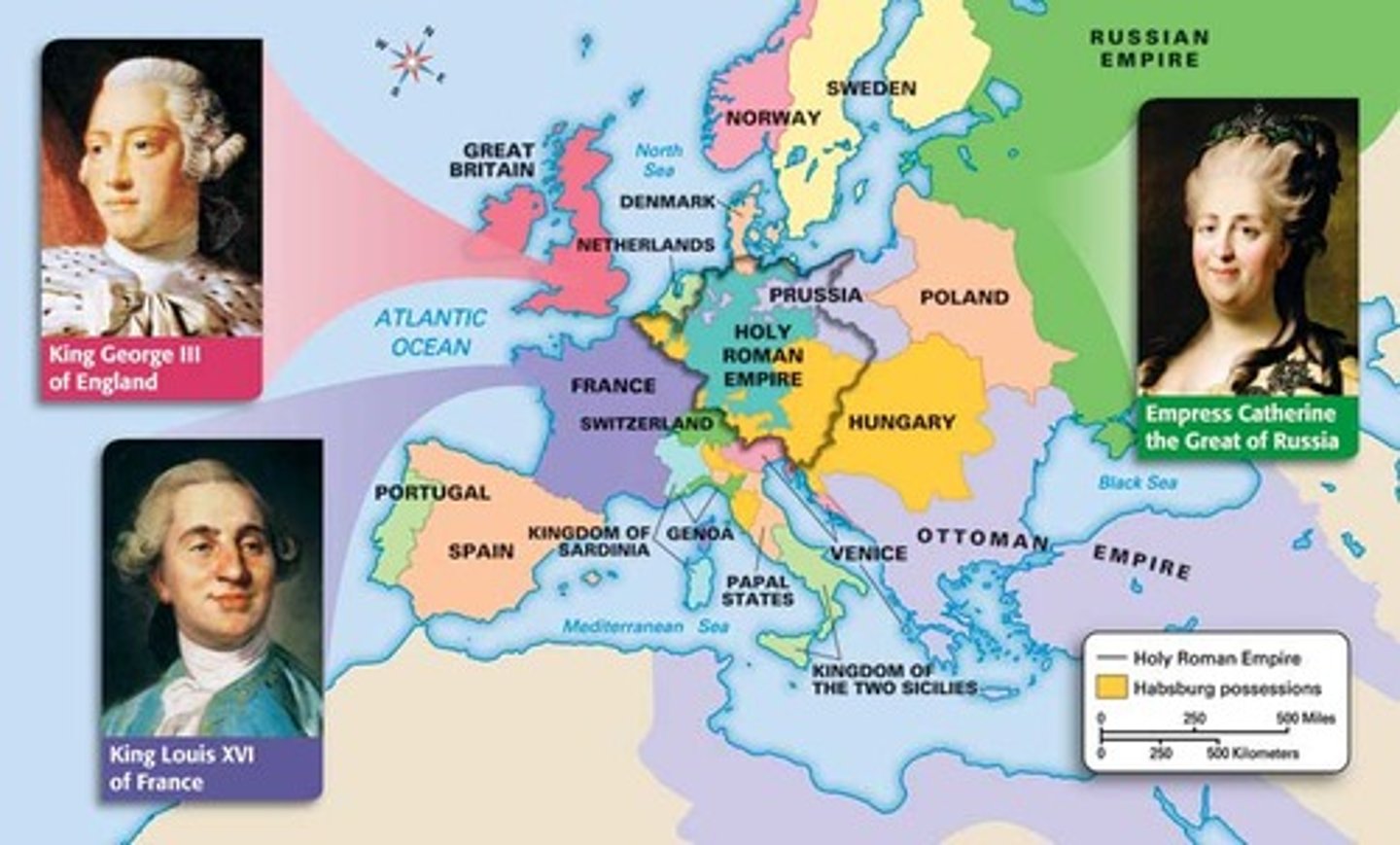
Absolutism, Enlightenment, Revolutions (1648-1815)
1/46
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Absolute Monarchy (Absolutism)
1- Ruler with complete power over the government and the people
2- Divine Right
3- Hobbes
4- Bousset
5-Louis XIV

Adam Smith, Wealth of Nations, 1776
Promoted laissez-faire, free-market economy, and supply-and-demand economics (1776).Father of Capitalism

Agricultural Revolution
A time when new inventions such as the seed drill and the steel plow made farming easier and faster. The production of food rose dramatically leading to population exlposion.
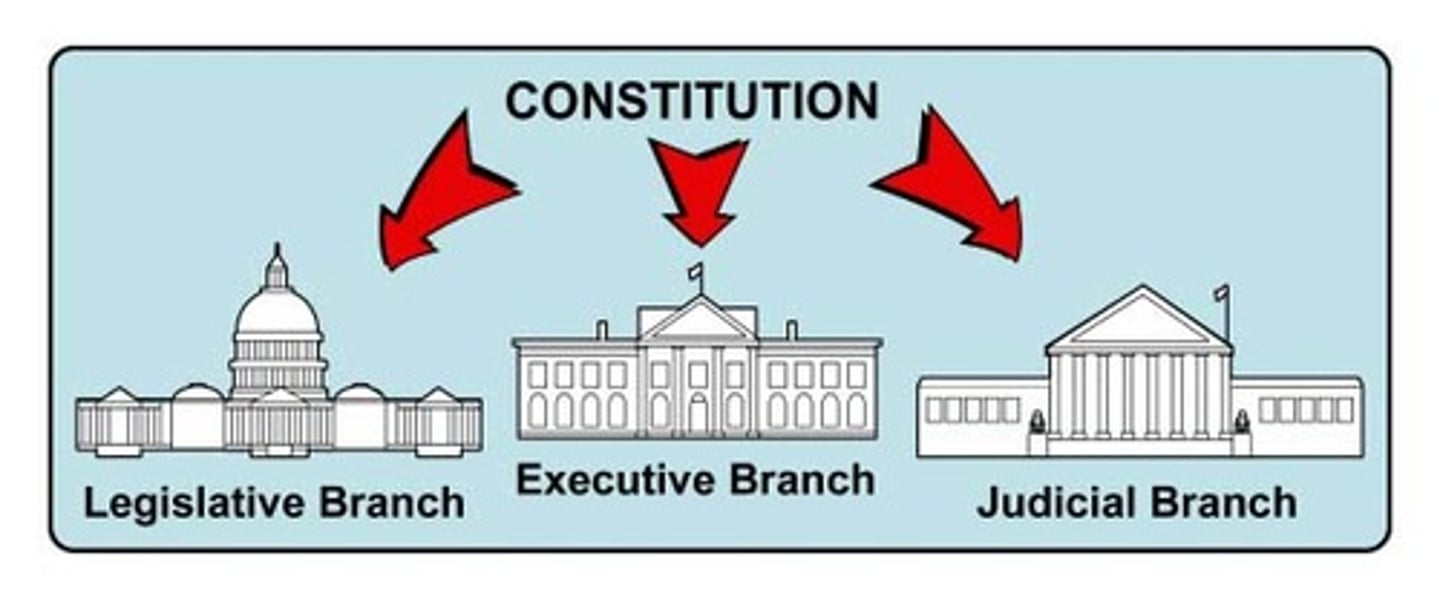
Baron de Montesquieu (1689-1755)
1-French aristocrat who wanted to limit royal absolutism;
2- Wrote The Spirit of Laws, urging that power be separated between executive, legislative, and judicial branches, each balancing out the others, thus preventing despotism and preserving freedom.
3- This greatly influenced writers of the US Constitution. He greatly admired British form of government.
Battle of Vienna (1683)
1- Last unsuccessful Ottoman attempt to take central Europe in 1683, cementing Habsburg control in southeastern Europe and ending Ottoman westward expansion.
2- Largest Cavalry charge in History!

Catherine the Great
1- This was the empress of Russia who continued Peter's goal to Westernizing Russia, created a new law code, and greatly expanded Russia.
2- Enlightened Despot

Classical Liberalism
1- The political ideology of individual liberty, private property, a competitive market economy, free trade, and limited government.
2- The idea being that the less government does, the better, particularly in reference to economic policies such as tariffs and incentives for industrial development.
3- Attacking corruption and defending private property, late-nineteenth-century liberals generally called for elite government and questioned full democratic participation.

Concordat of 1801
1- Napoleon's arrangement with Pope Plus VII to heal religious division in France with a united Catholic church under bishops appointed by the government.
2- State controlled religion

Congress of Vienna (1815)
1. Enacted a settlement that was acceptable to both the victors and to France
2. Created a balance of power that lasted until the unification of German in 1871
3. Underestimated the forces of liberalism and nationalism
4. Used the principle of legitimacy to restore the Bourbons to the French throne
5. United Belgium with the Netherlands to form a single kingdom of the Netherlands
6. Created a loose confederation of 39 German stated dominated by Austria
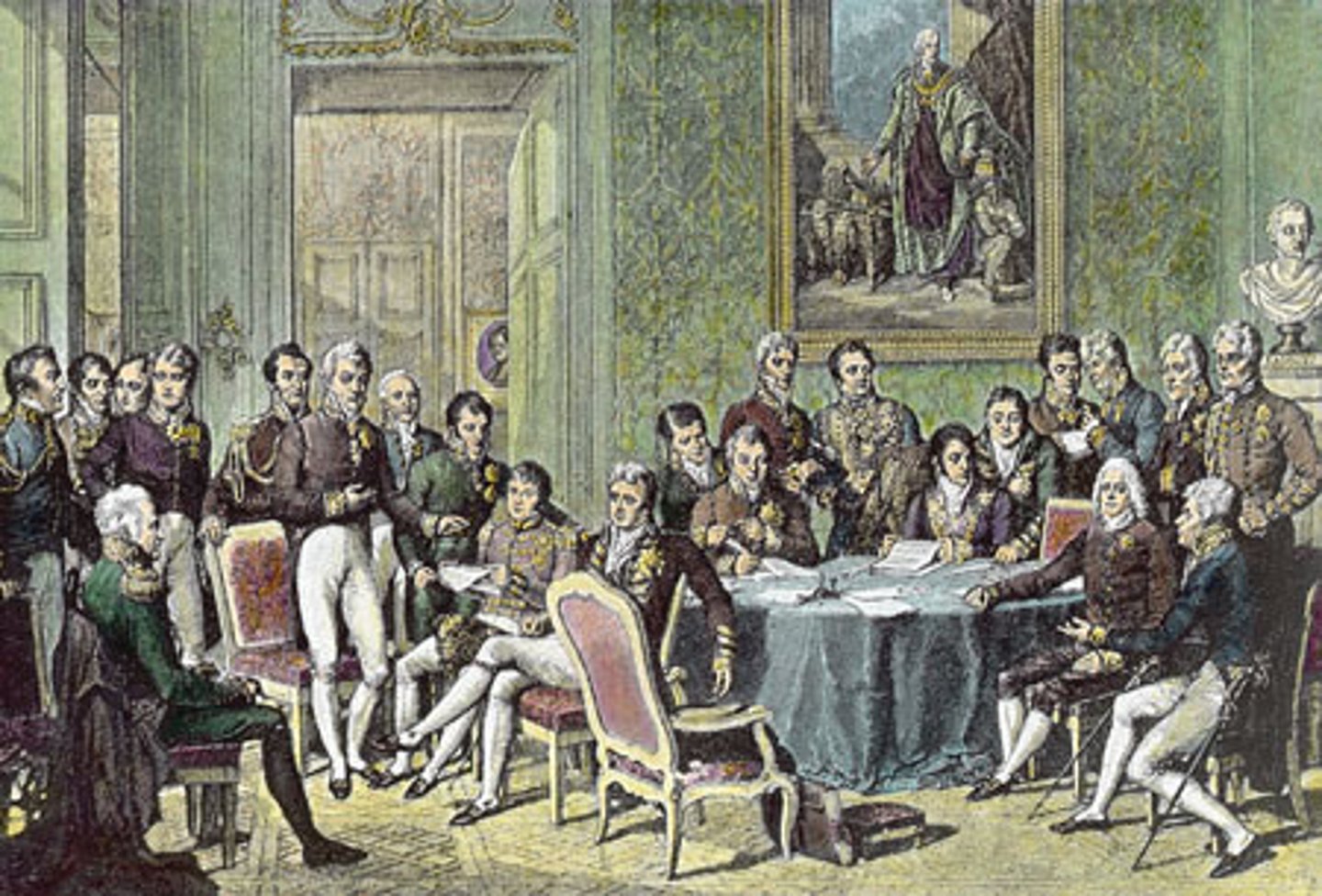
consumer culture
A culture in which personal worth and identity reside not in the people themselves but in the products with which they surround themselves

The Consumer Revolution
Textiles, hats, ceramics, glassware, carpets, and furniture

Conservatism
a political philosophy based on tradition and social stability, favoring obedience to political authority and organized religion

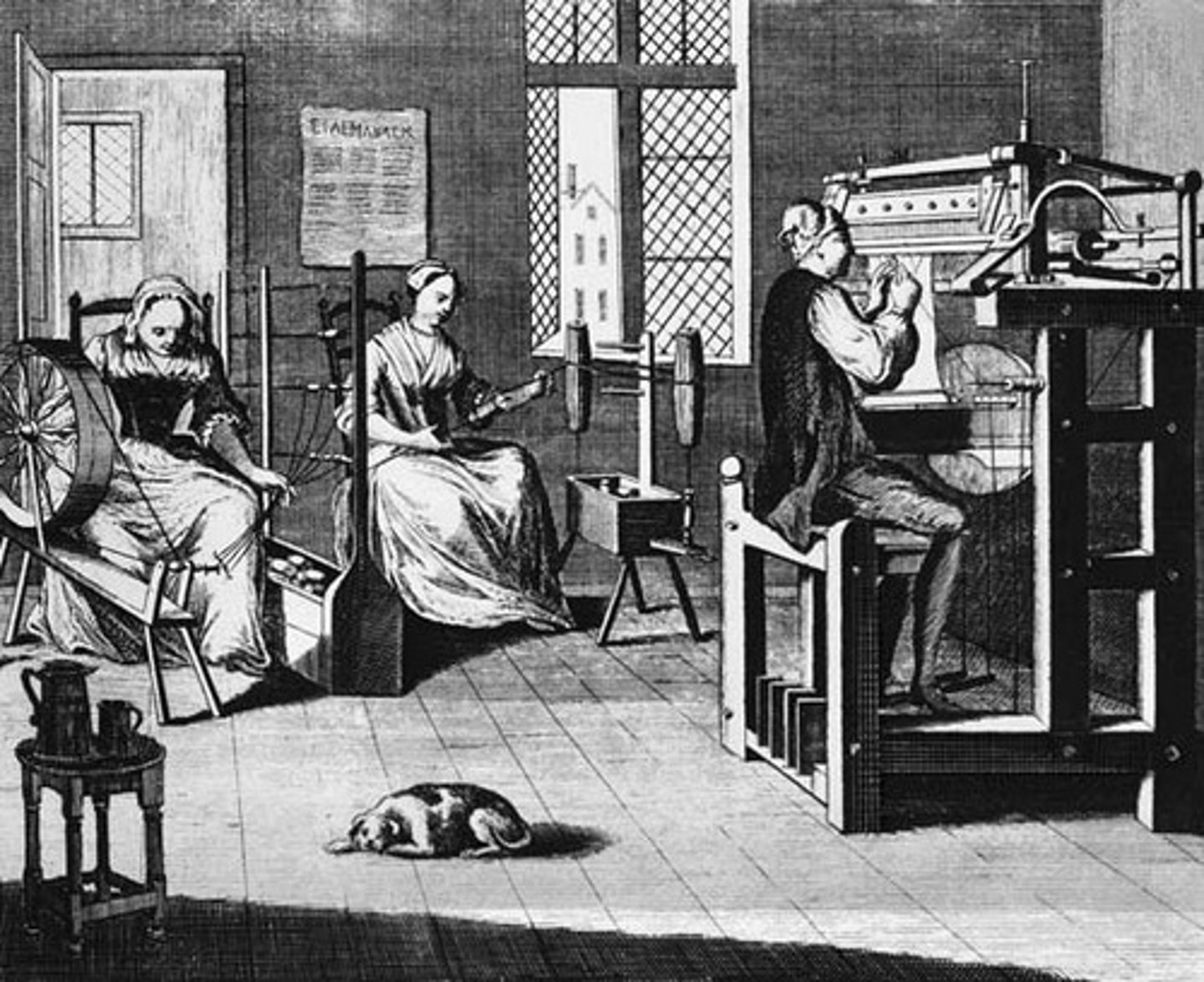
cottage industry/putting out system
A system of textile manufacturing in which laborers (rural proletariat or urban migrants) worked in homes or workshops through merchant intermediaries or workshop owners; marginalized guilds hold over production

Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
French Revolution document that outlined what the National Assembly considered to be the natural rights of all people and the rights that they possessed as citizens.
Guaranteed the rights of Men only, not women

Deism
1- God is a watchmaker; The religion of the Enlightenment (1700s).
2- Followers believed that God existed and had created the world, but that afterwards He left it to run by its own natural laws.

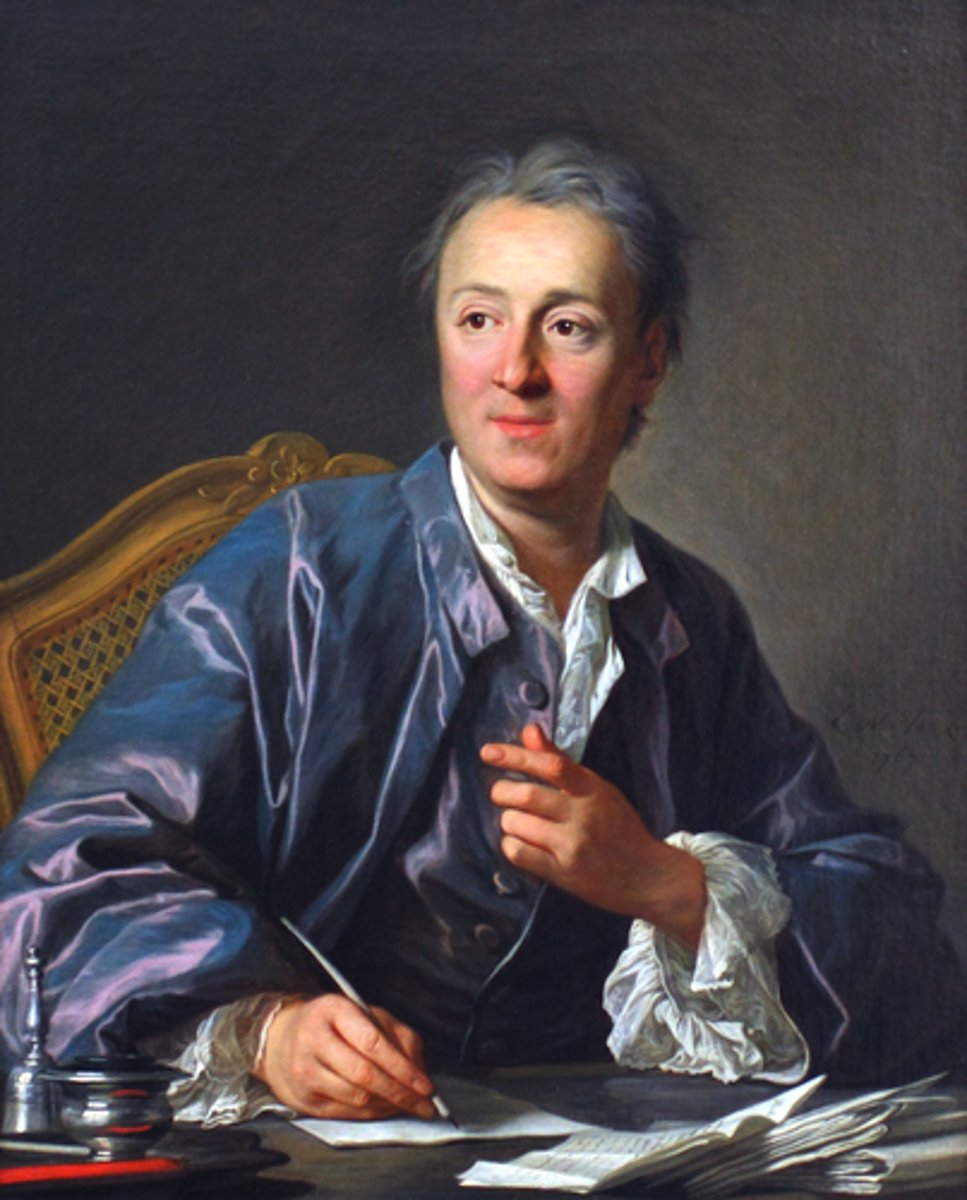
Denis Diderot
Enlightenment Philosophe who edited a book called the Encyclopedia which was banned by the French king and pope.

Empiricism
the view that knowledge originates in experience and that science should, therefore, rely on observation and experimentation
English Bill of Rights (1689)
1- William and Mary accepted this document.
It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently.
2- By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people.

Enlightened Despot
Absolute rulers who used their power to bring about political and social change.
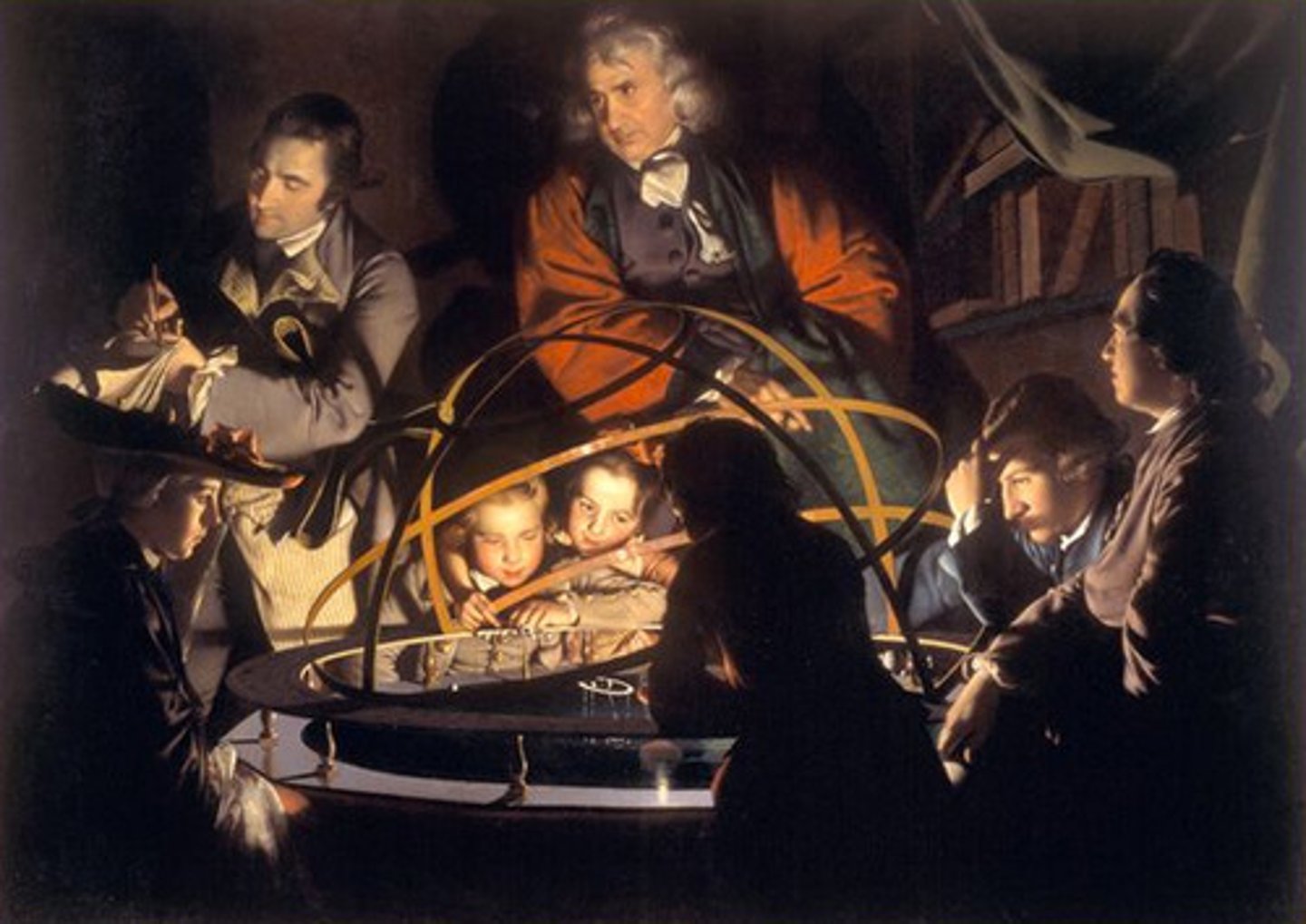
Enlightenment
1- A philosophical movement which emphasized REASON and the scientific method.
2- Writers of the enlightenment tended to focus on government, ethics, and science, rather than on imagination, emotions, or religion.
3- Many members of the Enlightenment rejected traditional religious beliefs in favor of Deism, which holds that the world is run by natural laws without the direct intervention of God.
Frederick II (the Great)
1- He followed his father, Frederick William's military policies when he came to power.
2-However, he also softened some of his father's laws.
3- With regard to domestic affairs, he encouraged religious toleration and legal reform. According to his theory of government, he believed that a ruler should be like a father to his people.

Frederick William I of Prussia
(1713-1740), truly established Prussian absolutism and gave it a unique character, infused strict MILITARY values into a whole society, intensely emotional attachment to the military life, dog-eat-dog view of international politics, tried with some success to develop the country economically

free trade
the movement of goods and services among nations without political or economic barriers
French Revolution (1789)
Reacting to the oppressive aristocracy, the French middle and lower classes (Estates) overthrew the king and asserted power for themselves in a violent and bloody revolution. This uprising was inspired by America's independence from England and the Enlightenment ideas.

Glorious Revolution
1- A reference to the political events of 1688-1689, when James II abdicated his throne and was replaced by his daughter Mary and her husband, Prince William of Orange through a peaceful transition.
2- Ended Absolutism in England, established Constitutional Monarchy

Jacobins
Radical republicans during the French Revolution. They were led by Maximilien Robespierre from 1793 to 1794. Reign of Terror

Jean Batiste Colbert
1- Louis XIV finance minister.
He imposed mercantilist policies to booster the economy.
2- Had new lands cleared for farming and built up trade.
3- To protect French manufacturing, he put a high tariff on imported goods.
4- He regulated trade with the colonies and made France a wealthy state.

Rousseau
(1712-1778) Believed that society threatened natural rights and freedoms. Wrote about society's corruption caused by the revival of sciences and art instead of it's improvement. He was sponsored by the wealthy and participated in salons but often felt uncomfortable and denounced them. Wrote "The Social Contract."

John Locke (1632-1704)
1. English philosopher who wrote "The Second Treatise of Government"
2. Viewed humans as basically rational beings who learn from experience
3. Formulated the theory of natural rights, arguing that people are born with basic rights to "life, liberty, and property"
4. Insisted that governments are formed to protect natural rights
5. Stated that the governed have a right to rebel against rulers who violate natural rights

Laissez-faire economics
Theory that opposes governmental interference in economic affairs beyond what is necessary to protect life and property.

Levee en Masse
Law that obligated all French men between certain ages to enlist in the army. (Draft)

Liberalism
A political ideology that emphasizes the civil rights of citizens, representative government, and the protection of private property. This ideology, derived from the Enlightenment, was especially popular among the property-owning middle classes.

Louis XVI of France
king of France-executed for treason by the National Convention-absolute monarch-husband of Marie Antoinette.

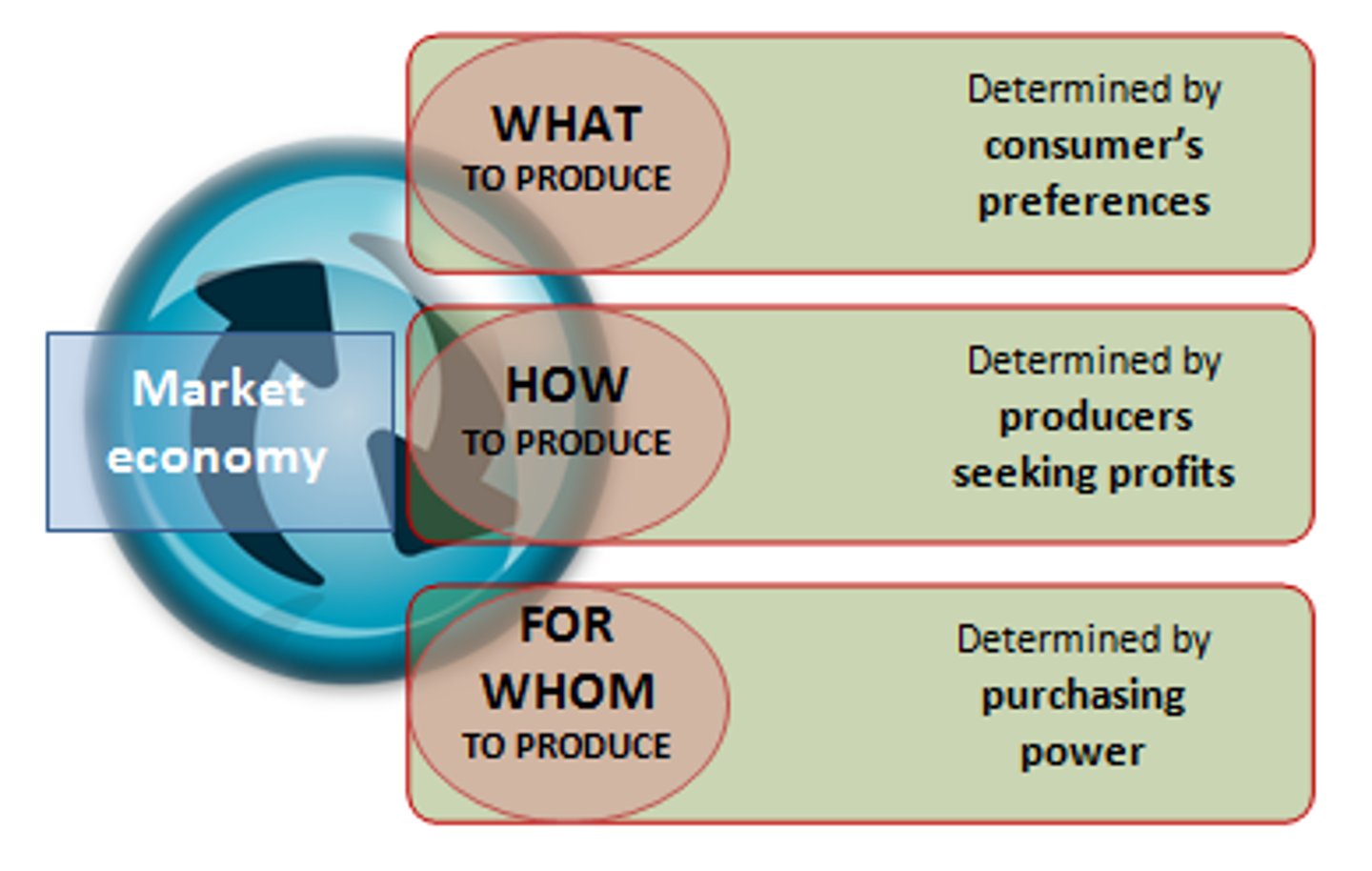
Market Economy (Capitalism)
An economic system based upon the fundamentals of private property, freedom, self-interest, and prices
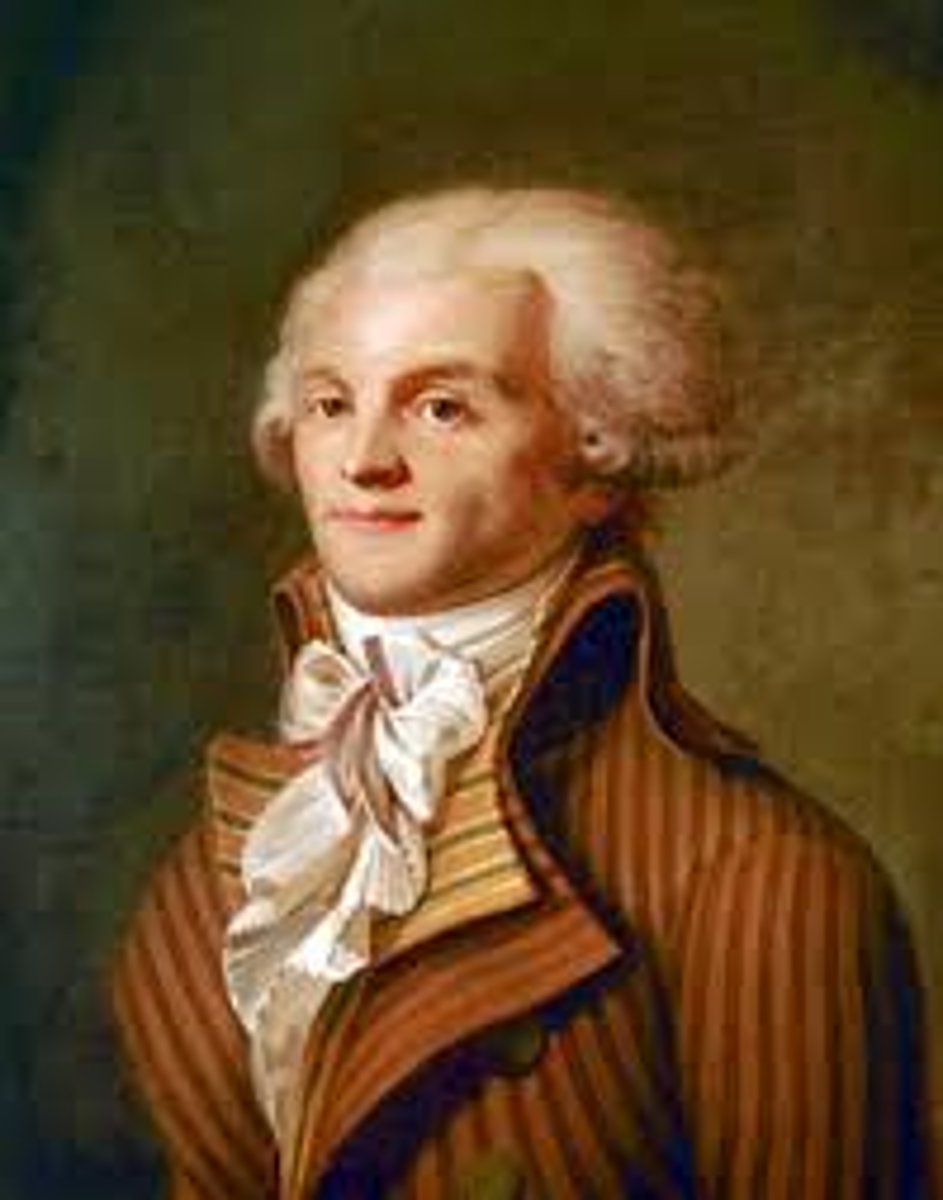
Robespierre (1758-1794)
Jacobin leader during the Reign of Terror (1793-1794).

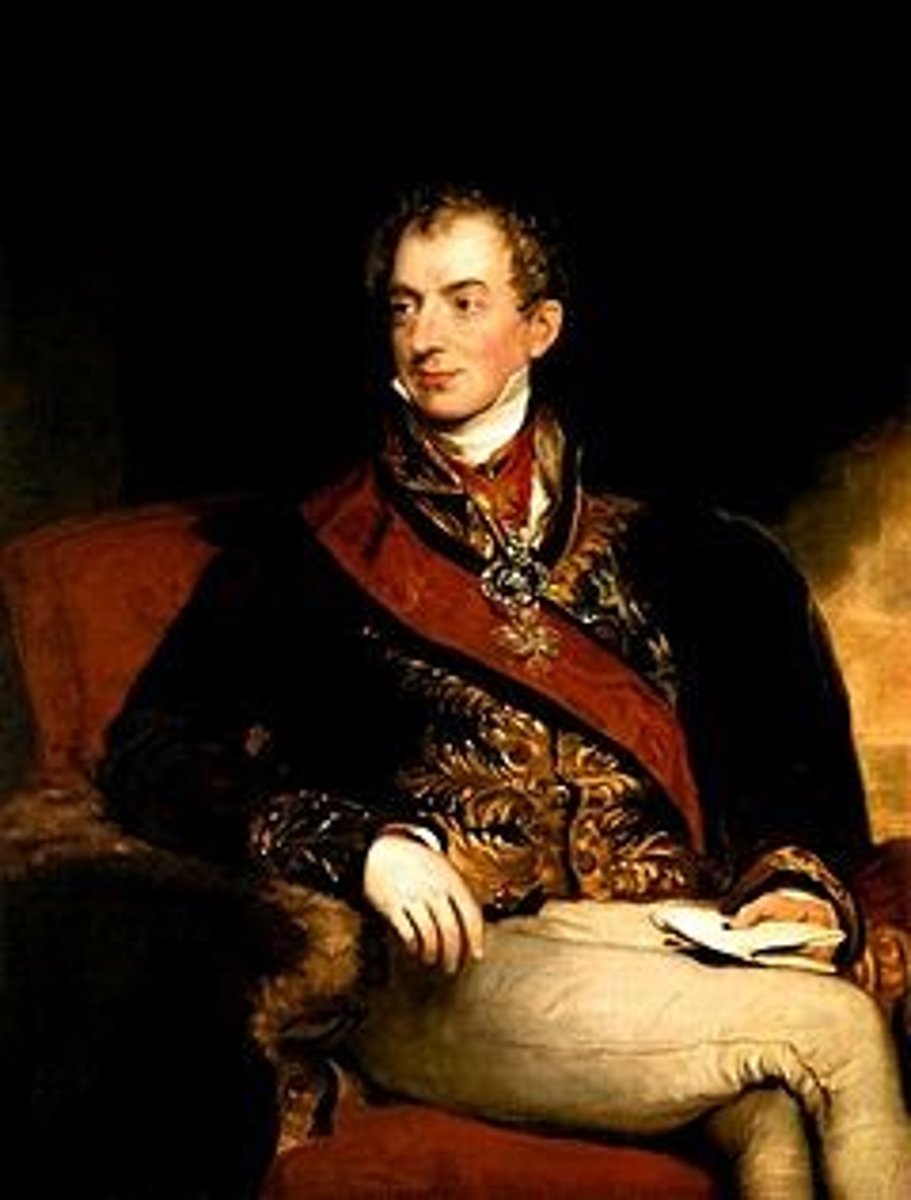
Metternich System
sought to eliminate any constitutional or nationalist sentiments that had arisen during the Napoleonic period through espionage, censorship, and repression

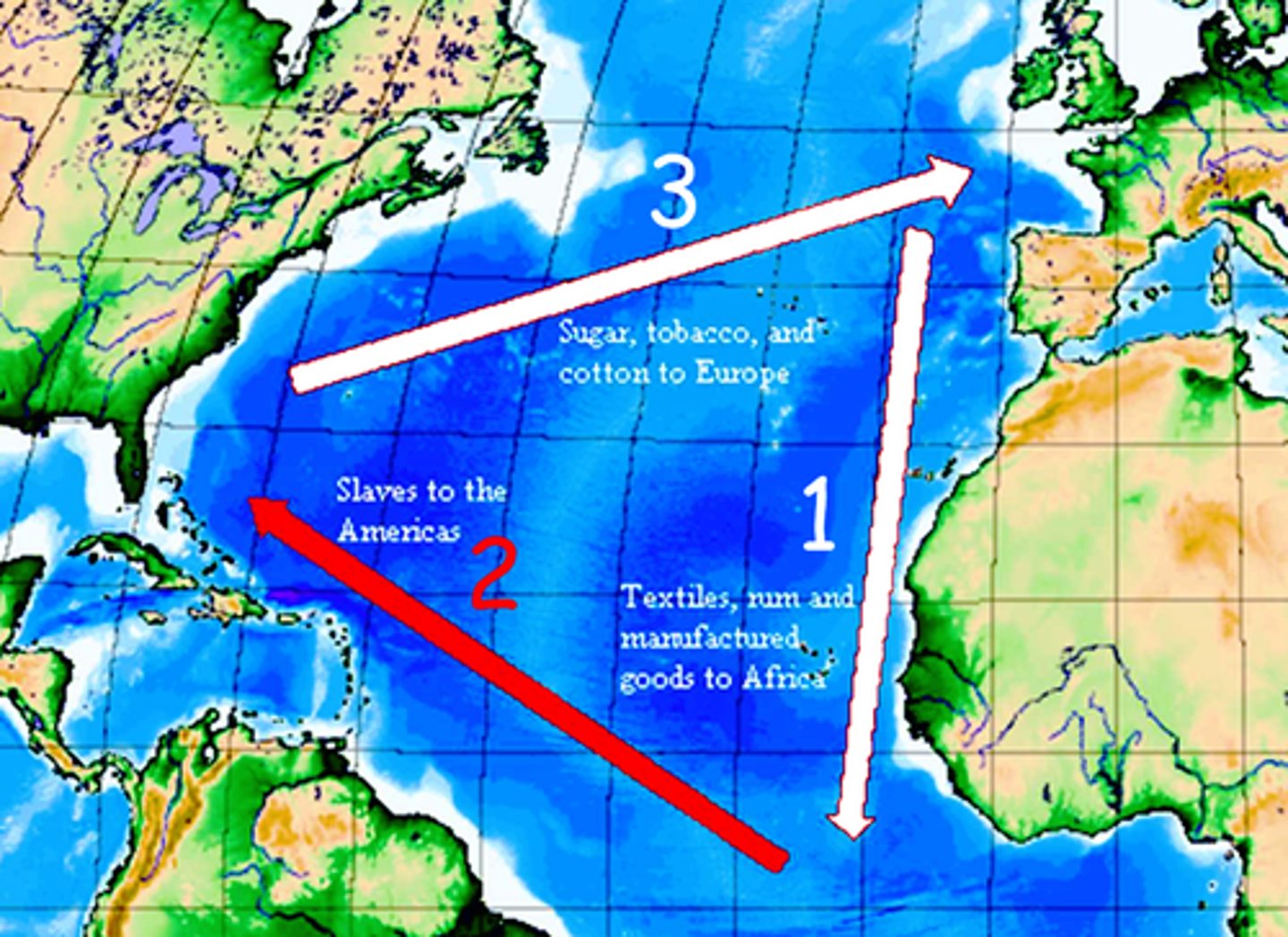
Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
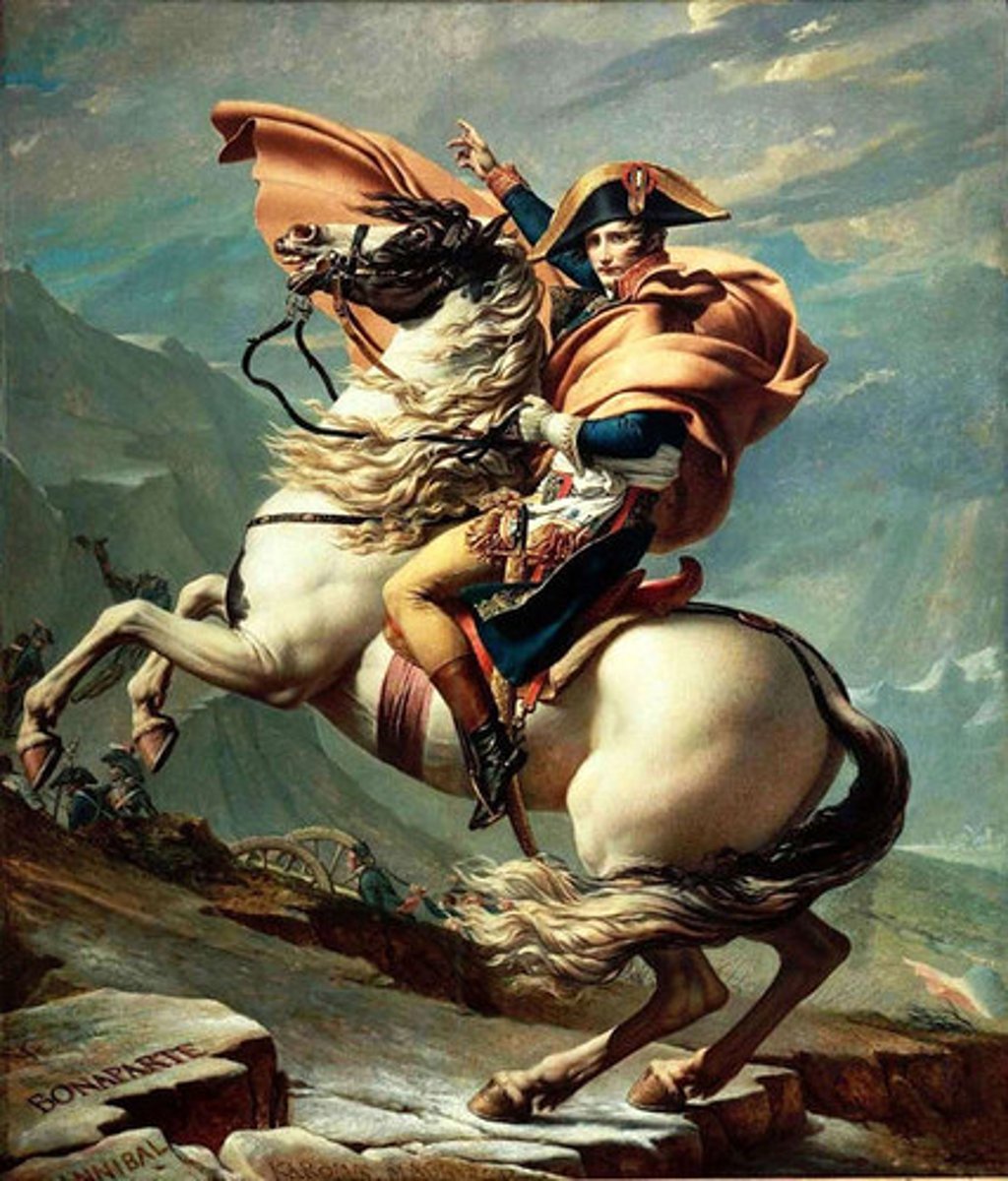
Napoleon Bonaparte
Overthrew the French revolutionary government (The Directory) in 1799 and became emperor of France in 1804. Failed to defeat Great Britain and abdicated in 1814. Returned to power briefly in 1815 but was defeated and died in exile.

Napoleonic Code (1804)
1- This code made laws uniform across the new French nation and eliminated many injustices.
2- it also promoted order and authority over individual rights. The code applied to only male citizens.

Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country, whose people speak the same language, share the same culture and history.

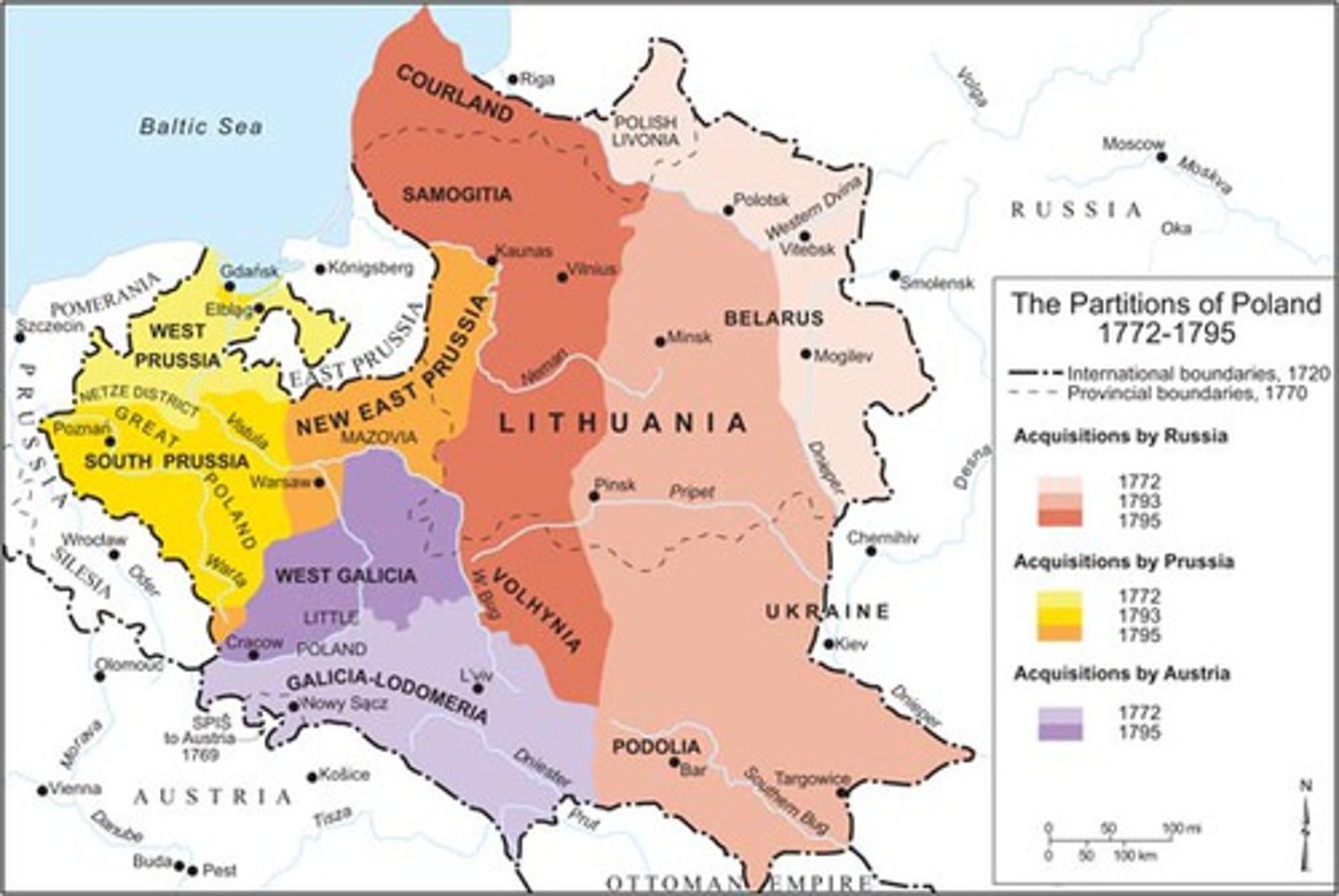
Partition of Poland (1772, 1793, 1795)
Division of Polish territory among Russia, Prussia, and Austria in 1772, 1793, and 1795. It eliminated Poland as an independent state, and helped expanded Russian influence in eastern Europe.
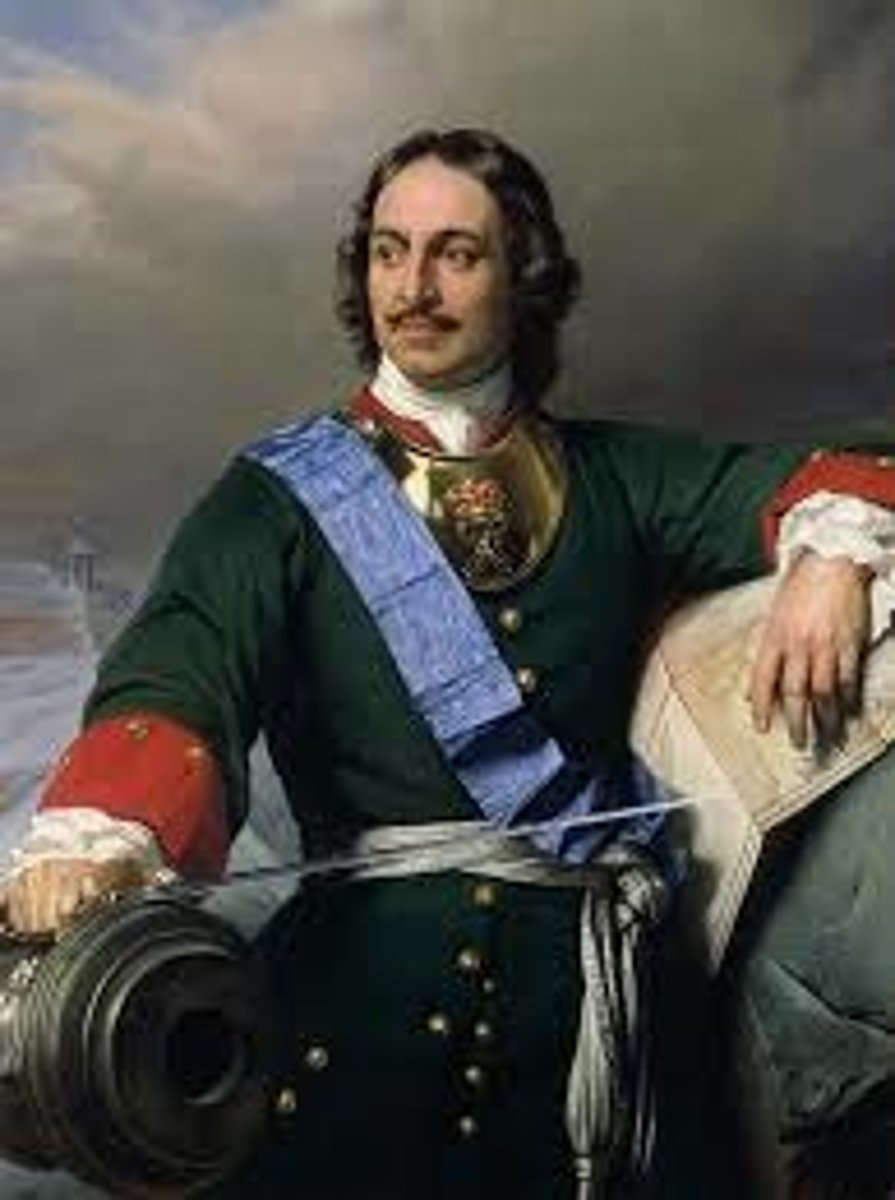
Peter the Great
This was the tsar of Russia that Westernized Russia and built up a massive Russian army.
1- Great Northern War
2- Azov Campaign

Romanticism
19th century artistic movement that appealed to emotion rather than reason. Grew out of a criticism of the enlightenment.

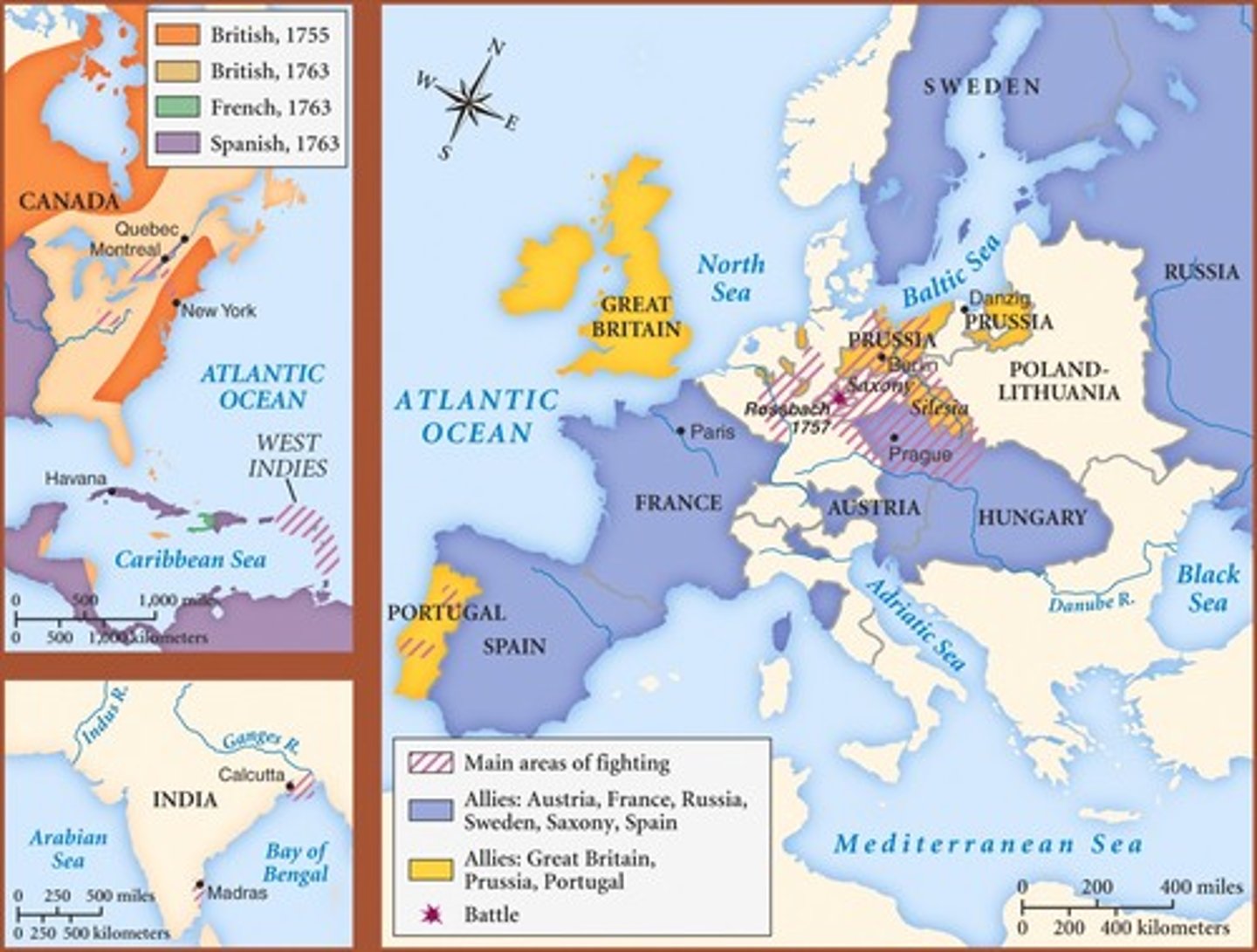
Seven Years' War (1756-1763)
Conflict fought in Europe and its overseas colonies; in North America, known as the French and Indian War
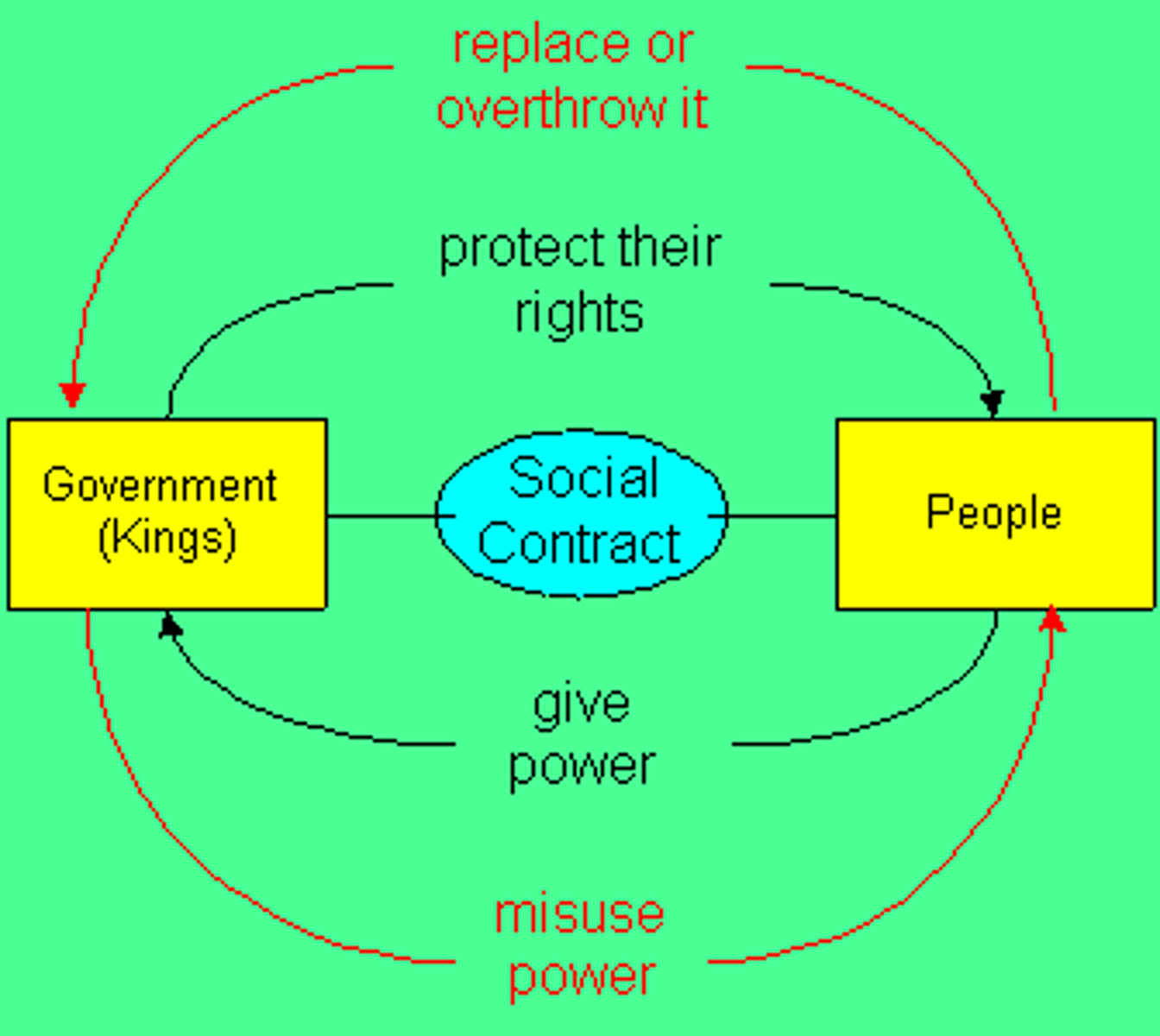
Social Contract Theory
The belief that the people agree to set up rulers for certain purposes and thus have the right to resist or remove rulers who act against those purposes.
Thomas Malthus (1766-1834)
English economist; believed poor families should have fewer children to preserve the food supply. In 1798 he wrote An Essay on the Principle of Population; opposite of Rousseau
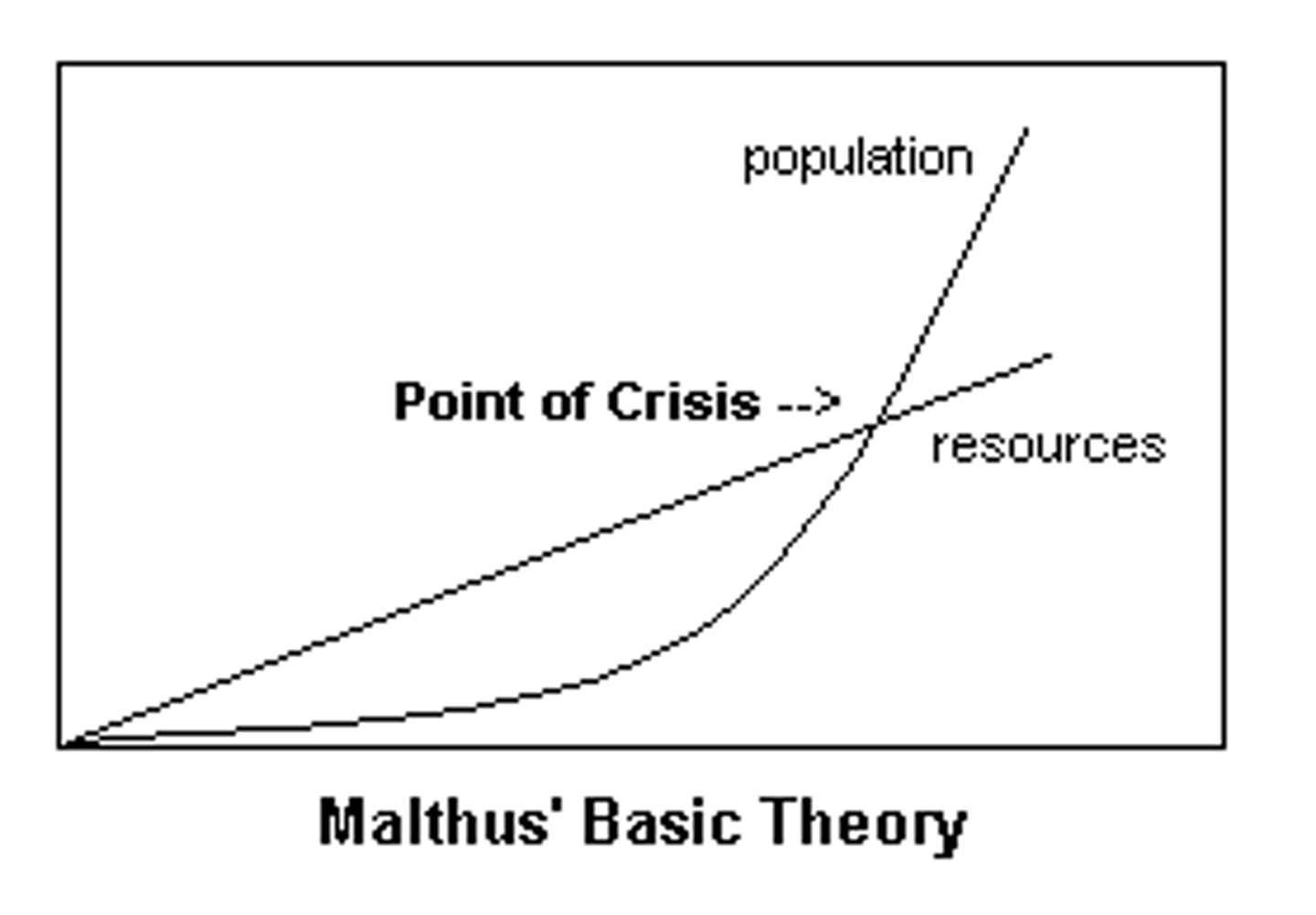
David Ricardo, "iron law of wages"
"iron law of wages" argued that raising wages arbitrarily would only increase the working population, and the availability of more workers would in turn cause wages to fall, thus creating a cycle of misery and starvation.
KEEP WAGES LOW TO CONTROL POPULATION!
