Che 2a: Midterm 1 - Hayashi
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Law Of Conservation of mass
(total mass of reactants)=(total mass of products)
Mass is conservced during any chemical reaction (not applicable to nuclear atoms)
law of definite proportions
all samples of the same compound have the same composition the same proportions by mass of the constituent elements
What are the small particles that make up each element?
Atoms
According to Dalton's Atomic Theory, can atoms be created or destroyed?
No, atoms are neither created nor destroyed.
What is true about all atoms of a given element according to Dalton's Atomic Theory?
All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and other properties.
How do atoms of one element differ from atoms of another element?
Atoms of one element differ from all other elements.
Law of multiple proportions
Compounds are formed when atoms of more than one element combine in whole number ratios
Law of Combining volumes ( 1809)
when gasses chemically react they do in volumes that are always in simple whole number ratios
Avogadros interpretation:
2H+ 1O -> 2 water molecule
Cathode tube ray
Vaccum tube containing an electron gun and a flourescent screen to detect the position of the cathode ray
Thomsons Cathode ray tube experiment (1897)
Thomson calc value of mass to charge ratio m /e of an electron by conducting the cathode ray tube experimnent a cathode ray tube is a vaccum tibe containing an electron gun
electron m/e= -5.6857 x 10^-9 g/ coloumb
Milikans oil drop experiment
Changed oil droplets accelerate due to the electric field
- milikan concluded that the magnitude of the charge on a droplet is an integer multople of the electric charge e
e = 1.602 x 10^-19C (elementary charge)
Who proposed the plum pudding model?
JJ Thompson
In the plum pudding model, what do the electrons represent?
Plums
In the plum pudding model, what does the positive charge represent?
Pudding
What is the main idea of the plum pudding model?
Electrons are surrounded by a positively charged cloud to balance their negative charge.
What was the Rutherford gold foil experiment?
An experiment where a beam of alpha particles was directed onto a sheet of thin gold foil.
What type of particles were used in the Rutherford gold foil experiment?
Alpha particles (He^2+).
What was the purpose of the evacuated chamber in the Rutherford gold foil experiment?
To prevent interference from air particles.
What was observed when alpha particles were directed at the gold foil?
Particles were deflected at various angles.
What did the detection of deflected particles in the Rutherford gold foil experiment indicate?
It indicated the presence of a small, dense nucleus in the atom.
Nuclear Atom
Most of the mass and all of the positive charge is concentrated in a small region referred to as the nucleus
compensating charge of electrons outside of the nucleus
What is the nucleus of an atom made of?
Protons and neutrons
How do the masses of protons and neutrons compare?
They are almost the same
What is the mass of an electron compared to a proton or neutron?
About 1/1800 times the mass of a proton or neutron
What is the atomic number?
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom.
What does the atomic number equal in a neutral atom?
In a neutral atom, the atomic number is equal to the number of electrons.
What is the mass number?
The mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons.
How is the mass number calculated?
The mass number (A) is calculated as A = p + n, where p is the number of protons and n is the number of neutrons.
Isotopic Mass
Mass of a specific atom
Atomic mass unit AMU
used to measure the isotopic mass
1 AMU+ 1/12 carbon 12
1 u = 1/12 x (mass of the 12 6 C atom)
Mass spectroscopy
used to est isotopic masses and percent natural abundance of isotoped of an element
Atomic Mass
Average of the isotopic masses, weihgted accoprding to the naturally occuring abundance of the isotopes of the element
Atomic mass of an element
(fractional abundance of isotope 1 x Isotopic mass of isotope 1 ) + (fractional abundance of isoptope 2 x isotopic mass of isotope 2 ) + ...
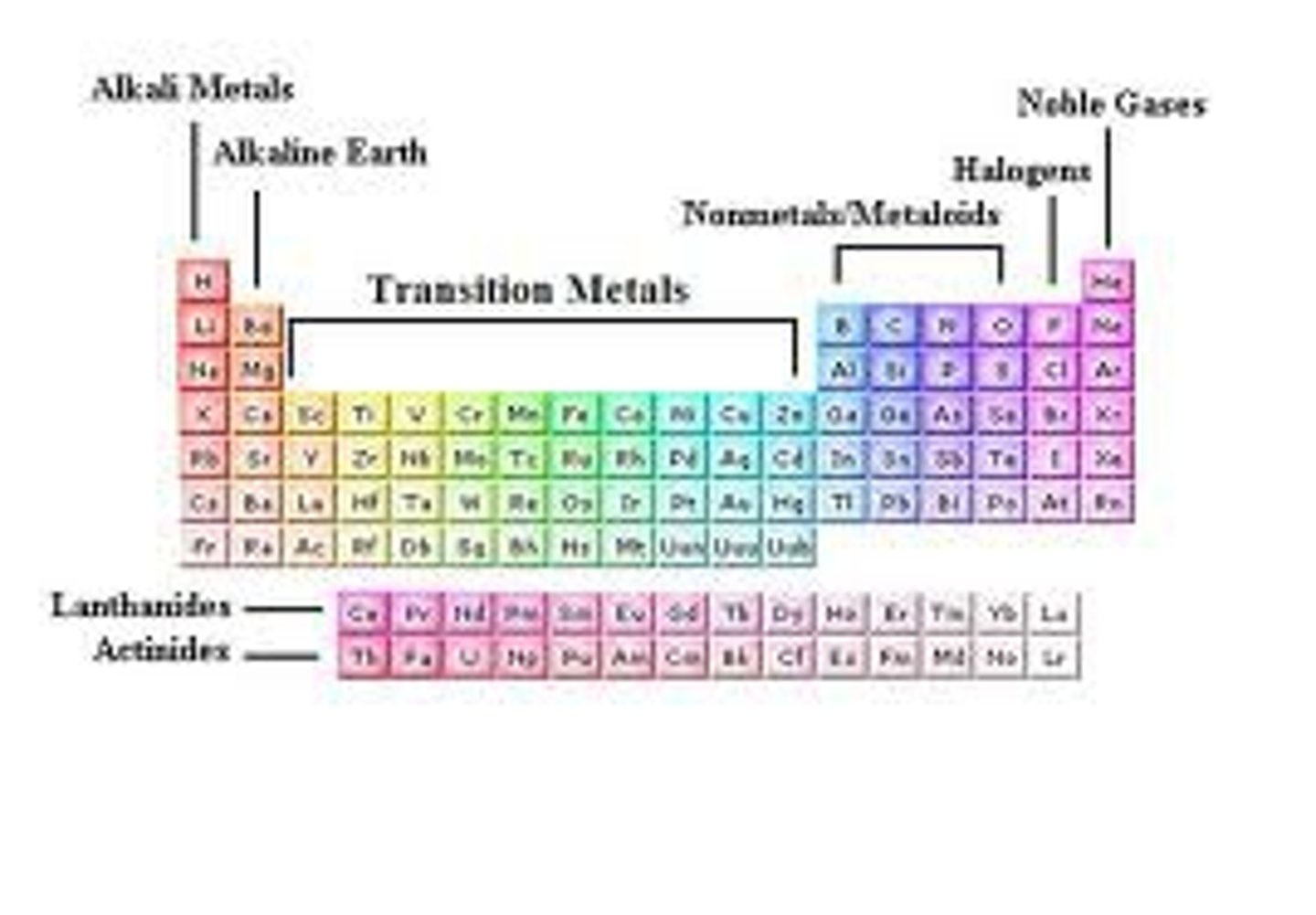
Periodic table groups
Alkali metals -1
Alkaline earths- 2
Transition Metals- 3-12
Halogens - 17
Noble gasses- 18
Molecular Compounds
Made of discrete units called molecules
each molecule consits of a certain number of non metal atoms held together by stron covalent bonds
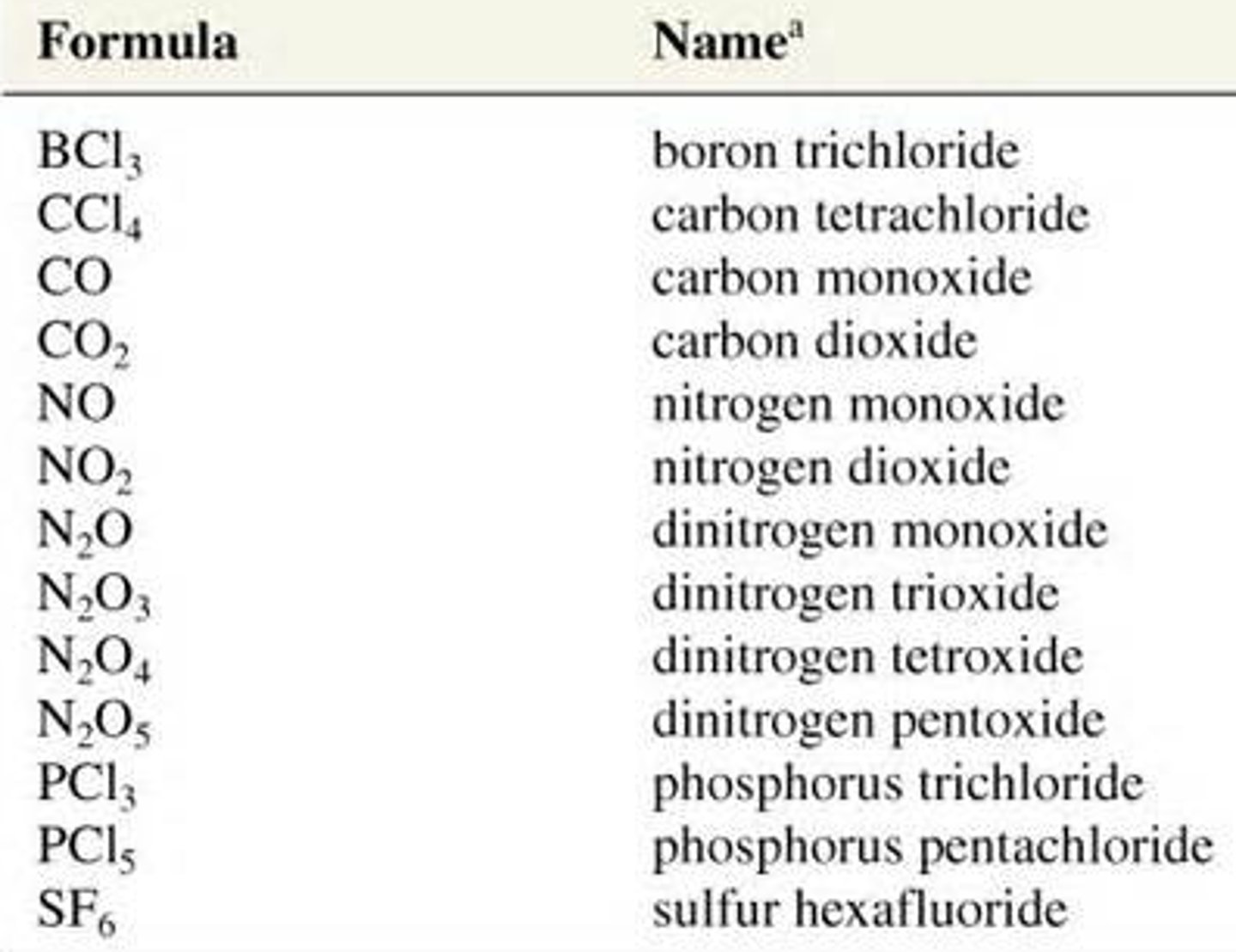
What is an empirical formula?
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
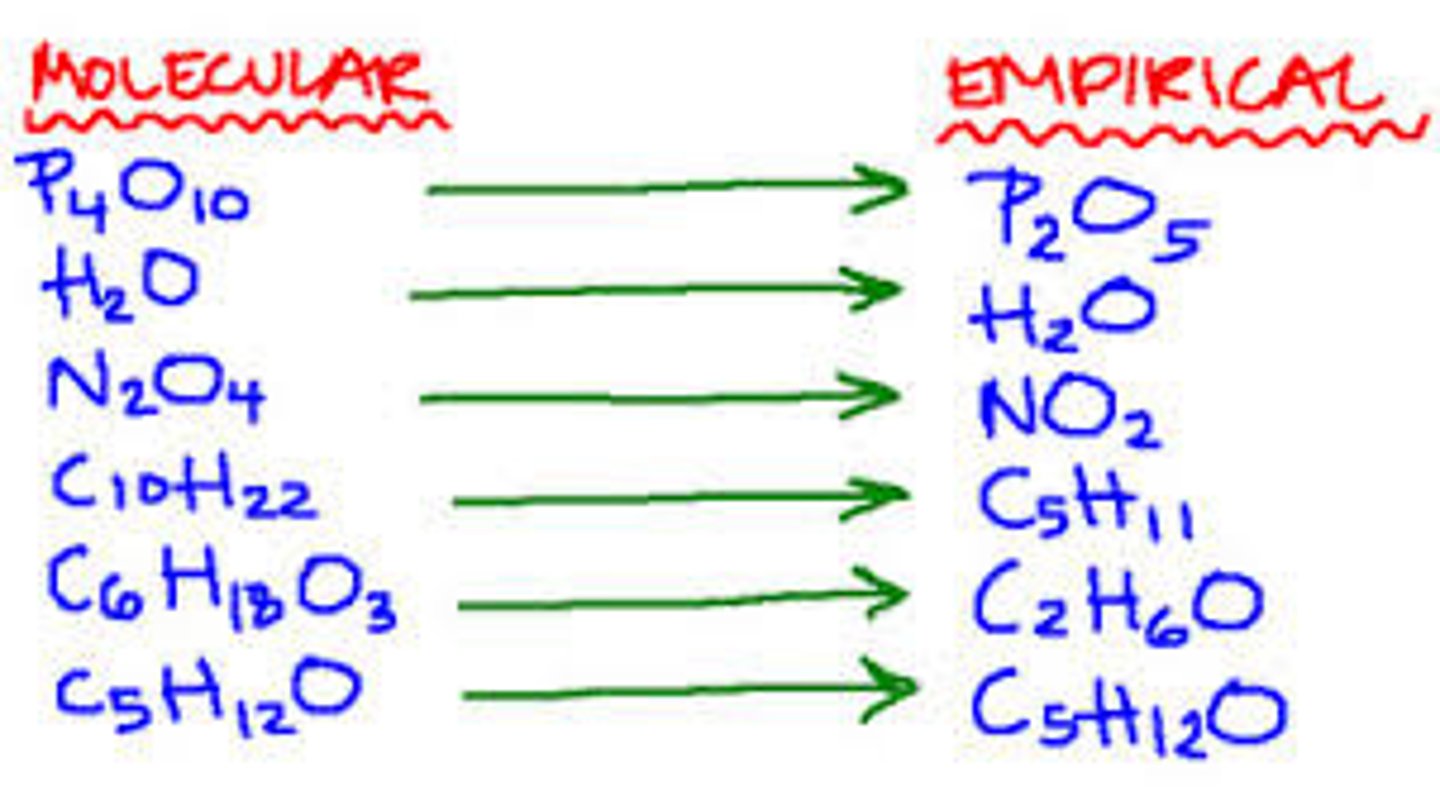
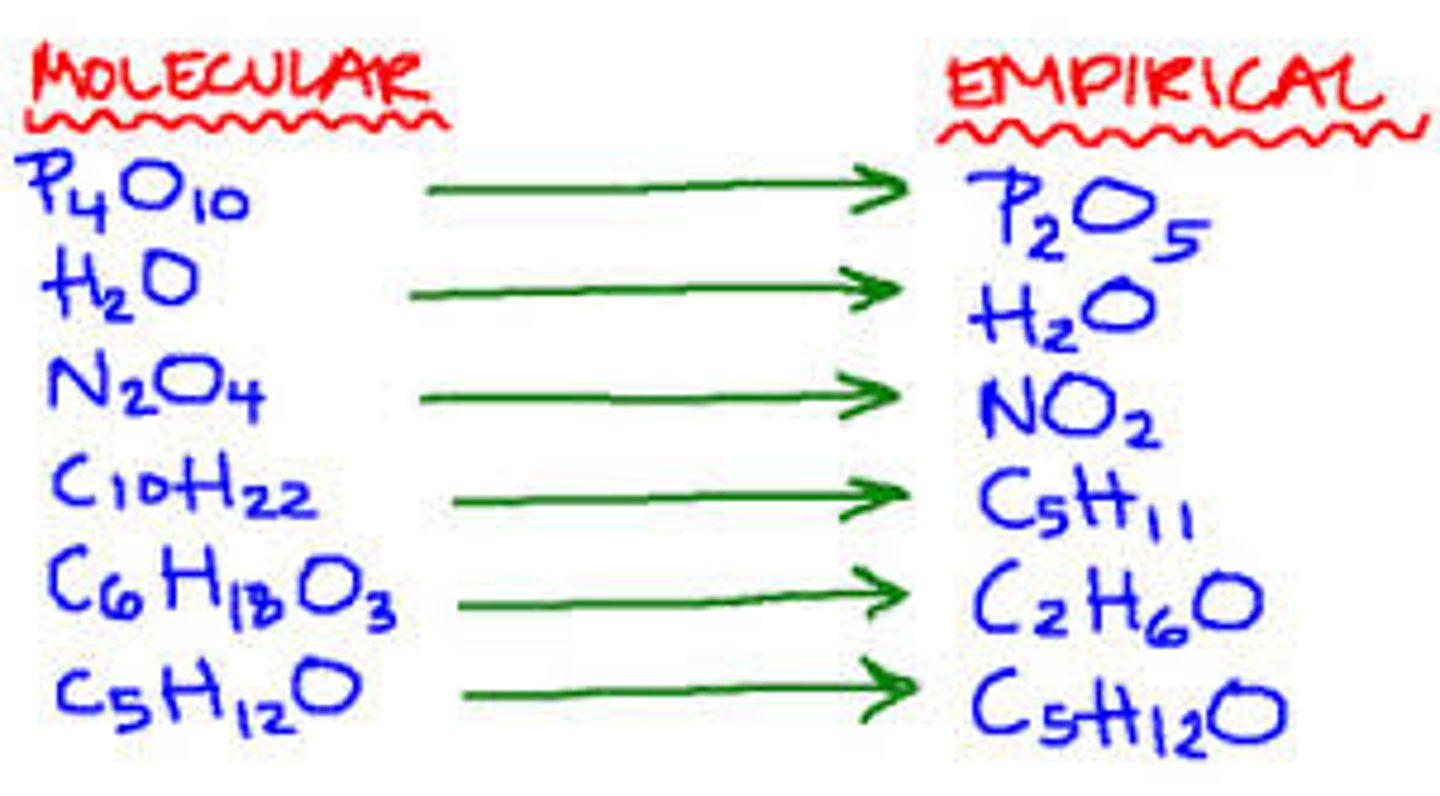
What is a molecular formula?
The actual molecule of an element or compound.
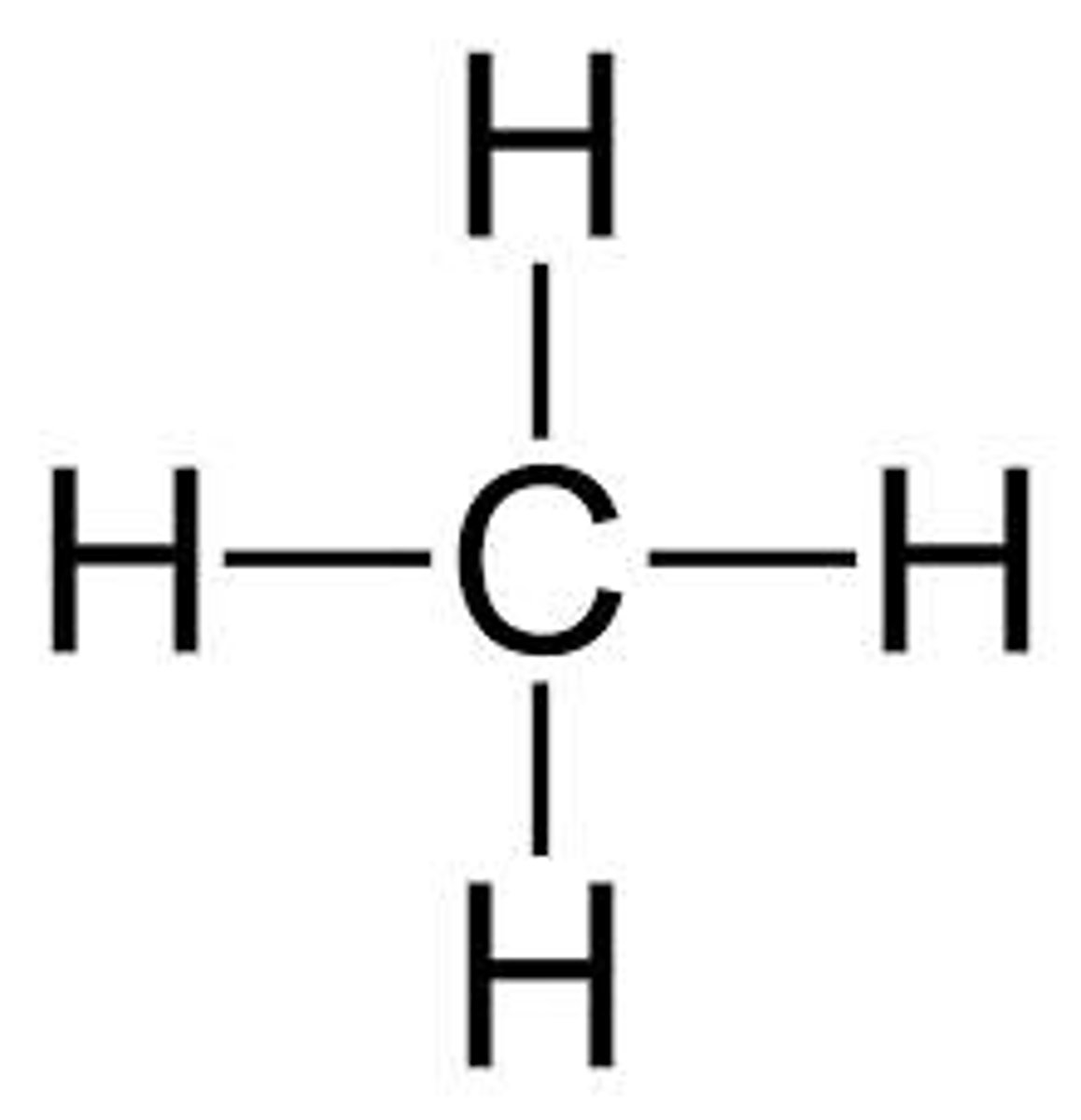
What does a structural formula provide?
The same information as a molecular formula but also shows the connectivity of atoms.
What are the two types of molecular models?
Space-filling models and ball-and-stick models.
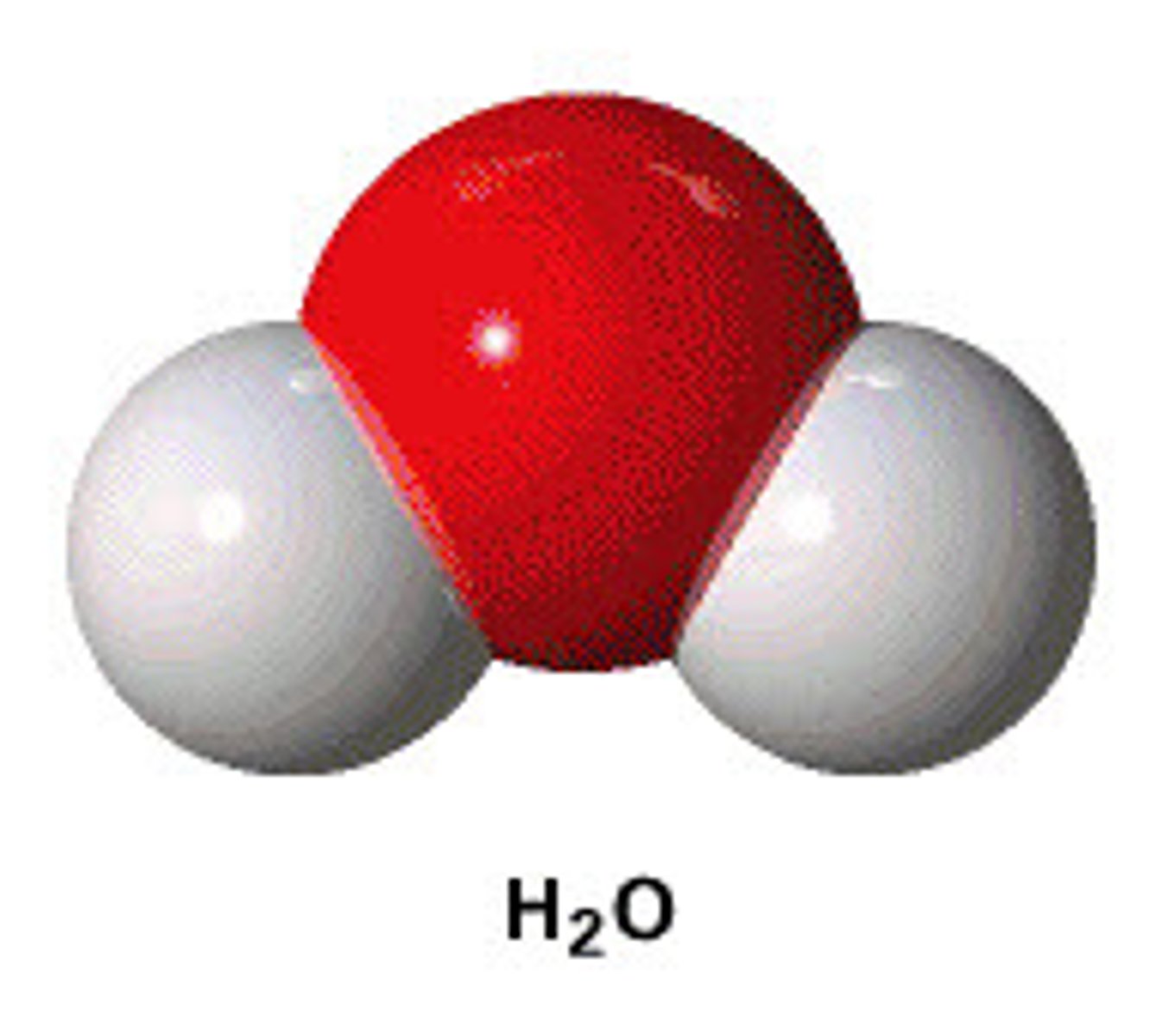
What is an extended structural formula?
A structural formula that shows the connectivity of all atoms explicitly.
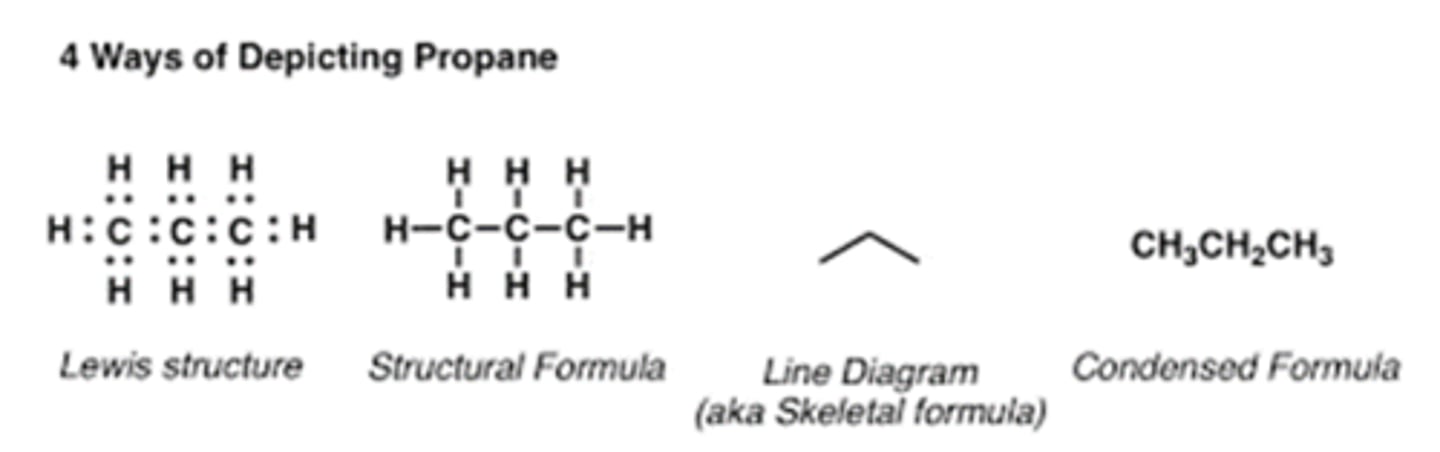
What is a condensed structural formula?
A structural formula that shows the connectivity of atoms in less detail.
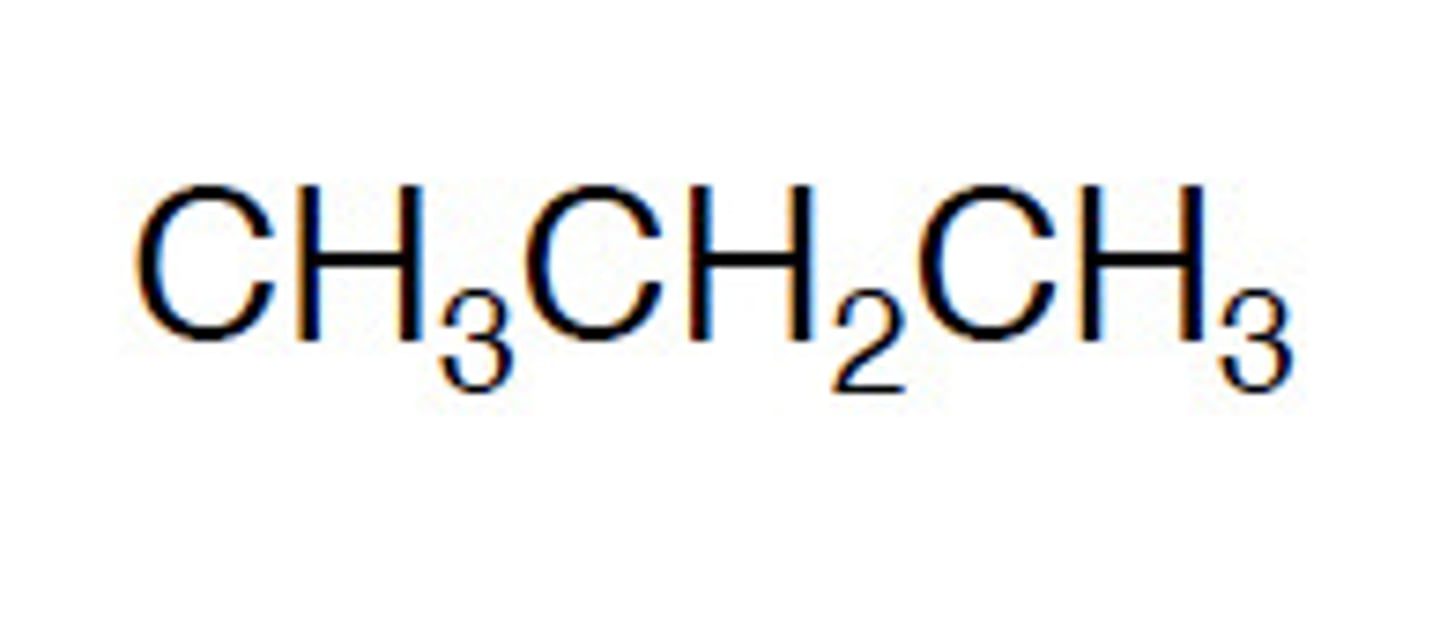
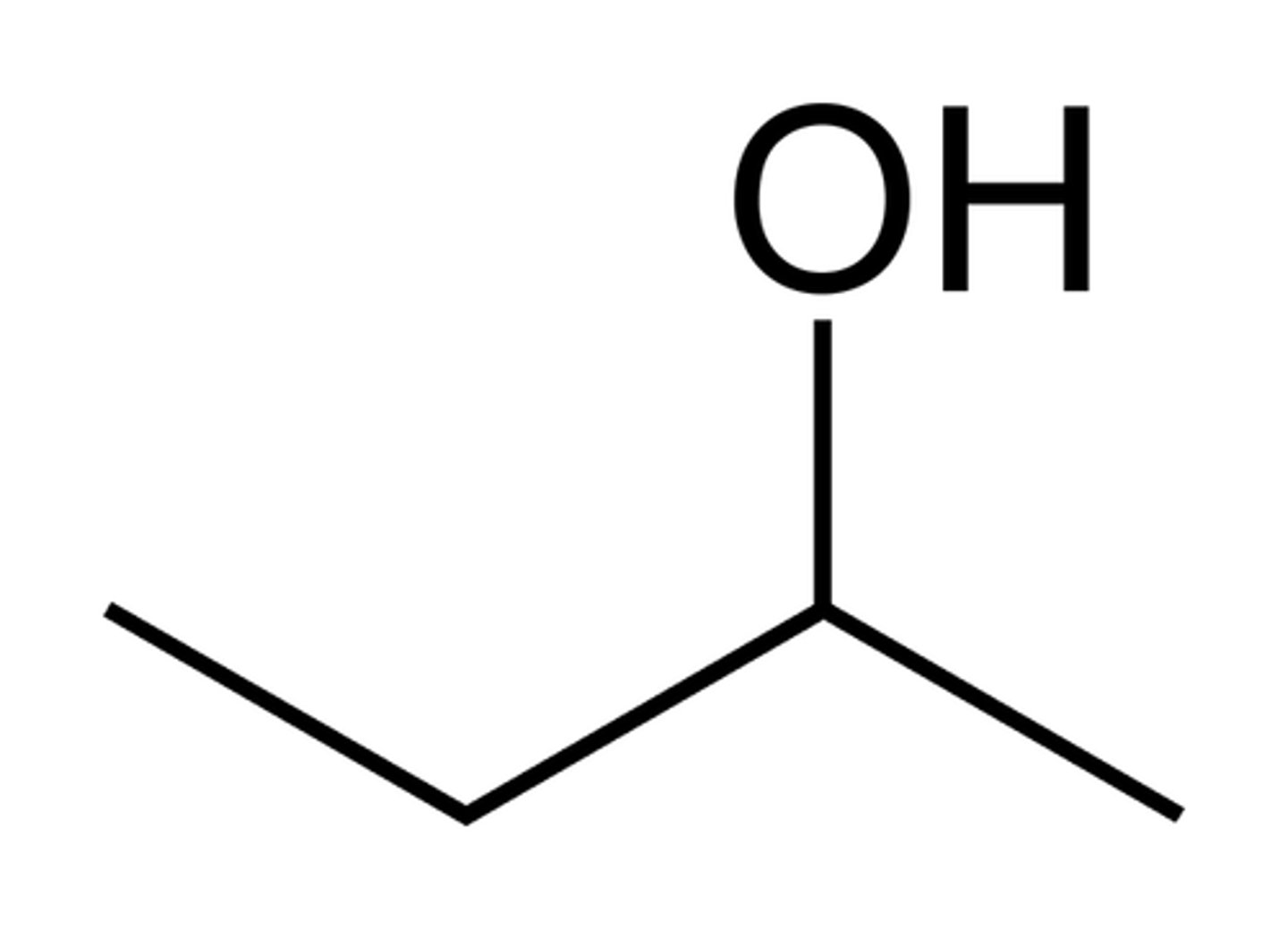
What is a line angle formula?
A simplified structural formula of an organic compound that does not show the C and H atoms explicitly.
What are ions?
Charged species formed when atoms gain or lose electrons.
What do metals tend to do with electrons?
Metals tend to lose electrons to form positively charged ions called cations.
What do non-metals tend to do with electrons?
Non-metals tend to gain electrons to form negatively charged ions called anions.
Formula unit
Smallest electrically nuetral connection of ions
Oxidation state
hypothetical chgargfe of an atom if all the shared electrons in its covalent bonds were assigned to the more electro negative atoms
What is the oxidation state of an individual atom in a free element?
0
What is the total oxidation state of all atoms in a neutral species?
0
What is the total oxidation state of all atoms in an ion?
The total charge on the ion
What is the oxidation state of a Group 1 metal in a compound?
+1
What is the oxidation state of a Group 2 metal in a compound?
+2
What is the oxidation state of fluorine in its compounds?
-1
What is the oxidation state of hydrogen in its compounds?
+1
What is the oxidation state of oxygen in its compounds?
-2
What is the oxidation state of halogens (Group 17) in binary compounds with metals?
-1
What is the oxidation state of halogens (Group 16) in binary compounds with metals?
-2
What is the oxidation state of halogens (Group 15) in binary compounds with metals?
-3
Alkali, Alkaline earth, Transition, Metalloids, Halogens, Noble gasses, Lanthanides, Actinides
Which is named first nonmetal or metal?
Metal is named first and then nonmetal
How does the metal element change?
The metal element doesn't change it remains the same
What ending does a nonmetal take?
Nonmetal element Becomes "-ide"
NaCl
Sodium Chloride
MgI2
Magenesium iodide
Al2O3
Aluminum oxide
What are the charges of Monatomic Ions?
Groups 1,2 :
1= +1
2=+2
Groups 7-12: +2 (variable)
Group 13: 3+
Group 14: +4
Group 15: -3
Group 16: -2
Group 17: -1
Name these Ions:
Fe +2, +3
Cu +1, +2
Au +1, +3
Hg +1(Hg2 2+), +2
Sn +2, +4
Pb +2, +4
Iron (II), Iron (III)
Copper (I), Copper (II)
Gold (I), Gold (III)
Mercury (I), Mercury (II)
Tin (II), Tin (IV)
Lead (II), Lead (IV)
Name these Ions: Alternate
Fe +2, +3
Cu +1, +2
Au +1, +3
Hg +1(Hg2 2+), +2
Sn +2, +4
Pb +2, +4
Ferrous, Ferric
Cuprous, Cupric
Aurous, Auric
Mercurous, Mercuric
Stannous, Stannic
Plumbous, Plumbic
Which O.S element is first (pos or neg)
( 2 nonmetals)
The positive O.S element is named first
What is the name of the first element in the formula ( 2 nonmetals)
the same
What does the second element end in ( 2 nonmetals)
- Ide
What is used to denote the number of atoms of each element?( 2 nonmetals )
Prefixes
Which prefix is never used? ( 2 nonmetals)
Mono (1)
Prefixes:
mono
di
tri
tetra
penta
heaxa
octa
nona
deca
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
When the prefix ends in "a" or "o" the element name begins with?
"a" or "o"
the final vowel of the prefix dropped
BCl3 Boron trichloride
CCl4 Carbon tertrachloride
CO Carbon monoxide
NO Nitrogen monoxide
Name these compounds?
NO2
N2O
N2O3
N2O4
N2O5
PCl3
PCl5
SF6
Nitrogen dioxide
Dinitrogen monoxide
Dinitrogen trioxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide
Phosphorous trichloride
Phosphorous pentachloride
Sulfur hexafluoride
Binary acids dissolved in water are named with the prefix "***-" and suffix "-*"
prefix "hydro-" and suffix "-ic"
Name these binary acides
HF(aq)
HCl ( aq)
HBr (aq)
HI(aq)
H2S (aq)
hydrofluoric acid
hydrochloric acid
hydrobromic acids
hydroiodic acid
hydrosulfuric acid
What forms a polyatomnic ion?
2 or more atoms joint by covalent bonds
What are Oxoanions ?
polyatomixc anions containing oxygen in combination with another nonmetal
Which oxoanions form a series of oxoanions contains different numbers oxygen atoms, what are their names related to?
Cl, N, P, S
Their names are related to the oxidation states of the nonmetal atoms to which O atoms are bonded.
What does increasing the oxidation state of a nonmetal do? ( us ClO as an ex ClO-, ClO -2, ClO-3, Clo-4)
Increases the number of O atoms
Hypo __ ite
__ite
___ate
per____ ate
hypochlorate,
chlorite
chlorate
perchlorate
NH4+
Ammonium ion
CH3COO-
Acetate ion
CO3 2-
Carbonate ion
HCO3 -
Hydrogen carbonate
or Bicarbonate
ClO-
Hypochlorite
ClO2-
Chlorite ion
ClO3-
Chlorate ion
ClO4-
Perchlorate ion
CrO4 2-
Chromate ion
Cr2O7 2-
Dichromate ion
CN-
Cyanide ion
OH-
Hydroxide ion
NO2-
Nitrite ion
NO3-
Nitrate ion
C2O4 2-
Oxalate ion
MnO4
Permaganate ion
PO4 3-
Phospate ion