Lecture 19.20.21 Solid particles and Particle Size: Importance in Dosage Forms
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
What is Particle size • What are the important properties of solid particles • Size and size distribution • Particle shape and surface area • Particle density • Powder flow properties • What is the importance of particle properties in various dosage forms • Solutions • Suspensions • Emulsions • Pulmonary dosage forms • Topical dosage forms • Parenteral products • Solid dosage forms: tablets, capsules, powders
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is particle size and what is it called when you study the properties of particles?
It is the notion used to compare dimensions of solid, liquid, or gaseous particles.
Micrometrics is the study of properties of particles
What is the significance of particle size and distribution in solid dosage form processes?
They affect powder mixing, powder flow, and compression behavior.
How does particle size influence liquid formulations such as suspensions and emulsions?
It affects sedimentation rate.
How does particle size and distribution affect solid dosage form performance?
It affects the wettability and dissolution rate.
How does particle size and distribution affect chemical stability?
The smaller the particle size, the increased surface area.
What size is preferred for particle size distribution?
a. bigger
b. narrow
b. narrow
How are the sizes of particles defined for a sphere and cube?
Sphere: Diameter d = 2r
Cube: Length
How are the sizes of particles defined for a particle that has a equivalent spherical diameter?
It is defined with the…
volume equivalent: πd3/6
surface area equivalent: πd2
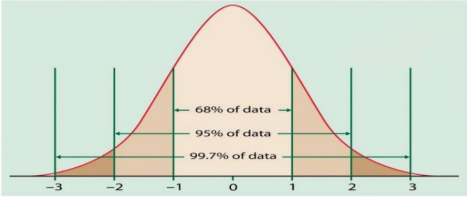
What is standard deviation?
It is the distribution of particles from the mean.
1 SD = 68% particles
2 SD = 95% particles
3 SD = 99.7% particles
Why is distribution important for particles?
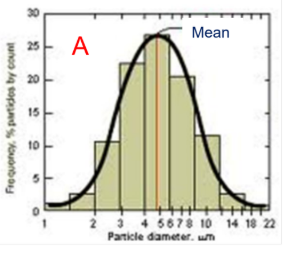
It demonstrates an understanding of the powder sample
what size appears most frequently
Normal distribution —> symmetrical curve
Select the following variables used to measure distribution:
a. Mode
b. Standard deviation
c. Mean
d. Frequency (f)
b. Standard deviation
c. Mean
d. Frequency (f)
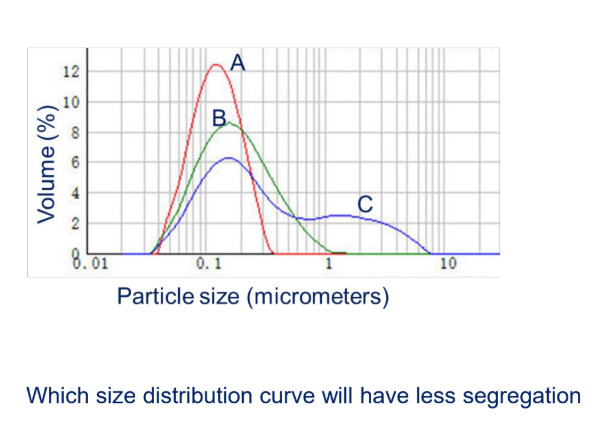

Which size distribution curve will have LESS segregation?
a. A
b. B
c. C
a. A
particles are more uniform —> has narrow particle size distribution
does not separate as easily when mixing or handling
True or false: There is a direct measurement method for determining particle size.
False!
There is no direct method. You assume particles are spherical —> use the diameter of equivalent sphere
Why is particle shape important for powders?
It affects the flow and packing properties of powder (process)
What are the three different kinds of particle shapes?
a. Cylindrical particles
b. Multiparticles
c. Irregular particles
d. Crystalline particles
e. Spheres
c. Irregular particles
equivalent spherical diameters
d. Crystalline particles (needles, plates, cubes)
different SA, solubility, surface activity (performance)
e. Spheres
greater asymmetry —> greater surface area/volume
What is the purpose of the surface area of powder?
Surface area is the inverse of particle size.
Importance:
helps in performance of super disintegrants, lubricants
Adsorption capacity: moisture/gases (can be a stability issue
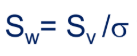
Define the factors that also calculate the surface area.
Sw = surface area/weight
Sv = surface area/volume
last symbol = density of particle
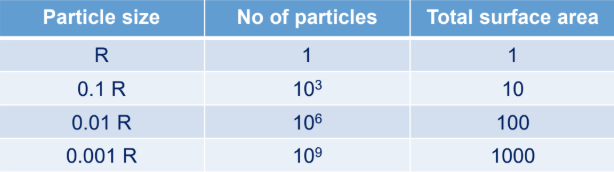
What two processes do particles form pores?
a. Adsorption
b. Crystallization
c. Prespiration
d. Condensation
b. Crystallization
d. Condensation
pores also form in: size reduction and in aggregates
Why are pore size important?
It is involved in the adsorption of water fapor, flavoring agents, volatile agents —> surface of powders, films, containers
i.e. water vapor adsorbed on excipients i.e. methyl cellulose, povidone
What two methods is pore size measured?
the diameter is measure assuming a cylindrical or width of opening
Gas adsorption —> allows gas to condense into pores
Mercury intrusion
True or false: It is difficult to estimate volume from microscopic cracks, internal pores, and capillary spaces.
True! There are 3 different types of densities that involve considering pore volume.
Match the type of density to its definition:
True density
a. material density (excludes volume of any open and closed pores)
b. material density + closed pore volume (intraparticle spaces)
c. material density + open and closed pore volume + inter particle spaces
a. material density (excludes volume of any open and closed pores)
Match the type of density to its definition:
Apparent density
a. material density (excludes volume of any open and closed pores)
b. material density + closed pore volume (intraparticle spaces)
c. material density + open and closed pore volume + inter particle spaces
b. material density + closed pore volume (intraparticle spaces)
Match the type of density to its definition:
Bulk density
a. material density (excludes volume of any open and closed pores)
b. material density + closed pore volume (intraparticle spaces)
c. material density + open and closed pore volume + inter particle spaces
c. material density + open and closed pore volume + inter particle spaces
depends on particle size distribution, shape, tendency to adhere
useful in solid handling —> determining appropriate size containers, mixing vessels, capsule size
Match the Methods of Determining Densities to the correct Type of Density:
Helium densitometer —> penetrates to smallest pores, not adsorbed
Vol of powder = vol of He filling empty apparatus — vol of He with powder
a. True density
b. Apparent density
c. Bulk density
a. True density
Match the Methods of Determining Densities to the correct Type of Density:
Liquid displacement (Pycnometer)
Displacement volume = wt of pycnometer with water - wt of pycnometer with powder + water
a. True density
b. Apparent density
c. Bulk density
b. Apparent density
Match the Methods of Determining Densities to the correct Type of Density:
Graduated cylinder method
50 ml powder sieved through US #20 mesh filled in cylinder
• 3 times drop from 1 inch height @ 2 sec intervals
a. True density
b. Apparent density
c. Bulk density
c. Bulk density
Which of the following is not a factor that influences good powder flow?
a. Fine particles 75-250 mcm
b. Particles between 250-2000 mcm with suitable shape
c. Spherical particles
d. high density, low porosity
a. Fine particles 75-250 mcm
does not flow well —> may or may not flow
What is angle of repose (φ) and what does it measure?
The maximum angle possible btwn surface of pile of powder & horizontal plane
Measures: frictional forces btwn particles
φ increases —> rougher, more irregular particles, decreased particle size

What is the Hausner ratio? What ratio determines poor flow?
a. <0.25
b. >1
c. >1.25
d. <1
c. >1.25
Hausner ratio: Ratio of trapped density/bulk density
A mixed powder is prepared as a uniform mixture and weighed out into individual powder papers wrapped for use.
True or false: It can be given as a powder to be swallowed.
False! It is used for pediatric & geriatric dosing —> single dose is in a wrapped paper and given dispersed in juice or mixed in apple sauce.
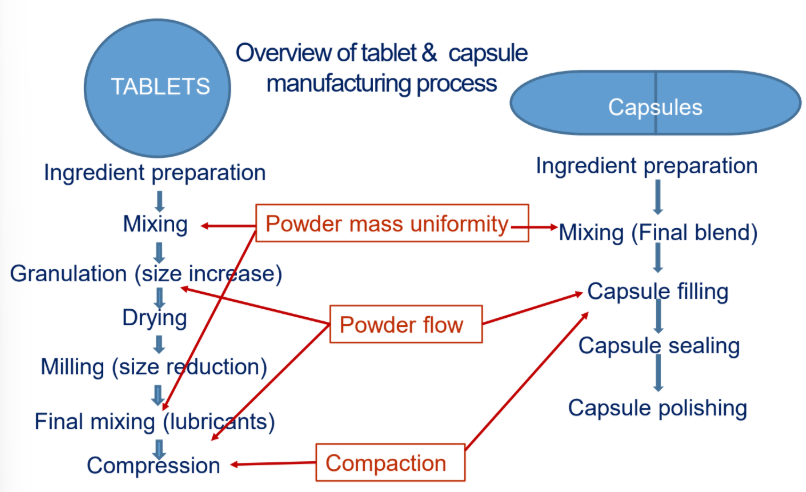
Describe drug content uniformity as a particle property.
Drug + excipients —> are uniformly distributed
If a drug is very fine compared to excipients… what happens?
Poor mixing
“Hot spots” (high-drug areas)
“Cold spots” (low-drug areas)
Failed content uniformity
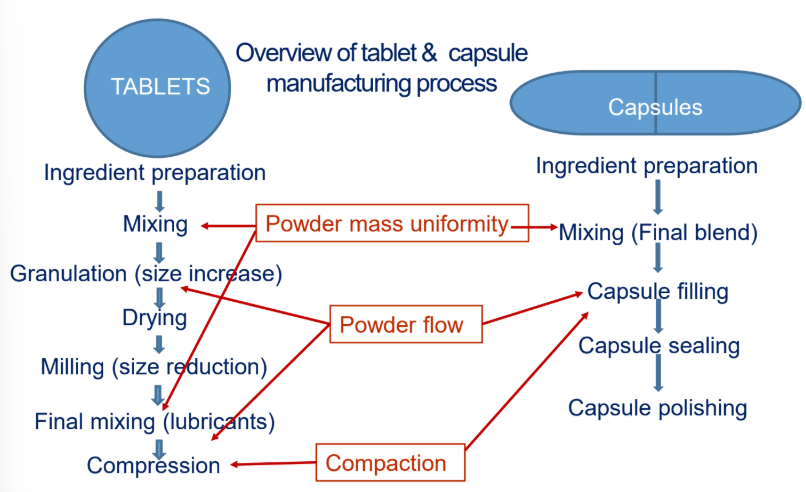
Describe what is needed to make powder flow a good particle property.
Particle size —> not too fine (granulation if needed)
Uniform size distribution (granulation, milling)
particle shape: spherical, less irregular (add glidants)
particle density —> smaller for all ingredients
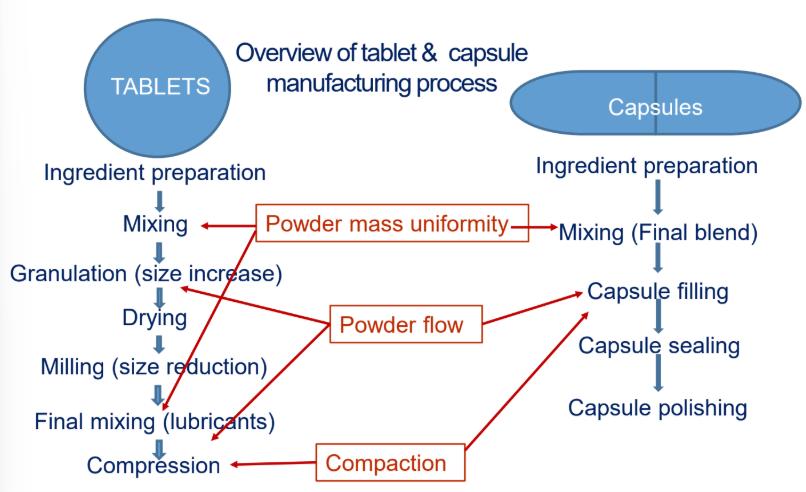
Describe what will make Compaction a good particle property.
Having the appropriate moisture content in powder
Addition of binding/granulating agents
Which of the following is NOT a way for manual capsule filling?
a. Orientation
b. Separation
c. Sealing
d. Filling
e. Mixing
e. Mixing
supposed to be Polishing
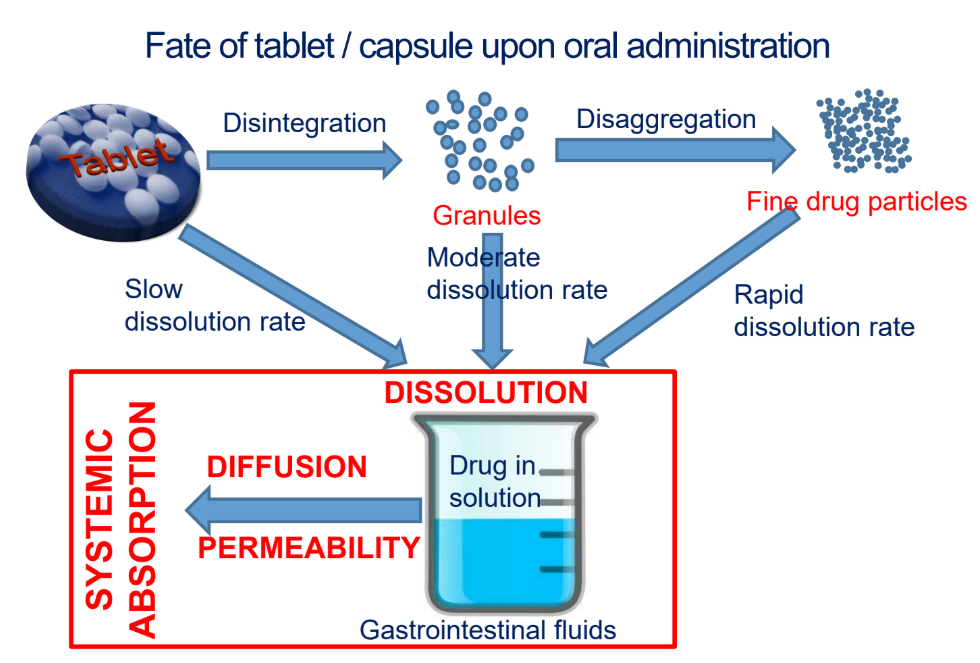
Look at image
I have looked at the image
Which of the following is NOT a way of drug release from tablet/capsule?
a. Dissolution
b. wetting of a particle —> contact angle, use of surfactants (Wetting agents)
c. Disengagement
d. Penetration of solvent (water) —> hydrophilic/hydrophobic material, particle porosity
e. disintegration/disaggregation (disintegrating agents —> starch)
f. swelling of particle
c. Disengagement
Name all the factors in the Noyes Whitney equation that describes drug (particle) dissolution

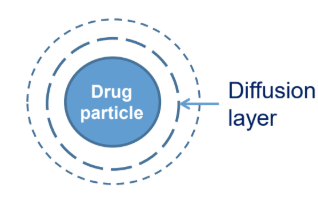
dC/dt = rate of dissolution
D = diffusion coefficient
A = surface area of particle
h = diffusion layer thickness
Cs = saturation solubility of drug
Ct = conc. of drug in solution at time t
D & h = constant for a particle under given conditions
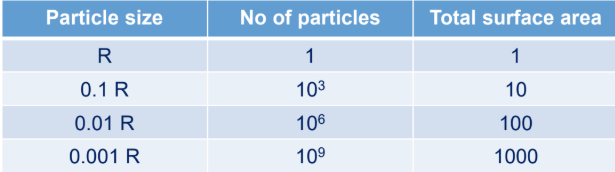
True or false: Surface area has a direct relation between surface area and dissolution rate.
True!
Surface area depends on particle size distribution
True or false: Reducing particle size (micronized) can increase dissolution rate.
True! It is a common approach to enhance bioavailability of poorly-water soluble drugs
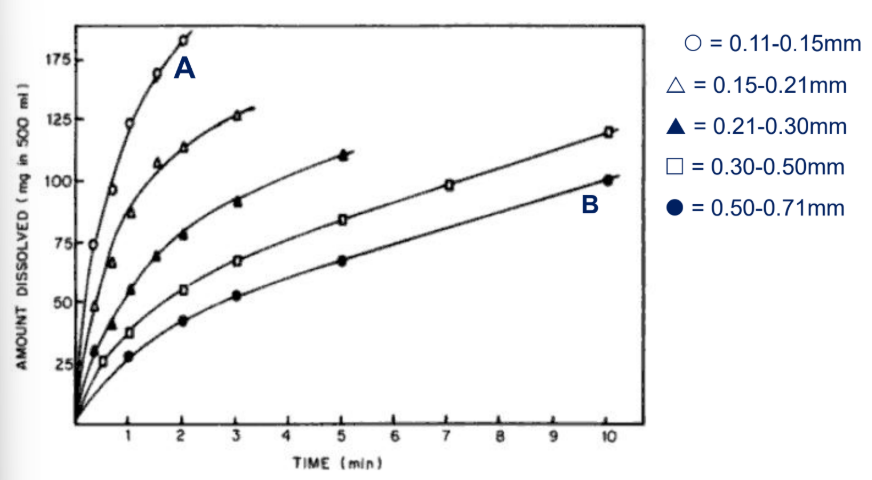
Which phenacetin granule dissolves faster?
A.
B.
A.
granule size is smaller (0.11-0.15mm)
smaller granular size —> greater surface area —> greater dissolution rate
What is the ideal particle size for pulmonary products? The goal is to reach deep into the lung (alveaolar region)
a. particles < 5mcm
b. particles > 10 mcm
a. particles < 5mcm
Match the pulmonary product to its definition:
Aerosols
a. micronized powder particles dispersed in air stream (i.e. Advair, Spiriva, Pulmicort)
b. delivered as fine mist upon activation; solution, emulsion, suspension in propellant
(i.e. Ventolin, symbicort)
b. delivered as fine mist upon activation; solution, emulsion, suspension in propellant
(i.e. Ventolin, symbicort)
Match the pulmonary product to its definition:
Dry powder inhalers (DPI)
a. micronized powder particles dispersed in air stream (i.e. Advair, Spiriva, Pulmicort)
b. delivered as fine mist upon activation; solution, emulsion, suspension in propellant
(i.e. Ventolin, symbicort)
a. micronized powder particles dispersed in air stream (i.e. Advair, Spiriva, Pulmicort)
Solids dispersed in creams and ointments is called…
a. emulsion
b. suspension
c. solution
b. suspension
Liquids dispersed in creams and ointments is called…
a. emulsion
b. suspension
c. solution
a. emulsion
Molecular dispersion of solute in solvent is called…
a. emulsion
b. suspension
c. solution
c. solution
What are some reasons that particles may be seen in a solution?
Precipitation
Drug-drug/drug excipient interaction
Contaminant
Which is true about suspensions?
a. Generally fine > 50 mcm
b. Thermodynamically unstable —> 2 phase system
c. Floccules are better than cakes
d. Large particle size is preferred
b. Thermodynamically unstable —> 2 phase system
c. Floccules are better than cakes
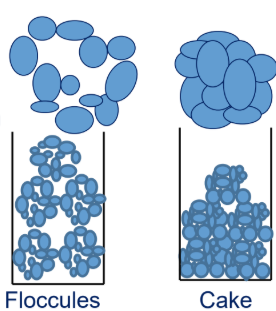
Flocculated suspensions settle faster but form a loose, easily redispersible sediment, unlike cakes, which are hard and difficult to redisperse.
Which is NOT true about Emulsions?
a. composed of 2 or more immiscible liquids
(O/W, W/O, W/O/W, O/W/O)
b. thermodynamically unstable —> 2 phase system
c. 10-200 nm droplets (microemulsions) are thermodynamically stable
d. less creaming —> irreversible, less coalescence —> reversible
d. less creaming —> irreversible, less coalescence —> reversible
FALSE —> its the opposite
less creaming —> reversible
less coalescence —> irreversible
Which of the following is a parenteral dosage form? (Select all that apply)
a. solutions
b. oral
c. buccal
d. emulsions
e. suspensions
a. solutions
d. emulsions
e. suspensions
parenteral —> anywhere not involved in GI/oral
How are parenteral dosage forms sterilized?
They are sterilized through filtration (0.2-0.22 mcm filters) —> removes bacteria
prevents embolism: where large particles can block capillaries
What does the USP define as particulate matter in injectable (parenteral) solutions?
Foreign, undissolved, mobile particles (other than gas bubbles) that are unintentionally present in parenteral formulations.
How is particulate matter in parenteral solutions commonly tested?
By visual observation.
What is the typical route of administration for parenteral suspensions?
Intramuscular.
What is the main purpose of parenteral suspensions?
(example of parenteral suspension: Penicillin G procaine)
To prolong drug release (depot preparations).
What is the ideal particle size range for parenteral suspensions?
a. 1 - 5 mcm
b. 200-250 mcm
c. 0.5-5 mcm
d. 100-150 mcm
c. 0.5-5 mcm
What factors must be considered when formulating parenteral suspensions?
Syringability, injection pain, and needle size.
What is a common example of a parenteral emulsion?
Propofol emulsion (general anesthetic, IV).
What is the typical droplet size range for parenteral emulsions?
a. 150-300 nm
b. 200-250 nm
c. 0.5-5 nm
d. 100-150 nm
a. 150-300 nm
What are pyrogens and what are the two types of pyrogens?
They are bacterial endotoxins, fever-causing agents which contaminate medicines and vaccines as a consequence of the manufacturing process.
Lipopolysaccharides (lipid substances)
Bacterial endotoxin
Match the type of Pyrogen to its definition:
From outer cell wall of gram (-) bacteria, thermostable and water soluble = can remain after sterilization thru autoclaving & filtration
a. Lipopolysaccharides
b. Bacterial endotoxin
a. Lipopolysaccharides
Match the type of Pyrogen to its definition:
Fever producing organic substances from microbial contamination
a. Lipopolysaccharides
b. Bacterial endotoxin
b. Bacterial endotoxin
Match the tests for Pyrogens to its definition:
Qualitative, less sensitive —> injects test solution thru IV —> measures the rise in temperature of 3 rabbits
a. Rabbit Pyrogen Test
b. The L.A.L test (Litmus amebocyte lysate)
a. Rabbit Pyrogen Test
Match the tests for Pyrogens to its definition:
Quantitative, more sensitive
(+) ONLY for endotoxins —> cannot detect other pyrogenic material
a. Rabbit Pyrogen Test
b. The L.A.L test (Litmus amebocyte lysate)
b. The L.A.L test (Litmus amebocyte lysate)