AP AFAM - Unit 1 Sources
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Black Studies National Conference Program
- National Council for Black Studies established in 1975
- African American scholars came together to formalize the study of the African diasporic experience and expand academic units and community programs for this cause
- First annual conference for NCBS held at the University of North Carolina in 1975

Medicine and Transportation
- Thelma Johnson Streat (1942 - 1944)
- Acknowledged and celebrated African American contributions to the fields of medicine and transportation

Outcast
- Claude McKay (1922)
- Deals with identity and navigating his African heritage
- He feels homesick for his native country
- The racism that he experienced in the U.S increases this longing
- He no longer belongs in Jamaica or America, that he has been away from Jamaica for so long that he no longer belongs anywhere
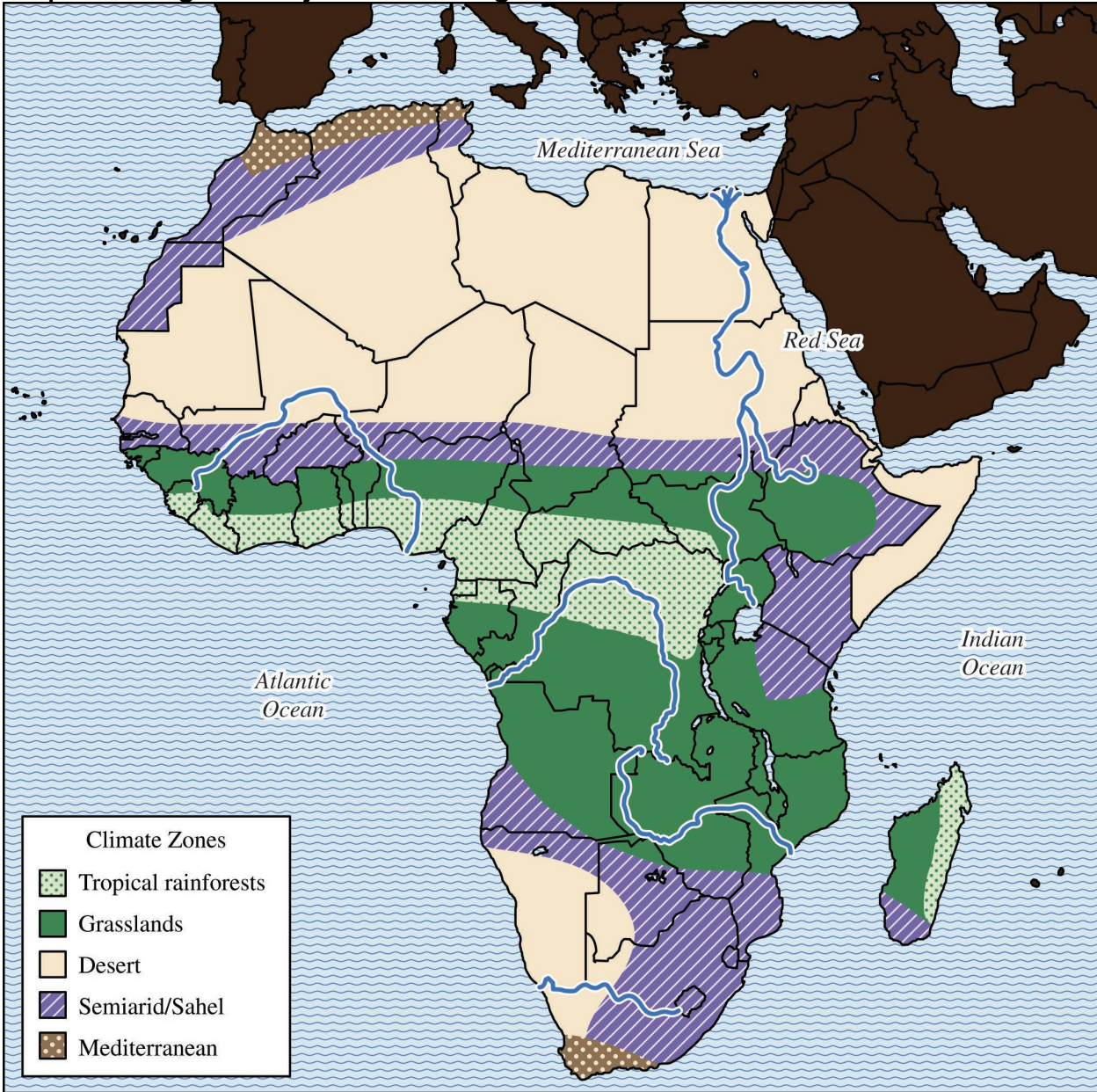
Map showing the major climate regions of Africa
- As the second largest continent, Africa is geographically diverse
- Variations in climate facilitated diverse opportunities for trade
Desert & semiarid areas: herders often nomadic and some traded salt
Sahel: people traded livestock.
Savannas: people cultivated grain crops
Tropical rainforests: people grew kola trees and yams and traded gold
Map showing the movement of Bantu people, languages, and technologies
- Technological and agricultural innovations led to population growth of West and Central African peoples
- Led to migrations throughout Africa called the Bantu expansion (1500 BCE - 500 CE)
- Bantu peoples developed new technologies (i.e., ironworking & agriculture)
- Bantu-speaking peoples’ linguistic influences spread throughout Africa
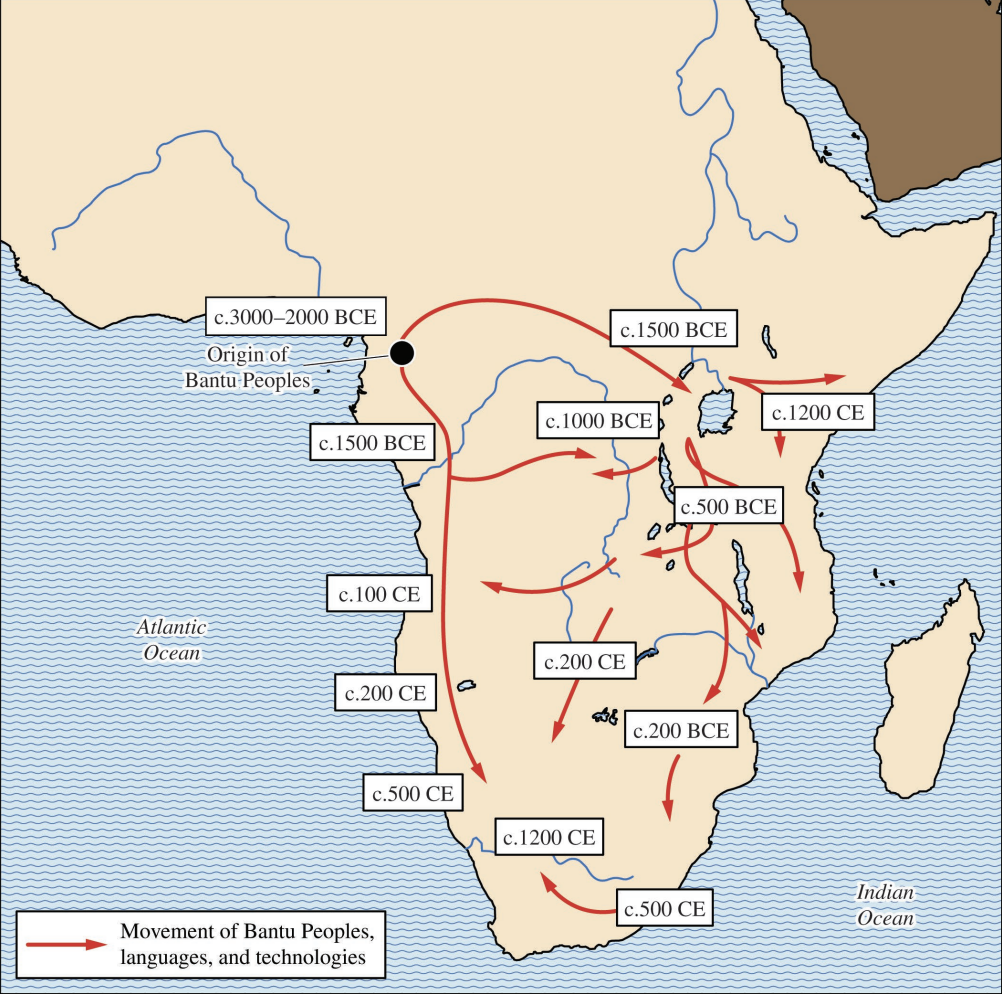
Image of Aksumite coin showing King Ezana
- c. 300–340
- Aksum first African society to adopt Christianity under leadership of King Ezana
- Reveals the availability of gold and luxury items in Ancient East Africa, which were used in trade
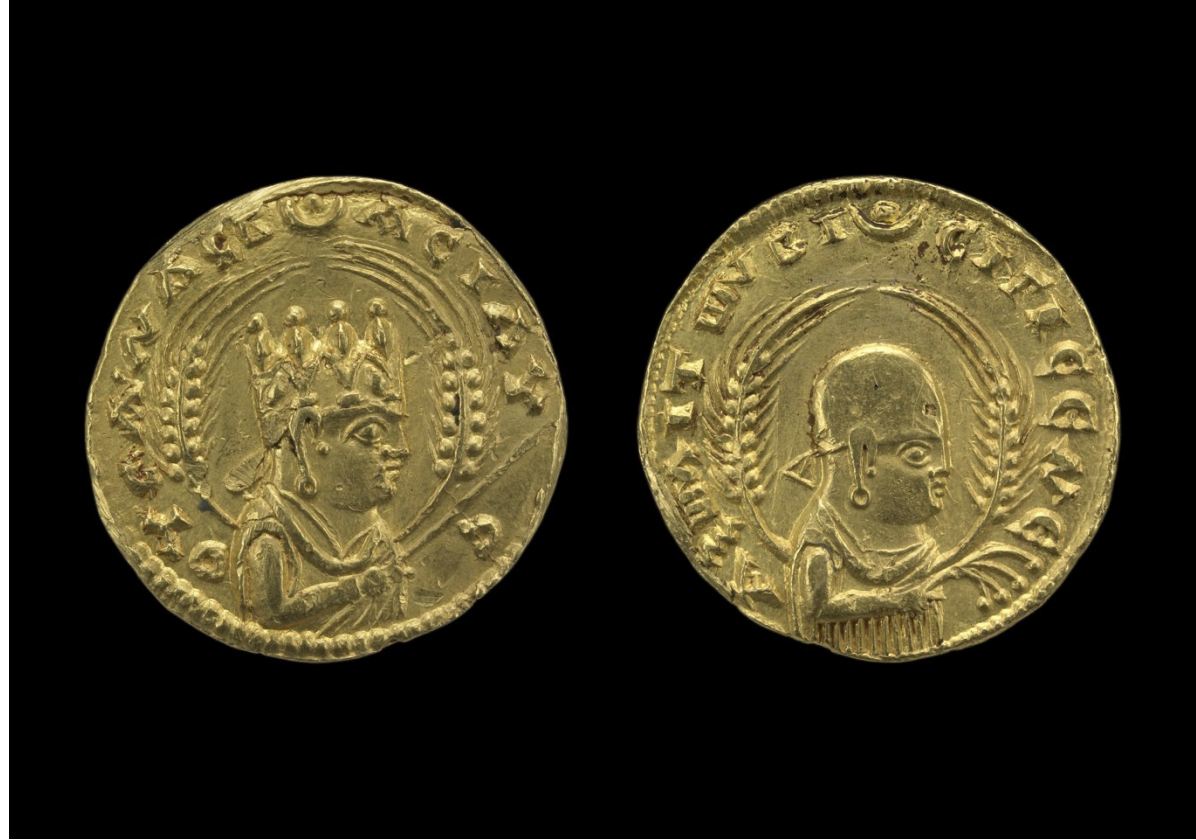

Image of Nok sculpture
- c. 900 BCE–200 CE
- Naturalistic sculptures of animals and of people with various hairstyles and jewelry
- Nok society first iron-working society
- Meticulousness of sculptures and their potential themes (wisdom, solemnity, etc.) reveal the sophistication of the Nok society

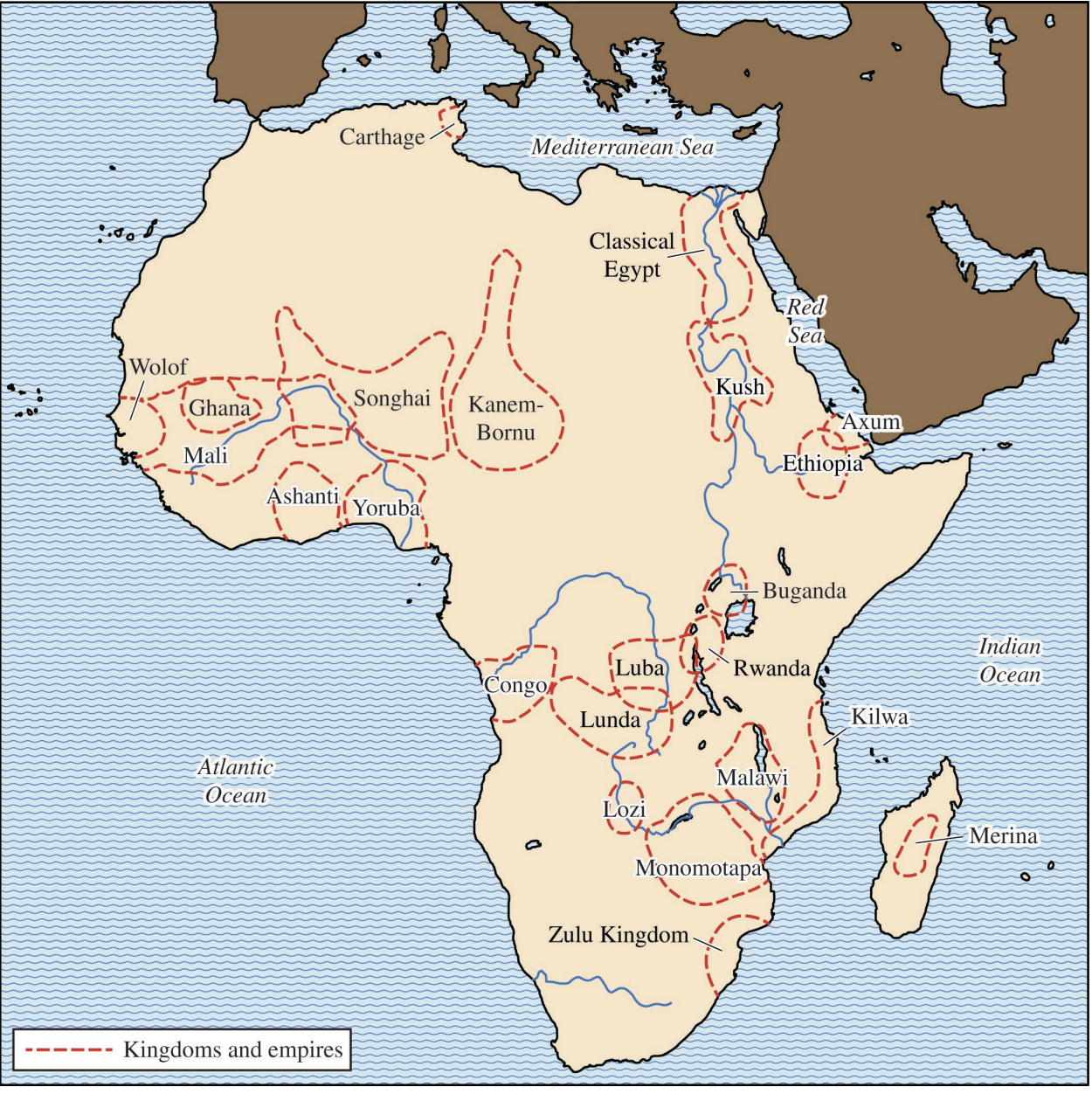
Map of Africa’s kingdoms and empires
- c. 600-1600 CE
- Ancient Ghana located in present-day Mauritania and Mali
- Present-day Republic of Ghana embraced name of the ancient empire when it achieved independence from colonial rule (1957)
Catalan Atlas
- By Abraham Cresques (1375)
- Details wealth and influence of Mansa Musa and the Mali Empire based on perspective of a cartographer from Spain
- Musa adorned with gold crown and orb
- Conveys influence of Islam on West African societies and the function of Mali as a center for trade and cultural exchange
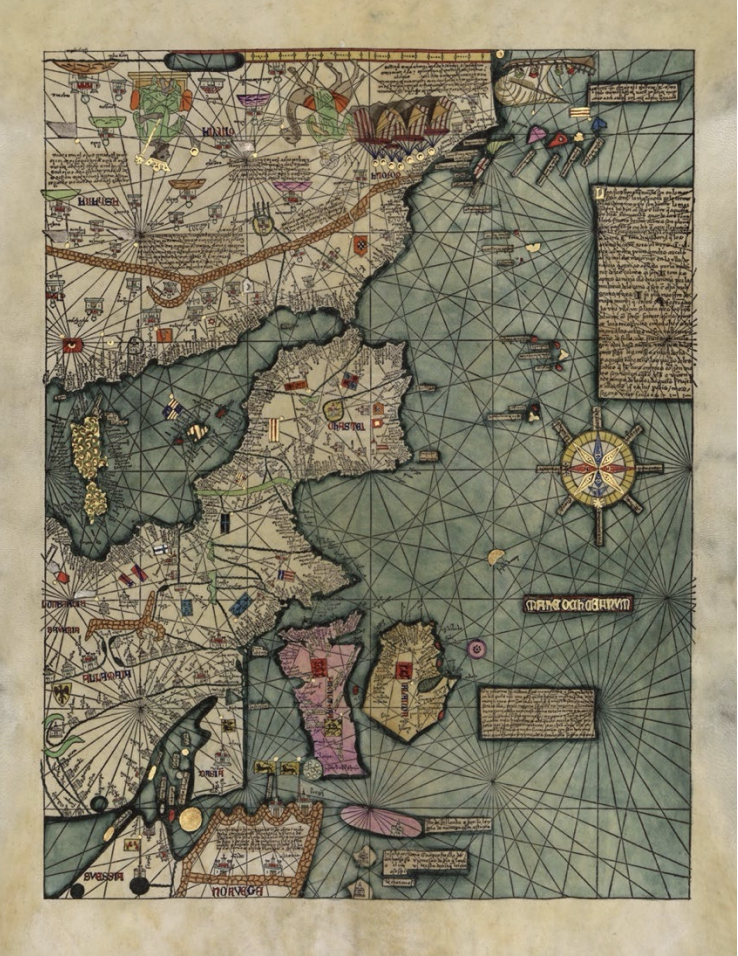
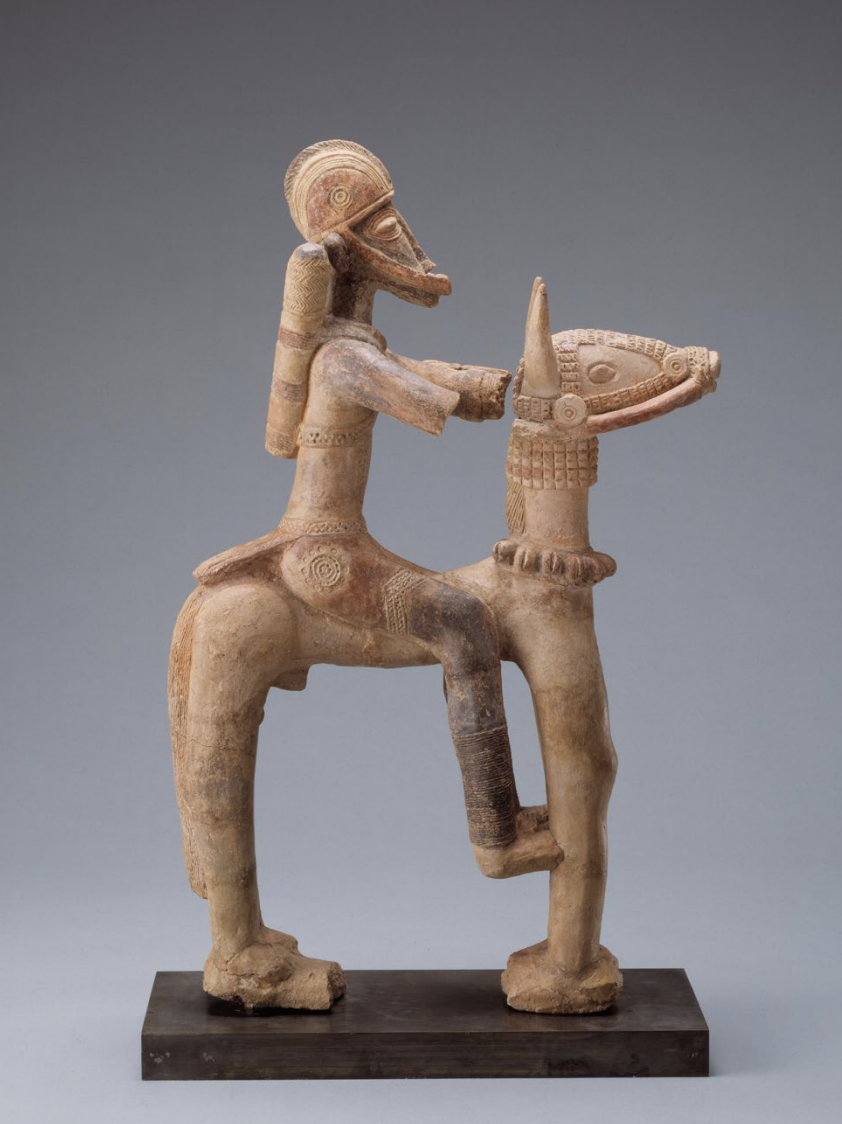
Image of Mali equestrian figure
- 13th–15th century
- Give a sense of people charged with their protection
- Man and horse defined by strong vertical and horizontal lines. Thus, the quiver slung diagonally across rider’s back was emblematic of royal power

The Sunjata Story—Glimpse of a Mande Epic
- A griot performance of The Epic of Sundiata (video)
- Mande griots/the jeli: preserved history through oral traditions
- Epic of Sundiata recounts early life of Sundiata Keita (founder of Mali Empire) and preserves the early history of Mande people
“Osain del Monte - Abbilona” (video)
- Osain del Monte worshipped by some as the “owner of nature”, a saint of the Yoruba religion
- These are spiritual songs worshipping the diety “Osain” → Used in ceremonies of consecration and purification
- The songs evokes his presence to purify the herbs used in healings.
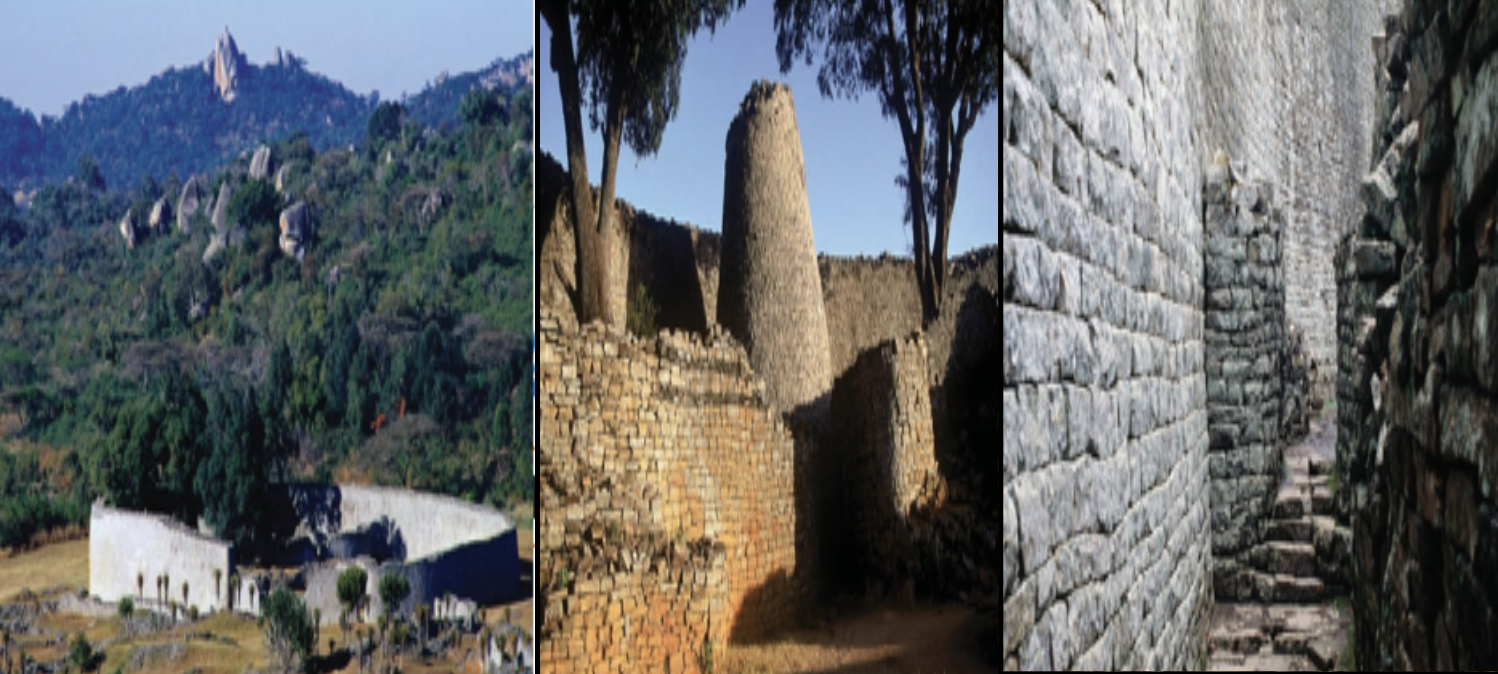
Images of Great Zimbabwe’s walls and stone enclosures
- 12th–15th century
- Offered military defense and served as a hub for long- distance trade
- Important symbol of prominence, autonomy, and agricultural advancements of the Shona kings (Shona = people of Kingdom of Zimbabwe) and early African societies

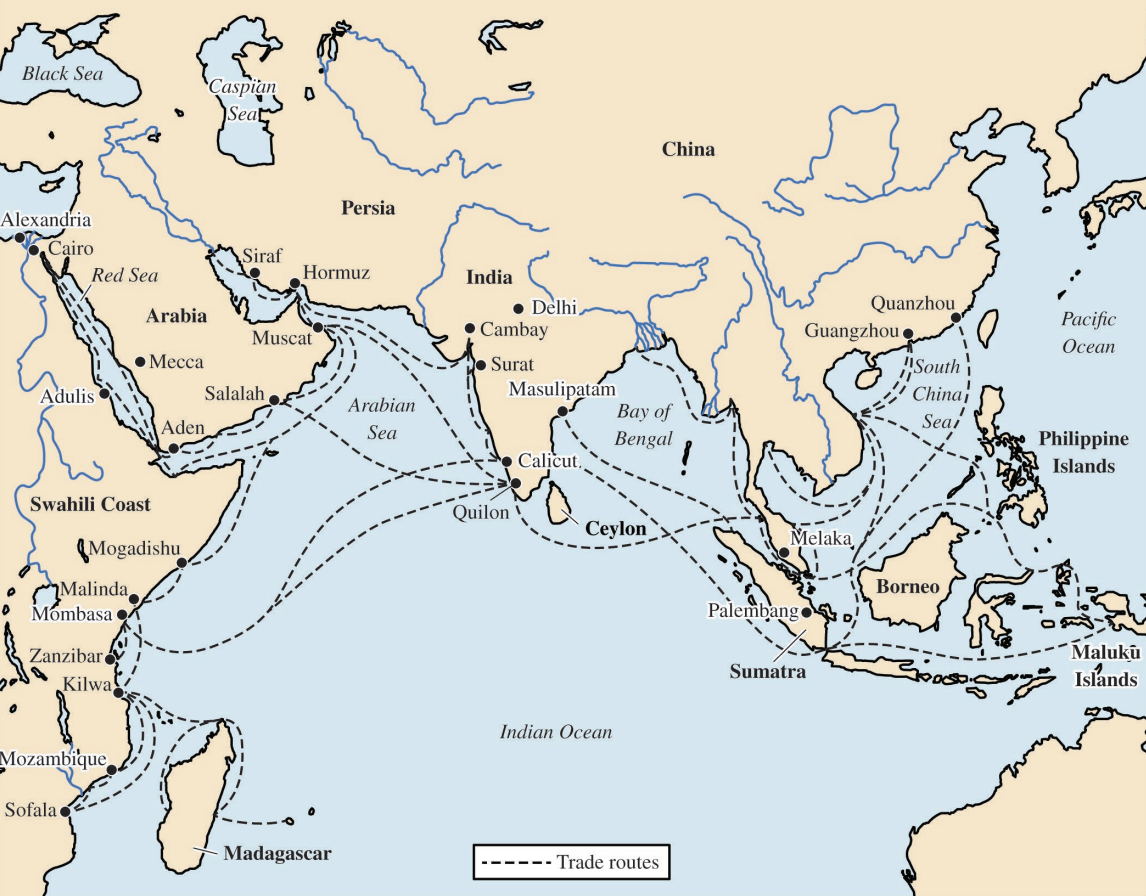
Map showing Indian Ocean trade routes from the Swahili Coast
- c. 600-1600
- Swahili Coast (named for the Arabic word for coast Sawahil) stretched from Somalia to Mozambique
- Coastal location of its city-states linked Africa's interior oto the Arab, Persian, Indian and Chinese trading communities
Excerpt of letter from Nzinga Mbemba to Portuguese King João III
- 1526
- Nzinga Mbemba (Afonso I): son of King Nzinga a Nkuwu (João I) of Kingdom of Kongo
- Mbemba urged an end to the slave trade in letter

Image of triple crucifix
- 16th - 19th century
- Illustrates how people of the Kongo engaged with Christian dogma AND with the European artistic forms that arrived in their land with the new religion

Illustration of Queen Njinga
- 1754
- Queen of kingdoms of Ndongo and Matamba (present-day northern Angola)
- Engaged in guerilla warfare against Portuguese
- Participated in slave trade to amass wealth and political influence
- Expanded Matamba’s military → offered sanctuary to those who escaped Portuguese enslavement and joined her forces
- Her influence led to led to ~ 100 more years of women rulers in Matamba
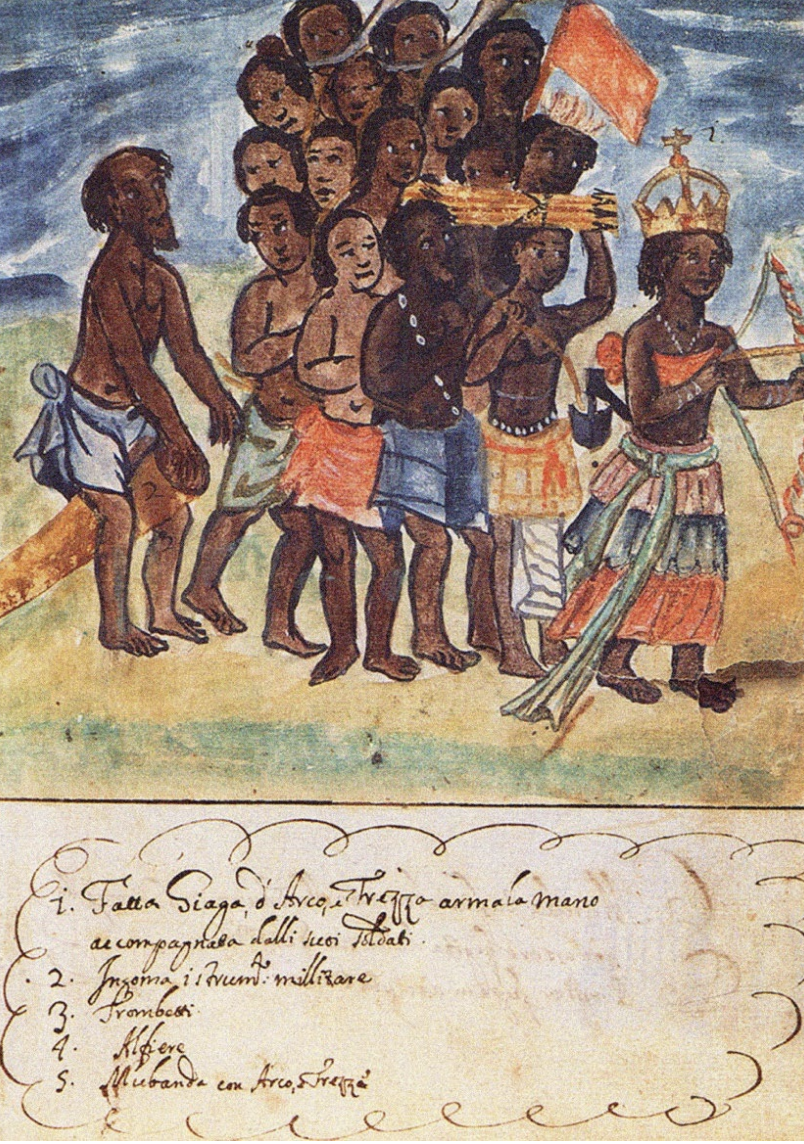

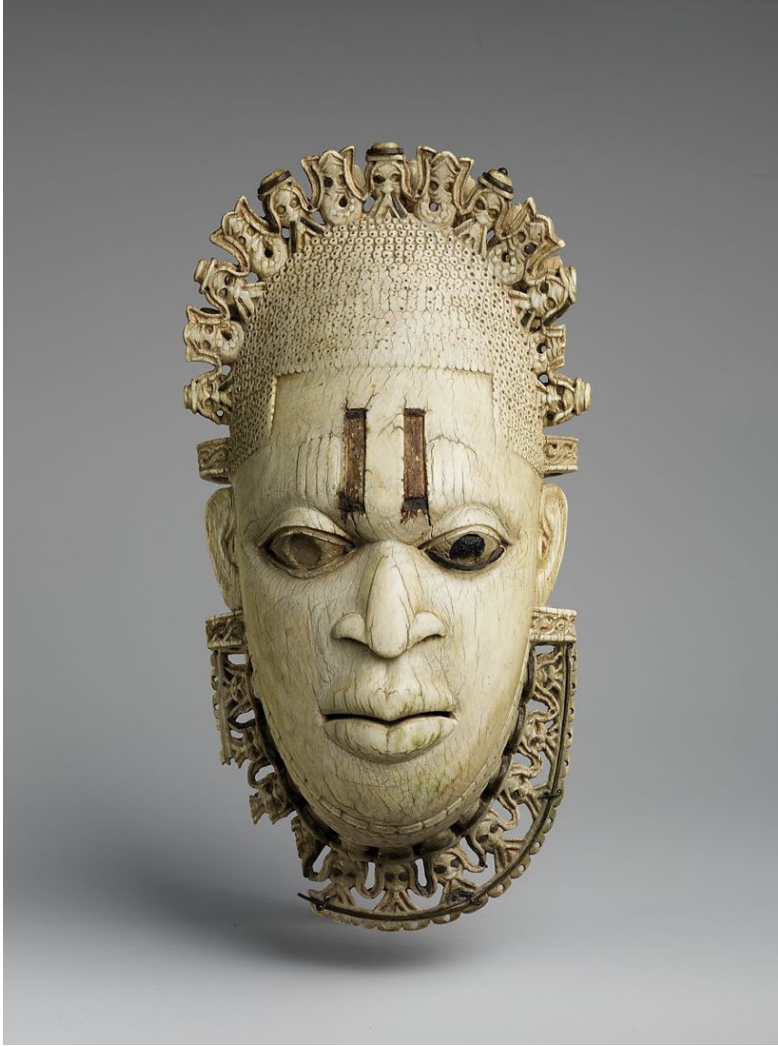
Image of Queen Mother Pendant Mask: Iyoba
- 16th century
- Made for the King/Oba Esigie, the king of Benin, to honor his mother, Idia
- Oba may have worn it at rites commemorating his mother; today such pendants are worn at annual ceremonies of spiritual renewal and purification

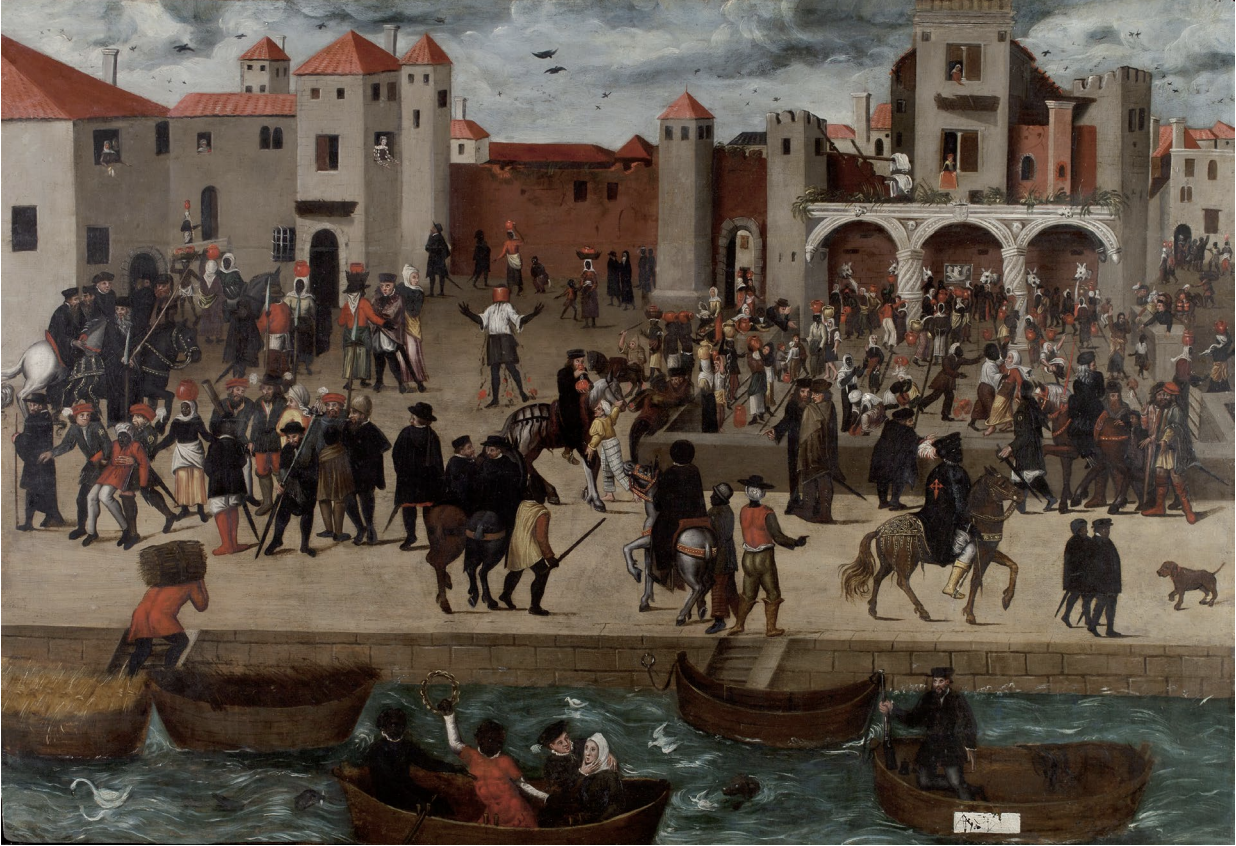
Chafariz d’El Rey (The King’s Fountain)
- 1570–1580
- Depicts João de Sá Panasco, an African Portuguese knight of the Order of Saint James
- Illustrates substantial presence of Africans and the range of roles they played in urban Iberian port cities in the 16th century
- Shows the interchange between African and European societies well before the height of the transatlantic slave trade
