W3: Advanced MRI modalities
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What is the fundamental unit of the CNS responsible for propagating information?
Neurons.
What are the two processes through which neurons transmit information?
Transmission of altered electrical potential
Release of neurotransmitters.
What is the term for the generation of spontaneous electrical activity by neurons?
Action potentials.
What is the role of the neuronal membrane?
It serves as an insulator and controls the diffusion of ions across the membrane.
What ionic concentration is higher in the intracellular space compared to the extracellular space in neurons?
K+ ions.
Between which two millivolt values does the membrane potential of neurons typically sit?
-80mV and -40mV.
How do neurons generate spontaneous electrical activity?
By transporting ions across the neuron membrane through ion channels.
What are the two types of channels involved in ion transport across the neuronal membrane?
Ion channels and ion pumps.
What is the function of neurotransmitters in neuronal communication?
They transmit signals across the synapse by opening ionic channels.
Why is neurotransmitter re-uptake important?
To maintain neuronal activity by restoring concentrations to original levels.
What does ATP stand for and what is its significance in the brain?
Adenosine triphosphate; it is the energy currency of the brain.
What are the two processes of glycolysis?
Aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis.
What is the preferred metabolic pathway for the human brain?
Aerobic glycolysis.
What is reactive hyperaemia?
The phenomenon by which blood flows to an area following a period of reduced blood flow.
What is the primary mechanism involved in neurovascular coupling?
The production of nitric oxide to relax smooth muscle and increase blood flow.
What is the direct relationship between neuronal activity and blood flow in fMRI?
Increase in neuronal activity leads to increase in blood flow.
How do oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin differ in terms of magnetic properties?
Oxygenated hemoglobin is diamagnetic, while deoxygenated hemoglobin is paramagnetic.
What is the significance of the transverse relaxation rate in relation to the MR signal?
It governs the amplitude of the signal, decaying faster in the presence of deoxygenated blood.
What is the BOLD signal and how is it related to brain activity?
Blood-Oxygen-Level-Dependent signal; it is related to synaptic and postsynaptic activity — i.e., it does not have a close relationship with the electrical activity of neurons b/c it depends on the supply of oxygen to the neurons to maintain this activity.
What does the term 'chemical shift' represent in MRS?
The location of a peak on the spectrum based on the frequency difference between a signal and a reference signal.
What is diffusion in the context of MR imaging?
The simple random movement of water molecules, measured as the mean square displacement increases over time
What does the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measure?
The mobility of water molecules inside biological tissues.
What is diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)?
A technique to create a 3D model of water molecular diffusion inside each voxel of the brain.
What is fractional anisotropy (FA) used for in DTI analysis?
To inform the organisation of brain microstructure.
What is the main advantage of tractography in brain imaging?
It allows the connection of different voxels based on their underlying white matter orientation.
What are the two main criteria used to track and stop tracking in diffusion tractography?
Anisotropy threshold and angle threshold.
Which brain metabolite is considered a marker of neuronal health and integrity?
N-acetyl aspartate (NAA).
What is the common internal reference used in MRS quantification?
Water or creatine.
Which neurotransmitter is often difficult to quantify in MRS due to its low concentration?
GABA.
What is a significant advantage of using short echo times (TE) in MRS?
Higher signal-to-noise ratio and allows detection of short T2 species.
What are the three main methods of MRS data analysis?
- Water and lipid suppression, 2. Voxel selection, 3. Echo time dependence.
What is the primary purpose of preprocessing in fMRI data analysis?
To prepare data for subsequent analysis and correct for individual differences.
What is the significance of the Talairach Atlas in fMRI preprocessing?
It is an older standardized brain atlas used for normalization.
What does motion correction address in fMRI data analysis?
Head movement during scanning, which can affect voxel responses.
What is Gaussian Random Field Theory used for in fMRI analysis?
To correct for familywise error and control false positives.
What is the effect of smoothing on fMRI images?
Increases signal-to-noise ratio and hides subtle normalization errors.
What does high-pass filtering do in fMRI preprocessing?
Removes low-frequency information while retaining high-frequency signals.
What are potential issues with tractography in brain imaging?
Data quality, diffusion model limitations, and false negatives.
What is the definition of mass-univariate analysis in fMRI?
Testing each voxel independently, which increases the risk of false positives.
How are contrast vectors used in fMRI analyses?
To test specific hypotheses by combining or comparing beta parameters.
What statistical method can be overly conservative and lead to Type II errors in fMRI analysis?
Bonferroni Correction.
What is the role of the cost function in image registration?
Measures how well-aligned two images are during the registration process.
What is the challenge of absolute quantification in MRS?
It is technically difficult in vivo and often requires a reference standard.
What does the presence of lactate in the brain typically indicate?
Anaerobic metabolism or disruptions in oxidative phosphorylation.
Which key brain metabolite is used as an internal standard in MRS and is involved in energy metabolism?
Creatine.
What is the impact of spin-spin coupling in MRS?
It leads to splitting of resonances into multiple peaks.
What is the classification of neurotransmistters based on?
Their molecular character (i.e., amino acids, monoamines, peptides, etc.)
Why is aerobic glycosis favoured over anaerobic glycosis?
Because it produces more ATP molecules (36) and doesn’t generate lactate, which impairs human brain functioning.
What is glycosis?
The breakdown of glycogen, a precursor molecule to ATP; process that generates ATP by converting glycol into pyruvate, which turns into ATP.
How much of the arterial blood supply’s oxygen is consumed by the brain?
20%
What is rCBF
Regional cerebral blood flow refers to the amount of blood flowing to specific regions of the brain within a given time.
Why are regional changes in neuronal activity and microcirculation (e.g., rCBF metabolism) important in neuroimaging?
Because PET and fMRI rely on the consistent relationship between these changes to map brain activity/structure.
What is haemoglobin?
A protein complex with four structures {heme groups), each of which carry oxygen.
Said of the magnetic properties of deoxygenated haemoglobin, what does paramagnetic mean?
It means that it (deoxygenated haemoglobin) can acquire magnetic properties in the presence of an external magnetic field.
What is magnetic susceptibility?
A physical parameter that describes the magnetic character of a molecule (or substance).
What is transverse relaxation rate (R2 or spin-spin relaxation)?
It corresponds to how quickly the magnetization decays perpendicular to the static magnetic field. This is hugely dependent on blood oxygenation state, which decays significantly faster in the presence of deoxygenated blood.
According to Seiji Ogawa’s 1990s experiment on blood oxygenation’s effect on MRI images, how are gradient echoes formed?
By the reversal of magnetic field gradient.
What does the amplitude of the BOLD contrast depend on?
Oxygen metabolism; i.e., the relationship between the oxygenation content of the tissue (which is governed by rCBF) & cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption.
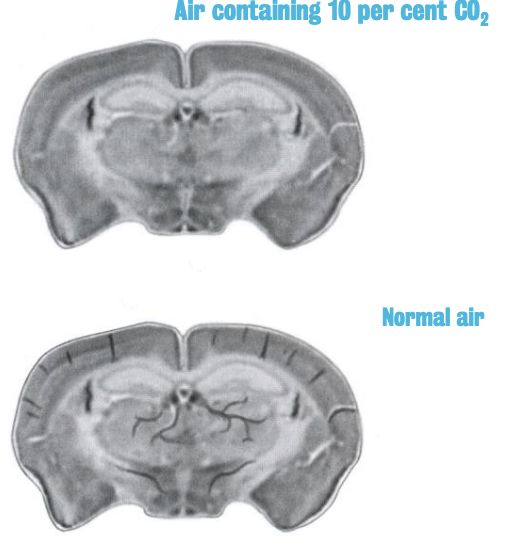
In this image, what does the dark vein effect in the bottom slice reflect?
Magnetic field distortions generated by deoxygenated blood.
What promoted the rise in the use of BOLD fMRI since 1992?
Its application in task-activated paradigms. studies of resting state functional activity & event-related designs
Non-invasiveness.
Sensitive to modulation by psychotropic drugs (:. huge application in pharmacological imaging).
Why does reactive hyperaemia occur?
There is no conclusive answer to that question.
What might affect the mobility of water molecules in the brain?
The presence of different biological structure (other than water).
What is diffusion MRI?
Non-invasive, in-vivo technique that allows for the measurement of molecular diffusivity of water inside biological tissues.
What is isotropy (isotopic diffusion)?
Refers to tissue with the same diffusion property along every direction.
What is anisotropy (anisotropic diffusion)?
Refers to tissue with a different diffusion properties along different direction
What challenged early interpretations of diffusion imaging maps?
Head orientation and the diffusion direction dependent nature of diffusion maps, leading to anisotropy resembling lesions.
What does a diffusion ellipsoid represent?
The actual 3D displacement water molecules in a fixed amount of time & captures all the information available in the diffusion tensor
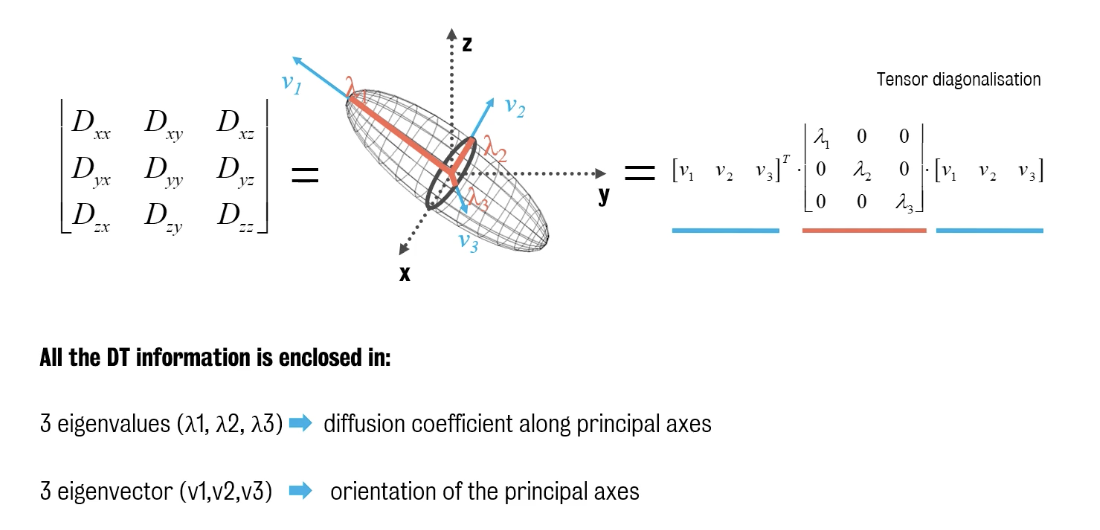
What do eigenvalues represent?
Diffusion coefficient (magnitude of diffusion) along the three principal axes
What does fractional anisotropy (FA) measure?
The directionality of water diffusion within a tissue.
What is the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) template?
Standard brain atlas used to calculate the mean FA & extract a skeleton, representing only the core of all white matter region
Why are eigenvalues (tensor diagonalisation measures) important?
These vectors indicate the orientation of these principal axes of the ellipsoid & allow us to extract DTI measures.
Why is tractography not an accurate representation of white matter track curvature?
Because it is a mathematical approximation based on the underlying movement of water molecules.
Which new method eliminates fibre crossing?
Spherical deconvolution tractography
How do NMR samples differ from MRI and MRS subject insertion?
They are put in glass tubes and performed on instruments with an upright magnet where the sample is introduced from the top.
What is the focus of MRS?
Metabolites in a volume (or voxel)
What gives rise to the MR signal?
The excess of spin-up protons
Chemical shift is generated as a result of what?
Difference in the resonance frequencies of protons
What are the 3 universally agreed upon preprocessing steps in fMRI data analysis?
Motion correction, normalisation to standard space & image smoothing (or blurring)