Edexcel IGCSE Physics - Changes of State
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what are the three states of matter?
solid
liquid
gas
describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a solid
strong forces of attraction hold the particles close together in a fixed, regular arrangement
particles don’t have much energy so they can only vibrate about their fixed positions
describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a liquid
weaker forces of attraction between the particles
particles are close together that can move past each other and form irregular arrangements
they have more energy than particles in a solid
they move in random directions at low speeds
describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a gas
virtually no forces of attraction between the particles
particles have the most energy out of the 3 states
they are free to move
travel in random directions at high speeds
what will a heating system do?
it will increase the kinetic energy store of the particles that are being heated
this will raise its temperature (average kinetic energy of particles) or cause a change of state
describe the changes in state for all changes
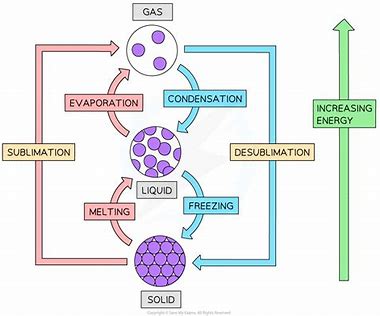
describe the changes that occur when a solid melts to become a liquid
when you heat a solid extra energy is transferred to the particles’ kinetic energy stores - making them vibrate faster
at some point, the energy will be enough to partly overcome the forces of attraction between the particles and the particles begin to move around
describe the changes that occur when a liquid boils to become a gas
when you heat a liquid, energy is transferred to the particle’s kinetic energy stores making them moving faster
eventually when enough of the particles have enough energy to overcome their attraction to each other, the liquid begins to boil
describe the general changes that occur during condensation or freezing
energy is given out to the surroundings which causes bonds to form between particles
what is evaporation?
when singular particles escape from a liquid to become gas particles - can happen at temperatures lower than a liquid boiling point
particles near the surface can evaporate if they are:
travelling in the right direction to escape the liquid
they are travelling fast enough to overcome the attractive forces of other particles in the liquid
what does evaporation result in?
the fastest particles are most likely to evaporate from the liquid
the average speed and energy in the kinetic energy stores of the remaining particles decreases
this mean that the temperature of the remaining liquid decreases
what happens to the temperature when a change of state occurs?
it remains constant as all energy is transferred to the weakening of forces of attraction or released as they are strengthened
what graph can be used to show changes of state?
temperature(y)-time(x) graph
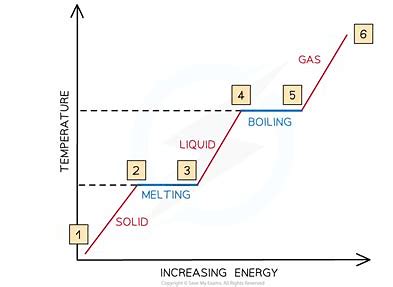
what doe straight lines on a temperature-time graph show?
changes of state - first is melting point, second boiling point
what do diagonal lines on a temperature-time graph show?
increases (or decreases) in temperature
how would you obtain a temperature time graph for water?
fill a beaker with crushed ice
place a thermometer into the beaker and record the temperature of the ice
gradually heat the beaker full of ice with a bunsen burner
every 20 secs record the temperature and state of the water until it begins to boil
plot a graph
what is the specific heat capacity?
the energy required to change the temperature of an object by 1C per kilogram of mass
what is the equation for specific heat capacity?
change in thermal energy (Q/J) = mass (m/kg) x specific heat capacity (c/ J/kgC) x change in temperature (T/C)
describe an experiment to find the specific heat capacity of water
use a mass balance to measure the mass of an insulating container
fill the container with water and measure the mass again, calculate the mass of water
set up the experiment as shown - put a lid on container, make sure joulemeter (can also use ammeter and voltmeter as well as stopwatch - E=IVt) is at 0
measure the temperature of the water then turn on the power
when the temperature has increased by 10C switch off the power and record the increase as well as the joulemeter reading
repeat the experiment and calculate means
calculate specific heat capacity using the equation
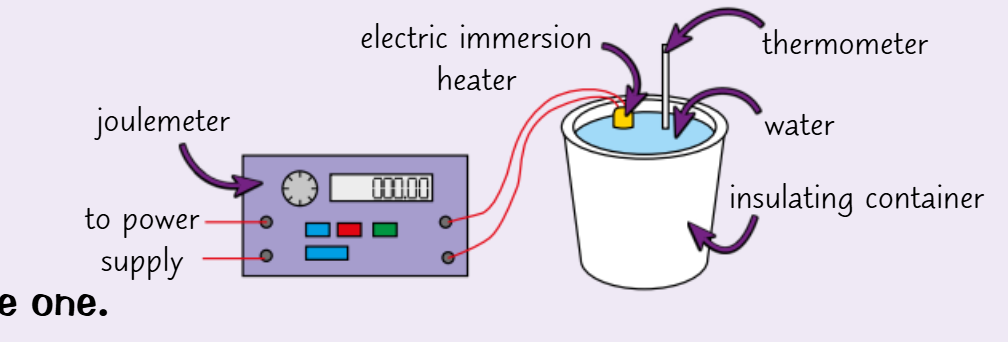
how would you modify this for a solid?
use a block of material of known mass with insulating material wrapped around it
make sure the block has two holes
don’t record the final temperature until it has stopped increasing
what is the main problem with this experiment?
heat loss to the surroundings