Chemistry - Topic 10 Organic Chemistry
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Homologous series
A family of compounds that differs only by the length of its hydrocarbon chain. Members share a general formula and chemical properties.
Melting/boiling points in a homologous series
increase going down the series or as LDF increases
empirical formula
The simplest ratio of elements in a compound.
molecular formula
The actual number of atoms of each element in a compound.
structural formula
A formula that shows the arrangement of atoms and bonds in a molecule.
condensed formula
A formula that shows the connectivity of atoms in a molecule, but does not show all the bonds.
skeletal formula
A simplified way of representing organic molecules by using lines to represent carbon-carbon bonds and omitting carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
Saturated compound
have single bonds
Unsaturated compound
have double/triple bonds
Cycloalkanes
Ring structures that contain only single bonds (C-C).
Arenes
Ring structures consisting of alternating double bonds (C=C).
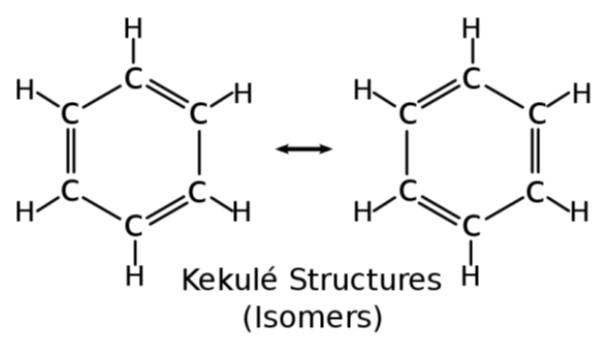
Benzene - Kekule Structures
Radicals
Species with unpaired electrons that are highly reactive.
Alkenes + Hydrogen
product = alkane; heat + nickel catalyst needed
Alkenes + Hydrogen halides
product = halogenoalkanes; no required conditions
Alkenes + Water
product = alcohol; steam + sulphuric acid catalyst
Polymerisation
Under certain conditions, alkene molecules can add to each other to form polymers.
Alcohols as Fuels
Alcohols combust more than alkanes but release less energy.
Oxidation of Alcohol
Alcohols can be oxidized to form aldehydes or carboxylic acids, depending on the conditions and the type of alcohol.
Alcohol Oxidation Agent
Potassium dichromate
Nucleophilic Substitution
A reaction where a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in a molecule. Halogenoalkanes can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Ester
A compound formed by the reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.