let's run up the bradford hill
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/95
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
1
New cards
search for additional cases and clues regarding source & mode of transmission
shoe leather epidemiology
2
New cards
measures exposure & early biological response by 1) evaluating host characteristics 2) using biochemical markers of a positive effect to refine disease categories
molecular epidemiology
3
New cards
Establishes 1) a genetic part to disorder 2) relative size of that genetic effect in relation to other sources of variation in disease risk & 3) responsible genes
genetic epidemiology
4
New cards
1) Pathogen must be present in case of disease
2) Pathogen can be isolated from infected host & grown in pure culture
3) Pathogen must cause disease when injected into new susceptible host
4) Pathogen reisolated from new host must be same as og inoculated pathogen
2) Pathogen can be isolated from infected host & grown in pure culture
3) Pathogen must cause disease when injected into new susceptible host
4) Pathogen reisolated from new host must be same as og inoculated pathogen
kochs postulates
5
New cards
1) Single pathogen can cause multiple disease
2) vice versa of 1 (one disease can be caused by multiple pathogens)
3) Some pathogen only cause disease in human and can’t be cultured in a lab
2) vice versa of 1 (one disease can be caused by multiple pathogens)
3) Some pathogen only cause disease in human and can’t be cultured in a lab
exceptions of kochs postulates
6
New cards
entire pop affected
holoendemic
7
New cards
persistent, high level disease
hyperendemic
8
New cards
disease constantly at low incidence = little or no immunity
hypoendemic
9
New cards
disease caused by doctor or meds
iatrogenic
10
New cards
disease w unknown cause
idiopathic
11
New cards
denominator of person time rate
\# of people followed multiplied by # of years
12
New cards
indirect measurement
proxy measurement
13
New cards
microbes that usually do not cause disease in healthy people, but may become virulent with immunocompromised and unhealthy individuals
opportunistic pathogen
14
New cards
LD50
Lethal Dose. dose that causes the death of 50% of a group of test animals
15
New cards
MRSA stands for
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus
16
New cards
MMWR
Morbidity mortality weekly report
17
New cards
When was WHO founded? (Month day, year)
April 7, 1948
18
New cards
What is a serial interval?
Duration between onset of secondary case from primary case
19
New cards
What is the chain of transmission triad?
Agent, vector, host
20
New cards
Pros of public health surveillance (3)
Timeliness, simplicity, felxibility
21
New cards
Cons of public health surveillance (3)
Expensive, not reproducible
22
New cards
What are the 5 steps of good surveillance?
Data collection, analysis, interpretation, dissemination, action
23
New cards
What are the pros of passive surveillance? (3)
Cheap, good for monitoring trends over time, large-scale
24
New cards
What are the cons of passive surveillance? (3)
Underreporting, low sensitivity, not representative
25
New cards
What are the pros of active surveillance? (3)
More information, better quality, high sensitivity
26
New cards
What are the cons of active surveillance? (3)
High use of resources, time consuming, hard to sustain over time
27
New cards
What are the pros of sentinel surveillance? (3)
High-quality, fast, cheap
28
New cards
What are the cons of sentinel surveillance? (3)
Bad for rare diseases, won’t report stuff outside sites, bad in monitoring incidence over time
29
New cards
What are the pros of syndromic surveillance? (3)
Low bias, cheap, fast
30
New cards
What are the cons of syndromic surveillance? (3)
Low specificity, bad for big outbreaks, inaccurate
31
New cards
What are the 13 steps of an outbreak investigation?
Prepare for field work, establish existence of disease, verify diagnosis, form case definition, find cases systematically and record info, use descriptive epidemiology, find hypothesis, evaluate hypotheiss, reconsider, refine, re-evaluate hypothesis, compare and reconcile with lab, control/prevent measures, initiate/maintain surveillance, communicate findings
32
New cards
What are the 9 Bradford hill criteria?
Strength of association, consistency, specificity, alternative explanation/casuality, temporality, dose-response/biological gradient, biological plausibility, experimental evidence, coherence
33
New cards
Single cause cause specific effect means what?
Specificity
34
New cards
What does it mean to consider multiply hypothesis before saying association causal or not?
Alternative explanation/causality
35
New cards
What does cause/exposure must precede outcome mean?
Temporality
36
New cards
What does it mean to have a stronger response when there’s more exposure?
Dose-response
37
New cards
What does it mean to be able to alter the condition or prevent/accelerate it?
Experimental evidence
38
New cards
What does it mean when the association is compatible with existing theory and knowledge of past cases?
Coherence
39
New cards
What case compares patients to themselves?
Case-crossover
40
New cards
What study is risk factors known, disease not known?
Cohort
41
New cards
What study is disease known, risk factors not known?
Case-control
42
New cards
What do you use for cohort studies?
Risk ratio
43
New cards
What do you use to calculate case-control studies?
Odds ratio
44
New cards
What are the pros for cohort? (3)
Good for long term disease, good for rare exposure, assess multiple outcomes for 1 exposure
45
New cards
What are the cons for cohort? (3)
Bias, costly, need large population
46
New cards
What are the pros for case-control? (3)
Cheap, good for rare & long latency period disease, shorter
47
New cards
What are the cons for case-control? (3)
Unreliable information, confounding variable, can’t calculate prevalence
48
New cards
What do you use to calculate cross-sectional?
Prevalence
49
New cards
What are the pros of cross-sectional? (3)
Quick, cheap, easy
50
New cards
What are the cons of cross-sectional? (3)
Low response, no causality, recall bias
51
New cards
Selection bias, patients lost to follow up exluded
Attrition bias
52
New cards
Selecting people from subpop
Berkson’s (selection) bias
53
New cards
Bias toward belief we already have
Confirmation bias
54
New cards
How can confounding be prevented?
Randomization, restriction, matching
55
New cards
When correlation at group level doesn’t accurately represent correlation at the individual level
Ecological fallacy
56
New cards
When people in survey don’t include dead/ill
Late look bias
57
New cards
Systematic difference between reported & unreported
Reporting bias
58
New cards
Groups differ in ways other than exposure
Selection bias
59
New cards
People with severe illnesses can’t fill out survey & excluded from study
Neyman bias
60
New cards
Out of how many people who have the disease, how many people actually test positive?
Sensitivity
61
New cards
Out of all the people who do not have the disease, how many people actually test negative?
Specificity
62
New cards
Out of all the people who test positive, how many people actually have the disease?
PPV
63
New cards
Out of all the people who test negative, how many people actually don’t have the disease?
NPV
64
New cards
Father of modern surgery
Joseph Lister
65
New cards
Created polio vaccine
James Salk
66
New cards
Landmark analysis of mortality data
John Graunt
67
New cards
Made smallpox vaccine
Edward Jenner
68
New cards
Father of epidemiology
John Snow
69
New cards
Made anthrax vaccine
Louis Pasteur
70
New cards
Primary control example (3)
Public education, vaccine, ban products
71
New cards
Primordial control example (3)
Optimal diet, remove barriers to exercise, government tax on cigarettes
72
New cards
Secondary control example (3)
Screening, physical exam, colonoscopy
73
New cards
Tertiary control example (3)
Rehab, surgery, speech therapy
74
New cards
Quaternary control example (3)
Pull plug on patient, anti arrhythmic drug, hormone replacement therapy
75
New cards
Public policy to restrict spread of agent before people begin to protect against agent
Control
76
New cards
Reduction to 0 of incidence of infection caused by specific agent in geographical area
Elimination
77
New cards
Permanent reduction to 0 of worldwide incidence of infection
Eradication
78
New cards
Agent does not exist in nature or in lab
Extinction
79
New cards
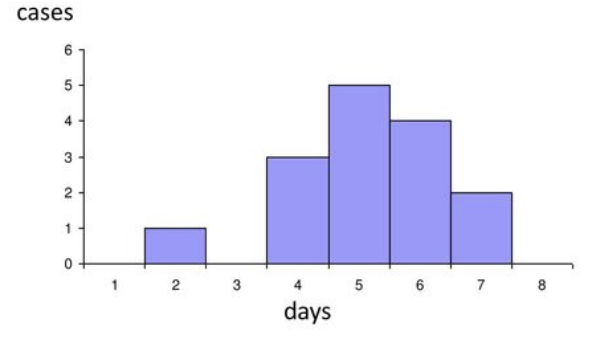
What graph is this and what spread is this?
Common continuous, water borne
80
New cards
What graph is this and what spread is this?
Point source, foodborne
81
New cards
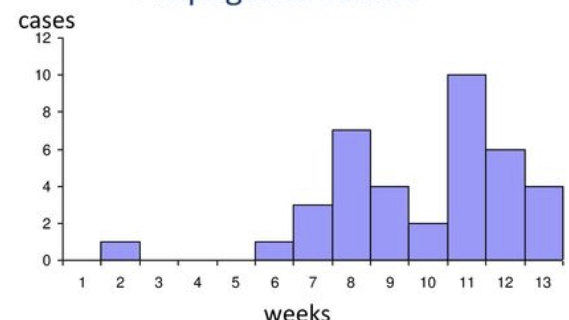
What graph is this and what spread is this?
Propagated, person-perosn
82
New cards
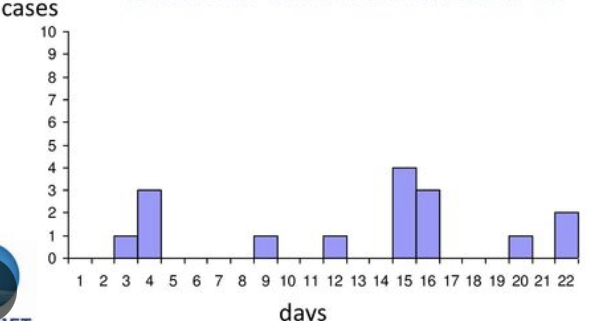
What graph is this and what spread is this?
Intermittent, sporadic
83
New cards
What is leading rabies vector
Bats
84
New cards
Why cooked food still cause harm? 3
Temperature not hot enough, toxin is heat stable, release endotoxin from dead agent
85
New cards
Science of causes and effects of disease
Pathology
86
New cards
Study of cause of disease
Etiology
87
New cards
Biochemical test that measures presence/concentration of macromolecule in solution through proteins/antigens
Immunoassay
88
New cards
A study design in which the investigator specifies the type of exposure for each study participant
Experimental
89
New cards
A study in which a sample of persons from a pop are enrolled and their exposures and health outcomes measured simultaneously
Cross-sectional
90
New cards
What study is least subject to recall bias
Prospective cohort study
91
New cards
Want to test a hypothesis but don’t have funding or time. Have national data on masking policies and number of students in each district. What study design do you use?
Ecological
92
New cards
T/F One can skip the preparing for field work step of outbreak investigation unless one is traveling.
F
93
New cards
You have unlimited budget and access to labs but little time.
Case control
94
New cards
what case
Case control
95
New cards
some people may be infected with SARS/CO-V and have a negative test. What source of error (bias) is this?
Misclassification bias
96
New cards
Vector in which the parasite multiplies in numbers/undergoes developmental change in life cycle
Biologic vector