scales, Keys, and Modes
0.0(0)Studied by 8 people
Card Sorting
1/58
Last updated 8:14 PM on 3/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
Tonality
________- The principle of organizing a composition around that keynote or tonic.
2
New cards
Enharmonic equivalent flats
________ are used for the descending scale.
3
New cards
Sharps
________ are used for the ascending scale.
4
New cards
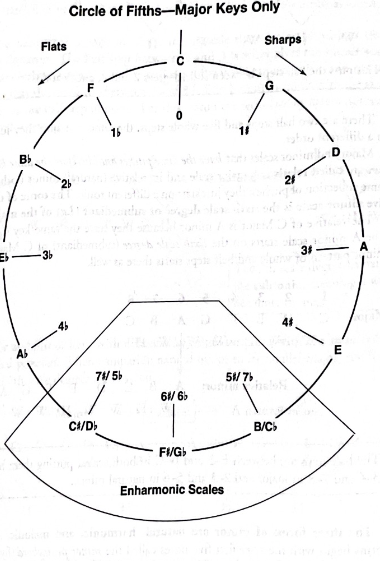
circle
The ________ of fifths- Demonstrates the relationship of the tonal centers to each other.
5
New cards
Heptatonic
________ scales- There are seven tones in the scale.
6
New cards
Dorian
Phrygian, Aeolian, and ________ are minor modes.
7
New cards
tonic triad
It has a diminished ________, so its not a major or minor.
8
New cards
key signature
Relative- Major and minor scales that have the same pitches and ________.
9
New cards
Tonic
________- The beginning pitch of the scale.
10
New cards
Lydian
________ is similar to Ionian with a raised 4th scale degree.
11
New cards
Mixolydian
________ is similar to Ionian with a lowered 7th scale degree.
12
New cards
Phrygian
________ is similar to Aeolian with a lowered 2nd scale degree.
13
New cards
Ionian
Lydian, Mixolydian, and ________ are major modes.
14
New cards
Ionian mode
________- Same pattern as the major scale.
15
New cards
Artificial scales
________- When forms of the minor vary from the key signature and require the use of additional accidentals to create the scale.
16
New cards
Harmonic form
________ of minor- The 7th scale degree is raised both ascending and descending.
17
New cards
Chromatic scale
________- Symmetrical scale with all pitches spaced a half step apart.
18
New cards
Scalar variance
________- The use of natural, harmonic, and melodic minor within one composition.
19
New cards
Chromatic scale
Symmetrical scale with all pitches spaced a half step apart
20
New cards
Major scale
Created using a pattern for whole and half steps
21
New cards
Church mode
A scale containing five whole steps and two half steps

22
New cards
Ionian mode
First rotation, it is a major scale pattern
23
New cards
Aeolian mode
Sixth rotation, its a minor scale pattern
24
New cards
Key
A specific series of pitches based on a pattern of whole and half steps that define a tonality
25
New cards
Key of G
The series of notes using the major scale pattern centered around, or starting with G
26
New cards
Tonality
The principle of organizing a composition around that keynote or tonic
27
New cards
Mode
An issue of scale type
28
New cards
Key signature
A form of shorthand that dispenses with the writing of accidentals (sharps and flats) for the notes affected by the pattern
29
New cards
For sharps
The last sharp in the key signature is scale degree 7, so the name of the key is up one-half step
30
New cards
For flats
The last flat in the key signature is scale degree 4, so the name of the key is the next to the last flat in the key signature
31
New cards
The circle of fifths
Demonstrates the relationship of the tonal centers to each other
32
New cards
Natural minor scale
The sixth scale in the rotation of church modes
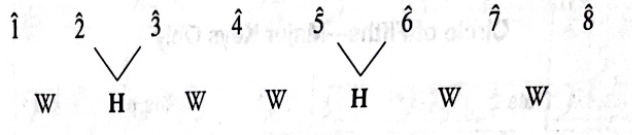
33
New cards
Relative
Major and minor scales that have the same pitches and key signature
34
New cards
Three forms of minor
Natural, harmonic, and melodic
35
New cards
Minor pentachord
Same first five notes that the three forms of minor start with
36
New cards
Parallel
Major and minor keys with different key signature but same tonic
37
New cards
Natural form of minor
No alterations to the key signature
38
New cards
Harmonic form of minor
The 7th scale degree is raised both ascending and descending
39
New cards
Melodic form of minor
The 6th and 7th scale degrees are raised
40
New cards
Scalar variance
The use of natural, harmonic, and melodic minor within one composition
41
New cards
Artificial scales
When forms of the minor vary from the key signature and require the use of additional accidentals to create the scale
42
New cards
Scale degree
Each step of the scale
43
New cards
Tonic
The beginning pitch of the scale
44
New cards
Scale degree 1
The tone on which the scale is built, the tonal center
45
New cards
Scale degree 2
Above the tonic
46
New cards
Scale degree 3
Halfway between the tonic and dominant
47
New cards
Scale degree 4
A fifth below the tonic
48
New cards
Scale degree 5
Perfect fifth above the tonic
49
New cards
Scale degree 6
In between the subdominant and the tonic
50
New cards
Scale degree 7
Half step below Do
51
New cards
Active tones
Scale degrees 4, 6, and 7
52
New cards
Heptatonic scales
There are seven tones in the scale
53
New cards
Hexatonic scale
There are six tones in this scale
54
New cards
Whole-tone scale
Each pitch is a whole step apart
55
New cards
Pentatonic scale
Has five tones
56
New cards
Major pentatonic
To build it, in the Circle of Fifths, start from C up to 5 consecutive pitches
57
New cards
Relative minor pentatonic
It uses the same pitch as the C pentatonic but it starts on A
58
New cards
Ionian mode
Same pattern as the major scale
59
New cards
Aeolian mode
Same pattern as the natural minor scale