Subluxation Analysis: X-Ray Exam
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Chiropractic x-rays:
usually taken weight bearing
most taken A-P and analyzed P-A
Spinography:
Chiropractic analysis of x-rays
Technique specific analysis
Order of patient encounter:
History
Examination: visualization, posture, ROM, leg check, ortho/neuro…
Instrumentation
Static and motion palpation
Diagnostic imaging (if warranted)
Diagnosis and prognosis
Treatment
What are the advantages of X-rays?
Correlate posture findings
Confirm static findings
Identify pathologies
Increases specificity (LOC, SCP, listings, etc.)
What are disadvantages to x-rays?
Exposure
Limited sensitivity to pathologies
Static picture of a dynamic spine (snapshot in time)
Cost
Maintenance
What part of the VSC does x-ray fall under?
Kinesiopathology → relative position
Histopathology → osteological changes
What part of the PART system does x-ray fall under?
A → asymmetry/misalignment
R → range of motion
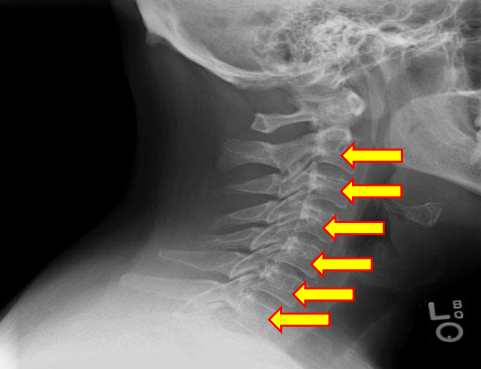
Vertebral bodies
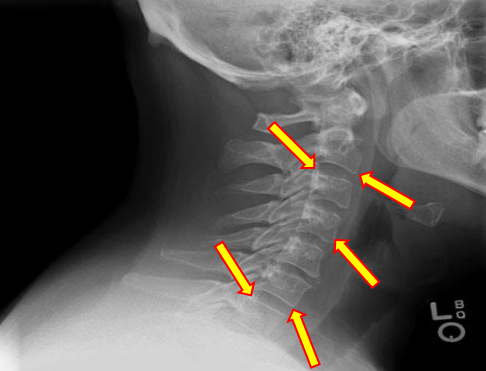
Superior and inferior endplates
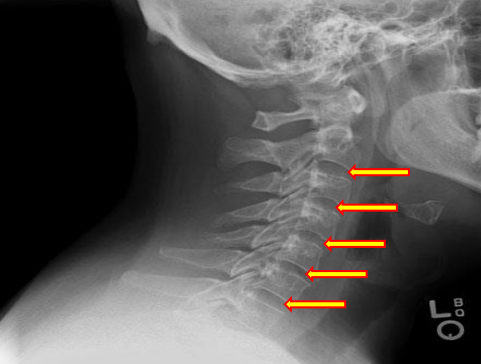
Disc space
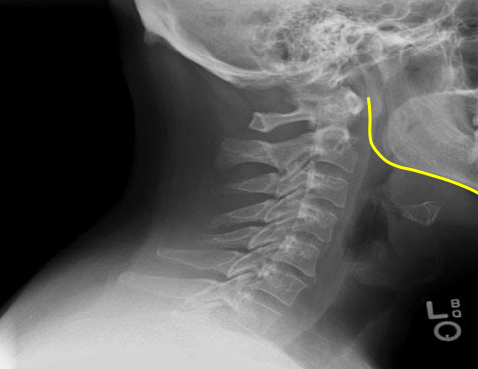
Mandible
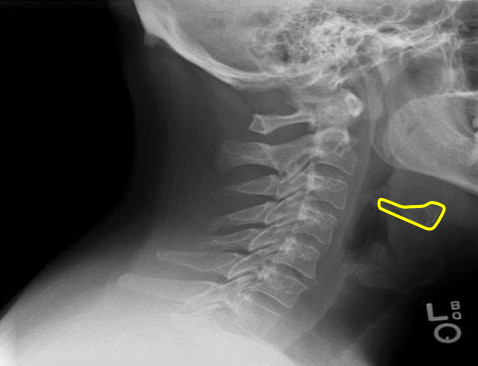
Hyoid bone
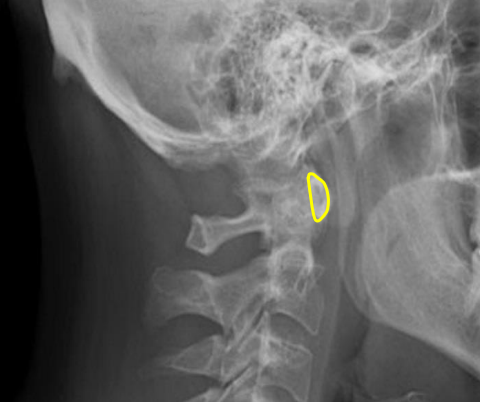
Mitchel marker
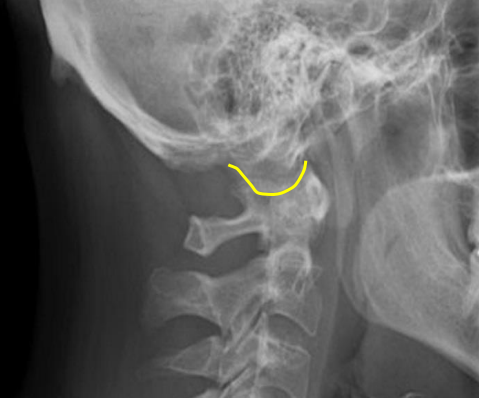
Occipital condyle
C1 anterior tubercle
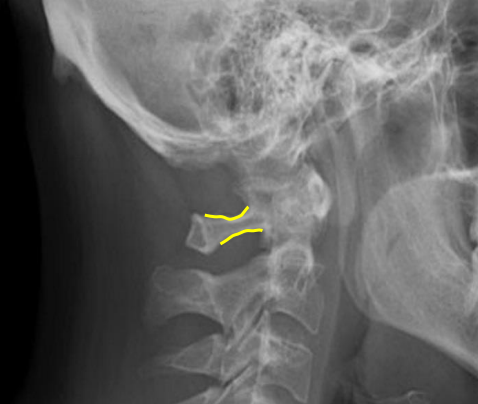
C1 posterior arch
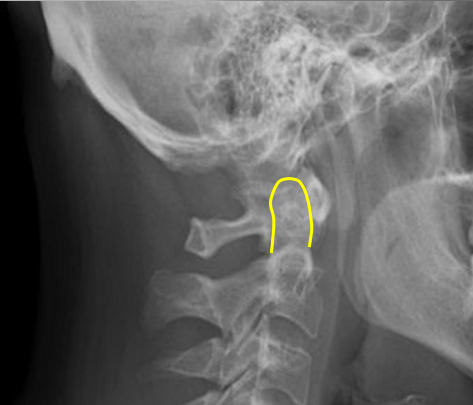
Odontoid process
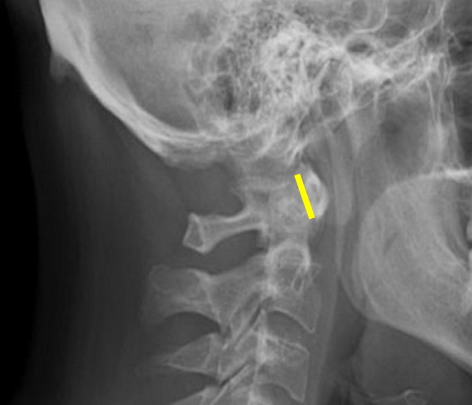
Atlanto-Dental interspace
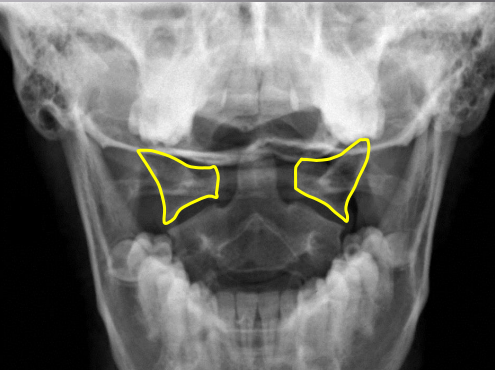
C1 lateral masses
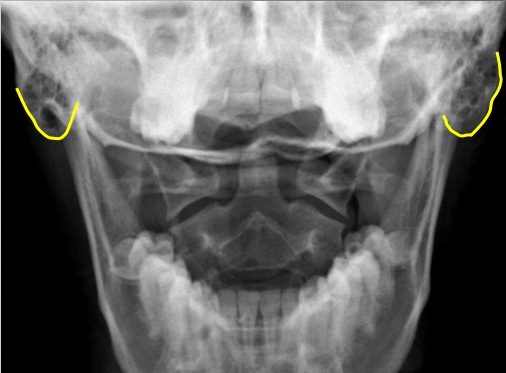
Mastoid process
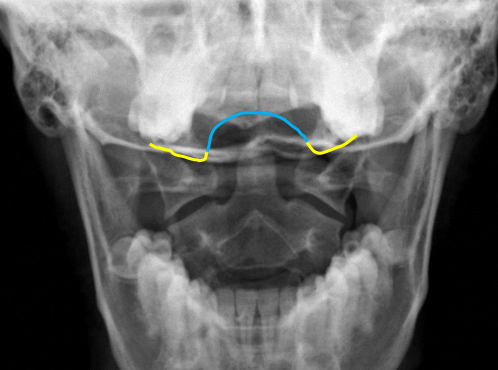
yellow
Occipital condyles
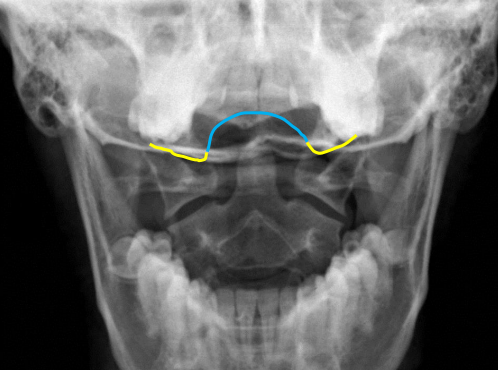
blue
Foramen magnum
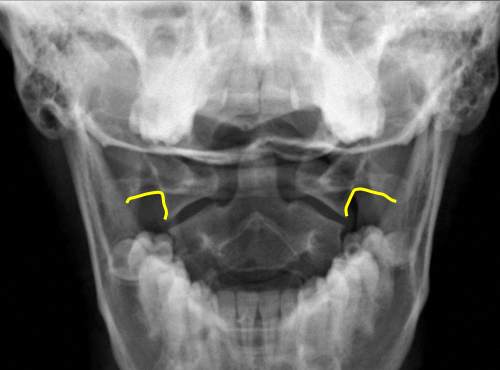
C1 TVP/ lateral mass junction
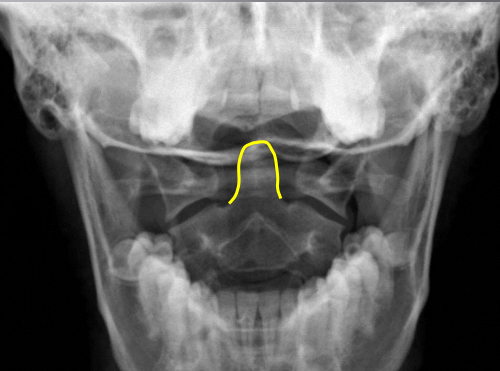
Odontoid process
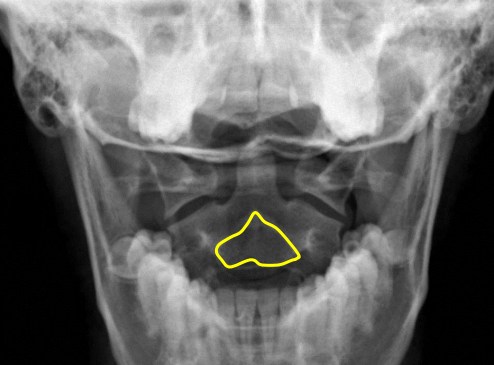
C2 spinous process
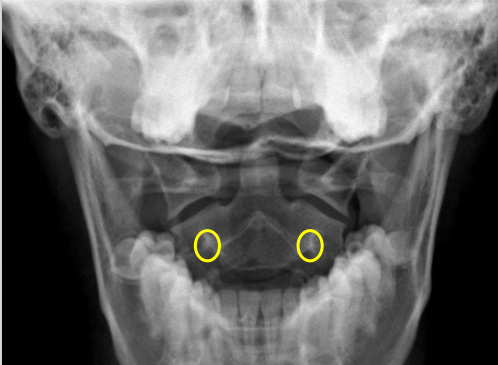
C2 pedicle shadow
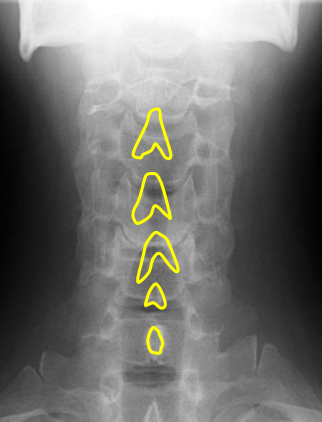
Junction of lamina (top of spinous)
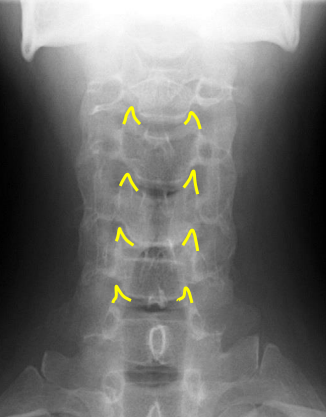
Uncinate processes
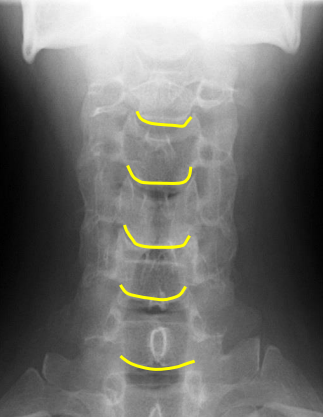
Inferior aspect of vertebral bodies
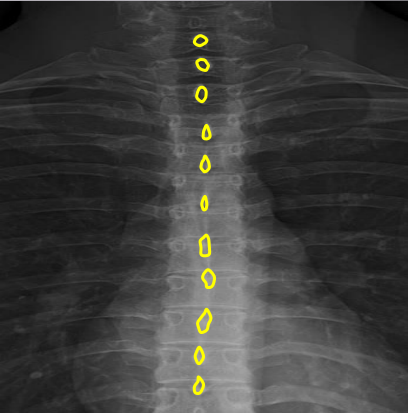
Junction of laminae
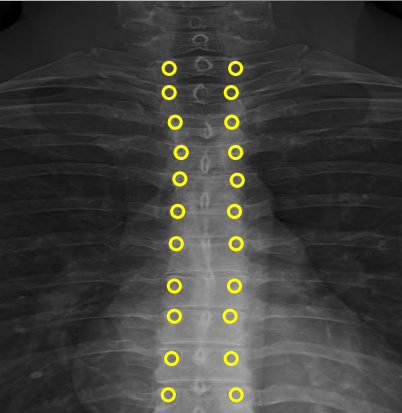
Pedicle shadows
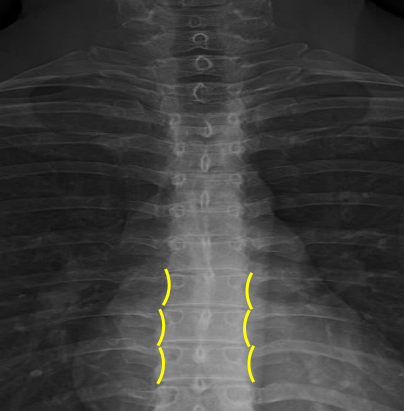
Vertebral waist
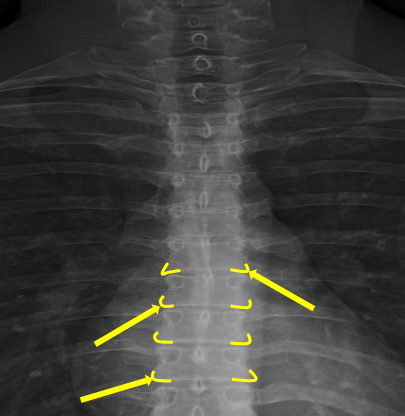
Inferior endplate tips
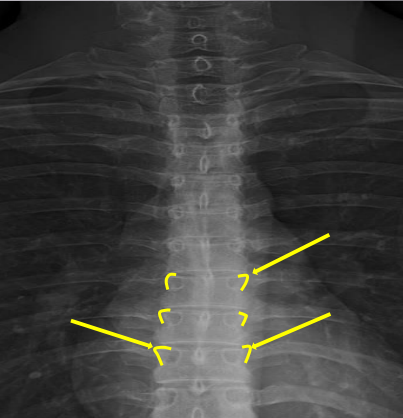
Superior endplate tips
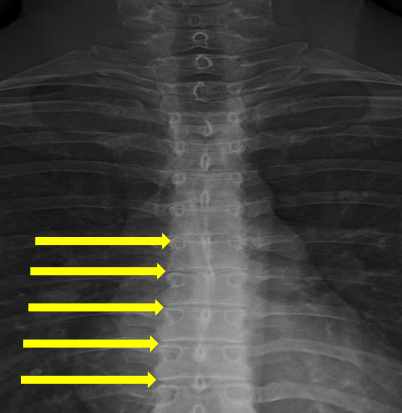
Disc spaces
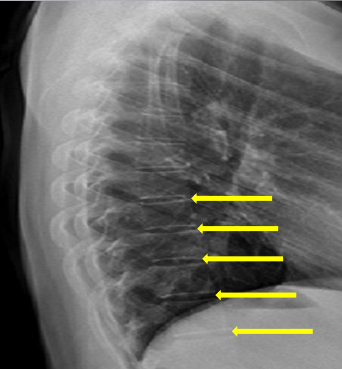
Disc spaces
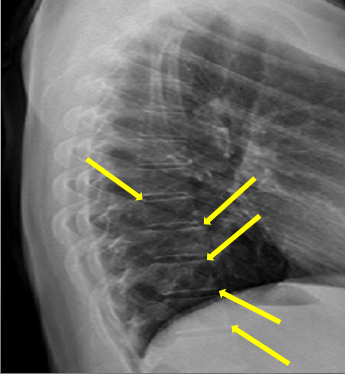
End plate tips
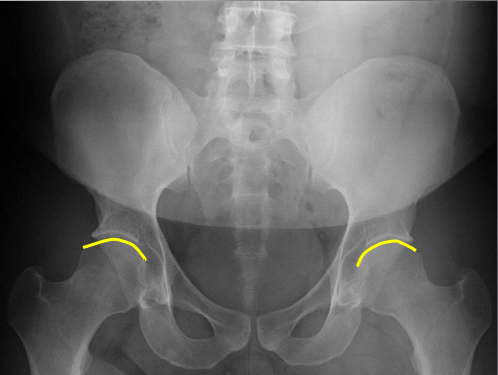
Femur heads
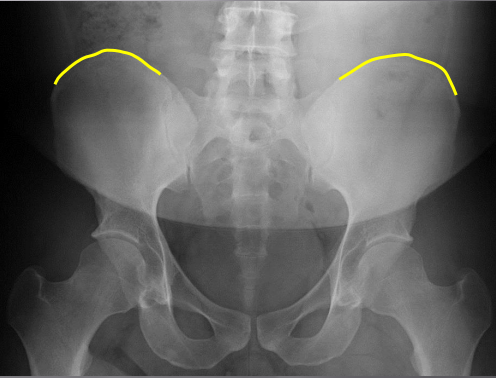
Superior iliac crests
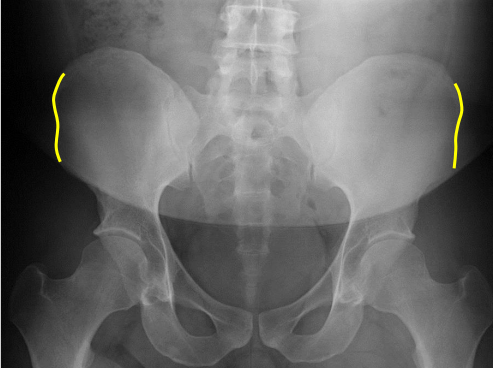
Lateral iliac crests
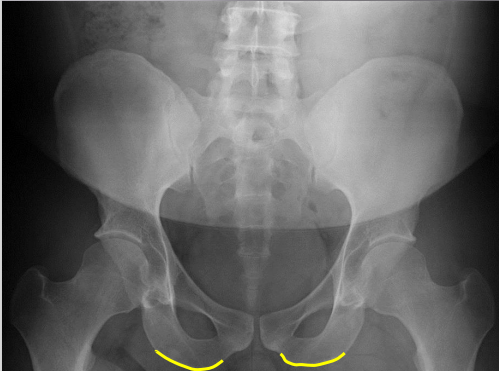
Ischial tuberosities
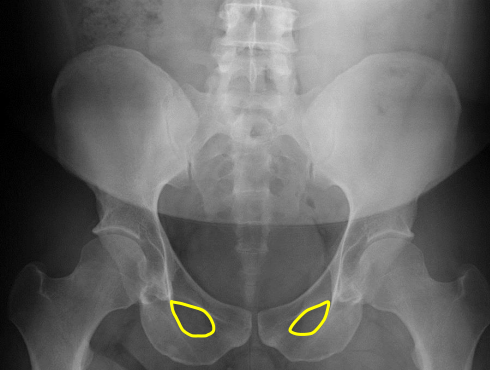
Obturator foramen
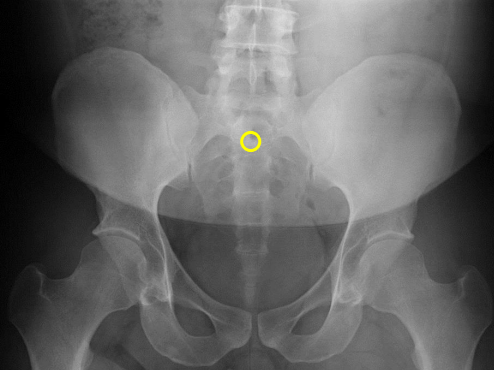
S2 tubercle
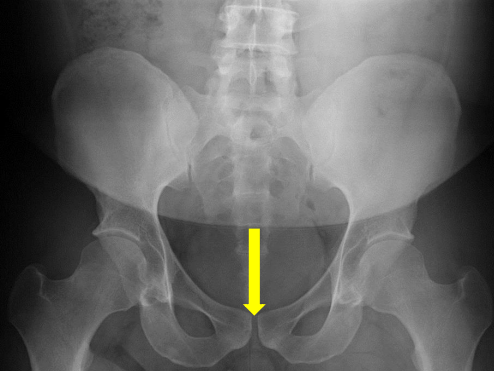
Pubic symphysis
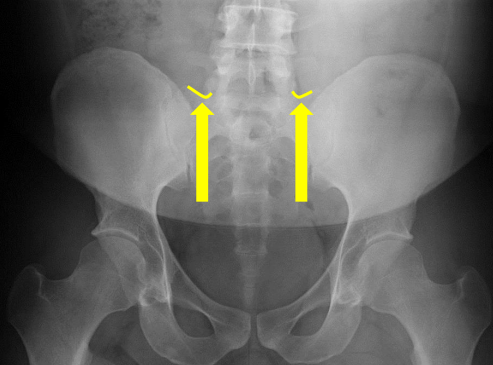
Sacral groove
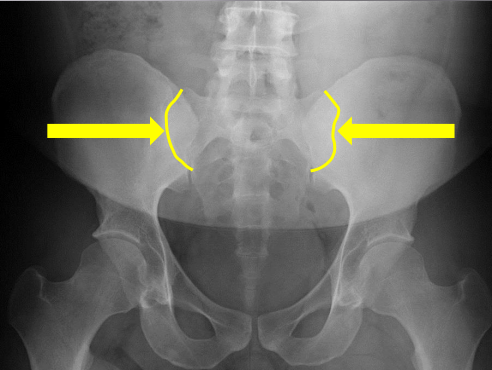
Lateral aspect of sacrum
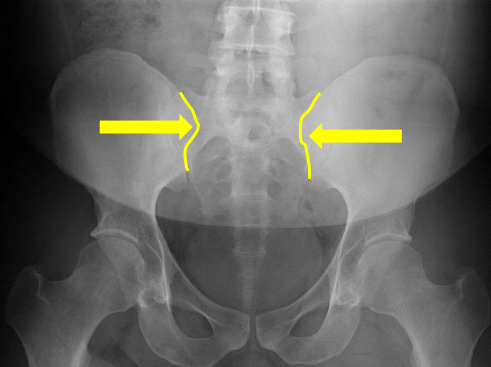
Medial aspect of ilium