Retake Development
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Conventional
level 2 of Kohlberg’s six stages, stage 3 “good boy good girl” orientation, focused on living up to social expectations and roles, finds peer approval very important. Stage 4 consider society as a whole when making judgments, respect authority and obeys without question
Preoperational
stage 2 in Piaget stages of cognitive development as representing things with words and images but lacking logical reasoning.
Ex. pretend play, egocentrism, language development
Preconventional
level 1 is Kohlberg’s six stages, stage 1-where the child is obeying only to avoid a punishment, or trying to determine a seance of right and wrong, stage 2-this is where a child will do a favor but want a favor in return, they seen everything in the “eye for an eye” philosophy.
Postconventional
level 3 in Kohlberg’s six stages, stage 5 having differing values, opinions, and beliefs but not willing to break laws for beliefs. stage 6 believing that there are high moral principles than those represented by social rules and customs, willing to break laws for what they believe is right.
Maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience, the development of neural pathways
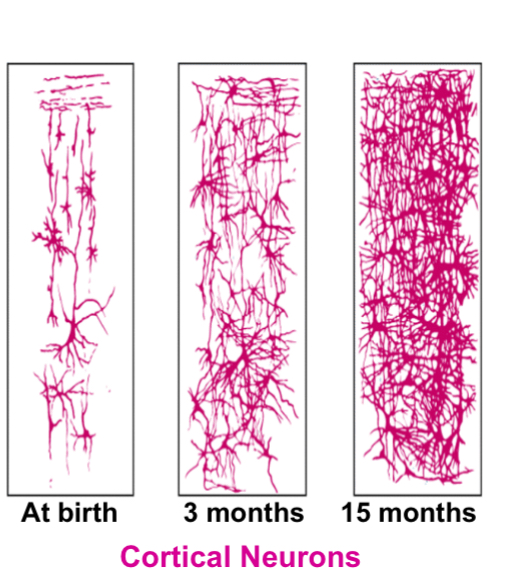
Concrete Operational
stage 3 on Piaget’s stages of cognitive development, this is the range when the child starts thinking logically about concrete things, grasping concrete analogies and preforming arithmetical operations
Ex. conservation, math transformations
Basic Trust
Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development, this is the infancy stage where if the child’s needs are met they will develop a sense of trust , stage Trust vs. Mistrust
Identity
Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development where a teenager is working on finding their sense of self and what their beliefs are, this is where teens tend to become confused on who they are
Harry Harlow
studied what caused the formation of attachment by using an animal model, he did an experiment with monkeys to test this theory
Mary Ainsworth
studied the relationship between mothers and children and described different styles of attachment, using the strange situation when parents leave the child with a stranger then return. found secure, insecure, avoidant, and disorganized attachments
Jean Piaget
study of developmental psychology who introduced a stage theory of congnitive development that lead to a better understanding of children’s thought processes
Erik Erikson
studied the stages of psychosocial development, like the crisises they we go through throughout our lives and why they are important and what we learn from them
Lawrence Kohlberg
He preformed a cross-sectional study and proposed a theory for how we develop ethical thinking. He also proposed that we all go through the same stages sequentially without skipping any