HSCI Lecture: Blood Vessels
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:54 AM on 2/11/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
1
New cards
Arteries
- carry blood away from heart (carry oxygen rich blood)
- carry blood that has high pressure
- carry blood that has high pressure
2
New cards
Capillaries
- smallest blood vessels
- deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues
- deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues
3
New cards
Veins
- carry blood from capillary beds back to heart (carry non-oxygen rich blood)
4
New cards
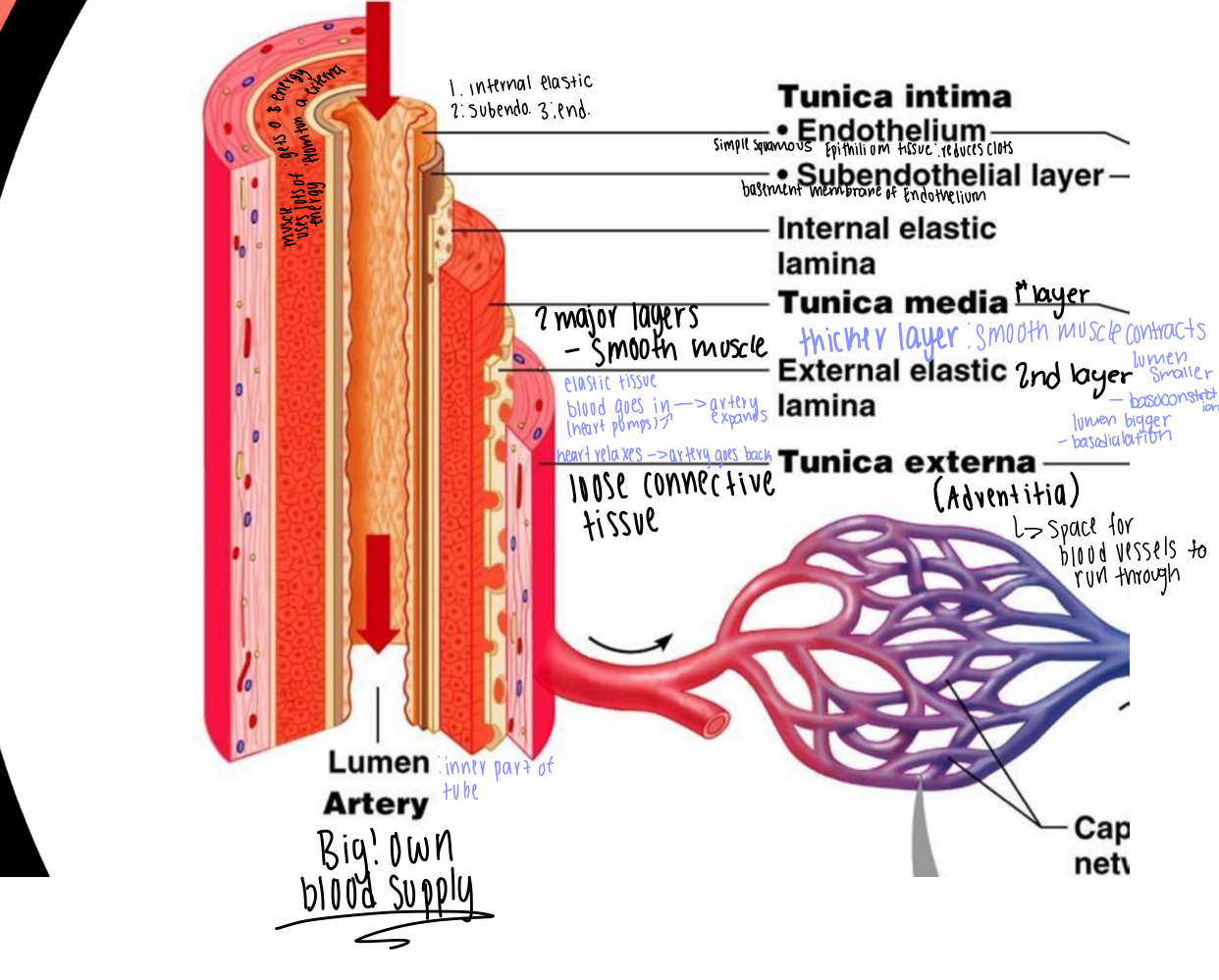
Structure of Arteries (lots of layers)
lots of layers because blood pressure is high in arteries
- leads to thicker walls then veins that are the same size
- arteries are so big they has their own blood supply
1st (outermost) Layer : Tunica Externa
- loose connective tissue (adds structure)
- holds capillaries, and nerves that feed the artery
2nd (middle) layer: Tunica Media (divided into two parts/2 layers)
- (1st part/layer) large layer of smooth muscle = TUNICA MEDIA
-thicker then in veins -> allows artery to contract or relax
- contracts = causes diameter of lumen to get smaller = called
VASOCONSTRICTION
- relax's = causes diameter of lumen to get bigger = called
VASODIALATION
- (2nd part/layer) = EXTERNAL ELASTIC LAMINA
* when heart pumps a large amount of blood gets pushed into artery which causes artery to expand and then heart relax's = artery has to go back to normal shape
- layer of elastic tissue = allows artery to stretch and go back to
its shape quickly
3rd (innermost) layer = Tunica Intima (made up of 3 sub layer's)
- (1st layer) INTERNAL ELASTIC LAMINA
- layer of elastic tissue = allows artery to stretch and go back to
its shape quickly
- (2nd layer) SUBENDOTHELIAL LAYER
- basement membrane for endothelium
- (3rd layer) ENDOTHELIUM (endo- = inside of something)
- is simple squamous epithelium (agains lumen) (reduces clots
from forming)
* lumen = hollow space inside structure
- leads to thicker walls then veins that are the same size
- arteries are so big they has their own blood supply
1st (outermost) Layer : Tunica Externa
- loose connective tissue (adds structure)
- holds capillaries, and nerves that feed the artery
2nd (middle) layer: Tunica Media (divided into two parts/2 layers)
- (1st part/layer) large layer of smooth muscle = TUNICA MEDIA
-thicker then in veins -> allows artery to contract or relax
- contracts = causes diameter of lumen to get smaller = called
VASOCONSTRICTION
- relax's = causes diameter of lumen to get bigger = called
VASODIALATION
- (2nd part/layer) = EXTERNAL ELASTIC LAMINA
* when heart pumps a large amount of blood gets pushed into artery which causes artery to expand and then heart relax's = artery has to go back to normal shape
- layer of elastic tissue = allows artery to stretch and go back to
its shape quickly
3rd (innermost) layer = Tunica Intima (made up of 3 sub layer's)
- (1st layer) INTERNAL ELASTIC LAMINA
- layer of elastic tissue = allows artery to stretch and go back to
its shape quickly
- (2nd layer) SUBENDOTHELIAL LAYER
- basement membrane for endothelium
- (3rd layer) ENDOTHELIUM (endo- = inside of something)
- is simple squamous epithelium (agains lumen) (reduces clots
from forming)
* lumen = hollow space inside structure
5
New cards
Tunica Externa
the blood vessels within the tunica externa supply blood and energy to tunica media (smooth muscle)
6
New cards
Classifications of Arteries
Elastic Arteries (closer to heart)
- big and thick
- super stretchy to handle pressure of blood from heart
- cause a consistant flow (laminer flow) of blood to veins and capillaries
Muscular Arteries (muscular)
- usually off of the aorta
- thick tunica media!!!
- slightly smaller then elastic arteries
- go to entire organs
- more control (can restrict amount of blood going in)
- muscles in walls causes contractions (blood in)
Arterioles (smallest)
- permit or restrict blood flow to capillary beds through vasoconsrtiction and vasodilation
- big and thick
- super stretchy to handle pressure of blood from heart
- cause a consistant flow (laminer flow) of blood to veins and capillaries
Muscular Arteries (muscular)
- usually off of the aorta
- thick tunica media!!!
- slightly smaller then elastic arteries
- go to entire organs
- more control (can restrict amount of blood going in)
- muscles in walls causes contractions (blood in)
Arterioles (smallest)
- permit or restrict blood flow to capillary beds through vasoconsrtiction and vasodilation
7
New cards
to much blood pressure (in elastic artieries)
* blood pressure= systolic pressure-> systoli= highest number
* diastolic pressure-> lowest number
***** stiffining of arteries (age) = increase pressure-> damage walls
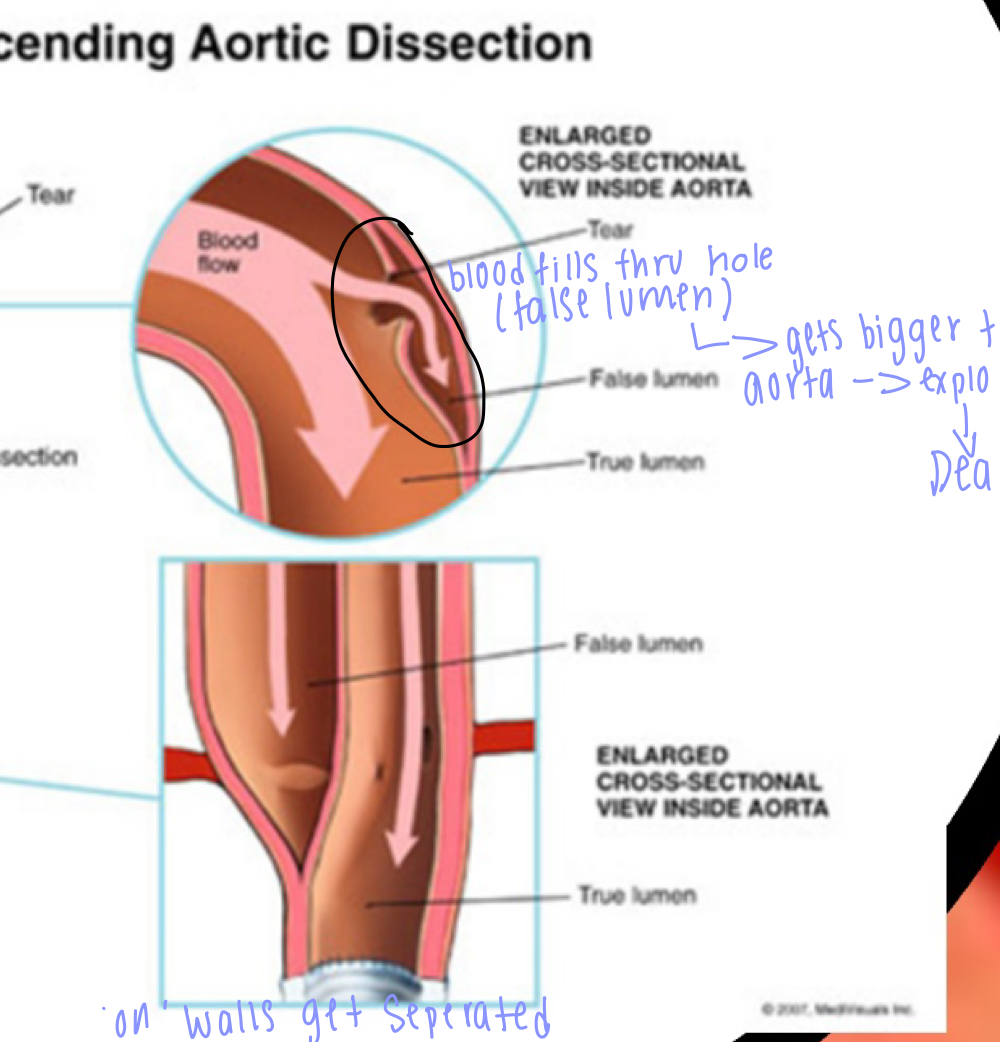
- aortic dissection (high blood pressure is the cause)= tunica intima breaks down, endothelium (simple squamous epithilium) -> false lumen (hole in the wall) = starts to disect the tunica intima from the tunica media = false lumen gets filled with blood (ANYERISM) false lumen really big compressing real lumen (blood cant get through) POP! of false lumen= dead!
- symptoms: see pulsing of persons abdomin, chest pain, fatigue, indigestion
- solutions: put in a graph cavelar graph
* diastolic pressure-> lowest number
***** stiffining of arteries (age) = increase pressure-> damage walls
- aortic dissection (high blood pressure is the cause)= tunica intima breaks down, endothelium (simple squamous epithilium) -> false lumen (hole in the wall) = starts to disect the tunica intima from the tunica media = false lumen gets filled with blood (ANYERISM) false lumen really big compressing real lumen (blood cant get through) POP! of false lumen= dead!
- symptoms: see pulsing of persons abdomin, chest pain, fatigue, indigestion
- solutions: put in a graph cavelar graph
8
New cards
Capillaries
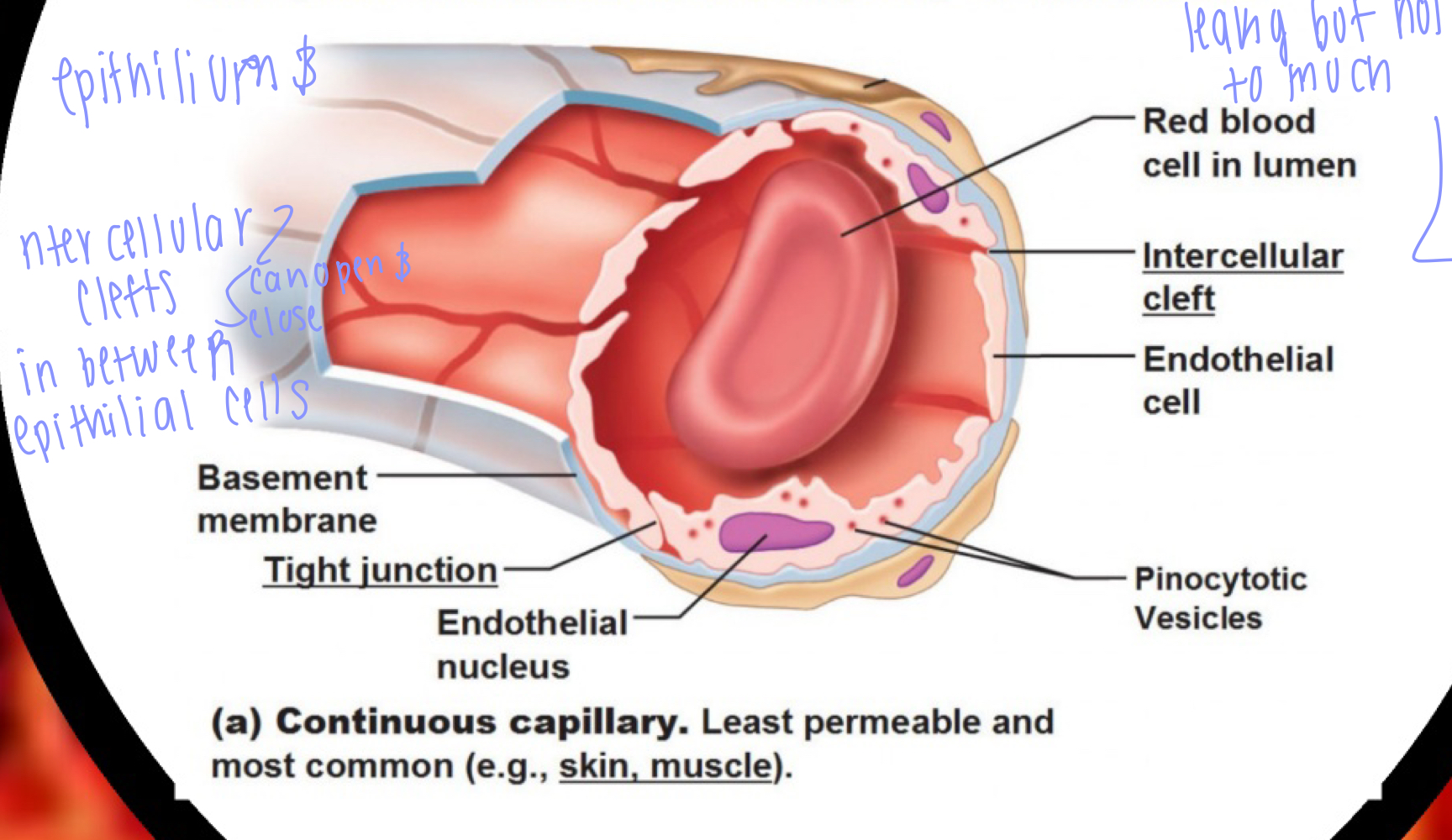
Structure (selectively leakyness) (very delicate)
1st layer (simple squamous endothilium)
2nd layer (basement membrane)
- is made up of tight junctions with spaces called intercellular clefts (small molecules can pass through)
- intercellular clefts (small holes in between epithieleal cells) can open (clefts get bigger) and close (clefts get smaller)
- one blood cells pass at a time (in a line)
**** selective leakiness
Inflamation: makes capillaries more leaky ->fluid, antibodies, proteins, and white blood cells start leaking out BUT you don't want red blood cells leaking out (bleeding)
*******In a healthy inflammatory response there should be no red blood cells leaking out!!!!!
1st layer (simple squamous endothilium)
2nd layer (basement membrane)
- is made up of tight junctions with spaces called intercellular clefts (small molecules can pass through)
- intercellular clefts (small holes in between epithieleal cells) can open (clefts get bigger) and close (clefts get smaller)
- one blood cells pass at a time (in a line)
**** selective leakiness
Inflamation: makes capillaries more leaky ->fluid, antibodies, proteins, and white blood cells start leaking out BUT you don't want red blood cells leaking out (bleeding)
*******In a healthy inflammatory response there should be no red blood cells leaking out!!!!!
9
New cards
Pulmonary edema
- capillaries to leaky which causes fluid (plasma, white blood cells) build up in lungs
- pressure of blood in right side of heart increases dramatically left side HEART FALIURE causes this -> congestion (blood getting stuck in heart) all the way back to capillaries in lungs = leak!!!
- massive accumulation of fluid in lungs caused by excess leakage of fluid out of capillaries in lungs = caused by congestion
solution:
stop leaking!
diuretics (pee a lot) = dehydrate us (drains water in blood) -> blood volume gets reduced = less pressure = reduce leakiness (less blood to leak out)
- pressure of blood in right side of heart increases dramatically left side HEART FALIURE causes this -> congestion (blood getting stuck in heart) all the way back to capillaries in lungs = leak!!!
- massive accumulation of fluid in lungs caused by excess leakage of fluid out of capillaries in lungs = caused by congestion
solution:
stop leaking!
diuretics (pee a lot) = dehydrate us (drains water in blood) -> blood volume gets reduced = less pressure = reduce leakiness (less blood to leak out)
10
New cards
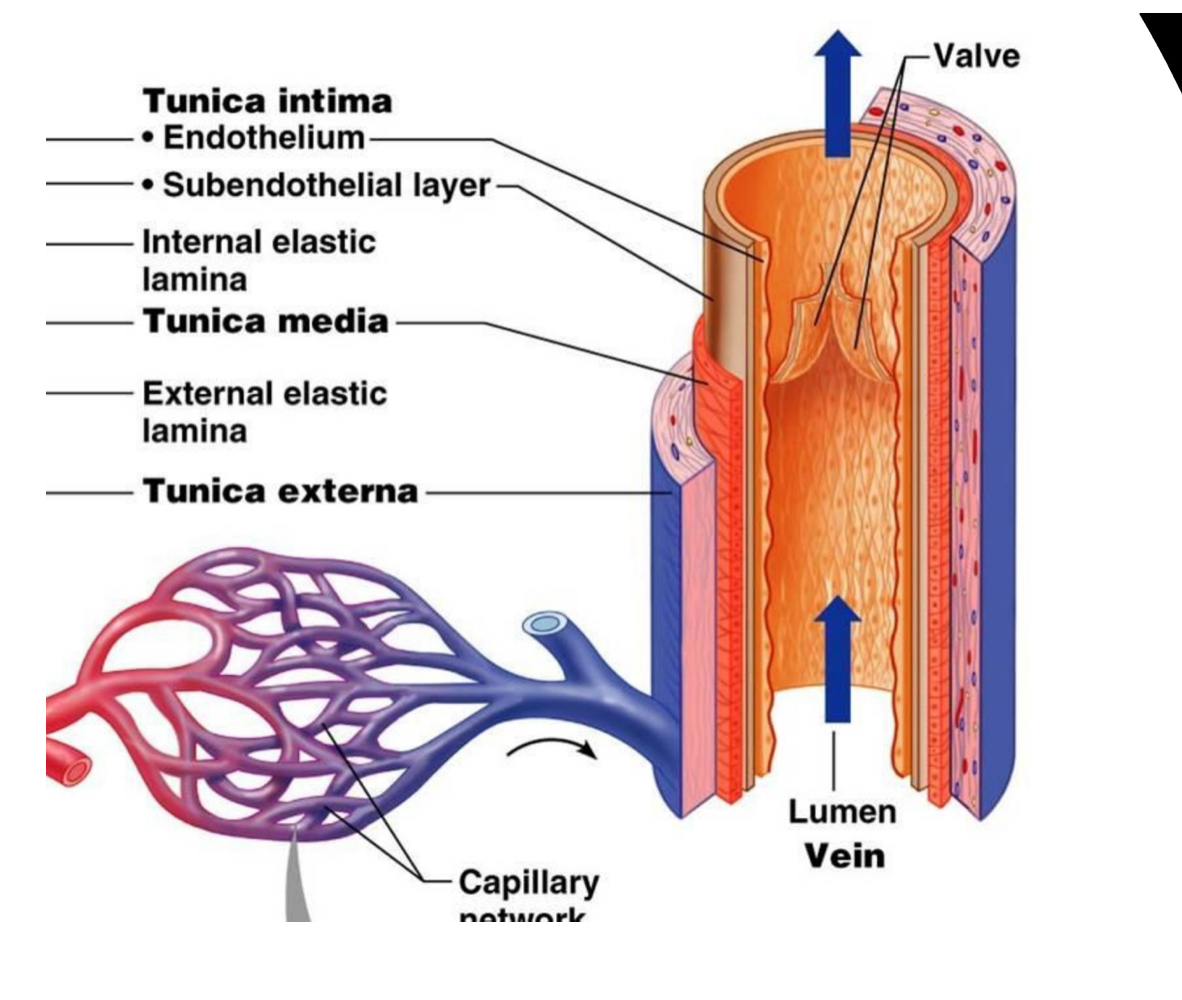
Veins (carries deoxygenated blood to heart)
larger lumen = carries more blood but low blood pressures
Structure:
- 1st (outermost) layer: Tunica Externa
- loose connective tissue
- same function as in arteries (structure and holds other blood vessels to feed tunica media)
-2nd (middle) layer: tunica media
NO ELASTIC LAMINA, just smooth muscle but a lot thinner then in arteries
- 3rd (innermost) layer: tunica intima
- subendothelial layer
- endothelium
LUMEN: contains a valve that keeps blood flowing in one direction (up not down). valves fail= verricose veins
Structure:
- 1st (outermost) layer: Tunica Externa
- loose connective tissue
- same function as in arteries (structure and holds other blood vessels to feed tunica media)
-2nd (middle) layer: tunica media
NO ELASTIC LAMINA, just smooth muscle but a lot thinner then in arteries
- 3rd (innermost) layer: tunica intima
- subendothelial layer
- endothelium
LUMEN: contains a valve that keeps blood flowing in one direction (up not down). valves fail= verricose veins
11
New cards
Verricose Veins
occur with age
- valves in vein start failing causes pooling (build up of blood in veins)
- vein gets stretched out by blood build up = FAT VEINS
TREATMENT: burn the vein (let it die let it die let it shrivel up and die)
- valves in vein start failing causes pooling (build up of blood in veins)
- vein gets stretched out by blood build up = FAT VEINS
TREATMENT: burn the vein (let it die let it die let it shrivel up and die)
12
New cards
Classifications of Veins
Veins (largest veins) (superior and inferior vena cava's)
- carry large volumes of blood, low bp,
- has valves to prevent back flow, this walls
- run close to skeletal muscle to get blood back to heart CONTRACTION OF MUSCLE PUSHES BLOOD UP TO HEART
Venule (very small)
- collects blood leaving capillary beds and merge into veins
- very thin
- easy to break
- easy to restrict
- easy to collapse
- carry large volumes of blood, low bp,
- has valves to prevent back flow, this walls
- run close to skeletal muscle to get blood back to heart CONTRACTION OF MUSCLE PUSHES BLOOD UP TO HEART
Venule (very small)
- collects blood leaving capillary beds and merge into veins
- very thin
- easy to break
- easy to restrict
- easy to collapse