Electricity
1/15
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
E.M.F.
The electrical energy given to charge carriers per unit charge
Internal resistance
The resistance of a source that resulted in energy loss as a charger passes through the source causing a difference between EMF and terminal p.d.
Tenner potentially difference
The p.d. supplied by an electrical power source
Potential divider equation
Equation here
Series rules
RT=R1+R2+…+Rn
IT=I1=I2=In
VT=V1+V2+…+Vn
Parallel rules
Resistance rule
IT=I1+I2+…+In
VT=V1=V2=Vn
Kirchhoff's second law
Sum of EMF=sum of p.d. in closed loop
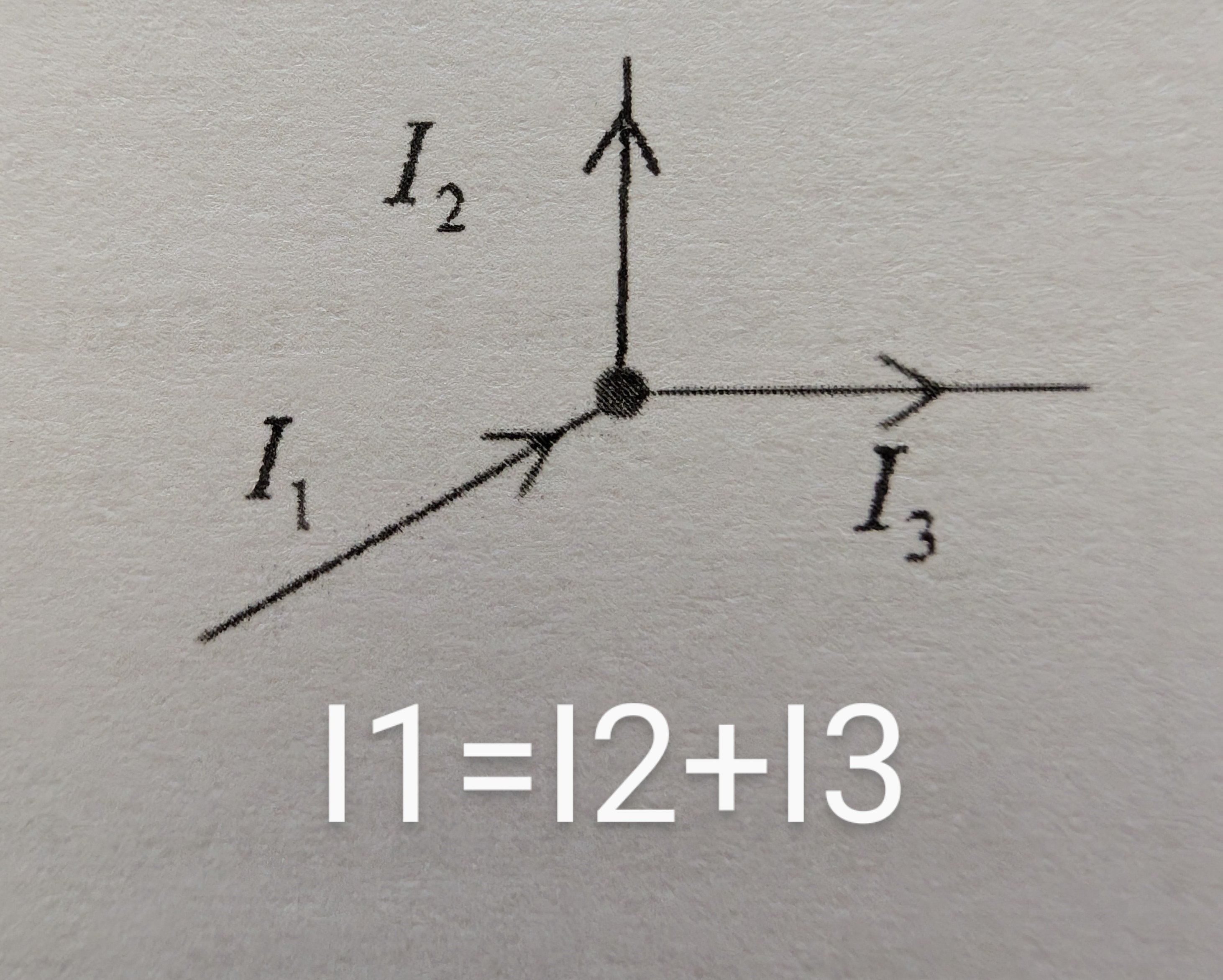
Kirchhoff's first law
The sum of the current into a point = sum of the current out
Potential difference
The work done per unit charge
Current
The rate of flow of charge though a conductor
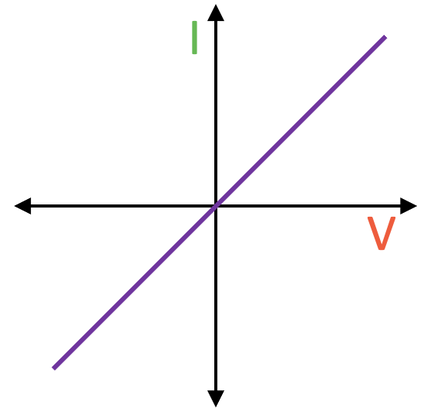
Ohmic conductor graph
Gradient change with resistance
Stepper → lower R
Shallower → higher R
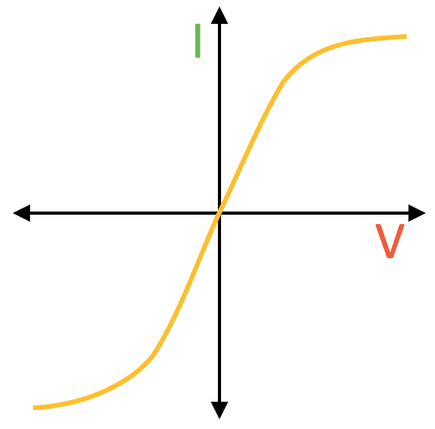
Semiconductor graph
Zero current until a set p.d.
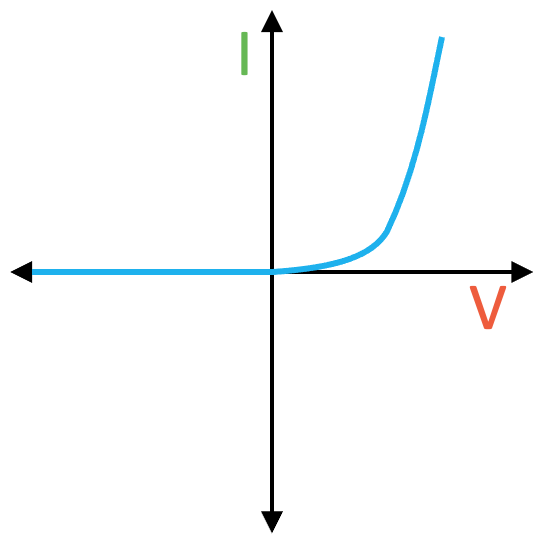
Filament bulb
Due to temperature changes not linear
But x=0 symmetrical
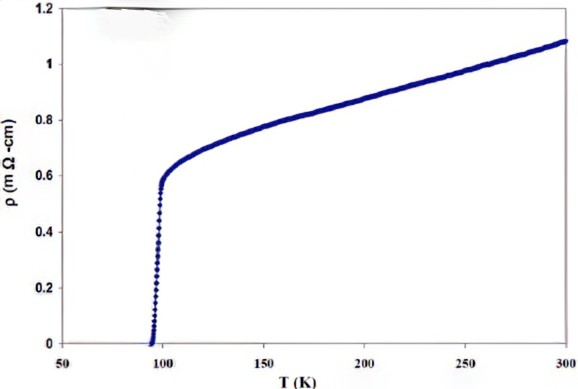
Superconductivity
Resistivity decreases to zero as temperature lowers
The critical temperature is the point at with the resistivity it above zero
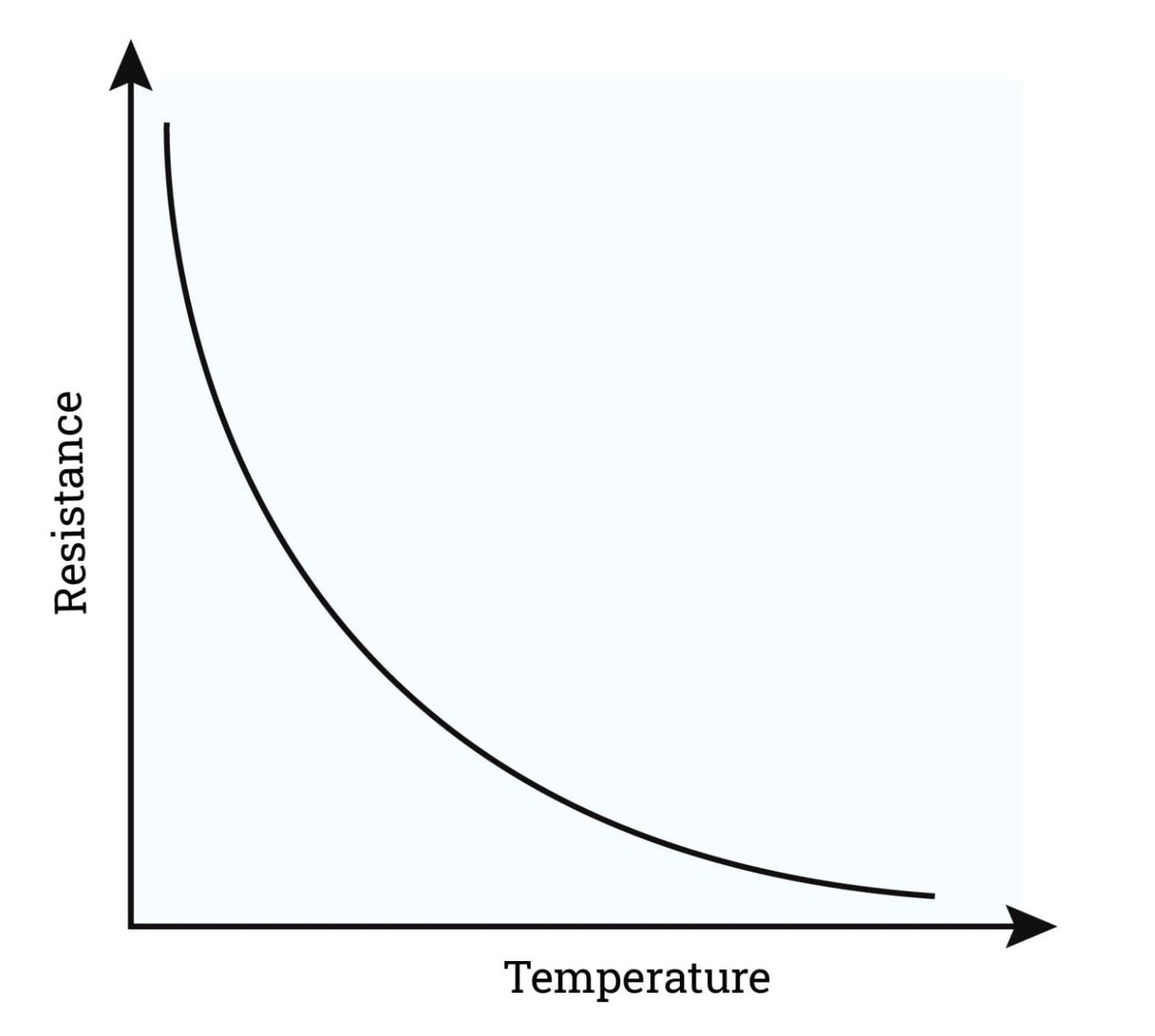
Thermistor definition and uses
A negative temperature coefficient
T ∝ -R
Uses:
Thermostat
Measure temperature in electronics
Resistivity
The product of Resistance per unit length and the cross section area
ρ=RA/L
R∝L
R∝1/A