Chapter 23: Indian and Southeast Asian Art
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Art History
AP Art History
Bodhisattva
Buddha
Mudra
Nirvana
Stupa
Vishnu
Wat
Buddhist Philosophy and Art
Gandharan
Jowo Rinpoche
Great Stupa
Borobudur Temple
Hindu Philosophy and Art
Hinduism
Buddhism
Hindu Sculpture
Nataraja
Hindu Architecture
Angkor Wat Temple
Lakshmana Temple
Jahangir Preferring a Sufi Shaikh to Kings
12th
Last updated 9:07 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
Ashlar masonry
carefully cut and grooved stones that support a building without the use of concrete or other kinds of masonry
2
New cards
Bas-relief
a very shallow relief sculpture
3
New cards
Bodhisattva
a deity who refrains from entering nirvana to help others
4
New cards
Buddha
a fully enlightened being. There are many Buddhas, the most famous of whom is Sakyamuni, also known as Gautama or Siddhartha
5
New cards
Cella
the main room of a temple, where the god is housed
6
New cards
Darshan
in Hinduism, the ability of a worshipper to see a deity and the deity to see the worshipper
7
New cards
Garbha griha
a “womb chamber,” the inner room in a Hindu temple that houses the god’s image
8
New cards
Horror vacui
(Latin, meaning “fear of empty spaces”) a type of artwork in which the entire surface is filled with objects, people, designs, and ornaments in a crowded and sometimes congested way
9
New cards
Hypostyle
a hall with a roof supported by a dense thicket of columns Iconoclasm— the destruction of religious images that are seen as heresy
10
New cards
Mandorla
(Italian, meaning “almond”) an almond-shaped circle of light around the figure of Christ or Buddha
11
New cards
Mithuna
in India, the mating of males and females in a ritualistic, symbolic, or physical sense
12
New cards
Mudra
a symbolic hand gesture in Hindu and Buddhist art
13
New cards
Nirvana
an afterlife in which reincarnation ends and the soul becomes one with the supreme spirit
14
New cards
Puja
a Hindu prayer ritual Sakyamuni
15
New cards
Shikara
a bee-hive shaped tower on a Hindu temple
16
New cards
Shiva
the Hindu god of creation and destruction
17
New cards
Stupa
a dome-shaped Buddhist shrine
18
New cards
Torana
a gateway near a stupa that has two upright posts and three horizontal lintels. They are usually elaborately carved
19
New cards
Urna
a circle of hair on the brows of a deity, sometimes represented as focal point
20
New cards
Ushnisha
a protrusion at the top of the head, or the top knot of a Buddha
21
New cards
Vairocana
the universal Buddha, a source of enlightenment; also known as the Supreme Buddha who represents “emptiness,” that is, freedom from earthly matters to help achieve salvation
22
New cards
Vishnu
the Hindu god worshipped as the protector and preserver of the world
23
New cards
Wat
a Buddhist monastery or temple in Cambodia
24
New cards
Yakshi
female and male figures of fertility in Buddhist and Hindu art
25
New cards
The Lion
a symbol of Buddha’s royalty
26
New cards
The Wheel
Buddha’s law
27
New cards
Lotus
a symbol of Buddha’s pure nature. The lotus grows in swamps, but mud slides off its surface.
28
New cards
Columns surrounded by a wheel
Buddha’s teaching
29
New cards
Empty Throne
Buddha, or a reminder of a Buddha’s presence.
30
New cards
Bodhisattvas
helpers of the Buddha, are usually depicted near the Buddha.
31
New cards
mudras
Buddhas' moods vary but most suggest meditation. Hand gestures called \____, reveal Buddhas' actions and feelings.
32
New cards
ushnisha
The head has an \______ or top knot, hair has tight curls, and extremely long ears.
33
New cards
Yakshas and yakshis
These are distinctive figures that appear frequently in Indian popular religion and are often incorporated into the Buddhist pantheon.
34
New cards

Gandharan
* By Buddha from Bamiyan (400–800)
* First colossal Buddhas.
* Pilgrimage site linked to the Silk Road.
* These Buddhas served as models for later large-scale rock-cut images in China.
* First colossal Buddhas.
* Pilgrimage site linked to the Silk Road.
* These Buddhas served as models for later large-scale rock-cut images in China.
35
New cards
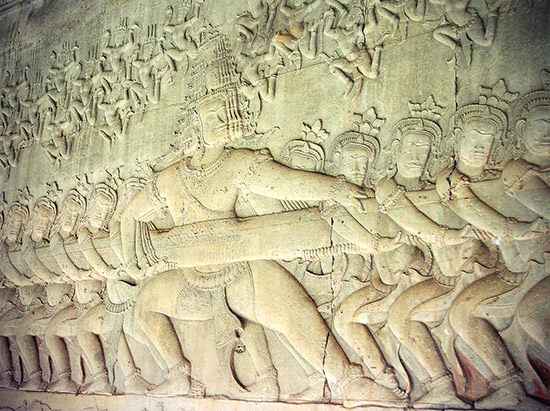

churning of the ocean of milk
one of the central events in the ever-continuing struggle between the devas (gods) and the asuras (demons, or titans).
36
New cards

Jowo Rinpoche enshrined in the Jokhang Temple
* Statue thought to have been blessed by the Buddha himself
* Temple founded in 647 by the first ruler of a unified Tibet.
* Disappeared in 1960s during China’s Cultural Revolution.
* Temple founded in 647 by the first ruler of a unified Tibet.
* Disappeared in 1960s during China’s Cultural Revolution.
37
New cards
Mt. Meru
The stupa represents _____, the mountain at the center of the world in Buddhist cosmology that connects the earth and the heavens.
38
New cards
giant hemisphere
The stupa's distinctive shape, like a ____, and the direction of prayer with the sun, give it cosmic symbolism.
39
New cards
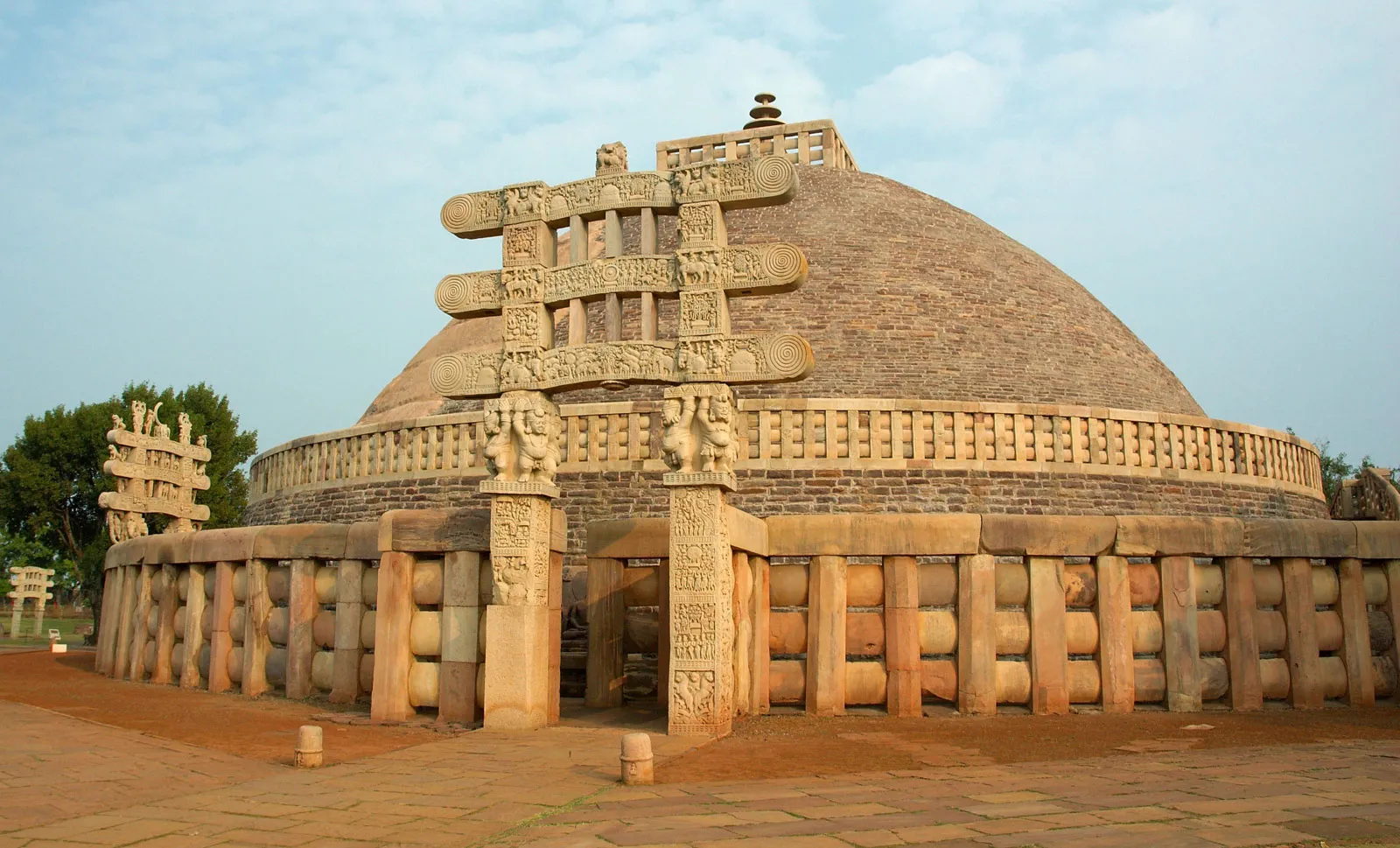

Great Stupa
* Pilgrimage site.
* A Buddhist shrine, mound shaped and faced with dressed stone containing the relics of the Buddha.
* The worshipper circumambulates the stupa clockwise along the base of the drum
* A Buddhist shrine, mound shaped and faced with dressed stone containing the relics of the Buddha.
* The worshipper circumambulates the stupa clockwise along the base of the drum
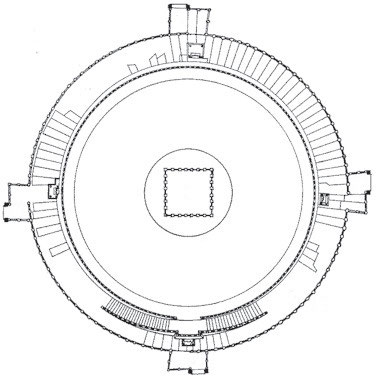
40
New cards
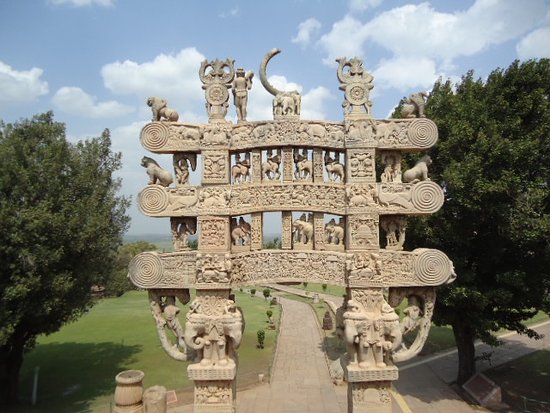

Great Stupa Torana
* orientation and direction of ritualistic circumambulation correspond with the direction of the sun’s course
* richly carved scenes on the architraves
* richly carved scenes on the architraves
41
New cards
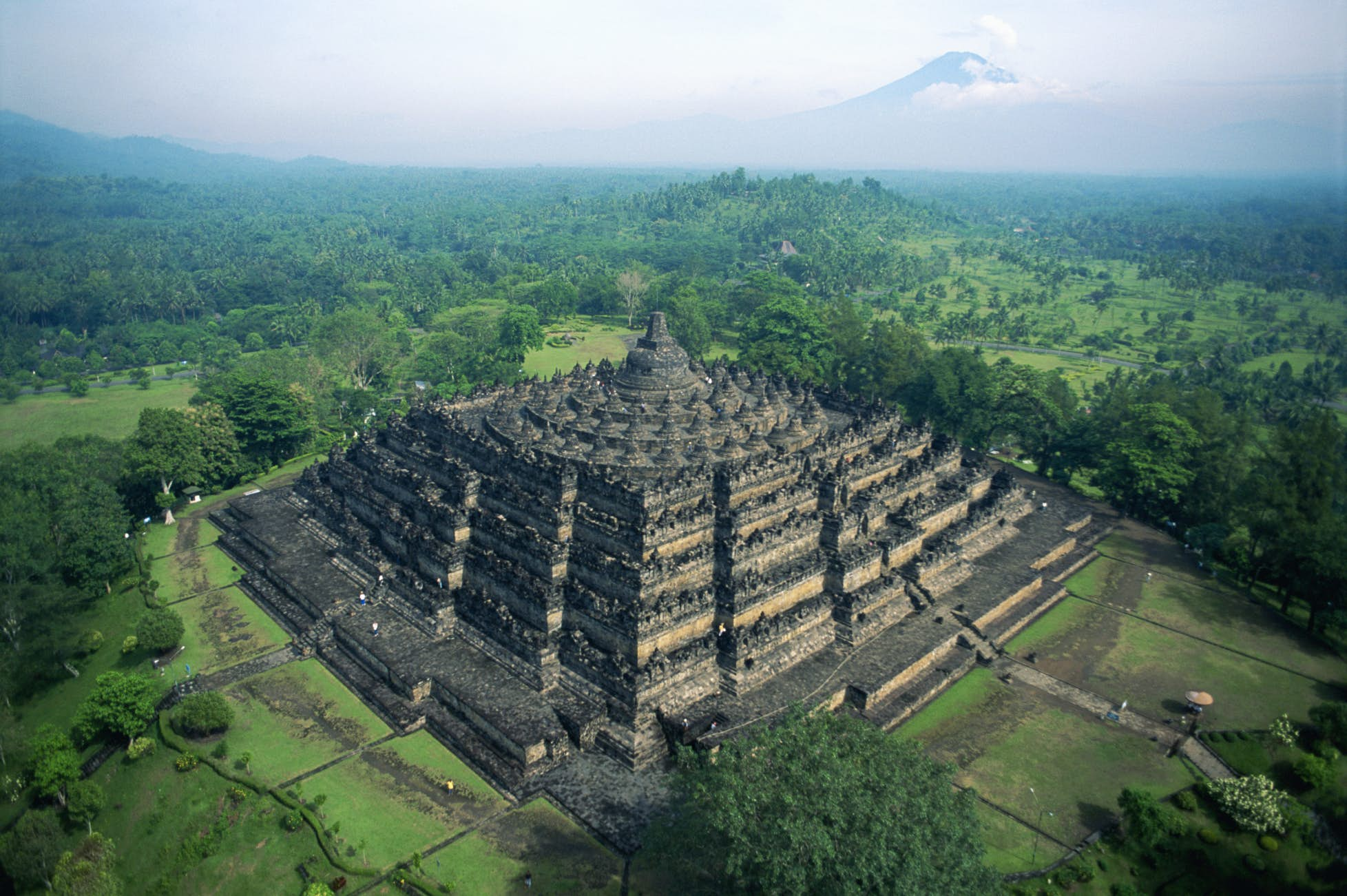

Borobudur Temple
* Pyramid in form; aligned with the four cardinal points of the compass.
* This massive Buddhist monument contains 504 life-size Buddhas, 1,460 narrative relief sculptures on 1,300 panels 8,200 feet long.
* Meant to be circumambulated on each terrace
* This massive Buddhist monument contains 504 life-size Buddhas, 1,460 narrative relief sculptures on 1,300 panels 8,200 feet long.
* Meant to be circumambulated on each terrace
42
New cards
Borobudur Temple Body
* five terraces in which people abandon their earthly desires;
* this is the world of forms—people have to control these negative impulses;
* sculptures here show the pilgrimage of the young man, Sudhana, who sets out in search of the Ultimate Truth.
* this is the world of forms—people have to control these negative impulses;
* sculptures here show the pilgrimage of the young man, Sudhana, who sets out in search of the Ultimate Truth.
43
New cards
Borobudur Temple Superstructure
an area that represents a formless world, in which a person experiences reality in its purest stage, where the physical world and worldly desire are expunged.
44
New cards
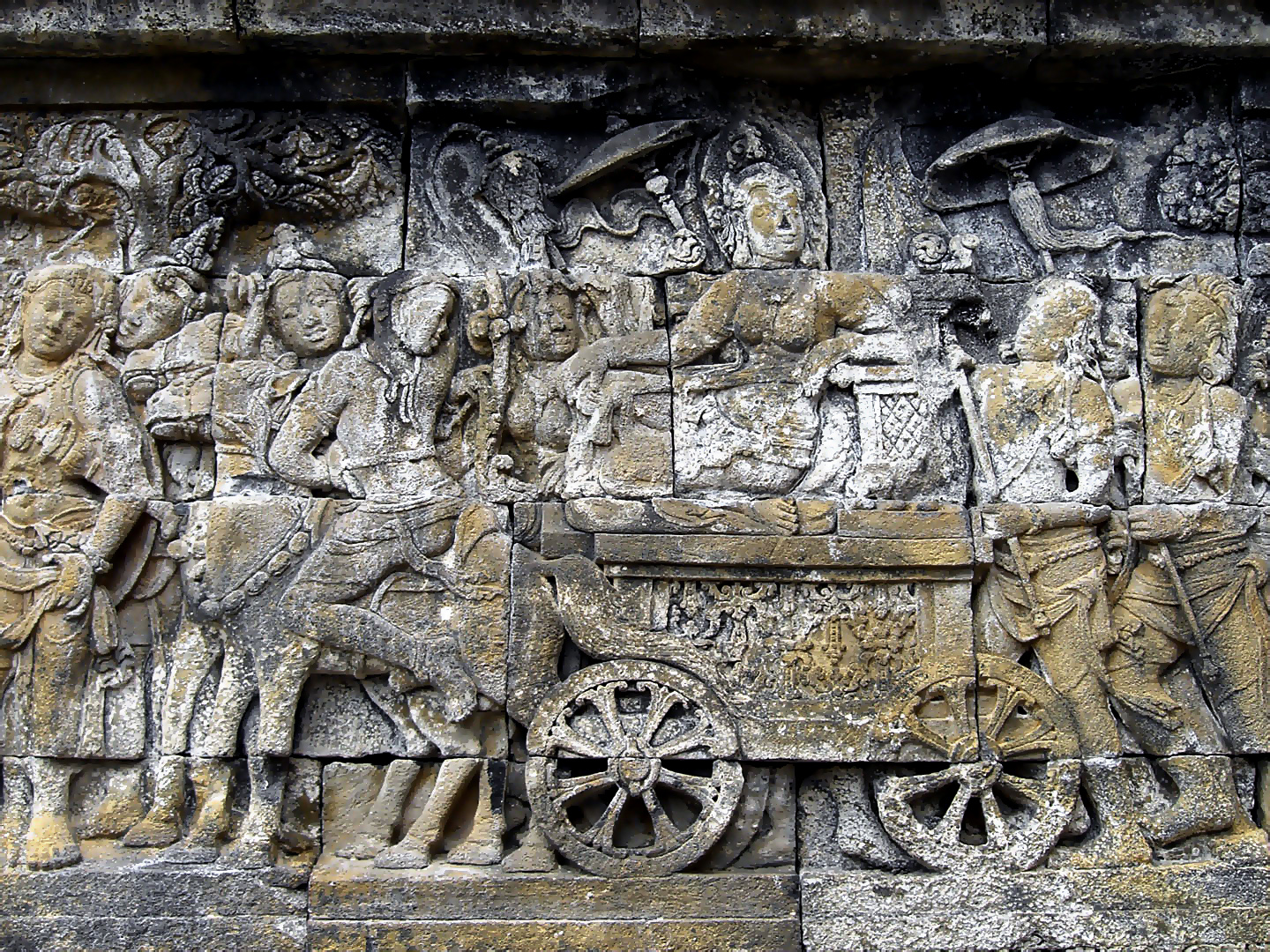

Queen Maya riding a horse carriage retreating to Lumbini to give birth to Prince Siddhartha Gautama
* Densely packed scene; horror vacui.
* The queen is majestic and at rest before giving birth.
* Ready to give birth to her son, Prince Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha.
* She is brought to the city in a great ceremonial procession.
* The queen is majestic and at rest before giving birth.
* Ready to give birth to her son, Prince Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha.
* She is brought to the city in a great ceremonial procession.
45
New cards
Brahmins
Orthodox Hindus accept the Vedic texts as divine in origin and maintain aspects of the Vedic social hierarchy, which assigns a caste of ritual specialists known as _____ to officiate between the gods and humankind.
46
New cards
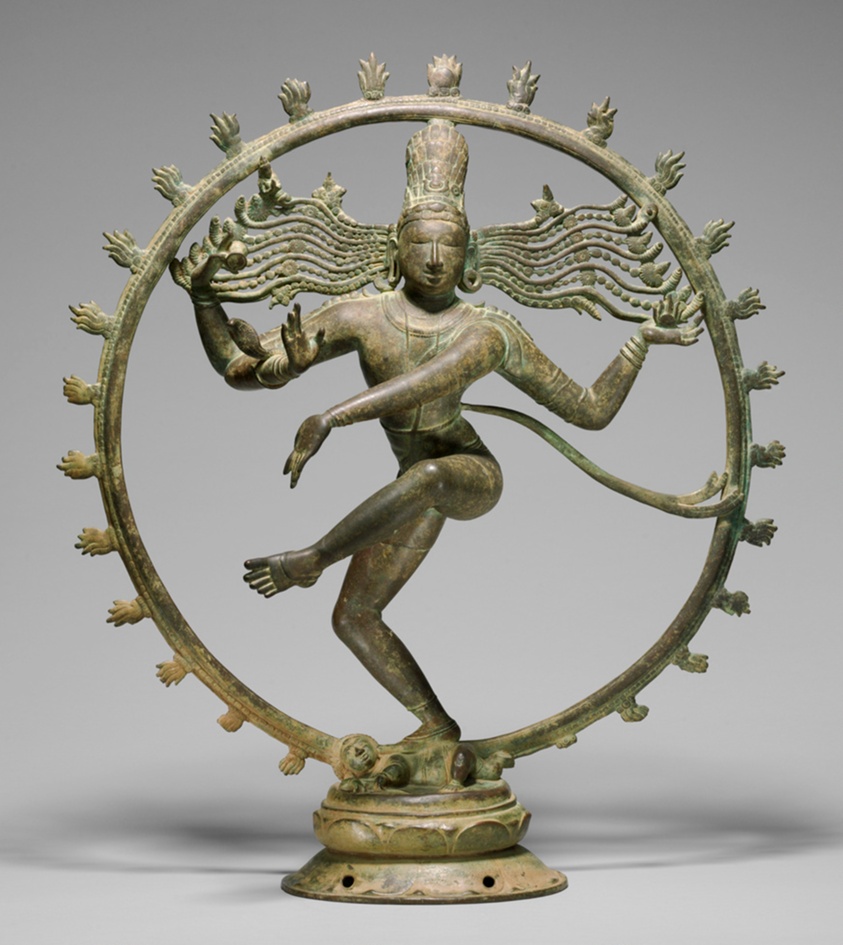

Shiva as Lord of Dance (Nataraja)
* Shiva has four hands.
* The sculpture becomes the receptacle for the divine spirit when people pray before it
* The distribution of this figure due to the patronage of a queen, Mahadevi.
* The sculpture becomes the receptacle for the divine spirit when people pray before it
* The distribution of this figure due to the patronage of a queen, Mahadevi.
47
New cards

Lakshmana Temple
* The temple is placed on a high pedestal, or plinth, to be seen from a distance. It appears like rising peaks of a mountain range.
* It is a Hindu temple grouped with a series of other temples in Khajuraho.
* The temple is dedicated to Vishnu.
* It is a Hindu temple grouped with a series of other temples in Khajuraho.
* The temple is dedicated to Vishnu.
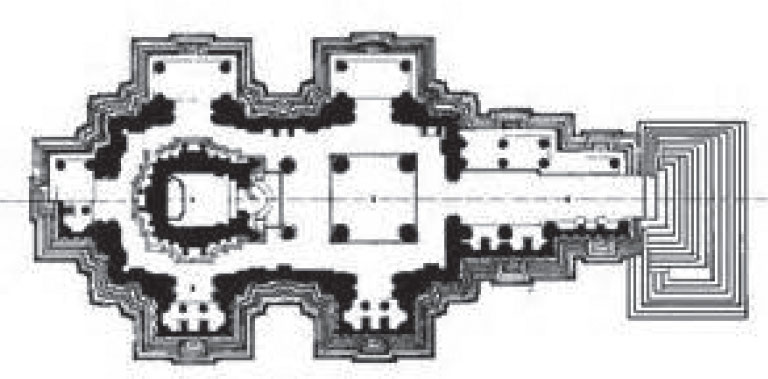
48
New cards
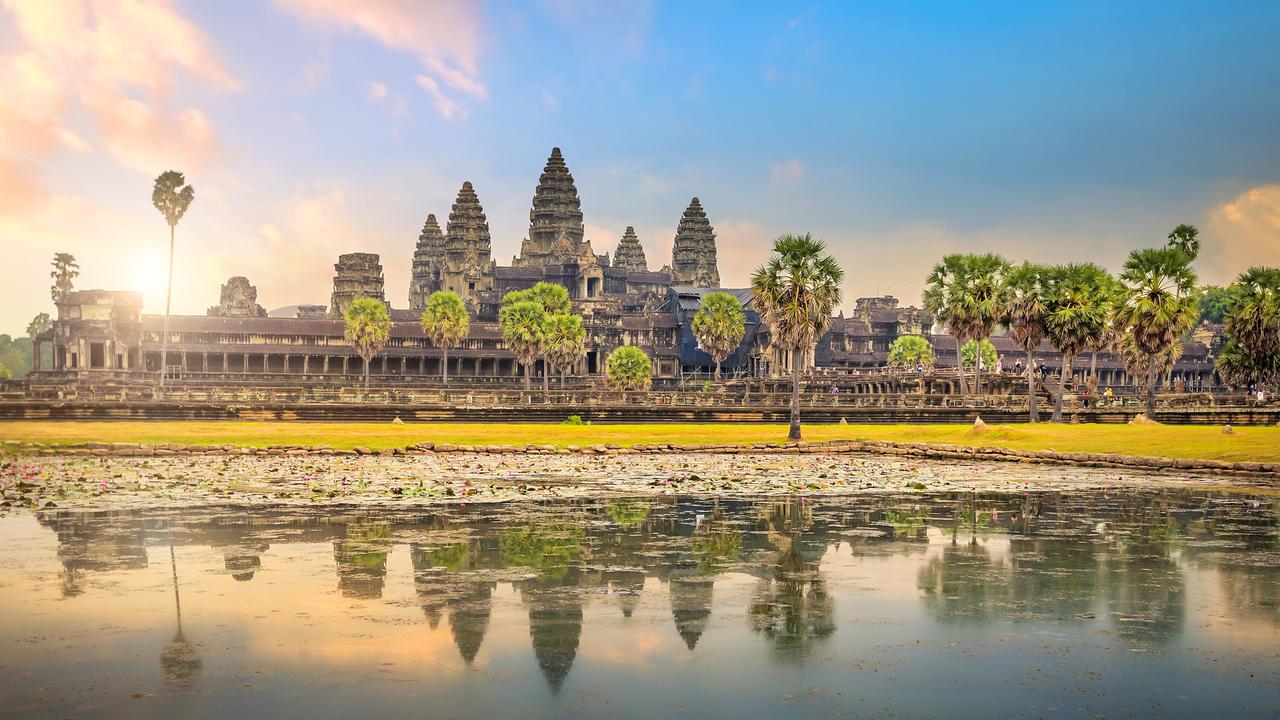

Angkor Wat Temple
* Dedicated to Vishnu; most sculptures represent Vishnu’s incarnations.
* May have been intended to serve as the king’s mausoleum.
* built by King Suryavarman II.
* Mountain-like towers symbolize the five peaks of Mount Meru
* May have been intended to serve as the king’s mausoleum.
* built by King Suryavarman II.
* Mountain-like towers symbolize the five peaks of Mount Meru
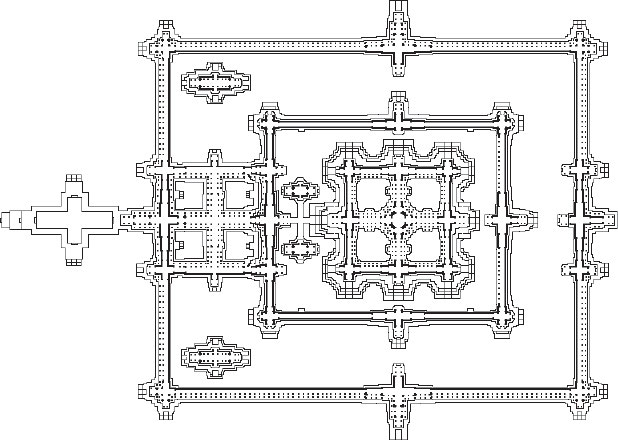
49
New cards

South Gate of Angkor Wat Temple
* **one of the 5 gates which guard the ancient city of Angkor Thom**, and is the best preserved of all the gates.
* It was built by King Jayavarman VII in the late 12th Century, serving as 1 of the 5 holy Buddhist gateways to Angkor Thom.
* It was built by King Jayavarman VII in the late 12th Century, serving as 1 of the 5 holy Buddhist gateways to Angkor Thom.
50
New cards

Jayavarman VII as Buddha
He was considered to be a living Buddha, or bodhisattva who turned his back from the brink of enlightenment to redeem or save his people from suffering; he imagined himself in a role similar to that of the present day Dalai Lama of Tibet.
51
New cards

Jahangir Preferring a Sufi Shaikh to Kings
* By Bichitr (c. 1620)
* Great interest in the Mughal court for European allegorical portraits, techniques, and motifs.
* Quotation, in frame: “Though outwardly shahs stand before him, he fixes his gazes on dervishes.”
* Great interest in the Mughal court for European allegorical portraits, techniques, and motifs.
* Quotation, in frame: “Though outwardly shahs stand before him, he fixes his gazes on dervishes.”