Human Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1 [Ch. 1-3] *only parts of ch. 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:55 AM on 9/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space.
2
New cards
Chemical Element
The simplest form of matter, elements are made up of all the same atoms—cannot be broken down by any chemical means.
3
New cards
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that enters chemical reactions.
4
New cards
Proton
Positively charged particle in the nucleus of the atom.
5
New cards
Neutron
Non-charged particle in the nucleus.
- Isotopes: of the same element have different numbers of neutrons.
- Radioisotopes: decompose spontaneously into more stable forms giving off radiation.
- Isotopes: of the same element have different numbers of neutrons.
- Radioisotopes: decompose spontaneously into more stable forms giving off radiation.
6
New cards
Electron
Negatively charged particle that orbits the nucleus — sometimes may be gained or lost from an atom or molecule to conform to a stable number in the outer shell — usually 2 or 8.
7
New cards
Ion
An atom or molecule with an unequal number of protons and electrons — therefore has some charge — and is formed by the gain or loss of electrons
8
New cards
Electrolytes
Forms an ion in water [H₂O].
9
New cards
Free Radicals
Highly reactive electron in the outer shell (eg. superoxide).
10
New cards
Anatomy
The study of body structure.
Ana: "apart"
Tome: "cut"
Ana: "apart"
Tome: "cut"
11
New cards
Physiology Subdivisions
Based on organ systems. Begins at molecular and cellular level. The body's abilities depend on chemical reactions in body cells.
12
New cards
Subdivision Examples of Anatomy
Gross: visible
Microscope: too small to see with naked eye (microscope)
Developmental: traces structural changes that occur in the body throughout the life span
Microscope: too small to see with naked eye (microscope)
Developmental: traces structural changes that occur in the body throughout the life span
13
New cards
To Study Anatomy Clinically:
Observation: looking
Manipulation: moving
Palpation: touching
Auscultation: listening
Manipulation: moving
Palpation: touching
Auscultation: listening
14
New cards
Physiology
The study of body function.
Physis: "nature/life"
Logos: "study of/discourse"
Physis: "nature/life"
Logos: "study of/discourse"
15
New cards
Conceptual Knowledge in Physiology
Focus at many levels: chemical --> organism
Basic physical principles: electricity, molecular movements
Basic chemical principles: chemical RxNs
Basic physical principles: electricity, molecular movements
Basic chemical principles: chemical RxNs
16
New cards
Homestasis
The essential concept of physiology: to maintain relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside worlds world changes continuously.
17
New cards
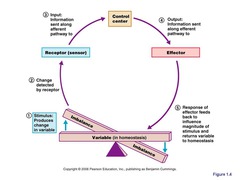
Homeostatic Control Mechanisms
Monitor change (variable) and respond. Communication; e.g. nervous and endocrine systems
Three Interdependent Components:
1) Receptor - sensor that monitors the environment and responds to stimuli
2) Control Center - which determines the set point [maintained condition], analyzes the input it receives and then determines the appropriate response or course of action.
3) Effector - response (output) to the stimulus. [Need to do to maintain homeostasis]
Three Interdependent Components:
1) Receptor - sensor that monitors the environment and responds to stimuli
2) Control Center - which determines the set point [maintained condition], analyzes the input it receives and then determines the appropriate response or course of action.
3) Effector - response (output) to the stimulus. [Need to do to maintain homeostasis]
18
New cards
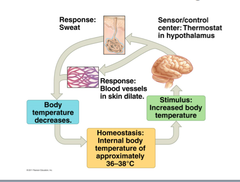
Negative Feedback Mechanism
Keeps body conditions relatively constant.
- Most feedback mechanisms in body (maintains homeostasis)
- Response reduces or shuts off original stimulus
- Most feedback mechanisms in body (maintains homeostasis)
- Response reduces or shuts off original stimulus
19
New cards
Negative Feedback Examples
body temperature (nervous) , blood pressure, glucose regulation (endocrine)
20
New cards
Positive Feedback Mechanism
The response enhances or exaggerates the original stimulus; exhibits an amplifying effect; usually controls infrequent events.
21
New cards
Positive Feedback Examples
Childbirth and blood clotting [makes a change]
![Childbirth and blood clotting [makes a change]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/83b44a1477aa46799accc1d323c5d768.jpg)
22
New cards
Anatomical Position
The common reference standard:
- Body upright and palms forward
- Always use directional term as if body is in a anatomical position
- Right vs. Left [subjects point of view]
- Body upright and palms forward
- Always use directional term as if body is in a anatomical position
- Right vs. Left [subjects point of view]
23
New cards
Sagittal Plane
Vertical division of the body into right and left portions.
- Midsagittal (median) Plane: equal right and left
- Parasaggital Plane: unequal right and left
- Midsagittal (median) Plane: equal right and left
- Parasaggital Plane: unequal right and left
24
New cards
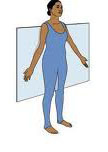
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Vertical plane dividing the body or structure into anterior and posterior portions.
25
New cards
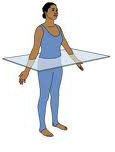
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
Divides the body into superior and inferior parts.
- Cross Section: across the length
- Oblique Section: at an angle
- Cross Section: across the length
- Oblique Section: at an angle
26
New cards
Superior (Cranial)
Higher on the body, nearer to the head.
27
New cards
Inferior (Caudal)
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below.
28
New cards
Ventral (Anterior)
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of.
29
New cards
Dorsal (Posterior)
Toward or at the back of the body; behind.
30
New cards
Medial
Toward the midline of the body.
31
New cards
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body.
32
New cards
Intermediate
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure.
33
New cards
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
34
New cards
Distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
35
New cards
Superficial (External)
toward or at the body surface.
36
New cards
Deep (Internal)
Away from the body surface; more internal.
37
New cards
Dorsal Body Cavity
Protects the fragile nervous system organs, has two subdivisions:
1) Cranial Cavity - in the skull, encases the brain
2) Vertebral Cavity - runs within the bony vertebral column, encloses the spinal cord.
1) Cranial Cavity - in the skull, encases the brain
2) Vertebral Cavity - runs within the bony vertebral column, encloses the spinal cord.
38
New cards
Ventral Body Cavities
The more anterior and larger of the closed body cavities, two sub divisions:
1) Thoracic Cavity - surrounded by the ribs and and muscles of the chest. Further divided into three components. [Pleural cavities (lungs), Mediastinum cavities (lungs), Pericardial cavities (heart)]
2) Abdominopelvic Cavity - Below diaphragm, two parts. [Abdominal cavity, Pelvic cavity]
1) Thoracic Cavity - surrounded by the ribs and and muscles of the chest. Further divided into three components. [Pleural cavities (lungs), Mediastinum cavities (lungs), Pericardial cavities (heart)]
2) Abdominopelvic Cavity - Below diaphragm, two parts. [Abdominal cavity, Pelvic cavity]
39
New cards
Nine Abdominopelvic Regions
Major : central portions [epigastric, umbilical, hypogastric]
Right + Left [hypochondriac, lumbar, iliac (inguinal)]
Right + Left [hypochondriac, lumbar, iliac (inguinal)]
![Major : central portions [epigastric, umbilical, hypogastric]
Right + Left [hypochondriac, lumbar, iliac (inguinal)]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/13de47734fe942c78a99059614dac9f9.png)
40
New cards
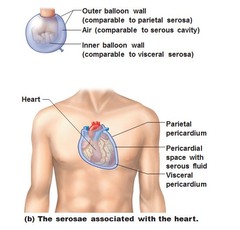
Membranes in Ventral Body Cavity
Serous membrane (serosae) = "watery" membrane
- parietal membrane: lines cavity walls
- visceral membrane: covering surface of organs
- Serous fluid: between parietal and visceral membrane
- parietal membrane: lines cavity walls
- visceral membrane: covering surface of organs
- Serous fluid: between parietal and visceral membrane
41
New cards
Other Body Cavities
Oral and digestive, nasal, orbital, middle ear, synovial.
42
New cards
Chemical Bonds
The attractive forces that hold atoms together.
43
New cards
Covalent Bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms.
- Two or more atoms together = molecule
- Two or more atoms together = molecule
44
New cards
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond in which the bonding electrons are shared equally by the bonded atoms, resulting in a balanced distribution of electrical charge.
45
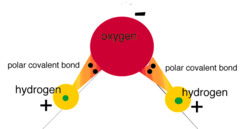
New cards
Polar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally.
46
New cards
Ionic Bonds
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
- Negatively Charged Ions: anions
- Positively Charged Ions: cations
- Ionic Compound: SALT
- Negatively Charged Ions: anions
- Positively Charged Ions: cations
- Ionic Compound: SALT
47
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule.
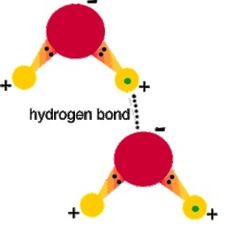
48
New cards
Van der Waal Forces
Non-polar regions of molecules are attracted to each other.
- Weak force
- Important in lipid molecule interaction (e.g. cell membrane)
- Weak force
- Important in lipid molecule interaction (e.g. cell membrane)
49
New cards
Solution
Homogenous mixtures of components that may be gases, liquids, or solids. Mixture at a molecular level (molecule) ex. mineral water
- Solvent: Substance present in the greatest amount.
- Solute: Substance present in smaller amount.
"can see through"
- Solvent: Substance present in the greatest amount.
- Solute: Substance present in smaller amount.
"can see through"

50
New cards
Colloid
Also called emulsions, are heterogeneous mixtures that often appear translucent or milky. Permanent mix of "chunks" not molecules. [e.g. milk --> chunks of fat and protein]
"can not see through"
"can not see through"
![Also called emulsions, are heterogeneous mixtures that often appear translucent or milky. Permanent mix of "chunks" not molecules. [e.g. milk --> chunks of fat and protein]
"can not see through"](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/615689c20d8340edb583d148861eb30f.jpg)
51
New cards
Suspensions
Heterogeneous mixtures with large, often visible solutes that tend to settle out. Mix of "chunks" --> in time will settle out [e.g. blood]
52
New cards
Solutions in the Body
Main solvent is water (H₂O) which accounts for the majority of our body weight. [60 % +]
- Intracellular: 2/3
- Extracellular: 1/3
- Intracellular: 2/3
- Extracellular: 1/3
53
New cards
Characteristics of Water
1) Polarity: gives water its solvency and cohesion (liquid at room/body temp)
- Some molecules are hydrophilic (easily dissolved in H₂O)
- Some molecules are hydrophobic (not easily dissolved in H₂O)
2) Thermal Stability
- Heat capacity (stores heat)
- Heat of vaporization (increase of energy to H₂O liquid --> gas)
3) Chemical Reactivity
- Hydrolysis (add water to break apart macromolecules)
- Hydro "water" + Lysis "to break"
- Dehydration synthesis (condensation) (remove water to build macromolecules)
- Some molecules are hydrophilic (easily dissolved in H₂O)
- Some molecules are hydrophobic (not easily dissolved in H₂O)
2) Thermal Stability
- Heat capacity (stores heat)
- Heat of vaporization (increase of energy to H₂O liquid --> gas)
3) Chemical Reactivity
- Hydrolysis (add water to break apart macromolecules)
- Hydro "water" + Lysis "to break"
- Dehydration synthesis (condensation) (remove water to build macromolecules)
54
New cards
Solutes in the Body
1) Electrolytes: ions ionize in H₂O
Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca++, PO₄---, some amino acids
2) Non-electrolytes: not ionize in H₂O
Gases (O₂, N₂, CO₂), glucose, some amino acids
Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca++, PO₄---, some amino acids
2) Non-electrolytes: not ionize in H₂O
Gases (O₂, N₂, CO₂), glucose, some amino acids
55
New cards
Acids/Bases
Acids are proton (H+) donors:
- Increase [H+] in water. H+Cl- ---> H+ + CL-
Bases are proton acceptors:
- Decrease [H+] in water Na+OH- ---> Na+ +. OH-
pH = 1/log10 [H+]
- Increase [H+] in water. H+Cl- ---> H+ + CL-
Bases are proton acceptors:
- Decrease [H+] in water Na+OH- ---> Na+ +. OH-
pH = 1/log10 [H+]
![Acids are proton (H+) donors:
- Increase [H+] in water. H+Cl- ---> H+ + CL-
Bases are proton acceptors:
- Decrease [H+] in water Na+OH- ---> Na+ +. OH-
pH = 1/log10 [H+]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f5bbcbdb4c5d43faba62b9ca9170772c.png)
56
New cards
Anabolic Reactions (Synthesis)
Always involves bond formation.
A + B --> AB
- Building larger molecules from smaller molecules
- Generally requires energy input
- Protein synthesis is one example
A + B --> AB
- Building larger molecules from smaller molecules
- Generally requires energy input
- Protein synthesis is one example
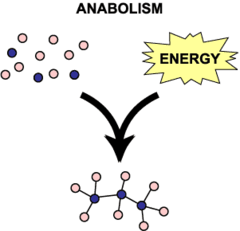
57
New cards
Catabolic Reactions (Decomposition)
AB --> A + B
- Breakdown larger molecules into smaller molecules
- Generally releases energy
- Examples: Glucose + O₂ --> CO₂ +H₂O + ENERGY
- Breakdown larger molecules into smaller molecules
- Generally releases energy
- Examples: Glucose + O₂ --> CO₂ +H₂O + ENERGY
58
New cards
Exchange Reactions
Involves both synthesis and decomposition; bonds are both made and broken.
AB + C --> AC + B
AB + C --> AC + B
59
New cards
Oxidation
When molecules give up electrons (or H) so they release energy.
60
New cards
Reduction
When molecules accept electrons (or H) so they gain energy.
61
New cards
Characteristics of Chemical Reactions
- Chemical reactions may be reversible:
AB + C --> AC + B
- The rate of a chemical reaction is dependent on many factors: concentration, temperature, an the presence of a catalyst (biological catalyst are called enzymes)
- Metabolism + Anabolism + Catabolism
AB + C --> AC + B
- The rate of a chemical reaction is dependent on many factors: concentration, temperature, an the presence of a catalyst (biological catalyst are called enzymes)
- Metabolism + Anabolism + Catabolism
62
New cards
Carbon Chemistry Overview
There are two major categories of molecules:
- inorganic (do not have carbon)
- organic (carbon + some hydrogen)
Four biological important macromolecules:
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids/fats
- Proteins
- Nitrogenous base molecules/DNA + RNA
Most of these are polymers made from monomers through dehydration synthesis.
- inorganic (do not have carbon)
- organic (carbon + some hydrogen)
Four biological important macromolecules:
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids/fats
- Proteins
- Nitrogenous base molecules/DNA + RNA
Most of these are polymers made from monomers through dehydration synthesis.
63
New cards
Carbohydrates
- Composed of Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), and Oxygen (O) in a ratio of 1C2H1O
- World's supply of carbohydrates is formed by photosynthesis (plants & algae)
- Example: sugars, starches, non-digestible fiber (e.g. cellulose)
- World's supply of carbohydrates is formed by photosynthesis (plants & algae)
- Example: sugars, starches, non-digestible fiber (e.g. cellulose)
64
New cards
Three Types of Carbohydrates
1. Monosaccharides: 3-7 carbons in a molecule. Example (glucose, the main form of energy delivered to our body'd cell) "one sugar"
2. Disaccharides: two monosaccharides joined together. Example [Sucrose (table sugars) = Glucose + Fructose] [Maltose] "two sugars"
3. Polysaccharides: Many monosaccharides together — may be a large molecule. Example [Glycogen, chain of glucose] [plant fiber + plant starches]
2. Disaccharides: two monosaccharides joined together. Example [Sucrose (table sugars) = Glucose + Fructose] [Maltose] "two sugars"
3. Polysaccharides: Many monosaccharides together — may be a large molecule. Example [Glycogen, chain of glucose] [plant fiber + plant starches]
![1. Monosaccharides: 3-7 carbons in a molecule. Example (glucose, the main form of energy delivered to our body'd cell) "one sugar"
2. Disaccharides: two monosaccharides joined together. Example [Sucrose (table sugars) = Glucose + Fructose] [Maltose] "two sugars"
3. Polysaccharides: Many monosaccharides together — may be a large molecule. Example [Glycogen, chain of glucose] [plant fiber + plant starches]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0069faa49660422b891c14fd6820f109.png)
65
New cards
Lipids
- Mainly composed of C, H, and O (with less oxygen than found in carbohydrates therefore less oxidized, more energy, more calories per gram)
- Energy source, protection and insulation
- Energy source, protection and insulation
66
New cards
Four Types of Lipids
1. Fatty Acids: long chains of C with a Carboxyl group (COOH) at one end
- Saturated have NO double bonds (solid at room temp)
- Unsaturated have some (one or more) double bonds between carbons.
2. Neutral Fats: most important in humans are the Triglycerides. Made up of Glycerol (a three carbon modified sugar alcohol) and three long chains of fatty acids. Fats are unsaturated, saturated, or polyunsaturated depending on their fatty acids.
3. Phospholipids: Made up of Glycerol, two long fatty acid chains (non-polar, hydrophobic) and a molecule containing phosphate ion (polar; hydrophilic). Important part of the cell membrane as well as the fatty sheaths around the nerve cells.
4. Steroids: Made up of four interconnected rings of carbon atoms with various carbon chains attached. Examples [cholesterol, vitamin D, male and female hormones]
- Saturated have NO double bonds (solid at room temp)
- Unsaturated have some (one or more) double bonds between carbons.
2. Neutral Fats: most important in humans are the Triglycerides. Made up of Glycerol (a three carbon modified sugar alcohol) and three long chains of fatty acids. Fats are unsaturated, saturated, or polyunsaturated depending on their fatty acids.
3. Phospholipids: Made up of Glycerol, two long fatty acid chains (non-polar, hydrophobic) and a molecule containing phosphate ion (polar; hydrophilic). Important part of the cell membrane as well as the fatty sheaths around the nerve cells.
4. Steroids: Made up of four interconnected rings of carbon atoms with various carbon chains attached. Examples [cholesterol, vitamin D, male and female hormones]
67
New cards
Proteins
- "of first importance"
- Building blocks of all proteins are molecules called amino acids
- Amino acids are made up of C, H, O, and Nitrogen, with occasional phosphorous and sulfur. There are 20 different amino acids in humans — all with the same basic structures.
- directs cell function
- Building blocks of all proteins are molecules called amino acids
- Amino acids are made up of C, H, O, and Nitrogen, with occasional phosphorous and sulfur. There are 20 different amino acids in humans — all with the same basic structures.
- directs cell function
68
New cards
Peptide Bonds
Proteins are amino acids bonded together in a long chain by covalent bonds. Bond between Carbon and Nitrogen.
- Dipeptide "two"
- Tripeptide "three"
- Polypeptide "many
Protein is usually amino acids in chains of thousands
- Dipeptide "two"
- Tripeptide "three"
- Polypeptide "many
Protein is usually amino acids in chains of thousands
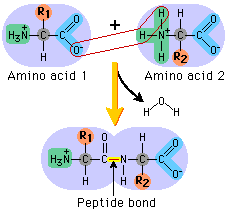
69
New cards
Four Primary Protein Shapes
1) Primary Structure: sequence of amino acids
2) Secondary Structure (the initial shape): H-bonds; Alpha = helix (spiral), Beta = pleated
3) Tertiary Structure: 3D shape
4) Quaternary Structure: Two or more 3D shapes together.
Conformation vs. Denaturation
- Normal shape vs. Not normal shape (heat, change in pH, radiation)
2) Secondary Structure (the initial shape): H-bonds; Alpha = helix (spiral), Beta = pleated
3) Tertiary Structure: 3D shape
4) Quaternary Structure: Two or more 3D shapes together.
Conformation vs. Denaturation
- Normal shape vs. Not normal shape (heat, change in pH, radiation)
70
New cards
Protein Function
Functions of protein are many because they can have such diverse structure:
- Globular Proteins: functional proteins; water soluble. "round, small"
- Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions
- Hemoglobin: carries gasses
- Antibodies: fight infections
- Receptors: bind to other molecules
- Fibrous Proteins: structural proteins; water insoluble. "round, large"
- Connective tissue: body support
- Muscle contractile proteins: movement
- Globular Proteins: functional proteins; water soluble. "round, small"
- Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions
- Hemoglobin: carries gasses
- Antibodies: fight infections
- Receptors: bind to other molecules
- Fibrous Proteins: structural proteins; water insoluble. "round, large"
- Connective tissue: body support
- Muscle contractile proteins: movement
71
New cards
Enzymes
Globular proteins that act as biological catalysts.
- Protein
- Act to regulate chemical reactions in the body:
- Substrate: what enzymes works on
- Enzymes align substrates so they can interact
- lowers activation energy required for a RxN
- Protein
- Act to regulate chemical reactions in the body:
- Substrate: what enzymes works on
- Enzymes align substrates so they can interact
- lowers activation energy required for a RxN
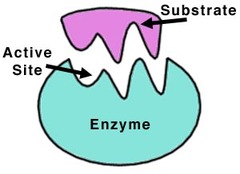
72
New cards
Properties of Enzymes
- Enzymes speed up chemical reactions or allow them to occur at lower temperatures. (They don't cause a reaction that would never otherwise occur)
- In reversible reactions, one enzyme may enable a reaction to go in either direction. [The direction is determined by the Law of Mass Action (concentration of reactants and products)]
AB + C
- In reversible reactions, one enzyme may enable a reaction to go in either direction. [The direction is determined by the Law of Mass Action (concentration of reactants and products)]
AB + C
73
New cards
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The major energy carrying molecule. Structure is similar to a nucleotide found in DNA and RNA, ATP is made up of:
- Adenine (nitrogenous base)
- Ribose (monosaccharide sugar)
- Three phosphate molecules — hence the word TRIphosphate
Function: Immediate energy source [INSIDE THE CELL} for chemical reactions
- ATP --> ADP (adenosine diphosphate) + Phosphate + Energy
- Phosphorylation: adding phosphate to another molecule to give energy
- Adenine (nitrogenous base)
- Ribose (monosaccharide sugar)
- Three phosphate molecules — hence the word TRIphosphate
Function: Immediate energy source [INSIDE THE CELL} for chemical reactions
- ATP --> ADP (adenosine diphosphate) + Phosphate + Energy
- Phosphorylation: adding phosphate to another molecule to give energy
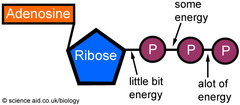
74
New cards
Nucleic Acids
Involved in cell control and heredity. Function = genetic coding, energy currency
75
New cards
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
- Double Stranded HELIX (think of a twisted ladder)
- Each section of the helix is made up of NUCLEOTIDES which are:
- Deoxyribose (a monosaccharide sugar)
- Phosphate
- Nitrogenous base
- Purine bases: Adenine, Guanine (double ring)
- Pyrimadine: Thymine, Cystosine (single ring)
- Twisted ladder shape: rungs on the ladder are bases, uprights of the ladder are sugar chains (deoxyribose) and phosphates
- Complimentary base pairings: Adenine with thymine, and Guanine with cytosine. Held by hydrogen bonds.
- Each section of the helix is made up of NUCLEOTIDES which are:
- Deoxyribose (a monosaccharide sugar)
- Phosphate
- Nitrogenous base
- Purine bases: Adenine, Guanine (double ring)
- Pyrimadine: Thymine, Cystosine (single ring)
- Twisted ladder shape: rungs on the ladder are bases, uprights of the ladder are sugar chains (deoxyribose) and phosphates
- Complimentary base pairings: Adenine with thymine, and Guanine with cytosine. Held by hydrogen bonds.
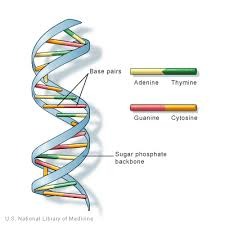
76
New cards
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
- Single stranded
- Instead of thymine, uses the base known as Uracil
- Sugar on backbone is ribose
- Instead of thymine, uses the base known as Uracil
- Sugar on backbone is ribose
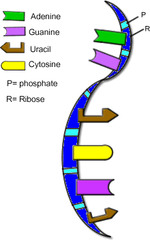
77
New cards
Cell Theory
Three main concepts:
1) Cell is structural + functional unit
2) All life is cellular
3) Cells came from preexisting cells
1) Cell is structural + functional unit
2) All life is cellular
3) Cells came from preexisting cells

78
New cards
Plasma Membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells. Properties of the membrane:
- Protein: Most weight of the membrane
- Integral: all the way through
- Peripheral: on the edge
- Many functions:
- Transport
- Receptor
- Attachment
- Enzyme
- Joining the cell
- Recognition
- Carbohydrates
- Glycoproteins (attached to proteins)
- Glycolipids (attached to fats)
- Full layer on outside = Glycocalyx
- Protein: Most weight of the membrane
- Integral: all the way through
- Peripheral: on the edge
- Many functions:
- Transport
- Receptor
- Attachment
- Enzyme
- Joining the cell
- Recognition
- Carbohydrates
- Glycoproteins (attached to proteins)
- Glycolipids (attached to fats)
- Full layer on outside = Glycocalyx
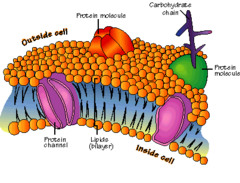
79
New cards
Cell Junctions
- Tight Junctions: a fusion of two cells' membrane proteins, prevents movement between cells
- Desmosome: a fusion of protein plates — anchored into cell. Acts to hold cells together. "joining body" D-somes break down --> shed skin cells
- Gap Junction: made of a large group of channels (connexons):
- Line up up connexons with adjacent cells
- electrochemically couples cells
- Desmosome: a fusion of protein plates — anchored into cell. Acts to hold cells together. "joining body" D-somes break down --> shed skin cells
- Gap Junction: made of a large group of channels (connexons):
- Line up up connexons with adjacent cells
- electrochemically couples cells
80
New cards
Surface Modifications
- Microvilli are finger like extensions: increase surface area (e.g. GI tract).
- Cilia provide motion in order to move, mucus.
- Cilia provide motion in order to move, mucus.
81
New cards
What does selectively permeable mean?
Only allows certain materials to pass through.
82
New cards
Passive Mechanisms To Cross Membrane
No energy used by the cell itself.
- Filtration — Hydrostatic Pressure (fluid pressure)
- Diffusion
- Channel/Carrier-Mediated Diffusion
- Channel-Mediated Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Dialysis
- Tonicity
- Filtration — Hydrostatic Pressure (fluid pressure)
- Diffusion
- Channel/Carrier-Mediated Diffusion
- Channel-Mediated Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Dialysis
- Tonicity
83
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- Why? Kinetic energy of molecules = molecules in constant motion
- Factors affecting rate of diffusion:
- Temperature (increase)
- Concentration gradient (increase)
- Solubility (increase)
- Molecular size/weight (decrease)
- Simple diffusion across membrane
- Lipid soluble solutes: O₂, CO₂, Alcohol
- Facilitated/Carrier-Mediated Diffusion:
- Carrier Proteins: Glucose + certain amino acids
- Channel-Mediated Diffusion:
- Specific Protein Channels: Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca+, ion
- Why? Kinetic energy of molecules = molecules in constant motion
- Factors affecting rate of diffusion:
- Temperature (increase)
- Concentration gradient (increase)
- Solubility (increase)
- Molecular size/weight (decrease)
- Simple diffusion across membrane
- Lipid soluble solutes: O₂, CO₂, Alcohol
- Facilitated/Carrier-Mediated Diffusion:
- Carrier Proteins: Glucose + certain amino acids
- Channel-Mediated Diffusion:
- Specific Protein Channels: Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca+, ion
84
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of H₂O through selectively permeable membrane.
"water follows solute"
"water follows solute"
85
New cards
Dialysis
Diffusion of solute through selectively permeable membrane.
86
New cards
Tonicity of Solution
What does the cell do in various of solutions?
- Isotonic ("same tension/tone")
- Hypertonic ("more"): Crenation
- Hypotonic ("less"): swell, may burst
- Isotonic ("same tension/tone")
- Hypertonic ("more"): Crenation
- Hypotonic ("less"): swell, may burst
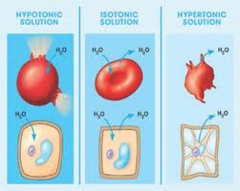
87
New cards
Active Transport To Cross Membrane
Requires energy in form of ATP.
88
New cards
Primary Active Transport
Active transport that relies directly on the hydrolysis of ATP.
- Most investigated example: sodium-potassium pump
[BIGGEST USER OF ENERGY IN THE BODY]
-Solute (ion) against concentration gradient
- What happens?
- Solute binds: to membrane protein
- ATP: Phosphorylates enzyme
- Protein changes shape: ion pumped
- Na+K+ ATP Pump:
- 1 ATP pumps: 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ into cell
- Sets up: concentration gradient across all cell membranes
- Most investigated example: sodium-potassium pump
[BIGGEST USER OF ENERGY IN THE BODY]
-Solute (ion) against concentration gradient
- What happens?
- Solute binds: to membrane protein
- ATP: Phosphorylates enzyme
- Protein changes shape: ion pumped
- Na+K+ ATP Pump:
- 1 ATP pumps: 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ into cell
- Sets up: concentration gradient across all cell membranes
89
New cards
Secondary Active Transport
Form of active transport which does not use ATP as an energy source; rather, transport is coupled to ion diffusion down a concentration gradient established by primary active transport.
90
New cards
Bulk Transport
Endocytosis: "into cell movement"
- Phagocytosis: "cell eating" solids
- Pinocytosis: "cell drinking" Liquids
- Receptor: Mediated Endocytosis will use specific protein receptors on cell surface to engulf specific substances
Exocytosis: Secretion/add/change membrane "out of the cell movement"
- Vesicles, using snare proteins, attach to membrane surface: secrete substances or add/change membrane. "fluid sac"
- Phagocytosis: "cell eating" solids
- Pinocytosis: "cell drinking" Liquids
- Receptor: Mediated Endocytosis will use specific protein receptors on cell surface to engulf specific substances
Exocytosis: Secretion/add/change membrane "out of the cell movement"
- Vesicles, using snare proteins, attach to membrane surface: secrete substances or add/change membrane. "fluid sac"
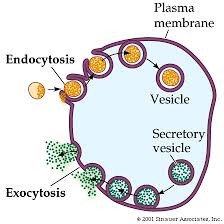
91
New cards
Role of Membrane Receptors
Ligand-Gated Ion Channel:
- Ligand is a chemical that binds to protein
- Binds and opens ion channel to cause ions to diffuse across membranes.
G-Protein Receptor
- Makes 2nd messenger inside the cell
-Ligand binds to receptor
- G protein stimulated (uses energy molecule GTP)
- Effector protein stimulated
- 2nd messenger created inside cell
- Most common is cAMP, made from ATP, creates the effects inside cell
- Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate
- Ligand is a chemical that binds to protein
- Binds and opens ion channel to cause ions to diffuse across membranes.
G-Protein Receptor
- Makes 2nd messenger inside the cell
-Ligand binds to receptor
- G protein stimulated (uses energy molecule GTP)
- Effector protein stimulated
- 2nd messenger created inside cell
- Most common is cAMP, made from ATP, creates the effects inside cell
- Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate
92
New cards
Electro-Chemical Gradient
The diffusion gradient of an ion, representing a type of potential energy that accounts for both the concentration difference of the ion across a membrane and its tendency to move relative to the membrane potential.
Set up by Na+ K+ ATP Pump. Membrane potential voltage. Charge INSIDE cell is negative. More Na+ outside, more K+ inside.
Set up by Na+ K+ ATP Pump. Membrane potential voltage. Charge INSIDE cell is negative. More Na+ outside, more K+ inside.
93
New cards
Aquaporins
Water channel proteins
94
New cards
Cytoplasm
Everything inside the membrane but the nucleus.
95
New cards
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm. "cell solution" ---> H₂O + solutes
96
New cards
Inclusions
Chemical substances such as stored nutrients or cell products.
97
New cards
Organelles
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell.
98
New cards
Mitochondria
- Threadlike or sausage-shaped membraneous organelles.
- Enclosed by two membranes: inner (folds inwards, cristae) and outer (smooth).
- Contain their own DNA and RNA and are able to reproduce themselves.
- Similar to a group of Bacteria
- Function: "power plant" = convert energy
food + O₂ ---> CO₂ + H₂O + Energy
- Enclosed by two membranes: inner (folds inwards, cristae) and outer (smooth).
- Contain their own DNA and RNA and are able to reproduce themselves.
- Similar to a group of Bacteria
- Function: "power plant" = convert energy
food + O₂ ---> CO₂ + H₂O + Energy
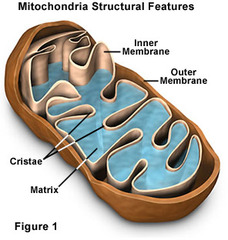
99
New cards
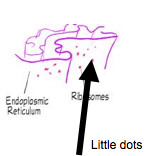
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Extensive system of interconnected tubes and parallel membranes enclosing fluid filled cavities that coil or twist through cytosol.
Two types:
1) Smooth ER: Less common, no ribosomes
- fat metabolism, making membrane for cell
- Ca++ stores in muscle
- Liver detoxing enzymes
2) Rough ER: Common, ribosomes attached
- ribosomes: make protein
- Proteins usually exported from cell
"network within cytoplasm"
Two types:
1) Smooth ER: Less common, no ribosomes
- fat metabolism, making membrane for cell
- Ca++ stores in muscle
- Liver detoxing enzymes
2) Rough ER: Common, ribosomes attached
- ribosomes: make protein
- Proteins usually exported from cell
"network within cytoplasm"
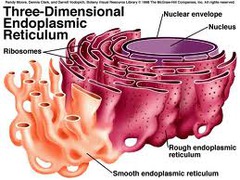
100
New cards
Ribosomes
Small, dark staining granules composed of proteins and a variety of RNA called ribosomal RNA.
- Protein synthesis
- Two subunits: large and small
- Two types of ribosomes:
- Bound (on rough ER): proteins usually for export/secreted from cells
- Free/ Not bound to the ER, usually makes proteins for cell use.
- Protein synthesis
- Two subunits: large and small
- Two types of ribosomes:
- Bound (on rough ER): proteins usually for export/secreted from cells
- Free/ Not bound to the ER, usually makes proteins for cell use.