Biochemistry Functional Groups: Structures, Properties, and Nomenclature
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
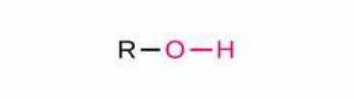
Hydroxide
Structure: -OH; Properties: Polar, hydrogen bonds, increases solubility; Nomenclature: Suffix -ol, prefix hydroxy- (if another group has priority); Examples: Ethanol (C₂H₅OH), 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid).
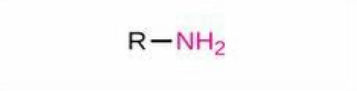
Amino
Structure: -NH₂; Properties: Basic, hydrogen bonds, forms amines; Nomenclature: Suffix -amine, prefix amino-; Examples: Methylamine (CH₃NH₂), 2-aminopropanoic acid (alanine).
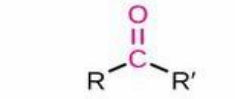
The general term
Carbonyl
structure: C=O (bonded to two atoms, placement varies); Properties: Strongly polar, reactive electrophilic center; Nomenclature: Not named alone; appears in aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides; Examples: Seen in formaldehyde (aldehyde), acetone (ketone).
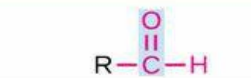
Aldehyde
Structure: -C(=O)H (carbonyl at end of chain); Properties: Reactive, easily oxidized; Nomenclature: Suffix -al, prefix formyl-; Examples: Methanal (formaldehyde), Ethanal (acetaldehyde), Glucose (aldose sugar).
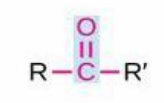
The one in the middle of a chain
Ketone
Structure: -C(=O)- (carbonyl within chain); Properties: Polar, less reactive than aldehydes, common in metabolism; Nomenclature: Suffix -one, prefix oxo- (if another group dominates); Examples: Propanone (acetone), Butanone, Fructose (a ketose sugar).
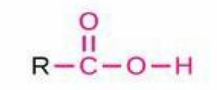
Carboxylic Acid
Structure: -C(=O)OH; Properties: Acidic, donates H⁺, often ionized at physiological pH; Nomenclature: Suffix -oic acid, prefix carboxy-; Examples: Ethanoic acid (acetic acid), Hexadecanoic acid (palmitic acid).
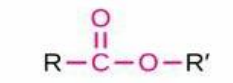
Ester
Structure: -C(=O)OR; Properties: Formed from carboxylic acid + alcohol, often fragrant; Nomenclature: Alkyl (from alcohol) + alkanoate (from acid); Examples: Ethyl ethanoate (ethyl acetate), Methyl butanoate.
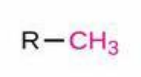
Methyl
Structure: -CH₃; Properties: Nonpolar, hydrophobic, common substituent, modifies DNA/proteins; Nomenclature: Prefix methyl- (always a substituent, never a suffix); Examples: Methylbenzene (toluene), Methylpropane (isobutane).
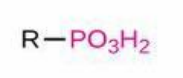
Phosphate
Structure: -PO₄ (commonly -OPO₃²⁻ when bonded); Properties: Negatively charged, stores energy in phosphoanhydride bonds; Nomenclature: Suffix -phosphate, prefix phospho-; Examples: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), Glycerol-3-phosphate.
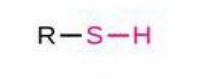
Sulfhydryl
Structure: -SH; Properties: Can form disulfide bridges, stabilizes protein folding; Nomenclature: Suffix -thiol, prefix mercapto-; Examples: Methanethiol, Cysteine (-CH₂-SH in side chain).