1.4 Enzymes and Digestion 🦠
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Biology Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Cells, Living Processes & Biodiversity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Economical benefit of enzymes in industry
lower the energy needed, take place at lower temperatures, make processes quicker and cheaper
responsible for releasing small, soluble molecules from food
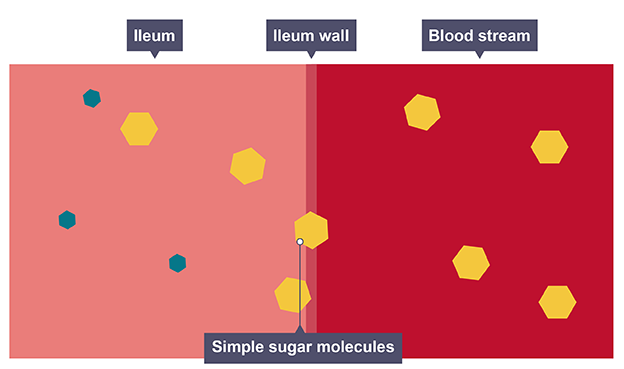
where small soluble molecules are absorbed into the bloodstream
Ileum
last portion of small intestine, the walls of which can produce enzymes to aid digestion
proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions without being used up
Adaptations of the ileum for digestion
large folded structure to increase surface area for diffusion
permeable to allow molecules to easily pass through
thin to reduce distance to reach the blood
rich blood supply maintains steep gradient to optimise rates of diffusion and absorption
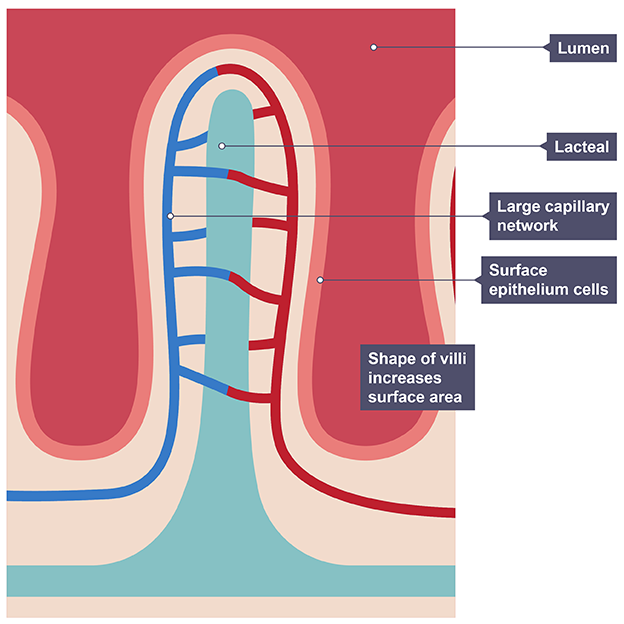
finger like projections called villi to further increase surface area
Small finger-like projections on the walls of small intestine
Adaptations of the villi
good blood supply as large network of capillaries maintains concentration gradient
single layer of epithelial cells to reduce diffusion distance to blood
permeable so digested food can pass through easily
lacteal to absorb fat products into blood
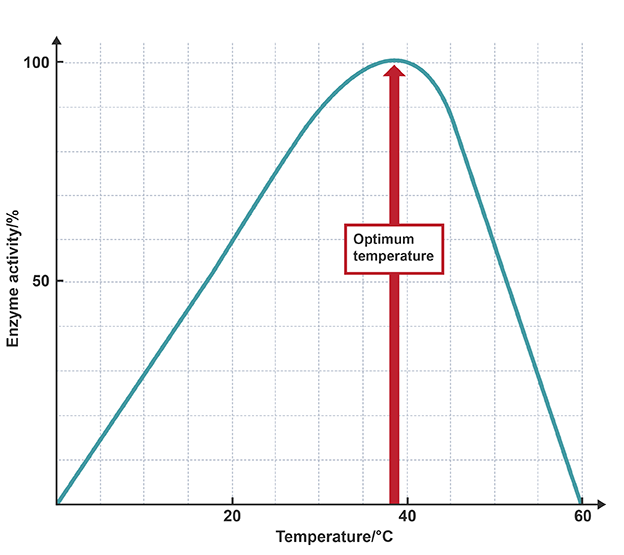
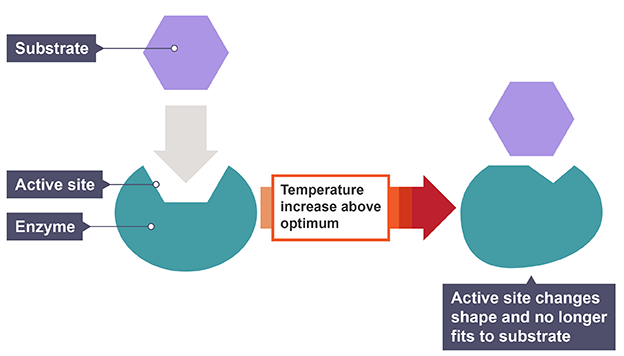
Enzymes and temperature
reaction rate increases as temperature causes kinetic energy and collisions, up to an optimum, after which the enzyme becomes denatured
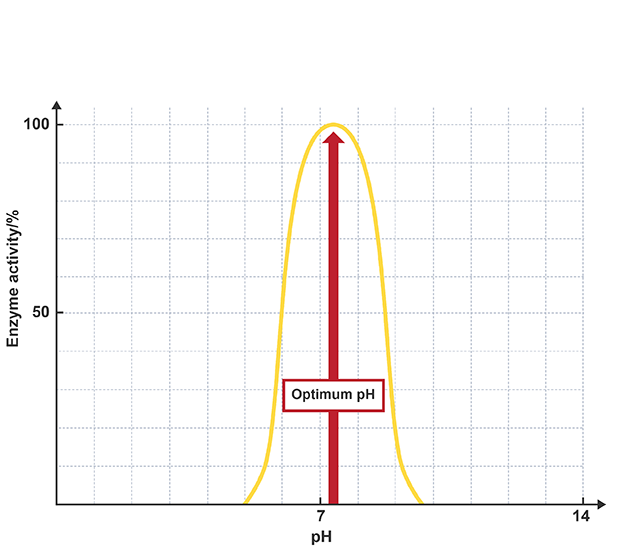
Enzymes and pH
reaction rate decreases as the pH moves away from the enzyme's optimum
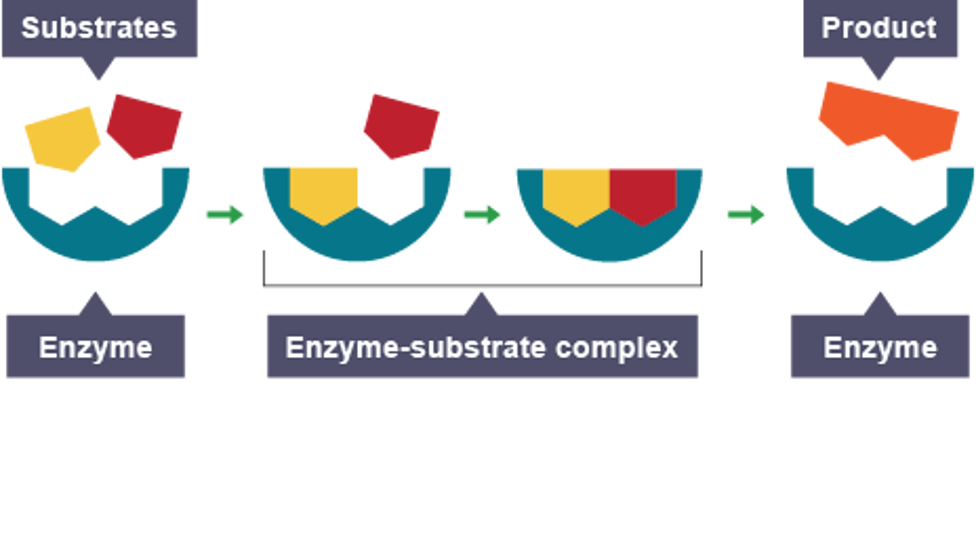
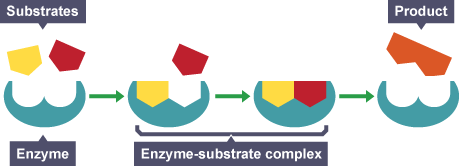
Enzyme action
enzyme’s active site and substrate are complementary in shape
they collide to form complexes
substrates are broken down or built up quickly
products are released and enzyme can be used over again
active site changes shape and can no longer bind to a substrate, permanent
Inhibitor
partially fits into active site and prevents substrate from being broken down (slows enzyme rate)
Lock and key theory
substrate fits into its enzyme just like a key fits a lock, specific to each other and can be used again
Starch
large carbohydrate found in plants made up of many glucose molecules
Buffer solution
controls and keeps the pH of solution to specific range
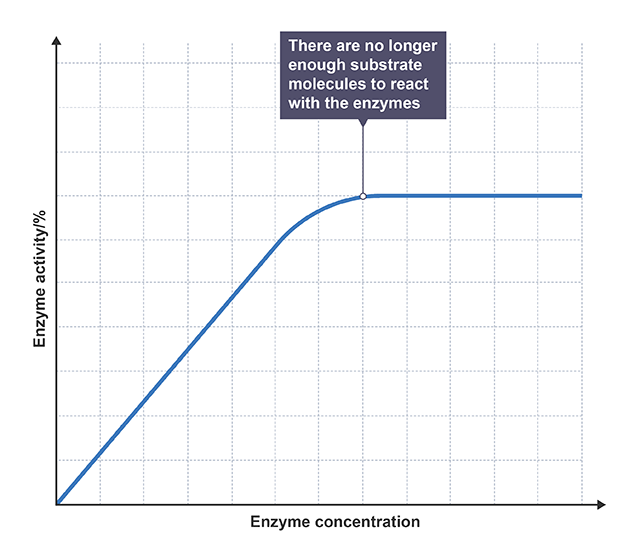
Effect of enzyme concentration
as concentration increases so will rate of reaction, until saturation is reached (not enough substrate)
found in saliva and small intestine that breaks the chemical bonds in starches
found in stomach and small intestine that breaks down proteins into amino acids
Lipase
found in the small intestine that breaks down lipids into glycerol and 3 fatty acids
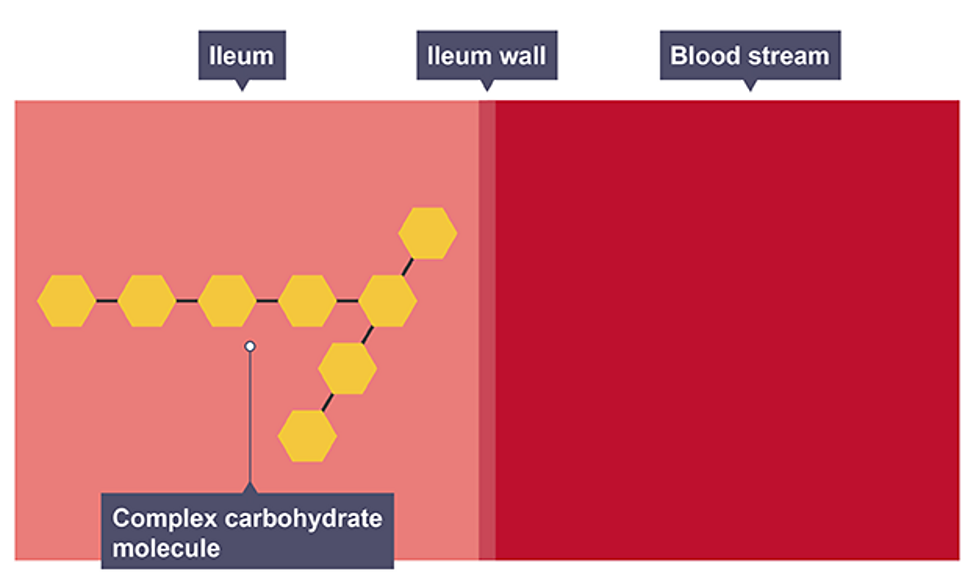
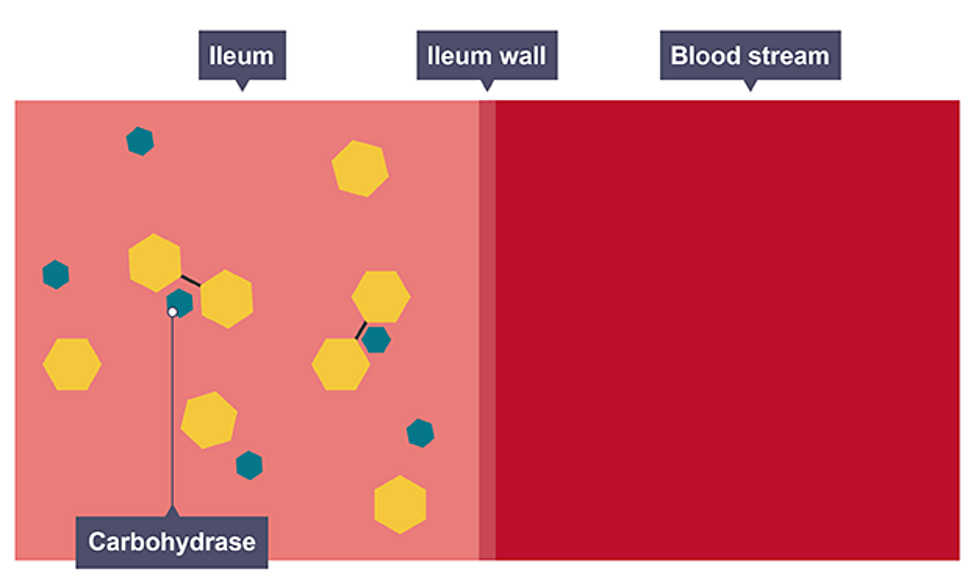
Carbohydrase
speed up the breakdown of carbohydrates into simple sugars
Absorption
small soluble molecules can be absorbed in small intestine following digestion
they diffuse into blood and are transported around body for specific purposes
Commercial and industrial use
used in detergents, making cheese, alcohol and bread
thermostable
can work at a wide range of temperatures
Biological detergents
Washing powders contain enzymes to save energy by working at lower temperatures
however are denatured at temperatures above 40°C and allergies can lead to skin irritation