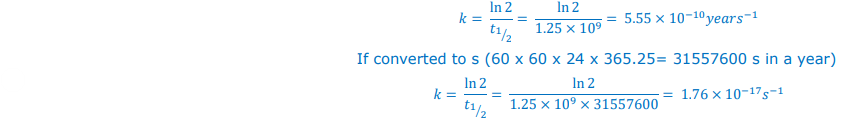Rates of Reaction
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Flask A = 1g Zn, 100cm3 1moldm-3 HCl at 35C
Flask B = 1g Zn, 100cm3 2moldm-3 HCl at 35C
Explain why the rate of reaction in Flasks A and B are different?
The concentration of the acid is higher in Flask B, so the frequency of collisions of acid particles with zinc is higher, resulting in a faster rate of reaction.
Conc-Time graph for 1st Order Reactant
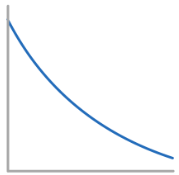
Conc-Time graph for 2nd Order Reactant
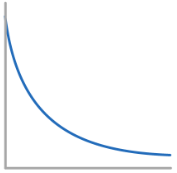
Conc-Time graph for 0th Order Reactant
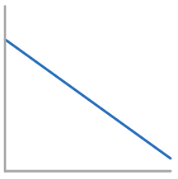
Rate-Conc graph for 1st Order Reactant
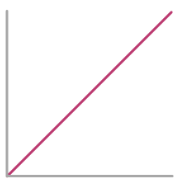
Rate-Conc graph for 2nd Order Reactant
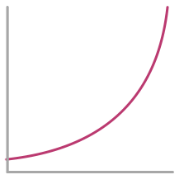
Rate-Conc graph for 0th Order Reactant

Arrhenius Equation
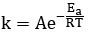
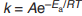
What does each letter in the Arrhenius equation stand for?
k = rate constant
A = pre-exponential factor (frequency factor)
e = base number of natural logarithms (SHIFT-ln on calculator)
Ea = Activation energy ( J mol⁻¹ )
R = Gas constant (8.314 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹ )
T = Temperature in kelvin
What's the effect on the value of k when the temperature is increased?
Increases k
More frequent collisions and more collisions have energy equal to or greater than the activation energy.
What's the effect on the value of k when the activation energy is increased?
Decreases k
Fewer collisions have energy equal to or greater than the activation energy.
What's the effect on the value of k when the pre-exponential factor is decreased?
Less frequent collisions
Logarithmic Form of Arrhenius Equation
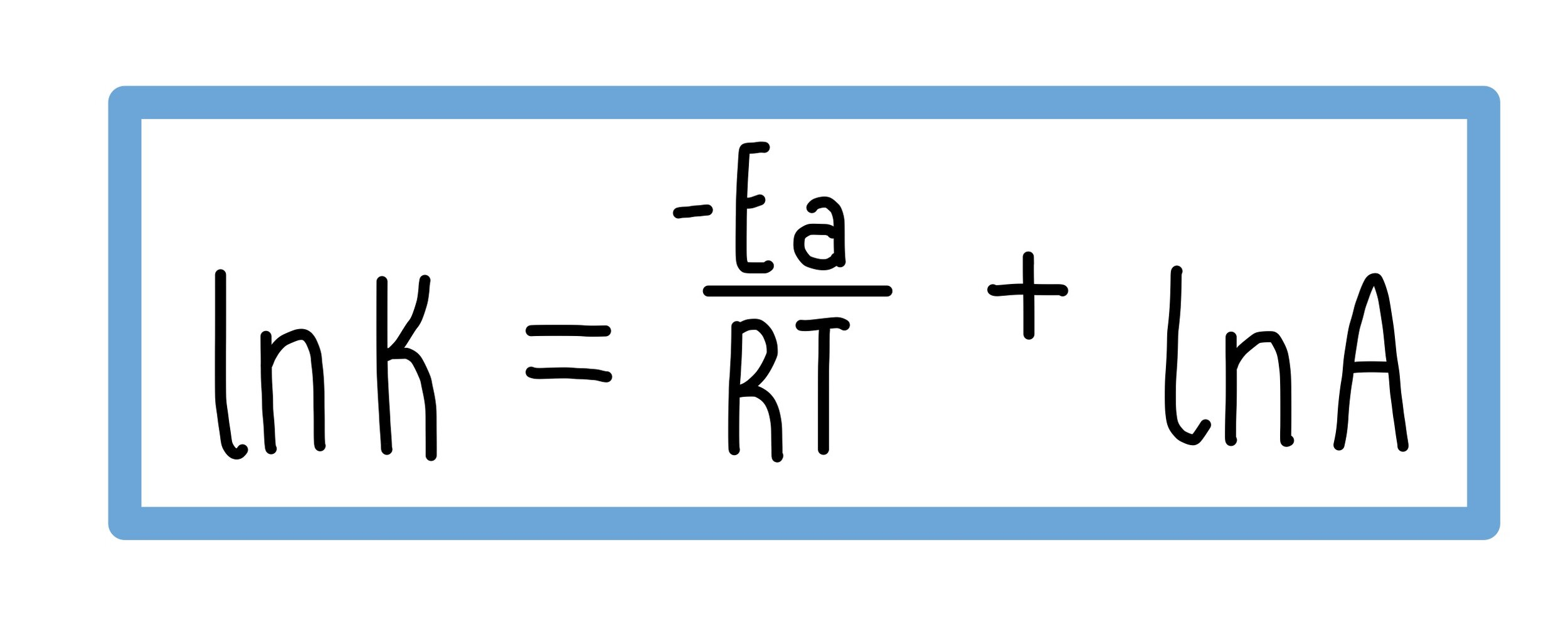
Compare the log form of Arrhenius Equation with a straight line:
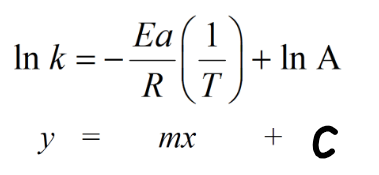
What does the gradient of the graph (m) represent?
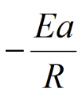
What does the y-intercept of the graph (c) represent?
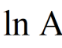
How to work out Ea from the graph?
Gradient = -Ea/RT
Ea = -Gradient × R
How to calculate A?
lnk = -Ea/RT + lnA
lnA = lnk + Ea/RT
A = elnA
Ea the subject
Ea = RT (lnA - lnk)
A the subject
A = k * eEa/RT
T the subject
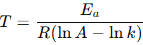
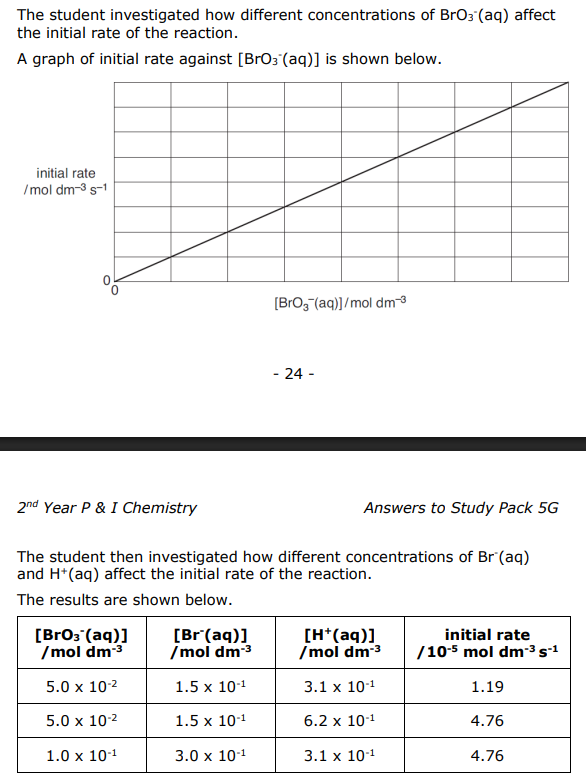
Use the results from the student’s experiments to deduce the rate equation for this reaction. Justify your reasoning.
Straight line through origin 1st order wrt BrO3-
Between expt 1 and 2, [H+] x 2, rate x 4
Rate ∝ [H+] 2 , so 2nd order wrt H+
When [H+] constant and [BrO3-] x2 and [Br-] x 2, rate x 4
Since BrO3 - is first order, doubling [Br- ] has doubled rate, so it is 1st order wrt Br-
Rate = k [BrO3-][Br-][H+]2
How to calculate rate constant (k) from a graph?
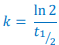
What is the rate constant (k) for this radioactive decay?
The half life is 1.25 × 109 years