Biology AQA-5.Homeostasis and Response (copy)
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Students should be able to identify the position of the following on a diagram of the human body: pituitary gland pancreas thyroid adrenal gland ovary testes., Students should be able to identify the following structures on a diagram of the eye and explain how their structure is related to their function: retina optic nerve sclera cornea iris ciliary muscles suspensory ligaments., Students should be able to identify the cerebral cortex, cerebellum and medulla on a diagram of the brain, and describe their functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
homeostasis
the regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions for function in response to internal and external changes
Homeostasis maintains optimal conditions for…
enzyme action and all cell functions.
Homeostasis in the human body, includes the control of:
blood glucose concentration
body temperature
water levels.
All control systems include:
cells called receptors, which detect stimuli (changes in the environment)
coordination centres (such as the brain, spinal cord and pancreas) that receive and process information from receptors
effectors, muscles or glands, which bring about responses which restore optimum levels.
The nervous system enables…
humans to react to their surroundings and to coordinate their behaviour.
Information from receptors passes along cells (neurones) as…
electrical impulses to the central nervous system (CNS)
central nervous system (CNS)
the brain and spinal cord
The CNS coordinates the…
response of effectors which may be muscles contracting or glands secreting hormones.
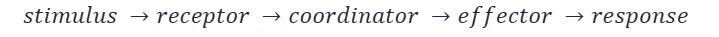
Reflex actions
a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus that does not involve the conscious brain, which makes it faster.
What are the main components of a reflex arc?
Receptor – detects the stimulus (e.g., pain, heat).
Sensory neurone – carries the impulse to the spinal cord.
Synapse – gap where chemical signals pass between neurones.
Relay neurone – transmits the signal within the spinal cord.
Motor neurone – carries the impulse to the effector.
Effector – a muscle or gland that carries out the response.
The brain is made of…
billions of interconnected neurones and has different regions that carry out different functions.
Neuroscientists have mapped brain functions by:
Studying patients with brain damage
Electrically stimulating areas of the brain
Using MRI scans to observe brain activity
Why is it difficult to investigate and treat brain damage or disease?
The brain is complex and delicate
Damage may be permanent or have unpredictable effects
Treatments can be risky or cause unintended side effects
Some brain areas are inaccessible for surgery or testing
Accommodation
the process of changing the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects.
To focus on a near object the eyes…
ciliary muscles contract
the suspensory ligaments loosen
the lens is then thicker and refracts light rays strongly.
To focus on a distant object the eyes…
ciliary muscles relax
the suspensory ligaments are pulled tight
the lens is then pulled thin and only slightly refracts light rays.
Two common defects of the eyes are…
myopia (short sightedness) and hyperopia (long sightedness) in which rays of light do not focus on the retina.
defects of the eyes are generally treated by…
spectacle lenses which refract the light rays so that they do focus on the retina but New technologies now include hard and soft contact lenses, laser surgery to change the shape of the cornea and a replacement lens in the eye.
Body temperature is monitored and controlled by the…
thermoregulatory centre in the brain.
The thermoregulatory centre contains…
receptors sensitive to the temperature of the blood.
The skin contains…
temperature receptors and sends nervous impulses to the thermoregulatory centre.
If the body temperature is too high…
blood vessels dilate (vasodilation) and sweat is produced from the sweat glands. Both these mechanisms cause a transfer of energy from the skin to the environment.
If the body temperature is too low…
blood vessels constrict (vasoconstriction), sweating stops and skeletal muscles contract (shiver).
The endocrine system is…
composed of glands which secrete chemicals called hormones directly into the bloodstream.
blood carries the hormone to a…
target organ where it produces an effect.
Compared to the nervous system the effects of the endocrine system are…
slower but act for longer
The pituitary gland in the brain is a…
‘master gland’ which secretes several hormones into the blood in response to body conditions
pancreas
controls blood glucose concentration
If the blood glucose concentration is too high…
the pancreas produces the hormone insulin that causes glucose to move from the blood into the cells
In liver and muscle cells excess glucose is converted to…
glycogen for storage.
Type 1 diabetes
a disorder in which the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin
has uncontrolled high blood glucose levels and is normally treated with insulin injections.
Type 2 diabetes
body cells no longer respond to insulin produced by the pancreas
carbohydrate controlled diet and an exercise regime are common treatments
If the blood glucose concentration is too low, the pancreas produces the hormone…
glucagon that causes glycogen to be converted into glucose and released into the blood.
How does the body lose water, ions, and urea?
Lungs – water lost during exhalation (no control)
Skin – water, ions, and urea lost in sweat (no control)
Kidneys – remove excess water, ions, and urea in urine (controlled)
What happens if cells gain or lose too much water by osmosis?
Too much water enters the cell → cell may swell and burst
Too much water leaves the cell → cell may shrink and stop working
How does the body deal with excess amino acids from digestion?
In the liver, excess amino acids are deaminated (the nitrogen is removed)
This produces ammonia, which is toxic
Ammonia is immediately converted to urea, a safer substance
Urea is transported to the kidneys and excreted in urine
kidneys
produce urine by filtration of the blood and selective reabsorption of useful substances such as glucose, some ions and water.
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
released by the pituitary gland when blood becomes too concentrated
It makes the kidney tubules more permeable, so more water is reabsorbed into the blood
This helps dilute the blood and reduce water loss in urine
How is ADH release controlled?
ADH release is controlled by negative feedback
If blood becomes too dilute, less ADH is released → less water is reabsorbed
This keeps the body’s water level stable
People who suffer from kidney failure may be treated by…
organ transplant or by using kidney dialysis
During puberty reproductive hormones cause…
secondary sex characteristics to develop.
Oestrogen
the main female reproductive hormone produced in the ovary
Ovulation
At puberty eggs begin to mature and one is released approximately every 28 days
Testosterone
the main male reproductive hormone produced by the testes and it stimulates sperm production.
Several hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle of a woman:
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) causes maturation of an egg in the ovary.
Luteinising hormone (LH) stimulates the release of the egg.
Oestrogen and progesterone are involved in maintaining the uterus lining.
Fertility can be controlled by a variety of…
hormonal and non-hormonal methods of contraception.
contraceptives
oral contraceptives
contain hormones to inhibit FSH production so that no eggs mature
contraceptives
injection, implant or skin patch of slow release progesterone
inhibit the maturation and release of eggs for a number of months or years
contraceptives
barrier methods
condoms and diaphragms which prevent the sperm reaching an egg
contraceptives
intrauterine devices
prevent the implantation of an embryo or release a hormone
contraceptives
spermicidal agents
kill or disable sperm
contraceptives
other methods
abstaining from intercourse or surgical methods of sterilisation.
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) treatment.
IVF involves giving a mother FSH and LH to stimulate the maturation of several eggs.
The eggs are collected from the mother and fertilised by sperm from the father in the laboratory.
The fertilised eggs develop into embryos.
At the stage when they are tiny balls of cells, one or two embryos are inserted into the mother's uterus (womb).
fertility treatment is
very emotionally and physically stressful, success rates are not high and can lead to multiple births which are a risk to both the babies and the mother.
Adrenaline
produced by the adrenal glands in times of fear or stress. It increases the heart rate and boosts the delivery of oxygen and glucose to the brain and muscles, preparing the body for ‘flight or fight’.
Thyroxine
the thyroid gland stimulates the basal metabolic rate. It plays an important role in growth and development.
Thyroxine levels are controlled by…
negative feedback.
Plants produce hormones to…
coordinate and control growth and responses to light (phototropism) and gravity (gravitropism or geotropism).
Unequal distributions of auxin cause…
unequal growth rates in plant roots and shoots.
Gibberellins are important in…
initiating seed germination.
Ethene controls…
cell division and ripening of fruits.
Plant growth hormones are used in…
agriculture and horticulture.
Auxins are used:
as weed killers
as rooting powders
for promoting growth in tissue culture.
Ethene is used in the…
food industry to control ripening of fruit during storage and transport.
Gibberellins can be used to:
end seed dormancy
promote flowering
increase fruit size.