2.03 Leadership and Management
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Henri Fayol Key Functions of Management
Panning - tactical and strategic
Commanding - giving instructions/orders
Controlling - performance, health, safety,
Coordinating - departments work together
Organizing - organizing resources to achieve objectives.
Charles Handy Key Functions of Management
General Practitioners
Confronters of dilemmas
Balancers of cultural mixes
Effective managers requires to see the bigger picture of different situations.
Peter Drucker Key Functions of Management
Setting organizational objectives
Organizing tasks and people
Communicating with and motivating people.
Measuring performance.
Developing people
He argues that managers don’t get too involved with employee’s daily activities (decentralized structure), and that people are essential to a company’s success.
Leader & Leadership
A leader is someone who influence and inspire people to get things done. They foster motivation, respect, trust and loyalty.
Leadership is a process of influencing and inspiring others to achieve organization goals.
Leaders focuses on achieving broad goals with no definite time frame.
Manager & Management.
Management is the ‘art of getting things done through people’
Managers focus on achieving specific goals with a time frame.
They do problem solving, planning, organizing human/capital resources to achieve organizational objectives.
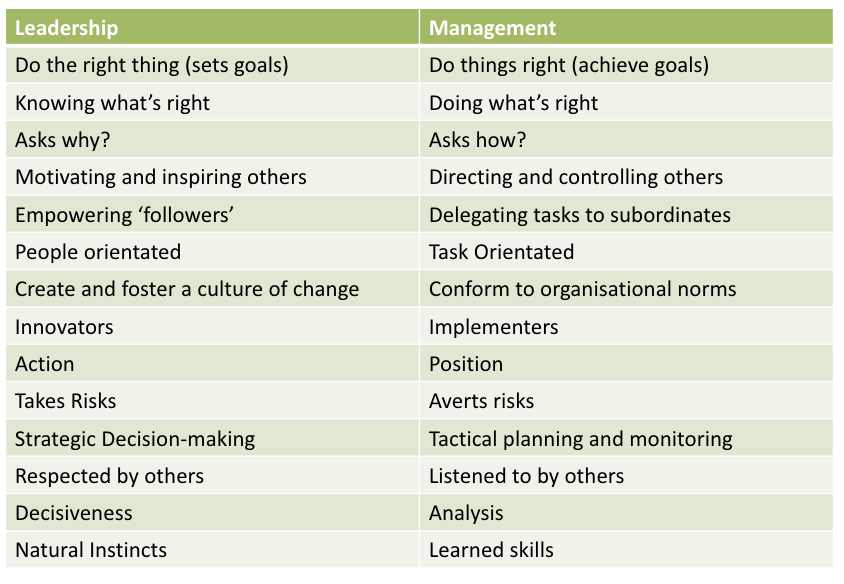
Leadership vs. Management
Leaders spend more time and devotion and a direct influence on employees by inspiring them to work. Leaders take risks and act upon their vision of the company’s best interest.
Managers spend less time and instruct employees to do work. They follow rules and don’t take risk as often.
The skills require to be an effective manager and leader have a lot of overlap despite the distinction. Being a leader almost is a innate characteristic.
5 Common Leadership Styles
Autocratic
Paternalistic
Democratic
Laissez-Faire
Situational Leadership
Autocratic Leadership
Makes all the decisions
Prefers not to delegate any responsibility
Only tell subordinate what to do.
This style is suitable when quick or critical decision-making is needed. This style also applies when workers are unskilled and depend on directions of leaders.
Autocratic Leadership Limitation
Communication is top-down and opinions of employees are ignored, which can demotivate them and create resentment in the workplace.
Paternalistic Leadership
Treat their employees like a family member by guiding them and acting in their best interest.
Exceptional organizational skills and build trust with teams.
Workers are expected to be loyal and obedient. This style works well in countries with cultures that enables people to work hard out of gratitude for leaders. In other cultures this might not work well, people don’t want to be dictated by others.
Positive vs. Negative Paternalistic Style
A negative paternalistic style occurs when leaders perceives the workers as less capable and therefore guide them
A positive paternalistic style occurs when leaders perceives the workers as highly capable so they nurtures and develop them.
Democratic Leadership
Involving employees in the decision making process, bringing out more employee satisfaction as employee have input.
Idea sharing can improve decisions.
This can work when leaders are not present, and employees remain on tasks.
Democratic Leadership Limitations
It can delay decision making because it involves many people and is not suitable for a large workforce.
Laissez-Faire (don’t care)
Minimal direct input in employee’s work and instead allow employees to make their own decisions.
Leader sets the objective, and the employee decide the best approach. This can highly motivate workers as they feel trusted and valued.
This style is suitable when creativity is important, such as computer software or advertising agencies.
Laissez-Faire Limitations
Coordination and decision-making can be time-consuming with lack of direct supervision or support.
It relies heavily on teamwork and the goodwill of employees to achieve the organizations goals.
Laissez-faire leadership can encourage slack and laziness since employees are not closely monitored.
Situational Leadership
This is a leadership style is not based on a dominant approach. It’s about using the right leadership style for the right situation. This style suggests that managers and leaders change their style to accommodate different situations.
Factors that Influence Situation Leadership (CLOTS)
Culture - The type of culture that exists in the organization and group norms
Leader - The trust leaders have for employees, how skilled they are, their preferred leading style
Organizational structure - What is the structure? Tall/Flat? Span of control?
Task - Task difficulty, urgency, importance.
Subordinate - Skills and number of employees.