AP Environmental Science Unit 4
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Layers of the Earth
crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
The three types of plate boundaries
Divergent plate (sea floor spreading), convergent plate (two plates colliding generating pressure), and transform fault (plates moving sideways past each other, causing seismic activity)
Forming of volcanoes
When plates move over hotspots and heat from the rising mantle plume melts the crust
Earthquake
The sudden movement or vibration of Earth's crust caused by a release of potential energy along a fault.
Prevailing Winds
caused by atmospheric convention currents (cells) and Coriolis Effect (how we predict the weather)
Cold air
Falls; because it more dense
Warm air
rises; less dense
Corilois Effect
The effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents.
The Three Rock Types
Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic
How each rock type is formed
Igneous: formed directly from magma
Sedimentary: formed from sediments such as mud, sand, or gravel and compressed by overlying sediment
Metamorphic: when sedimentary, igneous, or other metamorphic rock are subject to high temperatures and pressures
soil triangle
a graphic explanation of the proportions of sand, silt, and clay in soil
Five factors that determine how soil is formed
Parent material, climate, topography, organisms, and time
What can lead to soil degradation and erosion
Overuse by agriculture or whenever the topsoil or vegetation is removed from the soil.
The horizons of soil
O horizon- made of decomposing organisms/humus
A horizon- mixed minerals and topsoil/humus
E horizon- zone of leaching or eluviation
B horizon- subsoil and very little organic material
C horizon- similar to parent material, least weathered
Parent material
the rock material from which the inorganic components of soil are derived.
Biological properties of soil
Fungi, bacteria, and protozoan account for 80-90 percent of soil's productivity and can break down organic material.
Physical properties of soil
Permeability and the order of particle size: sand, silt, then clay.
Chemical properties of soil
Acidity that can be neutralized by base material (calcium, magnesium, sodium, and potassium)
Texture
The amount of rock, sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample.
Permeability
Allowing water and roots to move between the particles.
cation exchange
The ability of a particular soil to adsorb and release cations.
Microorganisms
Microscopic organisms which may exist in a single-celled form or in a colony of cells.
pH
potential of hydrogen
Detritovores
Organisms that eat dead and decaying organic matter.
Lithosphere
Contains the crust and upper mantle.. "plates for continents and oceans"
Mantle
Containing magma (molten rock).
Asthenosphere
Outer mantle of semi-molten, ductile, flexible rock. "converter belt for plates"
The movement of tectonic plates is made possible by
thermal energy (heat) from the mantle.
Which layer on earth has convection currents that move the continental and oceanic crust?
asthenosphere
Earth's lithosphere includes
oceanic and continental crust.
Seafloor spreading
The formation of new ocean crust as a result of magma pushing upward and outward from Earth's mantle to the surface.
Divergent plate boundary
The boundary between two oceanic plates that are moving away from each other to form new ocean crust
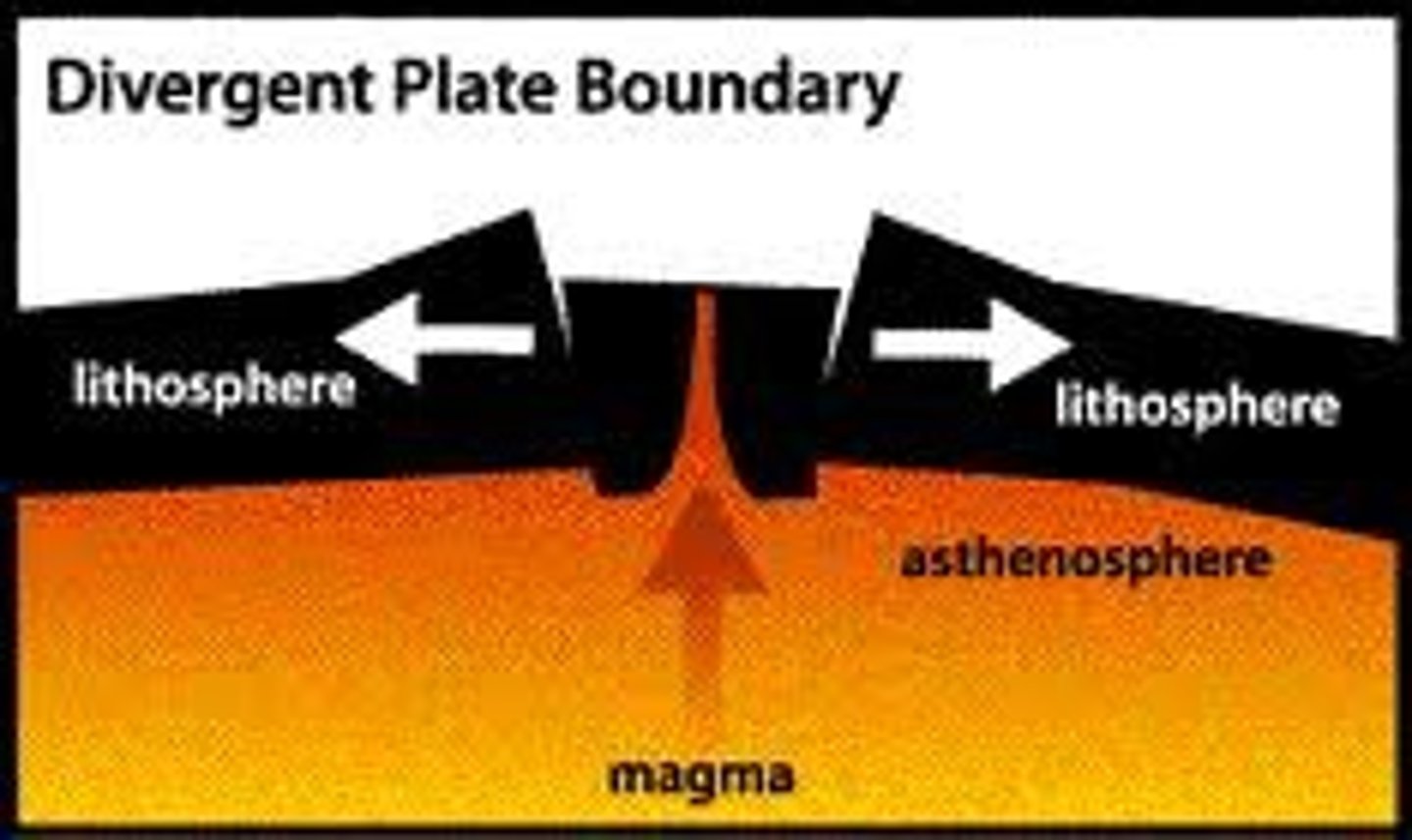
How is new oceanic crust formed?
2 oceanic crust moves away from each other > divergent boundary > zone of divergence >rift valley >shield volcanoes erupting basalt > new crust
heat and pressure leads to
metamorphic rock
Ring of Fire
A major belt of volcanic activity that rims the Pacific Ocean caused by oceanic - continental plates at convergent boundary overlapping
Convergent plate boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two plates collide, come together, or crash into each other.
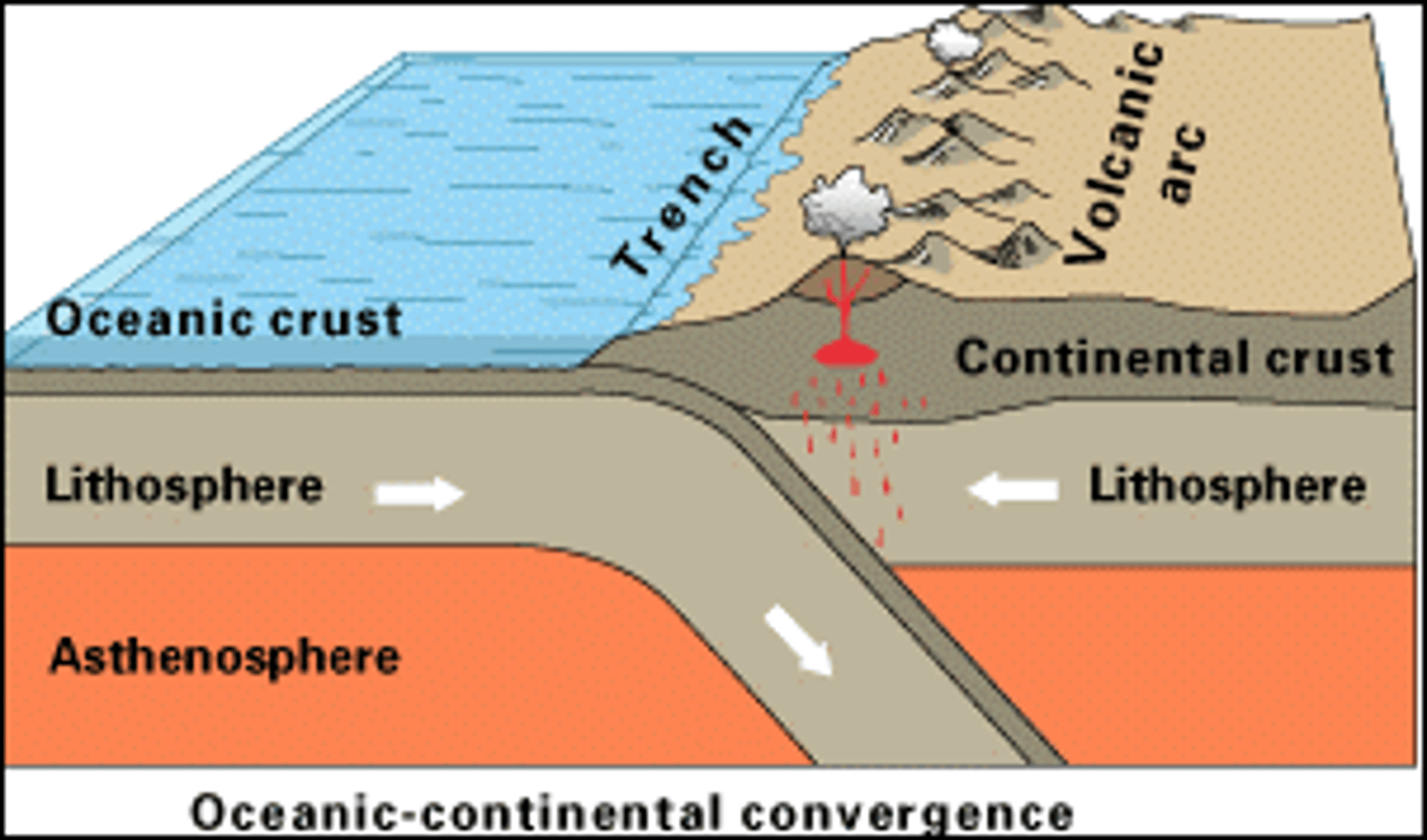
Continental-oceanic convergent plate
Subduction occurs here when oceanic and the continental plates collide and the oceanic plate bends and slides into the mantle
Two oceanic plates convergent plate
When two oceanic plates collide and one is pushed under the other causing magma to rise and a volcano forms
continental-continental convergent boundary
when two continental plates collide, mountain ranges are created as the colliding crust is compressed and pushed upward (ex: the Himalayas)
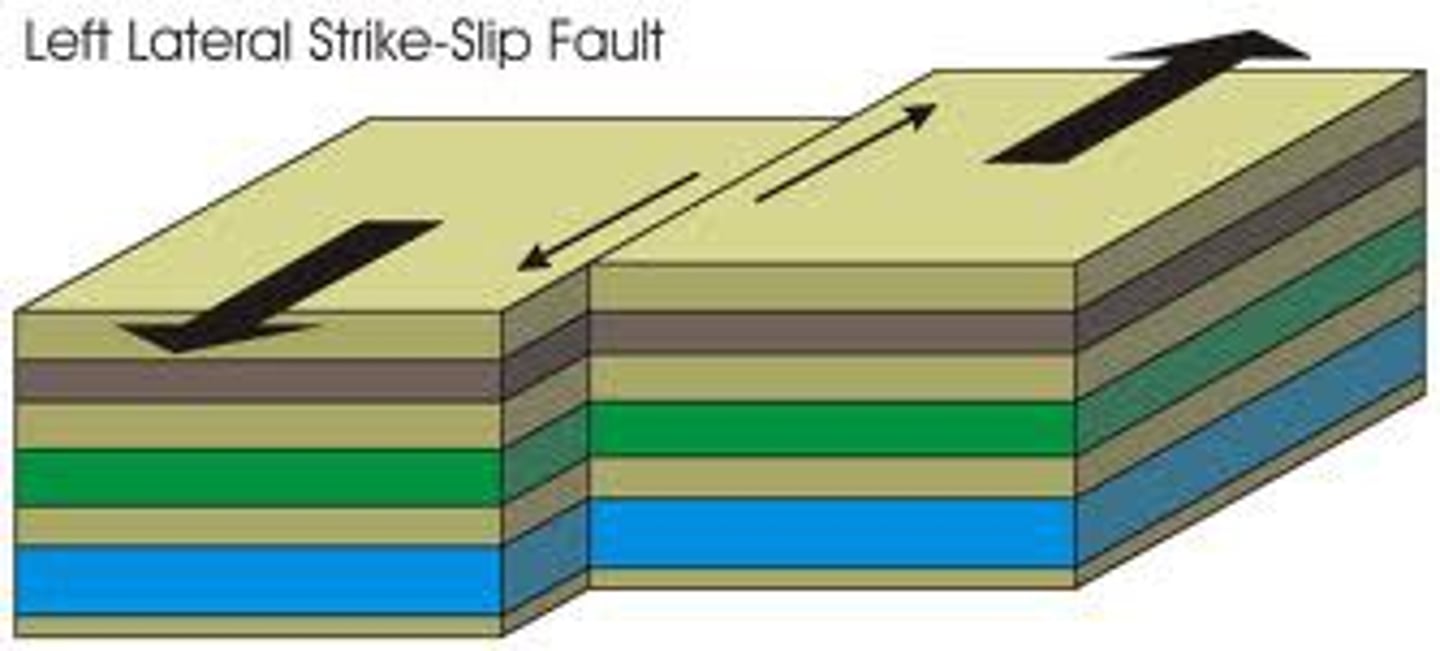
Transform plate boundary
Boundary between two plates that are sliding past each other.
Deep water trench
formed along convergent boundaries (subduction zone)
What type of land formation would you expect to find on the west coast of S. America?
Volcanoes.
Why do scientist find larger seismic activity around the ring of fire?
The pacific plate is large and is contacting many other plates moving in various directions.
What happens with oceanic crust diverges?
New ocean floor is created from the rising of magma (seafloor spreading)
The creation of mountains, island arcs, earthquakes, and volcanoes are likely to result from
convergent boundaries.
crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantle, outer core, inner core
layers of Earth in order (outside to inside)
Theory of Plate Tectonics
State that Earth's lithosphere is broken into huge, moving slabs of rock driven by motions in the mantle (asthenosphere) and this motion caused geological events.
The theory of plate tectonics explains
The formation, movement, and subduction of Earth's plates. As well as the changes in land masses such as Pangea.
Oceanic crust
thinner, more dense, younger crust made of basalt from shield volcanoes at the zone of divergence.
Soil
A mixture of mineral particles and organic material that covers the land, and in which terrestrial plants grow.
A horizon
Topsoil
Bacteria, Fungi and small animals (add organic matter)
Burrowing animals help circulate air and water and mix minerals. contains most humus
B horizon
Subsoil
Contains minerals brought by ground water or leeched from horizon a
high iron calcium and aluminum
made of clay
C horizon
partially weathered bedrock
some from parent material, some from other forms of past erosions
Bed rock
parent material
Horizon O
Made mostly of leaf litter and humus
Chemical weathering
The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes
physical weathering
Breaking down rocks through physical processes like freezing and thawing
Sizes of soil big to small
sand
silt
clay
Troposphere
75-80% of earths mass (most dense-closest to earth)
0-12/18 above sea level
biogeochemical cycles are here
Weather climate and life forms here
Altitude increase temperature decreases
Stratosphere
11km to 50km
contains the Ozone layer
less water
airplanes here
Altitude increase temperature increases
Mesosphere
50-80km above Earth's surface
little oxygen
Altitude increase temperature decreases
Thermosphere
Hot layer: Oxygen absorb solar energy
Uv rays
Altitude increase temperature increases
Exosphere
Where the international space station can be found