Disease Detectives - Vocab
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Science Olympiad > Disease Detectives > Basic Vocab from Scioly
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
population oriented, studies community origins of health problems related to nutrition, environment, human behavior, and the psychological, social, and spiritual state of a population.
Classical Epidemiology
The study of the distribution and determinants of health related states/events in a population and how we can control the spread of diease
Epidemiology
studies patients in health care settings in order to improve the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases and the prognosis for patients already affected by a disease.
Clinical Epidemiology
heavily dependent on laboratory support
Infectious Disease Epidemiology
dependent on complex sampling and statistical methods.
Chronic Disease Epidemiology
studies how different environments may result in physical or neurological outcomes.
Environmental Epidemiology
studies unintentional and intentional injuries across a lifespan
Violence and Injury Epidemiology
application of the practice of epidemiology to produce outcomes or research efforts designed to address public health issues.
Applied Epidemiology
aims to describe distributions of diseases and determinants(person, place, and time).
Descriptive Epidemiology
measures the association between a particular exposure and a disease, using information collected from individuals, rather than from the aggregate population(hypothesis testing - study design).
Analytic Epidemiology
(1) Collect Data (2) Assessment (3) Hypothesis Testing (4) Action
Steps in Solving Health Problems
Methods used for collecting, compiling, and preserving health records
Informatics
Perform tests that confirm viruses and disease
Laboratories
showing no signs or symptoms, although can be the carrier of a disease
asymptomatic
an aggregation of cases over a particular period closely grouped in time and space, regardless of whether the number is more than the expected number.
cluster
reduction to zero of a disease in a defined geographical area due to deliberate efforts. This requires continued intervention measures.
elimination
present at a continuous level throughout a population/geographical area; constant presence of an agent/health condition within a given geographical area/population; refers to the usual prevalence of an agent/condition.
endemic disease
large number of people over a wide geographical area are affected.
epidemic
study of the cause of a disease
etiology
a physical object that serves to transmit an infectious agent from person to person.
fomite
an illness that is caused by medication or a physician.
iatrogenic
time in between when a person comes into contact with a pathogen and when they first show symptoms or signs of disease.
Incubation Period
first patient in an epidemiological study
index case(a.k.a. patient zero or primary case)
rate of disease in a population
morbidity
rate of death in a population
mortality
an infection that is acquired in a hospital.
nosocomial disease
more cases of a particular disease than expected in a given area or among a specialized group of people over a particular period of time.
outbreak
an epidemic occurring over several countries or continents and affecting a large proportion of the population.
pandemic
a serious, potentially life-threatening infectious disease that is usually transmitted to humans by the bites of rodent fleas.
plague
the probability that an individual will be affected by, or die from, an illness or injury within a stated time or age span.
risk
number of deaths due to a disease/number with the disease
Case Fatality Rate
number of deaths due to a disease/number in population
Cause-Specific Mortality Rate
the systematic and ongoing collection, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of health data. The purpose of public health surveillance is to gain knowledge of the patterns of disease, injury, and other health problems in a community so that we can work towards their prevention and control.
surveillance
showing symptoms or signs of injury
symptomatic
an animal that transmits disease but is not the cause of the disease itself.
vector
an infectious disease that is transmissible from animals to humans.
zoonosis
number of new instances of disease in a population over a given time period. Expressed as X cases/Y population/Z time.
incidence
number of affected persons in the population at any given point in time. Expressed as X cases/Y population
prevalence
snapshot of the population and its rate of a certain disease at a point in time
point prevalence
tracks prevalence over a certain duration
period prevalence
diseases are reported by healthcare providers. This type, though simple and inexpensive, is often limited by incomplete reporting and quality variation in reporting.
passive surveillance
Health agencies contact health providers seeking reports. This ensures more complete reporting of conditions. Often used with specific epidemiological investigations or during an outbreak.
active surveillance
the syndrome of disease is monitored as a proxy for the disease. The syndrome must be infrequent and severe enough to warrant investigation of each identified case, and must be unique.
syndromic surveillance
professionals selected to represent a specific geographic area or group report health events to health agencies. This is used when high-quality data can't be obtained through passive surveillance. It involves monitoring trends or key health indicators and a limited network of reporting sites.
sentinel surveillance
humans are also capable of spreading disease following a period of illness, typically thinking themselves cured of the disease.
convalescent vectors
when an individual transmits pathogens immediately following infection but prior to developing symptoms
incubatory vectors
someone who can transmit a disease for a long period of time
chronic vector
has inherited a disease trait but shows no symptoms
genetic vector
someone who can transmit an infectious disease for a short amount of time
transient/temporary vector
person, place, and time
What is the first epidemiological triad?
An external agent, a vector or fomite that transmits the disease, and a susceptible host for the disease
What is the Chain of Transmission Triad?
to define the major points of a disease case
What is the Chain of Transmission Triad used for?
comparisons of geographical locations
ecological study
a survey, health questionnaire, “snapshot in time”
cross sectional study
compare people with and without disease to find common exposures
case-control studies
compare people with and without exposures to see what happens to each
cohort study
human experiment that randomly assigns participants to an experimental or control group
randomized controlled trial
research similarities with traditional experimental design or RCT, but lack element of random assignment to treatment/control; participants are assigned a group based on non-random criteria.
quasi experiments
most scientifically sound and best measure of exposure
advantages to trial study:
time consuming, unethical for harmful exposures, most expensive
disadvantages of trial study:
most accurate observational study, good measure of exposure, correct time sequence, good for rare exposures, easy risk calculation
advantages of cohort study:
time consuming, expensive, bad for rare diseases, possible loss of follow-up
disadvantages of cohort study:
can study rare diseases, relatively less expensive, relatively fast, good for rare diseases, good for long latency periods
advantages of case-control study:
possible time-order confusion, error in recalling exposure, only 1 outcome
disadvantages of case-control study:
fastest, least expensive, good for more than 1 outcome
advantages of cross-sectional study
possible time-order confusion, least confidence in findings
disadvantages of cross-sectional study:
a table which has two columns and rows for people with or without exposure and with or without disease; shows number of people with each characteristic
2×2 table
primary role is diagnosis and treatment of illness in individuals, preventive medicine(e.g., immunizations, smoking cessation, obesity counselling and other behavioral/lifestyle concerns) has only been addressed recently - focus remains on the individuals.
clinical approach
primary role is in control and prevention of disease in population or groups of individuals, some activities(e.g., diagnosing cases associated with outbreaks and treating persons with communicable diseases such as tuberculosis or syphilis) may overlap with those in clinical medicine.
public health approach
many microbes have a positive symbiotic relationship with other organisms
normal flora
both organisms benefit
mutualism
one organism and the other is not harmed or helped
commensalism
the condition(one organism is helped and the other is harmed) which takes place when humans are invaded by infectious microbes. A parasite-host relationship is created.
parasitism
chain of infection
agent
reservoir
portal of exit
mode of transmission
portal of entry
susceptible host
Koch’s Postulates
developed by German physician Robert Koch in the late 19th century to establish a causal relationship between a causative microbe and a disease
Evan’s Postulates
expanded on Koch’s postulates and addressed limitations in identifying causal relationships between diseases and infectious agents
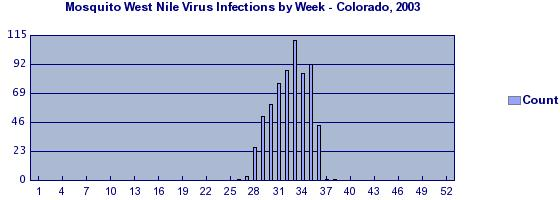
point source epidemics
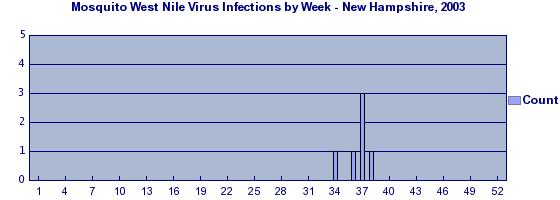
occurs when people are exposed to the same exposure over a limited period of time; curve rapidly rises and contains a definite peak followed by a gradual decline
exposure is prolonged over an extended period of time and may occur over more than one incubation period; down slope could be sharp or gradual
continuous common source epidemics
propoccurs when a case serves as a later source of infection; shape usually contains a series of successively larger peaks; as the outbreak progresses, the peaks flatten out
propagated (progressive source) epidemics
pertaining to how the participants are chosen or retained in a study; affects the accuracy and applicability of the data
selection biases
biases stemming from errors in accuracy or lack of completeness in data
performance biases
biases stemming from errors in accuracy or lack of completeness in data
measurement biases
biases stemming from errors in accuracy or lack of completeness in data
information biases
biases stemming from subjective judgement and irrational decision-making
cognitive biases
general errors affecting the entire study and framework
reporting biases
general errors affecting the entire study and framework
systemic biases
biases related to time in study design
temporal biases