2023.v3b_VA Nail Tech Theory Practice
1/255
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
256 Terms
Microbiology
The study of microorganisms
Bacteria
Also called germs, are one-celled microbes. both disease and non-disease producing single-celled microorganisms
Virus
a sub-microscopic infections agent that replicates only within the cell of a living host
Nonpathogenic
nondisease-producing bacteria
Pathogenic
Disease-producing bacteria
Carbon
One of the elements that makes up keratin
Cocci - Think, c=Circle and Cocci.
Spherical or round-shaped bacterial cells that appear singularly or in groups.
Staphylococci
Pus-forming bacteria that grow in clusters like a bunch of grapes. They cause abscesses, pustules, and boils.
Streptococci
Pus-forming bacteria arranged in curved lines, long chains, resembling a string of beads. They cause infections such as strep throat and blood poisoning.
Diplococci - think d= double and diplococci
Spherical bacteria that grow in pairs and cause diseases such as pneumonia.
Bacilli (bacillus)
Most common form of bacteria cell. rod-shaped bacteria (cause of tuberculosis, tetanus)
Spirilla -Think s = spiral and spirilla
spiral, coiled, corkscrew-shaped bacteria that cause highly contagious diseases such as syphilis and cholera.
Mitosis
During active stage, aka the vegetative stage, bacteria reproduce and grow rapidly. As the bacteria absorb food, each cell grows in size. When it is fully grown, it divides to create two cells.
Sanitization
the lowest level of infection control and serves as the foundation of your infection control program
Disinfection
Second level of infection control and means using products (or methods) that kill or destroy bacteria and a broad spectrum of viruses.
Sterilization
Is the third and highest level of infection control. It destroys all living organisms, including bacterial spores, which neither sanitization nor disinfection can kill.
Product Label
Lists ingredients including potential hazards.
MSDS- Material Safety Data Sheet
Must keep a copy of every MSDS in a file or binder that is easily accessible.
Section I: Product name and company name
Section II: Hazardous Ingredients
Section III: Physical and chemical ingredients
Section IV: Fire and Explosion hazard data
EPA registered, hospital level disinfectant
Includes: Germicidal, Fungicidal, Pseudomonacdial and Viricidal
Product efficacy label
Describes what a product is effective in fighting against
Onychosis (on-i-Ko-sis)
Any disease or disorder of the nail
Identification - of the disease or disorder
Etiology - the study of the cause of a disease or disorder
Indications-symptoms and appearance
Services-products used/recommended, techniques
Four factors of the study of Onychosis
Onychia (o-NIK-e-a)
Inflammation of the nail matrix - NO Service
Paronychia (par-o-NIK-e-a) or Felon
inflammation of the skin around the nail - NO Servicer
Onychomycosis (o-ni-ko-mi-KO-sis) or
Tinea unguim (TIN-ee-ah Un-gwee-um)
Ringworm of the nail - NO Service
Onychatrophia (o-ni-ka-TRO-fe-a)
Atrophy of the nail or wasting away of the nail - no service on affected nail
Onycholiysis (o-ni-KOL-i-sis)
refers to a loosening or separation of the nail - no service on affected nail
Onychomadesis (-on-i-ko-MAH-de-sis)
refers to loss of the nail plate with separation occurring at the nail matrix - no service on affected nail
Onychoptosis (o-ni-ko-to-sis)
Refers to shedding or falling off of nails - - no service on affected nail
Blue Nails
Appear bluish in color
Pterygium (te-RIJ-ee-uhm)
Living skin attached to the nail plate
Egg Shell Nails
Thin, soft nails - light pressure/nail strengthener
Corrugations
Horizontal ridges across the nail plate - lightly buff the surface
Koilonuchia (kol-e-o-NIK-e-a)
Nails with a concave shape - light pressure/nail strengthener
Furrows
Indented vertical lines down the nail plate - lightly buff the surface
Onychogryposis (o-ni-ko-GRI-po-sis)
Claw nail; increased curvature - Service is there is no sign of infection; do not trim the nail; file to shorten
Onychocryptosis (o-ni-KRI-to-sis)
Ingrown nail - service if no sign of infection/tenderness; trim straight across
Tile-shaped nails
Exaggerated or deep c-curve - use care when trimming; avoid trimming too short
Pincer nails (trumpet)
Corners fold inward at the tip of the finger or toe - use care when trimming; avoid trimming too short
Plicatured nails
90 degree or greater fold - use care when trimming; avoid trimming too short
Onychauxis (o-ni-KOK-sis) or hypertrophy
Thickening of the nail plate or an abnormal outgrowth of the nail - use caution
Onychophyma
Swelling of the nail - often associated with Onychauxis) - use caution
Agnails (hangnails)
Split cuticles - use cuticle conditioner
Bruised nails
Discoloration under the nail plate - no pressure on the nail
Onychophagy (o-ni-KOF-a-je)
Bitten nails - service
Onychorrhexis (o-ni-ko-REK-sis)
Brittle nails - use cuticle conditioner and lotion
Lueconychia (loo-ko-NIK-e-a)
White spots - service
Melanonychia (mel-an-oh-NIK-e-a)
Dark stipe down the nail - service
Six signs of infection
Pain, swelling, redness, local fever, throbbing and pus
Temperature of skin
Coldness may indicate poor circulation; heat may indicate infection
Skin texture/feel
May indicate need for moisture
Inflammation/redness on hand or nail
May indicate need for moisture or possible disease or disorder
Color/condition of nail bed
May identify visible injuries, disease and/or indication of poor circulation
Condition and length of free edge
May identify nail biter or “picker”; may indicate dry, brittle nails
Tenderness or stiff joints
May indicate need to alter massage to ensure client comfort
Shape and thickness of nail plate
may indicate a disease or disorder and how to properly file
Causes of nail diseases
Bacteria, fungi, viruses or illnesses
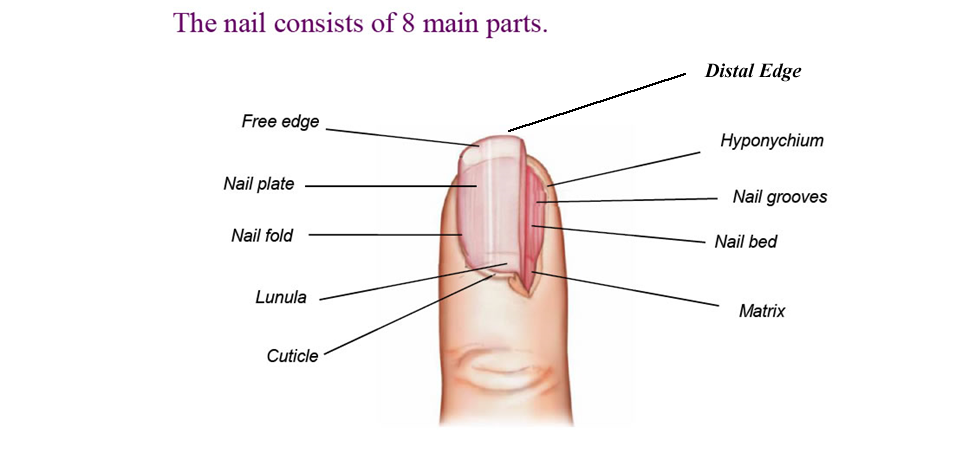
free edge
Part of the nail that extends beyond the finger or toe and protects the tips of the fingers and toes
Onychodermal Band
Appears as a glassy, grayish band at the point where the nail plate meets the hyponichium.
nail plate
The visible nail area from the nail root to the free edge, it is made up of several transparent layers of hardened cells, which do not contain any nerves or blood vessels
nail wall
Consists of the folds of skin on either side of the nail groove
lunula
Is the white, half- moon shape at the base of the nail
eponychium
the area that overlies the matrix at the base of the nail and provides a watertight seal that protects against infections
nail cuticle
the loose and pliable overlapping skin, which forms a watertight seal around the nail, it is a thing layer of skin that as it sheds attaches to the top layer of the nail plate
nail matrix
the active tissue that generates cells, which harden as they move outward from the nail root to the nail plate.
Contains lymph, blood vessels and nerves that create cells, which are pushed outward from the nail root.
nail root
Attached to the nail matrix at the base of the nail, under the skin and inside the mantle
mantle
Pocket like structure that holds the root and matrix
nail bed
the area of the nail on which the nail plate rests, nerves and blood vessels found here supply nourishment to the entire nail unit
nail body ligaments
Specialized ligaments; attach the nail bed to the bone
nail folds
Sometimes referred to as grooves, are the tracks on either side of the nail that the nail moves on as it grows
perionychium
the skin that touches, overlaps and surrounds the side of the nail
bed epithelium
Is a thin, sticky later of the epidermis (uppermost layer of skin) that attaches the nail plate to the nail bed
hyponychium
The skin under the free edge, which acts as a watertight seal to prevent bacteria from entering the nail bed
Integumentary system
made of the skin and its layers
On average, a nail grows how much per month
1/8” (.375 cm)
Six primary functions of the skin
Protection, absorption, secretion, excretion, regulation, sensation
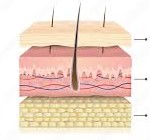
Three main layers of skin
Epidermis: outermost later (aka cuticle or scarf skin)
Dermis: underlying, or inner, second layer (aka derma corium, cutis or true skin)
Subcutaneous layer: located below the dermis and is composed primarily of adipose (fatty) tissue (aka subcutis or subdermal)(
five layers of the epidermis
Stratum Cornuem: uppermost layer, aka the horny layer, is the toughest layer of the epidermis and is composed of keratin protein cells that are constantly shed and replaced with cells from below.
Stratum Lucidum: is the transparent layer that lies between the stratum corneum and stratum granulosum
Stratum Granulosum: contains cells that are more regularly shaped and resemble many tiny granules
Stratum Spinosum: is often called the spiny layer because the connections between the cells appear like “spines”
Stratum Germinativum: the lowest layer of the epidermis, aka the basal layer. This layer contains basal cells that continually divide through the process called mitosis, to replace the cells that are lost from the hardened (keratinized) outermost layer, the stratum corneum
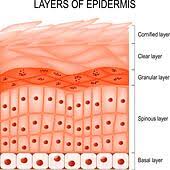
Keratinization
The chemical change of the living cells into dead protein cells, begins when the newly produced cells are pushed toward the surface
Melanocytes
Found in the stratum germinativum, produces melanosomes, or pigment granules containing melanin, that gives the skin color.
Dermis or dermal layer
Often referred to as the “true Skin” or corium
Also found in the dermis layer
Sudoriferous glands (sweat glands), Sebaceous glands (oil glands), sensory nerve endings and receptors, blood vessels, arrector pili muscles and a major portion of each hair follicle.
The symptoms or signs of a disease or disorder are divided into two classifications:
Subjective - those you feel
Objective - those you see
Three categories of skin lesions
Primary, secondary and tertiary
Primary skin lesions
Macule: is a discoloration appearing on the skin’s surface
Papule: is a hardened red elevation of the skin in which no fluid is present
Vesicle: is a fluid-filled elevations in the skin caused by localized accumulation of fluids or blood just below the epidermis
Bulla: is a lesion, like a vesicle, but larger. Found above and below the skin, bullae contain a clear, watery fluid, a friction blister is an example of a bulla
Pustule: is a small elevation of the skin similar to a vesicle in size and shape, but containing pus
Wheal: is a solid formation above the skin, often caused by an insect bite or allergic reaction
Tumor or nodule: is a solid mass in the skin. these lesions are usually more than 1 cm in diameter.
Cyst: is an abnormal membranous sac containing a gaseous, liquid or semi-solid substance
Secondary Skin Lesions
Scale: is a shedding of a dead cell from the uppermost layer of the epidermis
Crust: is a dried mass that is the remains of an oozing sore (scab)
Excoriation: is a mechanical abrasion to the epidermis (or an injury to the epidermis)
Fissure: is a crack in the skin. These lesions usually appear as cracks or lines that may go as deep as the underlying dermis (chapped lips)
Scar: is a formation resulting from a lesion, which extends into the dermis or deeper, as part of the normal healing process.
Ulcer: is a open lesion visible on the surface that may result in the loss of portions of the dermis and may be accompanied by pus
Verruca
Variety of warts - no service in affected area
Herpes Simplex
Blisters or sores around and on the mouth - service after proper handwashing
Tinea Manus
Ringworm of the hand - NO service
Tinea pedis
Athlete’s foot or ringworm of the feet - NO service
Contact dermatitis
Rash - NO service
Psoriasis
Thick, Scaly, Silvery skin patches surrounded by a red area - service unless skin is inflamed or broken in area to be serviced
Eczema
Dry or moist leasions, an eruption of small vesicles - service unless skin is inflamed or broken in area to be serviced
Hyperkeratoses
The thickening of the epidermis to protect the hands and feet due to friction or pressure. the excessive growth of keratin in the epidermis causes the skin to develop corns or calluses
Callus
Thickening of the epidermis. The technical term for callus is tyloma - service
Corn
A hard or soft tissue growth due to inflammation - service; use caution around affected area
Hyperpigmentation
An excess production of melanin causes the skin to appear darker in certain areas
Hypopigmentation
A lack of the production of melanin causes the skin to appear lighter in spots
Pigmentation Disorders
Melanoderma: Freckles
Chloasma: Liver Spots - usually on hands and face
Mole: small, brown pigmented spot
Naevus: Birthmark
Leukoderma: Hypopigmentation caused by a decrease in activity of the melanocytes
Albinish: skin’s failure to produce melanin
Vitiligo: oval or irregular patches of white skin that do not have normal pigment.
Anatomy
The study of the organs and the systems of the body