CHP.2 SLEEP
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
consciousness
the state of being aware of and responsive to one’s surroundings, including one’s own thoughts, feelings, and sensations
hypnosis
an induced, altered state of consciousness that heightens a person’s openness to responding to suggestion without losing his or her sense of self control
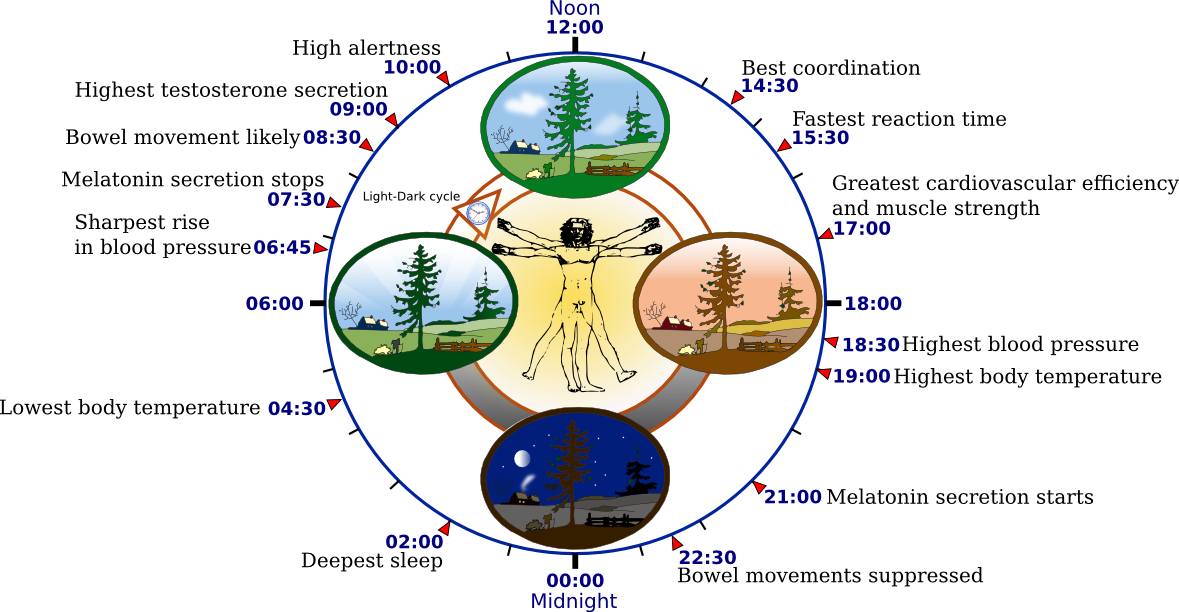
circadian rhythm
a 24-hour cycle biological clock
body temp rises and sets with the sun, reaching its peak at noon
jet lag
a disruption of the circadian rhythm, typically a byproduct of time zone changes
shift work
working specific time shifts that misalign with the circadian rhythm
melatonin
a “sleep” hormone secreted in the bloodstream
production is signaled to start by darkness, and signaled to end with light
EEG machine
monitors brain activity and can be used to measure the stages of sleep
beta waves
when you’re awake, active, and alert
alpha waves
when you’re relaxed, drowsy, or meditating
theta waves
when you’re in light sleep, predominantly in NREM stage 1
delta waves
when you’re in deep sleep, predominantly in NREM stage 3
NREM stage 1 sleep
lightest stage of sleep, often retaining awareness of surrounding stimuli
only lasts one to five minutes
NREM stage 2 sleep
the stage in which the most time sleeping is spent
lasts around twenty minutes, whilst heart rate slows and breathing shallows
time spent in this stage gets longer as the night progresses
NREM stage 3 sleep
as the night goes on, time spent in this stage diminishes
if awoken, an individual would be groggy and disoriented
vital for restoring body’s growth hormones and for good overall health
hypnagogic sensations
mild sensations, often of falling
signature to NREM stage 1
REM sleep
rapid eye moment, around every half minute your eyes dart around
20% of sleep time is spent here, with roughly 5 cycles per night, lasting 15-45 minutes out of every 90 minutes
when the most dreams occur, leading to elevated heart rate and rapid breathing
paradoxical sleep
motor cortex is active, but the brainstem blocks its messages to the rest of your body, preventing motion despite dreams
brain is extremely active, yet the body is paralyzed
REM rebound
the tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation
activation synthesis theory
our cerebral cortex is attempting to interpret random electrical activity that we have while asleep
the brain area processes visual images by result of stimulation, hence why dreams tend to make little sense
active; limbic system (emotional center) & amygdala (fear and aggro center)
idle; frontal lobe (logic, judgment, and reason center)
consolidation theory
the brain uses REM sleep periods and dreams as a means to sift, sort, and fix the day’s experiences in our memory
brain scans confirm a link between the amount of REM sleep acquired and memory
insomnia
persistent problems in falling asleep and staying asleep
most common sleep complaint among americans, found in 1/5 adults
some causes include stress, worrying, changing circadian rhythms, medical problems, and substance abuse
narcolepsy
marked by excessive sleepiness that may cause an individual to fall asleep at unpredictable or inappropriate times
“sleep attacks” lasting one to five minutes, directly into REM sleep
a result of a hypocretin deficiency (?)
REM sleep behaviour disorder
normal REM paralysis by result of brain-stem blockage does not occur, causing twitching, talking, or in severe cases attacking to occur
sleep apnea
a person stops breathing in their sleep for ten seconds or longer, causing them to wake up momentarily to gasp for air (snore)
affects 1/20 people, especially prevalent in heavy males
deprives NREM stage 3 sleep, and can be fatal
somnambulism
sleep walking, occurring in NREM stage 3 sleep in the earlier sleep hours
affects 1/15 people, can be genetically linked
usually occurs when an individual is stressed or sleep deprived
psychoactive drugs
chemicals that affect the brain
tolerance
the diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose of a drug, requiring a user to take larger and larger doses in an attempt to chase the desired effect
addiction
compulsive substance use that continues despite harmful consequences
withdrawal
the discomfort and distress that follows discontinuing an addictive drug or behaviour
depressants
drugs that calm neural activity and slow body functions
ex. alcohol, opioids
alcohol
slows neural processing, self-awareness, and brain activity that controls judgment and movement
disrupts the memory and increases harmful tendencies
opioids
serves as an agonist for endorphins, while slowing neural activity and temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
ex. heroin
stimulants
excites neural activity and speeds up bodily functions
ex. caffeine, cocaine
pupils dilate, heart rate and breathing hasten, blood sugar levels rise, appetite reduces, energy and self-confidence increase
caffeine
the world’s most widely consumed psychoactive substance
mild dose can last three to four hours, impairing sleep, boosting blood pressure, and leading to heartburn or ulcers
like most other drugs, can create tolerance and cause withdrawal
withdrawal symptoms include fatigue and headaches
cocaine
a powerful, addictive stimulant that can be snorted, injected, or smoked
enters the bloodstream quickly, producing a rush of euphoria that depletes the brain’s supply of the neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine
may lead to emotional disturbances, suspiciousness, convulsions, cardiac arrest, and respiratory failure
hallucinogens
distorts perceptions and evokes sensory images in the absence of sensory input, which is why they are often also referred to as psychedelics
ex. marijuana
marajuana
can be consumed (slow) or inhaled (quick)
contains THC, which may induce psychiatric symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and anxiety. may also amplify sensitivity to external stimuli, and lingers in the body for more than a week
impairs motor coordination, perceptual skills, reaction time, memory formation, and attention span
heroin
a type of opioid that offers a blissful pleasure that replaces pain and anxiety
causes the user’s pupils to contract, breathing to slow, and lethargy to kick in